Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
UMTSServices
Загружено:
Eka KosasihАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
UMTSServices
Загружено:
Eka KosasihАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
UMTS Services
UMTS Services
U101 UMTS Network Systems Overview
UMTS Services
Contents and Session Aims
UMTS Services and Applications Architecture of a UMTS Bearer Service UMTS Bearer Attributes UMTS QoS Classes Example UMTS Services
In this session we shall look at
services and QoS issues in UMTS
! !
UMTS services QoS Bearer Architecture and Attributes Service Classes Major Service Types
! !
U101 UMTS Network Systems Overview
UMTS Services
UMTS Services and Applications
Office Information Information
Intelligent Search and Filtering agents Internet Surfing On-line media Special Services On-line translation Security Service Local information Hotline Booking & Reservation Tele-medecine News Virtual Working Groups Tele-working Schedule Synchronisation
Telemetric Services
Machine-Machine Services Location Based Tracking Navigation Assistance Education Travel Information Virtual School Fleet Management On-line Laboratories Remote Diagnostics On-line Library On-line Training Remote Consultation
Communications
Video Telephony Video Conferencing Speech Email Announcing Services SMS Electronic Postcards
Financial Services
On-line banking Universal SIM & Credit Card Home Shopping Stock Quotes
Leisure
Public Services
Public Elections/Voting Public Information Help Broadcast Services Yellow Pages
Virtual Book Store Music on Demand Games on Demand Video-clips Virtual Sight Seeing Lottery Services
U101 UMTS Network Systems Overview
UMTS Services
Architecture of a UMTS bearer service
TE UE UTRAN CN
edge node
CN
gateway
TE
End-to-End Service
TE/UE Local Bearer Service
UMTS Bearer Service
Radio Access Bearer Service
CN Bearer Service
External Bearer Service
Radio Bearer Service
Iu Bearer Service
Backbone Network Service
UTRA FDD/TDD Service
Physical Bearer Service
U101 UMTS Network Systems Overview
UMTS Services
QoS Bearer Attributes
Maximum bitrate (kbps) Guaranteed bitrate (kbps) Delivery order (y/n) Maximum SDU size (octets) SDU format information (bits)
Transfer delay (ms) Traffic handling priority Allocation/Retention Priority
SDU error ratio Residual bit error ratio Delivery of erroneous SDUs
(y/n/-)
U101 UMTS Network Systems Overview
UMTS Services
Maximum bitrate
Maximum bitrate (kbps)
!
Maximum bitrate can be used to make code reservations in the downlink of the radio interface Its purpose is
" to limit the delivered bitrate to applications or external networks with such limitations " to allow maximum wanted user bitrate to be defined for applications able to operate with different rates
U101 UMTS Network Systems Overview
UMTS Services
Guaranteed bitrate
Guaranteed number of bits delivered by UMTS within a time period Guaranteed bitrate may be used to facilitate
! !
admission control based on available resources and resource allocation within UMTS.
Quality requirements expressed by e.g. delay and reliability attributes only apply to incoming traffic up to the guaranteed bitrate
U101 UMTS Network Systems Overview
UMTS Services
Delivery order
Indicates whether the UMTS bearer shall provide in-sequence SDU delivery or not. The attribute is derived from the user protocol (PDP type) and specifies if out-of-sequence SDUs are acceptable or not. This information cannot be extracted from the traffic class. Whether out-of-sequence SDUs are dropped or re-ordered depends on the specified reliability
U101 UMTS Network Systems Overview
UMTS Services
Maximum SDU size
The maximum allowed SDU size The maximum SDU size is used for admission control and policing.
U101 UMTS Network Systems Overview
UMTS Services
SDU format information
List of possible exact sizes of SDUs UTRAN needs SDU size information to be able to operate in transparent RLC protocol mode, which is beneficial to spectral efficiency and delay when RLC re-transmission is not used. Thus, if the application can specify SDU sizes, the bearer is less expensive
U101 UMTS Network Systems Overview
10
UMTS Services
SDU error ratio
Indicates the fraction of SDUs lost or detected as erroneous. Note that by reserving resources, SDU error ratio performance is independent of the loading conditions, whereas without reserved resources, such as in Interactive and Background classes, SDU error ratio is used as target value. Used to configure the protocols, algorithms and error detection schemes, primarily within UTRAN.
U101 UMTS Network Systems Overview
11
UMTS Services
Residual bit error ratio
Indicates the undetected bit error ratio in the delivered SDUs. If no error detection is requested, Residual bit error ratio indicates the bit error ratio in the delivered SDUs. Used to configure radio interface protocols, algorithms and error detection coding
U101 UMTS Network Systems Overview
12
UMTS Services
Delivery of erroneous SDUs
Indicates whether SDUs detected as erroneous shall be delivered or discarded. Used to decide whether error detection is needed and whether frames with detected errors shall be forwarded or not.
U101 UMTS Network Systems Overview
13
UMTS Services
Transfer delay
Indicates maximum delay for 95th percentile of the distribution of delay for
all delivered SDUs during the lifetime of a bearer service
Delay for an SDU is defined as the time from a request to transfer an SDU at
one SAP to its delivery at the other SAP.
Used to specify the delay tolerated by the application. It allows UTRAN to set transport formats and ARQ parameters Transfer delay of an arbitrary SDU is not meaningful for a bursty source,
since the last SDUs of a burst may have long delay due to queuing, whereas the meaningful response delay perceived by the user is the delay of the first SDU of the burst.
U101 UMTS Network Systems Overview
14
UMTS Services
Traffic handling priority
Specifies the relative importance for handling of all SDUs belonging to the UMTS bearer compared to the SDUs of other bearers. Within the interactive class, there is a definite need to differentiate between bearer qualities. This is handled by using the traffic handling priority attribute, to allow UMTS to schedule traffic accordingly. By definition, priority is an alternative to absolute guarantees, and thus these two attribute types cannot be used together for a single bearer.
U101 UMTS Network Systems Overview
15
UMTS Services
Allocation/Retention Priority
Specifies the relative importance compared to other UMTS bearers for allocation and retention of the UMTS bearer. The Allocation/Retention Priority attribute is a subscription parameter which is not negotiated from the mobile terminal. Priority is used for differentiating between bearers when performing allocation and retention of a bearer. In situations where resources are scarce, the relevant network elements can use the Allocation/Retention Priority to prioritise bearers with a high Allocation/Retention Priority over bearers with a low Allocation/Retention Priority when performing admission control
U101 UMTS Network Systems Overview
16
UMTS Services
Asymmetric Bearers
Uni-directional and bi-directional bearer services are supported. For bi-directional bearer services, the attributes Maximum bitrate and Guaranteed bitrate can be set separately for uplink/downlink in order to support asymmetric bearers.
U101 UMTS Network Systems Overview
17
UMTS Services
UMTS QoS Classes
UMTS attempts to fulfil QoS requests from the user Four traffic classes have been identified
! ! ! !
Conversational Streaming Interactive Background
Main distinguishing feature is delay sensitivity
U101 UMTS Network Systems Overview
18
UMTS Services
Conversational Class
Preserve time relation between information entities of the stream - transmission and reception in the same order Conversational pattern - symmetric Real time - low delay required Typically between peers Example Applications:
! ! !
Voice Videotelephony Video Games
U101 UMTS Network Systems Overview
19
UMTS Services
Streaming
Preserve time relation between information entities of the stream - transmission and reception in the same order Highly asymmetric Real time - relatively low delay required Typically between server and client Example Applications
! ! !
Web broadcast Video on demand Miscellaneous streaming multimedia
U101 UMTS Network Systems Overview
20
UMTS Services
Interactive
Request response pattern Preserve data integrity Relatively delay sensitive but not real time Treated as non-real time packet based Example applications:
! ! ! !
Web browsing Network games Location based services Database retrieval
U101 UMTS Network Systems Overview
21
UMTS Services
Background
Destination is not expecting the data within a certain time Preserve data integrity Treated as non-real time packet based Example Applications
! ! !
Download of emails SMS Reception of measurement records
U101 UMTS Network Systems Overview
22
UMTS Services
UMTS Circuit Switched Bearer Services
Five Circuit switched bearer services have been defined:
!
Speech
" Adaptive Multi Rate
Transparent Data (Unrestricted Digital Information)
" 32kbps, 56kbps, 64kbps
Transparent Data (Audio)
" 28.8kbps, 33.6 kbps
Non Transparent Fax
" 28.8kbps
Non Transparent Data
" 14.4kbps, 28.8kbps, 57.6kbps
U101 UMTS Network Systems Overview
23
UMTS Services
UMTS AMR Speech Codec
Standard codec likely to be the multirate coder developed for GSM
! !
provides EFR quality for good channel provides good quality in poor conditions
The multirate codec has 14 combined channel and codec modes
!
codec produces 8 source rates (4.75, 5.15, 5.9, 6.7(PDC-EFR), 7.4(IS641), 7.95, 10.2 and 12.2 kbps(GSM-EFR)) employs variable protection coding according to channel coding rate between 1/2 and 1/5 puncturing used to match bit rate to channel
! ! !
U101 UMTS Network Systems Overview
24
UMTS Services
Universal Personal Telecommunications
UPT means a user can be contacted wherever they are through a single number
!
User mobility rather than terminal mobility
The number translation capability of IN can be used to route a call to a convenient and suitably equipped local terminal
!
A number is associated with a person not a terminal or ID card
U101 UMTS Network Systems Overview
25
UMTS Services
Virtual Home Environment
The VHE means that a roaming user can access the services that he would have access to on his home network Ideally the user should not notice he is not in his home network
!
Again VHE can be implemented in UMTS through the inclusion of IN functionality
U101 UMTS Network Systems Overview
26
UMTS Services
SIM Application Toolkit
SIM Application Toolkit Features include:
!
Profile Download
" To verify support of the SIM Application Toolkit by both SIM and ME
Data Download
" To enable SMS to transfer data directly to an application on the SIM
Proactive SIM
" To allow the SIM to operate the call control functions of the ME
Menu Selection
" To enable an application on the SIM to create and operate a menu on the ME
Call Control by SIM
" All dialled digits may be passed to an application on the SIM which may bar, modify or allow the call
U101 UMTS Network Systems Overview
27
UMTS Services
Location Based Services
In many regions a Location Function is a condition of the license Location information may be provided on request from a client application (in either the UE or CN) There are three main types of location derivation
!
Cell Identity Based
" Giving a position within the cells coverage area
Timing Based
" Derived from relative timing measurements made on radio transmissions
Network Assisted GPS
" A UE is equipped with a GPS, whose performance may be improved by the network
U101 UMTS Network Systems Overview
28
UMTS Services
Questions
What are the four UMTS QoS Classes? How might location be determined for location based services in UMTS? What is the maximum and minimum rate of the AMR speech codec?
U101 UMTS Network Systems Overview
29
UMTS Services
Session Summary
In this session we have investigated
! ! ! !
QoS Architecture in UMTS Bearer attributes QoS Classes Example services such as the AMR
U101 UMTS Network Systems Overview
30
Вам также может понравиться
- The UMTS Network: 1.2 UMTS Evolution 1.3 UMTS Protocols 1.4 Performance Data 1.5 Key Performance IndicatorsДокумент64 страницыThe UMTS Network: 1.2 UMTS Evolution 1.3 UMTS Protocols 1.4 Performance Data 1.5 Key Performance IndicatorsHicham MadridОценок пока нет
- Evolution of Services in 3G Network: Lecture Notes Dea Misi 1 March 04Документ81 страницаEvolution of Services in 3G Network: Lecture Notes Dea Misi 1 March 04Hao NguyenОценок пока нет
- Wcdma (Umts) Tdcdma Cdma2000 Wcdma (Docomo) Td-Scdma Mobiles Bluetooth Homerf/Swap Wap GPRS, HSCSD Edge Camel, inДокумент6 страницWcdma (Umts) Tdcdma Cdma2000 Wcdma (Docomo) Td-Scdma Mobiles Bluetooth Homerf/Swap Wap GPRS, HSCSD Edge Camel, invipin171986Оценок пока нет
- Mentum Planet 5.7 WCDMAДокумент91 страницаMentum Planet 5.7 WCDMAIshanWeera1982Оценок пока нет
- UMTS Services and Applications: Jouni Salonen, Antti Toskala and Harri HolmaДокумент20 страницUMTS Services and Applications: Jouni Salonen, Antti Toskala and Harri Holmachintanjoshi001Оценок пока нет
- Guide to IEEE 802.11e and WMM for Quality of ServiceДокумент25 страницGuide to IEEE 802.11e and WMM for Quality of Serviceswathi sriniОценок пока нет
- UmtsДокумент23 страницыUmtsMitz PaminОценок пока нет
- CCNA 4 Examenesverdaderos6y8Документ48 страницCCNA 4 Examenesverdaderos6y8Uri7*14--100% (1)
- CCNA Exploration 4 Accessing the WAN - Chapter 1 & 2 Exam QuestionsДокумент27 страницCCNA Exploration 4 Accessing the WAN - Chapter 1 & 2 Exam QuestionsshowshangОценок пока нет
- UMTS Network Performance Modeling Service: Case StudyДокумент6 страницUMTS Network Performance Modeling Service: Case Studycma_ptОценок пока нет
- Basic Communication Model: - Components - Sender - Medium - Receiver - Message - ProtocolДокумент28 страницBasic Communication Model: - Components - Sender - Medium - Receiver - Message - ProtocolManoj BorahОценок пока нет
- Performance Enhancement of End-To-End Quality of Service in Wcdma Wireless NetworksДокумент8 страницPerformance Enhancement of End-To-End Quality of Service in Wcdma Wireless NetworksSarsij MishraОценок пока нет
- 3G NetworksДокумент9 страниц3G Networkschenjerai chabaraОценок пока нет
- The Universal Mobile Telecommunication System (UMTS)Документ20 страницThe Universal Mobile Telecommunication System (UMTS)Khiz JabiОценок пока нет
- Module 1 - Sample Paper: V! Vek PathakДокумент8 страницModule 1 - Sample Paper: V! Vek PathakdhruvidОценок пока нет
- Docslide Net - Umts ExplainedДокумент18 страницDocslide Net - Umts Explainedamos JosephОценок пока нет
- Introduction To WCDMA Fundamentals NokiaДокумент106 страницIntroduction To WCDMA Fundamentals NokiaSadasivan Ep100% (2)
- Evolution to 3G and BeyondДокумент33 страницыEvolution to 3G and BeyondVikash YadavОценок пока нет
- Physical Layer - Data Link LayerДокумент40 страницPhysical Layer - Data Link LayerMaxwellMenyatsoОценок пока нет
- LTE PosterДокумент1 страницаLTE PosterDirk LoosenОценок пока нет
- 6CS029 Lecture 4 - QoS ConceptsДокумент38 страниц6CS029 Lecture 4 - QoS Conceptsdushantha.ellewalaОценок пока нет
- Core network dimensioning for wireless broadbandДокумент34 страницыCore network dimensioning for wireless broadbandraj1978enatorОценок пока нет
- WCDMA Radio Network Capacity PlanningДокумент51 страницаWCDMA Radio Network Capacity Planningkumararyan1124100% (1)
- KEY Enabling Technologies and Features of LTEДокумент19 страницKEY Enabling Technologies and Features of LTE1DT18EC106 Y SAI MEGHANAОценок пока нет
- End-2-End QoS Provisioning in UMTSДокумент10 страницEnd-2-End QoS Provisioning in UMTSnassr89Оценок пока нет
- Emulation of A Downlink Spreading Factor Allocation Strategy For Rel'99 UMTSДокумент5 страницEmulation of A Downlink Spreading Factor Allocation Strategy For Rel'99 UMTSJef ImamОценок пока нет
- Computer Networks (3150710) : Chapter 3: Transport Layer Weightage: 25%Документ35 страницComputer Networks (3150710) : Chapter 3: Transport Layer Weightage: 25%urmilОценок пока нет
- FINAL Limitations and DisadvantagesДокумент8 страницFINAL Limitations and DisadvantageseustoquiocastroОценок пока нет
- QoS Mechanisms and Modular QoS CLIДокумент126 страницQoS Mechanisms and Modular QoS CLIZohaib Siddiqui100% (1)
- QoS: IntServ and DiffServДокумент41 страницаQoS: IntServ and DiffServRoberto Dell'OmoОценок пока нет
- MCRNC Configuration PrinciplesДокумент20 страницMCRNC Configuration PrinciplesAshok DwivediОценок пока нет
- Introduction to 4G Wireless NetworksДокумент32 страницыIntroduction to 4G Wireless NetworksAsaadОценок пока нет
- Performance Issues in ATM NetworkДокумент19 страницPerformance Issues in ATM NetworkHarsh SihotraОценок пока нет
- Zhiwei ThesisPresentation1Документ27 страницZhiwei ThesisPresentation1varajohnОценок пока нет
- UMTS Core Network Planning GuideДокумент8 страницUMTS Core Network Planning GuideEbere ObiaОценок пока нет
- Doc2-Radio Networks QoS Assessment and Evaluation ToolsДокумент46 страницDoc2-Radio Networks QoS Assessment and Evaluation ToolsAlexОценок пока нет
- Latency in LTE CommentsДокумент16 страницLatency in LTE CommentsVikas RanaОценок пока нет
- Tata Teleservices LTD PresentationДокумент88 страницTata Teleservices LTD PresentationIshankОценок пока нет
- UMTS coverage thresholds, network design considerations, and differences between CS and PS networksДокумент20 страницUMTS coverage thresholds, network design considerations, and differences between CS and PS networksManish M ShrivastavaОценок пока нет
- IP Interworking TransportДокумент23 страницыIP Interworking TransportAhmed AlsalamiОценок пока нет
- Evolving WCDMA: Tomas Hedberg and Stefan ParkvallДокумент8 страницEvolving WCDMA: Tomas Hedberg and Stefan ParkvallAkshay BajpaiОценок пока нет
- Whitepaperzte 5 Gprecisiontransportnetworksolution 1597168020185Документ6 страницWhitepaperzte 5 Gprecisiontransportnetworksolution 1597168020185Jose ValenzuelaОценок пока нет
- 5th Unit Pervasive ComputingДокумент13 страниц5th Unit Pervasive Computingashok2003Оценок пока нет
- Overview of QoS in GeneralДокумент6 страницOverview of QoS in GeneralVũ LongОценок пока нет
- Unit - Iv: Transport LayerДокумент55 страницUnit - Iv: Transport LayerSundaram MuthuОценок пока нет
- UMTS Fundamentals: Understanding 3G Technology and EvolutionДокумент71 страницаUMTS Fundamentals: Understanding 3G Technology and EvolutionCharlie CharlsОценок пока нет
- Acn - Dec 2018Документ22 страницыAcn - Dec 2018shraddha_mundadadaОценок пока нет
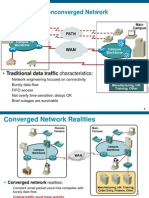
- Traditional Nonconverged Network: Traditional Data Traffic CharacteristicsДокумент40 страницTraditional Nonconverged Network: Traditional Data Traffic CharacteristicsCesar CriolloОценок пока нет
- Itc4303 - L4&L5Документ80 страницItc4303 - L4&L5KhalifaОценок пока нет
- Name-Suvajit Mondal. Stream-E.C.E. Roll No.-3047. Semester-8 - Subject-3G PresentationДокумент21 страницаName-Suvajit Mondal. Stream-E.C.E. Roll No.-3047. Semester-8 - Subject-3G PresentationSubir MaityОценок пока нет
- Section ThreeДокумент54 страницыSection ThreeRock DolphinОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2.3GConceptДокумент16 страницChapter 2.3GConceptmanojkumartomar7513Оценок пока нет
- Modeling and Dimensioning of Mobile Wireless Networks: From GSM to LTEОт EverandModeling and Dimensioning of Mobile Wireless Networks: From GSM to LTEОценок пока нет
- Concise Guide to OTN optical transport networksОт EverandConcise Guide to OTN optical transport networksРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (2)
- Mobile Network Optimization: A Guide for 2G and 3G Mobile Network OptimizationОт EverandMobile Network Optimization: A Guide for 2G and 3G Mobile Network OptimizationРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (3)
- Papers on the field QoS Measurement Of Services in mobile networks Using Aggregation MethodОт EverandPapers on the field QoS Measurement Of Services in mobile networks Using Aggregation MethodРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (2)
- GSM Security Overview: COMP128 Algorithm AttacksДокумент38 страницGSM Security Overview: COMP128 Algorithm AttacksEric TraoreОценок пока нет
- 2G Southern EJ CR-000000917037 - t200 Parameter Change - Malang - EJS - Eka KosasihДокумент8 страниц2G Southern EJ CR-000000917037 - t200 Parameter Change - Malang - EJS - Eka KosasihEka KosasihОценок пока нет
- 2G Southern EJ - INTRACH Disabling TrialДокумент15 страниц2G Southern EJ - INTRACH Disabling TrialEka KosasihОценок пока нет
- GSM OptimizationДокумент73 страницыGSM OptimizationmoveplanoОценок пока нет
- FH PlanningДокумент68 страницFH PlanningwonypayukОценок пока нет
- GERAN KPIs IUS 3.0Документ53 страницыGERAN KPIs IUS 3.0Eka Kosasih100% (1)
- RRG NemoДокумент16 страницRRG NemoEka KosasihОценок пока нет
- 3G FrequenciesДокумент4 страницы3G FrequenciesEka KosasihОценок пока нет
- Kathrein 2002Документ179 страницKathrein 2002MasTomОценок пока нет
- Dual Band Project in Targi Poznanskie: Network Development, System Engineering 0.3Документ17 страницDual Band Project in Targi Poznanskie: Network Development, System Engineering 0.3Eka KosasihОценок пока нет
- About The GSM-Dm-Channels: 0. A Little Bit of HistoryДокумент84 страницыAbout The GSM-Dm-Channels: 0. A Little Bit of HistoryottoalbinОценок пока нет
- Visual Basic Application Training (New)Документ1 страницаVisual Basic Application Training (New)Eka KosasihОценок пока нет
- Cell Reselect ParameterДокумент13 страницCell Reselect ParameterEka KosasihОценок пока нет
- GSM Location Update Sequence DiagramДокумент4 страницыGSM Location Update Sequence DiagramYogesh BindwalОценок пока нет
- TUTA-S30 User ManualДокумент29 страницTUTA-S30 User Manualalinm24Оценок пока нет
- GoIP Series User Manual V1.4BДокумент63 страницыGoIP Series User Manual V1.4BMarku MОценок пока нет
- Coban-Gps Tracker Price List For 50pcs 20161117Документ6 страницCoban-Gps Tracker Price List For 50pcs 20161117DANIELОценок пока нет
- GSmart F240 PDFДокумент16 страницGSmart F240 PDFAnonymous k2NqMoОценок пока нет
- TR 103Документ16 страницTR 103aerubio76Оценок пока нет
- Citycell AllДокумент90 страницCitycell AllNoor Ibne SalehinОценок пока нет
- Simcom Sim5320 Atc en V2.02 PDFДокумент550 страницSimcom Sim5320 Atc en V2.02 PDFCarlos Ramirez100% (1)
- Bgi Equipment Catalogue v1!1!2013 2014Документ82 страницыBgi Equipment Catalogue v1!1!2013 2014Chandra GalajuОценок пока нет
- GT02A User Manual PDFДокумент10 страницGT02A User Manual PDFsbloinazОценок пока нет
- MTX-Router-Titan-3G v3.00.3.02 Manual Usuario PDFДокумент191 страницаMTX-Router-Titan-3G v3.00.3.02 Manual Usuario PDFaldariz201181Оценок пока нет
- MY ALARM 2 UsermanualUKДокумент1 страницаMY ALARM 2 UsermanualUKbebe_roalbaОценок пока нет
- Alcatel 1035x 1035d User ManualДокумент29 страницAlcatel 1035x 1035d User ManualEdgar Jose Aranguibel MorilloОценок пока нет
- BEGECA Product Catalogue 2018 enДокумент8 страницBEGECA Product Catalogue 2018 enM B BОценок пока нет
- SIM Manual E64254 01Документ647 страницSIM Manual E64254 01CLeonel CasamalhuapaОценок пока нет
- A Study On The Customer Satisfaction of Mobile Network Service Providers (With Special Reference To Pollachi Taluk)Документ25 страницA Study On The Customer Satisfaction of Mobile Network Service Providers (With Special Reference To Pollachi Taluk)saran00708Оценок пока нет
- At CommandsДокумент208 страницAt Commandspkruchi10Оценок пока нет
- PPT-09 SancharsoftДокумент20 страницPPT-09 Sancharsofthem777Оценок пока нет
- 3GPP TS 22.011 V8.4.1 - Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects, Service AcessibilityДокумент25 страниц3GPP TS 22.011 V8.4.1 - Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects, Service AcessibilityRaissa BailloОценок пока нет
- FMB125v1 3Документ4 страницыFMB125v1 3Nawfal El-khadiriОценок пока нет
- Vodafone M2M Integrated M2M Terminals Overview BrochureДокумент4 страницыVodafone M2M Integrated M2M Terminals Overview BrochureJamie JordanОценок пока нет
- GSM Gate Control 1000 Installation ManualДокумент16 страницGSM Gate Control 1000 Installation Manualmanuel_lopescasa9273Оценок пока нет
- Yes 2 PrepayДокумент163 страницыYes 2 PrepayRajiv RanjanОценок пока нет
- What Is GMSK ModulationДокумент5 страницWhat Is GMSK Modulationtrivedi_urvi9087Оценок пока нет
- OpenVox G400P User ManualДокумент31 страницаOpenVox G400P User Manualmaple4VOIPОценок пока нет
- Q Mobile - X5 User ManualДокумент48 страницQ Mobile - X5 User Manualsajid93Оценок пока нет
- GSM Gateway 252236Документ16 страницGSM Gateway 252236muddogОценок пока нет
- Huawei E173 Dongle Mobile Broadband SpecificationДокумент21 страницаHuawei E173 Dongle Mobile Broadband SpecificationYBSTechОценок пока нет
- JioPhoneGuide (QuickStartGuide)Документ24 страницыJioPhoneGuide (QuickStartGuide)Sachin SajanОценок пока нет
- Ufone Prepaid SMS Bundle Offer - Ufone GSMДокумент5 страницUfone Prepaid SMS Bundle Offer - Ufone GSMNoman AnsariОценок пока нет
- Design and Implementation of Automatic Meter Reading System Using GSM, ZIGBEE Through GPRSДокумент5 страницDesign and Implementation of Automatic Meter Reading System Using GSM, ZIGBEE Through GPRSReeta DuttaОценок пока нет