Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Investigating On Yeast and The Enzyme Catalase On Hydrogen Peroxide - Real Version
Загружено:
AlaaaanИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Investigating On Yeast and The Enzyme Catalase On Hydrogen Peroxide - Real Version
Загружено:
AlaaaanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Alan Jones
Biology
IB
The effect of varying the concentration of substrate on yeast catalase
Introduction
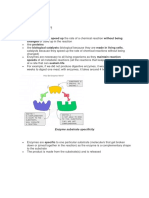
Enzymes are vital to stay alive and are proteins, which are made of long chains of amino acids. Enzymes have a 3D globular formation and tertiary structure level. The structure of an enzyme is held together by disulphide bonds and ionic bonds. Enzymes have optimal conditions that they work in. The factors that can affect this are temperature, pH and concentration of enzymes and substrates. Enzymes work best at an optimum temperature (usually around 40 C). They become ineffective at higher temperatures as their special shape changes. They become denatured, and substrate molecules no longer fit snugly into the active sites on the enzyme. If the pH is not at its optimum, it could denature the enzyme by changing its structure. If the structure changes a lot then the substrate could not fit into the active site. If the pH level is optimal, the rate of reaction would be maximal and work more at optimum efficiency. As mentioned, if the structure of an enzyme changes, it might not fit its active site. I will be investigating the enzyme catalase. Catalase turns hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen because hydrogen peroxide is otherwise harmful to the body. The optimum pH of catalase is approximately 7 and the optimum temperature is 37 degrees. Catalase is found in yeast.
Research Question
How does the amount of time affect how much gas is released when 10ml of catalase is dropped onto yeast?
Hypothesis
I think the optimal amount of time would 1 minute because after one minute the amount of gas released would significantly decrease.
Variables Independent Variable
My independent variable will be the amount of time I let the hydrogen peroxide react with catalase. The intervals I will choose will be 30 seconds, 1 minute, 2 minutes, 4 minutes and 6 minutes. I have chosen these intervals because they are a good range and the difference between 30 seconds and 6 minutes will be noticeable. It will affect my results because depending on the amount of time, the different amounts of gas will be released. It will be controlled by using a stopwatch.
Alan Jones
Biology
IB
Dependent Variable
My dependent variable will be the gas (mostly oxygen) that is released from the yeast and it will depend on the amount of time I leave it in the bowl for. To measure this, the gas syringe will be at 0cm and then I will measure the difference once the time has elapsed. This will be controlled by using a gas syringe.
Controlled Variables
Controlled variable Amount of hydrogen peroxide Amount of yeast Same gas syringe How will it be controlled? Will be measured before use. Will be measured before use. Wont change gas syringe. What effect does it have? Produce unfair results. Produce unfair results. Could lead to uncertainties
Apparatus
Stopwatch Knife Gas syringe with bung 300ml of catalase Bowl for gas syringe 500 grams of yeast Small pipette 250ml beaker Weighing boats
Health and Safety
The health and safety hazard in this experiment is the knife and it needs to be handled with caution. Hydrogen peroxide is a poisonous chemical and if it comes into contact with your skin make sure you wash thoroughly as soon as possible. Safety goggles are advised.
The Method
1. Place 20grams of yeast inside beaker. I use 20 grams because it is a sufficient amount to produce required results. 2. Take about 200ml of hydrogen peroxide. 3. Take 10ml of hydrogen peroxide into the pipette and have it ready to be applied to the yeast. 4. Try to apply to the centre as much as possible. 5. Once applied, seal the beaker with the gas syringe (making sure its at 0 before being placed on). 6. Time for 30 seconds.
Alan Jones
Biology
IB
7. Once 30 seconds have elapsed, see how many cm of difference there is on the gas syringe and make a note of it. 8. Once written down, take off the bung and clean out the bowl (or whatever else has been used). 9. Repeat this step with waiting 30 seconds 4 more times. 10. Once completed, move onto the other IVs and do those 5 times each.
Results Table
30 Time elapsed (seconds) 60 120 240 360 Result 1 Result 2 Result 3 Result 4 Result 5
With this data the research question can be addressed. The results will be presented using line graphs and processed results tables. This will be done via placing the data into Microsoft Office Excel. 5 suitable increments are used for the IV.
Bibliography
No external sources were used.
Amount of gas (cm) ( 0.2cm3)
Вам также может понравиться
- BIO IA (Yeast Population) !!Документ4 страницыBIO IA (Yeast Population) !!hunarsandhu33% (6)
- Sample Biology Lab For IBДокумент5 страницSample Biology Lab For IBVarun Pitambar0% (2)
- 6 L3dopa Lab Sm2012Документ6 страниц6 L3dopa Lab Sm2012alimisaghian62Оценок пока нет
- Bio Lab ReportДокумент10 страницBio Lab ReportMariamОценок пока нет
- Core Investigation - Why Does Colour Leak Out of Cooked Beetroot PlanningДокумент8 страницCore Investigation - Why Does Colour Leak Out of Cooked Beetroot PlanningRottenMessОценок пока нет
- Enzyme Activity With TemperatureДокумент3 страницыEnzyme Activity With TemperatureGuille PazОценок пока нет
- Elena Piovesan Lab ReportДокумент6 страницElena Piovesan Lab Reportelena piovesanОценок пока нет
- Enzyme Core PracticalДокумент7 страницEnzyme Core PracticalJackHowley123Оценок пока нет
- Enzymes Lab ReportДокумент7 страницEnzymes Lab ReportMemorie BrownОценок пока нет
- AP Biology Lab Two: Enzyme CatalysisДокумент4 страницыAP Biology Lab Two: Enzyme CatalysisCoolAsianDude95% (37)
- AP Biology Enzyme Kinetics Lab ReportДокумент22 страницыAP Biology Enzyme Kinetics Lab ReportVictor Martin88% (8)
- NATS 103 - The Biological World EnzymesДокумент3 страницыNATS 103 - The Biological World EnzymesVera MillerОценок пока нет
- Enzyme AP LabДокумент8 страницEnzyme AP LabMimiОценок пока нет
- The Effect of Temperature On The Rate of Reaction of YeastДокумент8 страницThe Effect of Temperature On The Rate of Reaction of YeastMatt BeaumontОценок пока нет
- Enzyme Lab ReportДокумент7 страницEnzyme Lab Reportapi-309561913Оценок пока нет
- Prelab Group3 Enzymatic ActivityДокумент5 страницPrelab Group3 Enzymatic ActivityRothmy LaquindanumОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5Документ7 страницChapter 5HashikaОценок пока нет
- Enzyme Cataylsis Lab 2016 Claire FellbaumДокумент7 страницEnzyme Cataylsis Lab 2016 Claire FellbaumMingОценок пока нет
- Ex Four AmylaseДокумент9 страницEx Four AmylaseoinkОценок пока нет
- Enzyme Lab ReportДокумент9 страницEnzyme Lab ReportSafaa TatouОценок пока нет
- Enzyme Pratica 2022Документ17 страницEnzyme Pratica 2022Nguyễn HuyềnОценок пока нет
- The Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide's Temperature On The Production of Oxygen Through The Use of Enzyme CatalaseДокумент5 страницThe Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide's Temperature On The Production of Oxygen Through The Use of Enzyme CatalaseJoseph ShorterОценок пока нет
- Biology Criterion B - How The...Документ5 страницBiology Criterion B - How The...Avaneesh Aravind HangalurОценок пока нет
- Investigating The Law of Conservation of Mass: Criterion B AssessmentДокумент7 страницInvestigating The Law of Conservation of Mass: Criterion B AssessmentMoopОценок пока нет
- Acara 2 Brahma Putra Nugraha B1A020084 B BIOKIMIAДокумент15 страницAcara 2 Brahma Putra Nugraha B1A020084 B BIOKIMIABrahma Putra NugrahaОценок пока нет
- Enzyme Lab Report FinalДокумент6 страницEnzyme Lab Report Finalrsenser2100% (2)
- Rate of Reaction Design LabДокумент3 страницыRate of Reaction Design LabVictoria PanОценок пока нет
- Enzyme Activity 04Документ5 страницEnzyme Activity 04Dhandapani PerumalОценок пока нет
- Lab Report Enzymes!Документ8 страницLab Report Enzymes!Francesco ChiocchioОценок пока нет
- Enzyme LabДокумент6 страницEnzyme LabinfinitememoryОценок пока нет
- Bio Lab - Enzymes and Temp.Документ2 страницыBio Lab - Enzymes and Temp.ZahraОценок пока нет
- Lab Report 8Документ6 страницLab Report 8Ng LeepingОценок пока нет
- The Effect of Temperature On The Activity of The Enzyme AmylaseДокумент12 страницThe Effect of Temperature On The Activity of The Enzyme AmylaseNathaniel Hammo50% (2)
- EnzymesДокумент23 страницыEnzymesAnas DarwishОценок пока нет
- AP Lab #2: Enzyme Catalysis LabДокумент4 страницыAP Lab #2: Enzyme Catalysis Labpointweb50% (2)
- Determination of Enzymatic Activity of Salivary Amylase Depending On The Effect of Temperature and PHДокумент11 страницDetermination of Enzymatic Activity of Salivary Amylase Depending On The Effect of Temperature and PHAmberValentineОценок пока нет
- Enzymes 2021Документ6 страницEnzymes 2021lowkeydeadОценок пока нет
- SA2 Criterion B and C-taskid16036TSK1120230412085553611Документ10 страницSA2 Criterion B and C-taskid16036TSK1120230412085553611Ashneel ChakravortyОценок пока нет
- AP Biology Lab 2 Enzyme CatalysisДокумент8 страницAP Biology Lab 2 Enzyme CatalysisJessica HughesОценок пока нет
- Ezra BiochemДокумент5 страницEzra Biochemyayayaniza100% (2)
- Effects of Sucrose Concentration On Cell Respiration in YeastДокумент7 страницEffects of Sucrose Concentration On Cell Respiration in YeastRachel Utomo83% (23)
- Biology Enzymes CourseworkДокумент4 страницыBiology Enzymes Courseworkkqosmkjbf100% (2)
- Expt 6 ActivityДокумент3 страницыExpt 6 ActivityAlthea ValenzuelaОценок пока нет
- Kethan IA BIO LAST PDFДокумент10 страницKethan IA BIO LAST PDFkozacioglukОценок пока нет
- Developed by Richard Giani Edited by Denise Clemens Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection WWW - Dep.pa - State.usДокумент5 страницDeveloped by Richard Giani Edited by Denise Clemens Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection WWW - Dep.pa - State.usCristobal ValdovinosОценок пока нет
- Lactase Enzyme SpectrophotometryДокумент9 страницLactase Enzyme SpectrophotometryBenito KameloОценок пока нет
- Properties of EnzymesДокумент8 страницProperties of Enzymesdtaku8892Оценок пока нет
- How Enzymes Work What Are Enzymes?: en Zyme Substrate SpecificityДокумент12 страницHow Enzymes Work What Are Enzymes?: en Zyme Substrate SpecificityRahil BhavanОценок пока нет
- Ap Cellular Respiration LabДокумент8 страницAp Cellular Respiration Labapi-382372564Оценок пока нет
- Measuring Gas Exchange & It S Relationship To SunlightДокумент6 страницMeasuring Gas Exchange & It S Relationship To SunlightSabhya SachdevaОценок пока нет
- Noah's Fascinating World of STEAM Experiments: Chemical Reactions: A Junior Scientist's Lab Notebook for Learning Scientific MethodОт EverandNoah's Fascinating World of STEAM Experiments: Chemical Reactions: A Junior Scientist's Lab Notebook for Learning Scientific MethodОценок пока нет
- Biological MoleculesДокумент4 страницыBiological MoleculesMonkey LoverОценок пока нет
- Core Practical 4 Enzyme Concentration For BiologyДокумент7 страницCore Practical 4 Enzyme Concentration For BiologyMitullesh EngarshalОценок пока нет
- StoichiometrylabkrobcharcДокумент3 страницыStoichiometrylabkrobcharcapi-239433858Оценок пока нет
- Enzyme-Substrate Reaction LabДокумент10 страницEnzyme-Substrate Reaction Labanon0% (1)
- Enzymes LolsДокумент38 страницEnzymes LolsThon JustineОценок пока нет
- Gravimetric AnalysisДокумент3 страницыGravimetric Analysismeibis monteverdeОценок пока нет
- How Is Enzyme Activity Affected by Different PHДокумент13 страницHow Is Enzyme Activity Affected by Different PHLuke Donnet100% (2)
- Practical 2Документ8 страницPractical 2Ibrahim Muhamad0% (1)
- Super Cool Science and Engineering Activities: with Max Axiom Super ScientistОт EverandSuper Cool Science and Engineering Activities: with Max Axiom Super ScientistОценок пока нет
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationДокумент14 страницCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Educationmina amir0% (1)
- Sensory Interventions - Literature ReviewДокумент26 страницSensory Interventions - Literature Reviewapi-446507356Оценок пока нет
- Dissertation ReportДокумент4 страницыDissertation ReportWameq SiddiquiОценок пока нет
- K. O'Halloran: Multimodal Discourse Analysis: Systemic FUNCTIONAL PERSPECTIVES. Continuum, 2004Документ3 страницыK. O'Halloran: Multimodal Discourse Analysis: Systemic FUNCTIONAL PERSPECTIVES. Continuum, 2004enviОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 - Mother TongueДокумент7 страницChapter 3 - Mother TongueCatherine BonОценок пока нет
- MKTG1100 Chapter 4Документ28 страницMKTG1100 Chapter 4Marcus YapОценок пока нет
- Knowing WomenДокумент332 страницыKnowing WomenAbbas AlkhudairyОценок пока нет
- Synopsis For IIT Research ParkДокумент11 страницSynopsis For IIT Research ParkDinesh JangirОценок пока нет
- DHDR Internal Job Advert August20192 PDFДокумент1 страницаDHDR Internal Job Advert August20192 PDFSreman ChandioОценок пока нет
- Clinical Evaluation Reports 6 Years After Meddev 27 - 1 Revision 4Документ4 страницыClinical Evaluation Reports 6 Years After Meddev 27 - 1 Revision 4יוסי קונסטנטיניסОценок пока нет
- Study Skills Handbook - (B Academic Skills)Документ16 страницStudy Skills Handbook - (B Academic Skills)Fatimah Al-ShammiriОценок пока нет
- CPSP COST Final Evaluation FormsДокумент12 страницCPSP COST Final Evaluation Formsjoy geli mozarОценок пока нет
- Sports Tourism in IndiaДокумент7 страницSports Tourism in Indiaabdul khanОценок пока нет
- Geostats Pty LTD: Sulphur Grade 29.11 % Standard Deviation 1.21 % Confidence Interval +/-0.236 %Документ1 страницаGeostats Pty LTD: Sulphur Grade 29.11 % Standard Deviation 1.21 % Confidence Interval +/-0.236 %rizaedlysamОценок пока нет
- PointersДокумент4 страницыPointersCatholica Fidei Defensoris100% (1)
- Health Information Management of A Strategic Resource 4th Edition Abdelhak Test BankДокумент8 страницHealth Information Management of A Strategic Resource 4th Edition Abdelhak Test Bankoglepogy5kobgk100% (32)
- Book - OT Manager - Chap 34 Supervising Other DisciplinesДокумент9 страницBook - OT Manager - Chap 34 Supervising Other DisciplinesWhitney JosephОценок пока нет
- NI LUH 2021 Company Value Profitability ROAДокумент11 страницNI LUH 2021 Company Value Profitability ROAFitra Ramadhana AsfriantoОценок пока нет
- 1957 23304 1 PBДокумент11 страниц1957 23304 1 PBBELAJAR BERSAMA. NETОценок пока нет
- MUG Business Models UplДокумент23 страницыMUG Business Models UplChristoph MagistraОценок пока нет
- Simplified Guide To Fingerprint AnalysisДокумент13 страницSimplified Guide To Fingerprint AnalysisPRINCES ALLEN MATULACОценок пока нет
- Self AssessmentДокумент4 страницыSelf Assessmentapi-579839747Оценок пока нет
- Use of PEARL in Assessing TRL AKB LДокумент28 страницUse of PEARL in Assessing TRL AKB LVikas Jawaria100% (1)
- Leadership Skill Leadership Skill: Lecture by Affifa Sardar Lecture by Affifa SardarДокумент42 страницыLeadership Skill Leadership Skill: Lecture by Affifa Sardar Lecture by Affifa SardarmeaowОценок пока нет
- Talaat A.Kader: QEHSS DirectorДокумент6 страницTalaat A.Kader: QEHSS DirectormohammedОценок пока нет
- Six Sigma Symbol: Bill Smith MotorolaДокумент7 страницSix Sigma Symbol: Bill Smith Motorolahansdeep479Оценок пока нет
- Deposit Analysis of Kumari Bank Limited: in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement For The Degree ofДокумент11 страницDeposit Analysis of Kumari Bank Limited: in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement For The Degree ofAa-ckC-restОценок пока нет
- Online Panel Data Quality: A Sentiment Analysis Based On A Deep Learning ApproachДокумент8 страницOnline Panel Data Quality: A Sentiment Analysis Based On A Deep Learning ApproachIAES IJAIОценок пока нет
- Business Models For Solar-Powered Irrigation in EthiopiaДокумент8 страницBusiness Models For Solar-Powered Irrigation in EthiopiaBasazinew A BasazinewОценок пока нет
- Confidence Level and Sample SizeДокумент19 страницConfidence Level and Sample SizeJoice Camelle PinosОценок пока нет