Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Operations Strategy: Origins and New Directions
Загружено:
akarim23Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Operations Strategy: Origins and New Directions
Загружено:
akarim23Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
OPERATIONS STRATEGY: ORIGINS AND NEW DIRECTIONS
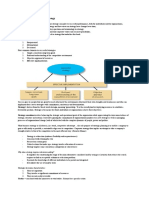
Introduction operations: all activities required to create and deliver a product or service, from procurement through conversion to distribution operations function can be a formidable competitive weapon if designed and managed properly operations strategy: set of goals, policies and self-imposed restrictions that describe how the organization plans to direct and develop all the resources invested in operations to best fulfill its mission mission: survival, profitability or growth through competitive advantage operating effectiveness is a key competitive advantage managers believe that marketing, sales or R&D can provide a more effective basis for achieving a competitive advantage dont realize the force operations play into this managers make makeshift measures that are indirectly linked to broader issues of general management concern Concept of Strategy establishment of objectives, the setting of direction and the development and implementation of plans with the goal of achieving victory must operate over an extended time horizon and comprise a wide variety of activities requires a company to make trade-offs corporate strategy: decisions regarding the industries and markets in which the organization participates, how it structures itself in order to attack those markets and how it acquires and allocates key resources
SBU strategy: specifies the scope of the business and its relationship to the overall organization and how it proposes to position itself within its particular industry to achieve a sustainable competitive advantage
functional strategy: supports the competitive advantage, marketing/sales or operations or financial control or R&D defined by the pattern of decisions actually made
vertical activities: activities that relate a given function to the business as a whole horizontal activities: activities that cut across multiple functions at fairly low levels in the organization, require more coordination and consistency
Company Values The Foundation for Strategy
strategy should be based on a set of values that are widely shared and expected to endure create a culture that ties people together, guides their efforts and gives meaning and purpose to their work operations organization is a major keeper of the companys values if managed properly, the operations function can contribute to the competitive success of a business and can play an important role in helping to support and enhance the values that provide the foundation for its strategies
The Operations Edge: Creating a Competitive Advantage Through Operations operations strategies help an operations organization in assembling and aligning the resources that will enable it to implement the companys competitive strategy too easy to develop an operations strategy based on the best practices of other companies
The American System: Mass Production for Mass Markets
mass markets, standard designs and mass production keys to low cost: o standardization and high volume, o work was done most efficiently when divided up and assigned to specialists o managers and staff experts should do the thinking for the workers o every process was characterized by an innate amount of variation o communication within an organization should be tightly controlled best manufacturing process was based on long runs, specialized equipment for each stage of process, matching capacities downsides were realized in 1980s and new approaches to competitiveness were evolving
The Japanese System: Lean Production
lean production system: characterized by an emphasis on reliability, speed and flexibility rather than volume and cost trained workers not specialized, working in teams, no rejects, communication horizontal rather than vertical, general purpose equipment, production throughput time was more important than labor or equipment utilization, inventory was waste, long-term and cooperative supplier relationships is it appropriate in all situations? adopting lean production does not enable operations to create an enduring strategic advantage
A Contingency Theory of Operations Strategy: Fit and Focus
different companies/SBUs have different strengths and weaknesses compete in different ways
different operating characteristics, making it easier or harder for a company to achieve a given form of differentiation seek fit between its SBUs chosen approach to competition and the way the operations function is designed, organized and managed
Different Approaches to Competitive Differentiation most critical element of competitive strategy that effects operations strategy is how it chooses to differentiate its products and services lowest price, higher quality, dependability, flexibility, speed/responsiveness devote resources to achieving one or two competitive dimensions not all Different Operating Systems Have Different Performance Characteristics different uses imply different designs coherent and consistent with the priorities required by the vehicles primary use An Operations Organizations Priorities Should Reflect Its SBUs Competitive Strategy an effective operations organization is one that meets the needs of its SBUs competitive strategy mgmt. must ensure that its operations organization is configured and managed in such a way that it can provide that form of differentiation Key Decisions Involved in Operations Strategy Implementation structural decisions: represent decisions regarding the organizations physical bricks-and-mortar attributes, require substantial capital investment, are difficult to alter or reverse
infrastructural policies and systems: describe the systems, policies and practices that determine how the organizations structural aspects are to be managed
Structural Decisions
capacity sourcing and vertical integration: how much of the total work required to create and deliver its products/services will be done internally and how much will be purchased from outside organizations facilities: how the total operating capacity is to be broken up into individual operating units information and process technology: choices among different types of equipment and how it should be located, connected together and coordinated
Вам также может понравиться
- Strategic Analysis of Internal Environment of a Business OrganisationОт EverandStrategic Analysis of Internal Environment of a Business OrganisationОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 - Competitiveness, Strategy & Productivity - 2Документ46 страницChapter 2 - Competitiveness, Strategy & Productivity - 2JeSsica Joy P. SantiagoОценок пока нет
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)От EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (25)
- OM CH 2Документ23 страницыOM CH 2Nicole Anne Villanueva PacificoОценок пока нет
- Building Winning Organisations: A complete guide to sustaining best-in-class performance for all organisationsОт EverandBuilding Winning Organisations: A complete guide to sustaining best-in-class performance for all organisationsОценок пока нет
- What Is Strategy and Why Is It Important?Документ43 страницыWhat Is Strategy and Why Is It Important?yadav poonamОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1: The Concept of StrategyДокумент36 страницChapter 1: The Concept of StrategyPalakОценок пока нет
- Unit 3 Strategic ManagementДокумент22 страницыUnit 3 Strategic ManagementCletus PaulОценок пока нет
- Operations Management 1 - BeaДокумент27 страницOperations Management 1 - BeaBea Renela Gabinete ConcepcionОценок пока нет
- Strategic ManagementДокумент10 страницStrategic ManagementDilip KushwahaОценок пока нет
- Stategic ManagementДокумент188 страницStategic Managementhammoudti100% (1)
- AdvantagesДокумент5 страницAdvantagesMergierose DalgoОценок пока нет
- Business Policy & Strategic Management-RДокумент27 страницBusiness Policy & Strategic Management-RDhara KanungoОценок пока нет
- Planning and Strategic ManagementДокумент31 страницаPlanning and Strategic ManagementCharm Mira100% (1)
- Porter - What Is Strategy - HBR-1Документ21 страницаPorter - What Is Strategy - HBR-1pwcanjiОценок пока нет
- OM and Strategic PlanningДокумент20 страницOM and Strategic PlanningPhooto StoridgeОценок пока нет
- Operations Strategy: Competitive AdvantageДокумент3 страницыOperations Strategy: Competitive AdvantageBao TranОценок пока нет
- Unit6 Business StrategiesДокумент55 страницUnit6 Business StrategiesArpit GajbhiyeОценок пока нет
- Operations StrategyДокумент26 страницOperations Strategysulabhagarwal1985Оценок пока нет
- Business and Functional Level StrategiesДокумент29 страницBusiness and Functional Level StrategiesDarlene MontillaОценок пока нет
- Porter - What Is Strategy - HBRДокумент21 страницаPorter - What Is Strategy - HBRbasmaОценок пока нет
- Strategic MNGT IMT-56Документ71 страницаStrategic MNGT IMT-56Deepak MahajanОценок пока нет
- 3 SummaryДокумент4 страницы3 Summaryhappy everydayОценок пока нет
- A Functional StrategyДокумент22 страницыA Functional Strategyjalaja munirajuОценок пока нет
- What Is Strategy and Why Is It Important?Документ24 страницыWhat Is Strategy and Why Is It Important?Khushbakht BalochОценок пока нет
- OS Lec 1 AutosavedДокумент24 страницыOS Lec 1 AutosavedParadise MessОценок пока нет
- Chapter ThreeДокумент8 страницChapter ThreeNura BasmerОценок пока нет
- Module 1 Management Accounting Overview: Australian Organisations in The 21st CenturyДокумент12 страницModule 1 Management Accounting Overview: Australian Organisations in The 21st CenturyAnna-Clara MansolahtiОценок пока нет
- What Strategy Is & Its Role: Gaining and Sustaining Competitive AdvantageДокумент5 страницWhat Strategy Is & Its Role: Gaining and Sustaining Competitive AdvantageSara GhassaniОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9: Funtional Level StrategiesДокумент4 страницыChapter 9: Funtional Level StrategiesAnonymous zHsbRY9Оценок пока нет
- Unit 8 Strategic Management What Is Strategy?Документ10 страницUnit 8 Strategic Management What Is Strategy?Nisha SherpaОценок пока нет
- Strategic Implementation & Control: Interacting SkillДокумент11 страницStrategic Implementation & Control: Interacting Skillbenn_sanjiviОценок пока нет
- Business Policy and StrategyДокумент9 страницBusiness Policy and StrategyRamesh Arivalan100% (7)
- Group 1Документ50 страницGroup 1Nick Jose100% (1)
- REVIEWERДокумент14 страницREVIEWERAudrey Ponce de leonОценок пока нет
- Porter - What Is Strategy - HBRДокумент21 страницаPorter - What Is Strategy - HBRmkkaran900% (1)
- Chapter 7 Developing A Business StrategyДокумент6 страницChapter 7 Developing A Business StrategySarah Girgis100% (1)
- Implementing: Realization of Strategy: Rodel C. Pomentil, MBAДокумент24 страницыImplementing: Realization of Strategy: Rodel C. Pomentil, MBAAnna SatordeОценок пока нет
- Functional StrategiesДокумент30 страницFunctional StrategiesSheena Doria de VeraОценок пока нет
- Strategic Cost Management Definition and ConceptДокумент2 страницыStrategic Cost Management Definition and ConceptMia Joyce Roselada PanesaОценок пока нет
- Strategy LevelsДокумент5 страницStrategy LevelsCarlos Chonlón QuirogaОценок пока нет
- Business Level StrategyДокумент24 страницыBusiness Level StrategyagrawalshrutiОценок пока нет
- Slot 2 SMДокумент17 страницSlot 2 SMSatish Kumar SatishОценок пока нет
- Strategic MGMTДокумент100 страницStrategic MGMTkausernazОценок пока нет
- ABM - Strategic ManagementДокумент23 страницыABM - Strategic ManagementAaisha GОценок пока нет
- Competitiveness Strategy and ProductivityДокумент34 страницыCompetitiveness Strategy and ProductivityRaymuel BelarminoОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Strategic ManagementДокумент52 страницыFundamentals of Strategic ManagementGennelyn Grace PenaredondoОценок пока нет
- Operations and Supply Chain JUNE 2022Документ11 страницOperations and Supply Chain JUNE 2022Rajni KumariОценок пока нет
- Module 2 Strat MGTДокумент11 страницModule 2 Strat MGTAllen Gevryel Ragged A. GabrielОценок пока нет
- Strategic MGTДокумент13 страницStrategic MGTSagor AftermathОценок пока нет
- 7 S ModelДокумент75 страниц7 S ModelPurushottam KumarОценок пока нет
- SGM5 Strategy Implementation and GenerationДокумент7 страницSGM5 Strategy Implementation and GenerationAngela AlizaОценок пока нет
- StrategyДокумент5 страницStrategyIFRA AFZALОценок пока нет
- Strategic Management: Tejal MahajanДокумент56 страницStrategic Management: Tejal MahajanTejal MОценок пока нет
- Policies in Functional AreasДокумент4 страницыPolicies in Functional AreasMonali Dravid100% (1)
- Strategic Management: "Insights and Hard Work Deliver Results"Документ22 страницыStrategic Management: "Insights and Hard Work Deliver Results"J César Corona CОценок пока нет
- Strategic Management Chapter 1Документ11 страницStrategic Management Chapter 1Peter John SabasОценок пока нет
- STRATEGYДокумент22 страницыSTRATEGYPRAGYAN PANDAОценок пока нет
- Strategic ManagementДокумент191 страницаStrategic Managementsanjay20207100% (2)
- Operations StrategyДокумент32 страницыOperations StrategyLieutenantОценок пока нет
- Ellomeh Hrs Coperate ProfileДокумент12 страницEllomeh Hrs Coperate ProfilepowellarryОценок пока нет
- Flexcon Decision - Rondeeda MagbyДокумент3 страницыFlexcon Decision - Rondeeda Magbyapi-376434895Оценок пока нет
- Certified in Production and Inventory Management (CPIM)Документ8 страницCertified in Production and Inventory Management (CPIM)dathient76Оценок пока нет
- SCM of Hewlett PackardДокумент7 страницSCM of Hewlett PackardSai VasudevanОценок пока нет
- The Toyota Way by DeepakДокумент17 страницThe Toyota Way by DeepakharpreetОценок пока нет
- Pursuit of Performance Findings From The 2014 Miller Heiman Sales Best Practices StudyДокумент37 страницPursuit of Performance Findings From The 2014 Miller Heiman Sales Best Practices StudyLoredanaОценок пока нет
- Political TheoryДокумент24 страницыPolitical Theorydivya shreeОценок пока нет
- Gazettee Notice Nominated County Assembly Wards PDFДокумент21 страницаGazettee Notice Nominated County Assembly Wards PDFLincoln_Wanjohi75% (4)
- Chapter 41 - Video Case Study 25Документ5 страницChapter 41 - Video Case Study 25uroojishfaqОценок пока нет
- Clay Platte Joint StatementДокумент1 страницаClay Platte Joint StatementThe Kansas City StarОценок пока нет
- Business Intelligence Competency Centers Creating A2541Документ23 страницыBusiness Intelligence Competency Centers Creating A2541hretamalesgОценок пока нет
- Liberias 2005 Presidential and Parliamentary ElectionsДокумент36 страницLiberias 2005 Presidential and Parliamentary ElectionsJima KromahОценок пока нет
- Life Cycle Logistics From DAU PDFДокумент2 страницыLife Cycle Logistics From DAU PDFSon of RizqОценок пока нет
- DataДокумент73 страницыDatasonu boseОценок пока нет
- Lagakali Tavaiqia and Glen Finau - Public Accountability Public Accounts and Constitutional Design 55-72Документ18 страницLagakali Tavaiqia and Glen Finau - Public Accountability Public Accounts and Constitutional Design 55-72vns.prОценок пока нет
- HR PlanningДокумент3 страницыHR PlanningJemilyn Cervantes-SegundoОценок пока нет
- CRMДокумент21 страницаCRMAlamelu duraisamyОценок пока нет
- Leadership TheoriesДокумент51 страницаLeadership Theoriestazman10102458Оценок пока нет
- Building and Maturing A Vendor Management Capability Primer For 2018Документ9 страницBuilding and Maturing A Vendor Management Capability Primer For 2018mwhaliОценок пока нет
- P6 QuestionsДокумент70 страницP6 QuestionsVipul Mistry100% (1)
- ISO 27001 Implementation - in SMEДокумент81 страницаISO 27001 Implementation - in SMEbudi.hw748Оценок пока нет
- Key Performace IdicatorsДокумент7 страницKey Performace IdicatorsDominic AndersonОценок пока нет
- The 28 Core Competencies Are Divided Into Five Leadership LevelsДокумент3 страницыThe 28 Core Competencies Are Divided Into Five Leadership LevelsKay OlokoОценок пока нет
- Constitutional Law 271 Test 2Документ3 страницыConstitutional Law 271 Test 2JeanОценок пока нет
- Approaches To System DevelopmentДокумент7 страницApproaches To System DevelopmentNitesh Kumar PalОценок пока нет
- Certified List of Candidates For Congressional and Local Positions For The May 13, 2013 2013 National, Local and Armm ElectionsДокумент2 страницыCertified List of Candidates For Congressional and Local Positions For The May 13, 2013 2013 National, Local and Armm ElectionsSunStar Philippine NewsОценок пока нет
- Research MASTER RefsДокумент10 страницResearch MASTER RefsFadzil Adly IshakОценок пока нет
- Certified List of Candidates: Iloilo - Estancia Iloilo - EstanciaДокумент3 страницыCertified List of Candidates: Iloilo - Estancia Iloilo - EstanciaShello DesalesОценок пока нет
- Cat LogisticsДокумент6 страницCat LogisticsSai VasudevanОценок пока нет
- Viii Why Do We Need A ParliamentДокумент23 страницыViii Why Do We Need A ParliamentmonitaОценок пока нет
- SYSTEMology: Create time, reduce errors and scale your profits with proven business systemsОт EverandSYSTEMology: Create time, reduce errors and scale your profits with proven business systemsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (48)
- Generative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewОт EverandGenerative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- Scaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0От EverandScaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Sales Pitch: How to Craft a Story to Stand Out and WinОт EverandSales Pitch: How to Craft a Story to Stand Out and WinРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- The Toyota Way (Second Edition): 14 Management Principles from the World's Greatest ManufacturerОт EverandThe Toyota Way (Second Edition): 14 Management Principles from the World's Greatest ManufacturerРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (121)
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)От EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (11)
- The Ruler's Guide: China's Greatest Emperor and His Timeless Secrets of SuccessОт EverandThe Ruler's Guide: China's Greatest Emperor and His Timeless Secrets of SuccessРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (14)
- The 10X Rule: The Only Difference Between Success and FailureОт EverandThe 10X Rule: The Only Difference Between Success and FailureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (289)
- Blue Ocean Strategy, Expanded Edition: How to Create Uncontested Market Space and Make the Competition IrrelevantОт EverandBlue Ocean Strategy, Expanded Edition: How to Create Uncontested Market Space and Make the Competition IrrelevantРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (387)
- Artificial Intelligence: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewОт EverandArtificial Intelligence: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (104)
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on AI, Analytics, and the New Machine AgeОт EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on AI, Analytics, and the New Machine AgeРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (69)
- How to Grow Your Small Business: A 6-Step Plan to Help Your Business Take OffОт EverandHow to Grow Your Small Business: A 6-Step Plan to Help Your Business Take OffРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (61)
- Elevate: The Three Disciplines of Advanced Strategic ThinkingОт EverandElevate: The Three Disciplines of Advanced Strategic ThinkingРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- 2022-2023 Price Action Trading Guide for Beginners in 45 MinutesОт Everand2022-2023 Price Action Trading Guide for Beginners in 45 MinutesРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (4)
- Create the Future: Tactics for Disruptive ThinkingОт EverandCreate the Future: Tactics for Disruptive ThinkingРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Strategy Skills: Techniques to Sharpen the Mind of the StrategistОт EverandStrategy Skills: Techniques to Sharpen the Mind of the StrategistРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5)
- Strategic Analytics: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewОт EverandStrategic Analytics: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (46)
- Lean Thinking: Banish Waste and Create Wealth in Your Corporation, 2nd EdОт EverandLean Thinking: Banish Waste and Create Wealth in Your Corporation, 2nd EdРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (17)
- How to Grow Your Small Business: A 6-Step Plan to Help Your Business Take OffОт EverandHow to Grow Your Small Business: A 6-Step Plan to Help Your Business Take OffРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Systems Thinking: A Guide to Strategic Planning, Problem Solving, and Creating Lasting Results for Your BusinessОт EverandSystems Thinking: A Guide to Strategic Planning, Problem Solving, and Creating Lasting Results for Your BusinessРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (80)
- HBR Guide to Building Your Business Case (HBR Guide Series)От EverandHBR Guide to Building Your Business Case (HBR Guide Series)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- Summary of Richard Rumelt's Good Strategy Bad StrategyОт EverandSummary of Richard Rumelt's Good Strategy Bad StrategyРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- The 22 Laws of Category Design: Name & Claim Your Niche, Share Your POV, And Move The World From Where It Is To Somewhere DifferentОт EverandThe 22 Laws of Category Design: Name & Claim Your Niche, Share Your POV, And Move The World From Where It Is To Somewhere DifferentОценок пока нет
- Why Digital Transformations Fail: The Surprising Disciplines of How to Take Off and Stay AheadОт EverandWhy Digital Transformations Fail: The Surprising Disciplines of How to Take Off and Stay AheadРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (9)
- Power and Prediction: The Disruptive Economics of Artificial IntelligenceОт EverandPower and Prediction: The Disruptive Economics of Artificial IntelligenceРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (38)