Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
What Is Static Electricity
Загружено:
Brian Yosua PratamaИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
What Is Static Electricity
Загружено:
Brian Yosua PratamaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
What is Static Electricity?
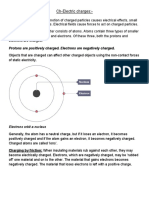
All physical objects are made up of atoms. Inside an atom are protons, electrons and neutrons. The protons are positively charged, the electrons are negatively charged, and the neutrons are neutral. Normally atoms have equal numbers of protons and electrons, so that positive and negative charges are compensated. Thus, the whole burden of the atom is neutral. But if two objects rub against each other, some electrons can pass from one atom to another. Atoms that gain new negatively charged electrons gain. The losers, are positively charged. When the charges are separated in this way is called static electricity. Static electricity results from electrons being knocked off of the surface of atoms, which leaves a net positive charge. If two things have different charges, they attract, or pull towards each other. If two things have the same charge, they reject, or push away from each other. If you walk across a carpet, electrons move from the rug to you. Now you have extra electrons. Touch a door knob and ZAP ! The electrons move from you to the knob. You get a shock. You come inside from the cold, pull off your hat and BOING !!! Static hair - that static electricity makes your hair stand straight out from your head.
How Static Electricity is created The atoms that form all objects contain electrons, which carry a negative charge. Certain types of atoms have outer shells of electrons which are nearly full, meaning they have 6 or 7 electrons in their outer shells, and are very receptive to attracting and taking on new electrons. Other types of atoms may only have a couple electrons in their outer shells, which can mean the electrons are weakly bound to the atom. When a surface with weakly bound atoms is rubbed across one which attracts electrons, the weakly bound atoms will transfer electrons to the other surface, causing it to be negatively charged, while the weakly bound atoms gain a positive charge. Since similar charges repel one another, it is possible to observe static charge when it builds up in strands of hair or fur, since the individual pieces of hair repel one another and stand up on end.
How Static Electricity Happen Sometimes, as you rub two materials together the tiny, negatively charged electrons move from one material to another. This means that one material has too many negatives, so becomes negative overall. The other material doesn't have enough negatives, so becomes positively charged
Lightning is caused by the discharge phenomena on the floor of the static electricity that is generated in clouds by the friction of the water crystals they contain. The burden is not created nor destroyed When you load an object with static electricity, electrons do not create or destroy, or do not appear or disappear protons. The electrons simply move from one place to another. The global burden, therefore, persists. This is what is called the principle of conservation of charge. Winter-summer Generally, only notice static electricity in winter when the air is very dry. During the summer, the air is humid. The water in the air helps electrons to leave our body because it is electrically conductive, and for this we can not carry us far enough.
References : http://www.loc.gov http://www.ehow.com http://www.sciencemadesimple.com
Вам также может понравиться
- Physics for Kids : Electricity and Magnetism - Physics 7th Grade | Children's Physics BooksОт EverandPhysics for Kids : Electricity and Magnetism - Physics 7th Grade | Children's Physics BooksРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Static Electricity: Everything Is Made of AtomsДокумент5 страницStatic Electricity: Everything Is Made of AtomsMuzammil HaqueОценок пока нет
- Physics-Static and Current ElectricityДокумент10 страницPhysics-Static and Current ElectricityCodeen WhiteОценок пока нет
- 1st WeekДокумент5 страниц1st WeekNanzkie Andrei SamanОценок пока нет
- 1 Static Electricity NoteДокумент2 страницы1 Static Electricity Noteapi-266021217Оценок пока нет
- 115 PPT Electrostatics Origin Electrostatics CapacitanceДокумент67 страниц115 PPT Electrostatics Origin Electrostatics CapacitanceErojo, Kyeane Red N.Оценок пока нет
- Static Electricity Is The Imbalance of Positive and Negative ChargeДокумент2 страницыStatic Electricity Is The Imbalance of Positive and Negative ChargeneelaОценок пока нет
- Static Electricity ExplainedДокумент6 страницStatic Electricity ExplainedAnnie KuhnОценок пока нет
- Suplemen of Static ElectricityДокумент10 страницSuplemen of Static ElectricityIndra CesaryantoОценок пока нет
- Phys 3Документ5 страницPhys 3Wyndle PachecaОценок пока нет
- Medical PhysicsДокумент371 страницаMedical PhysicsAhmed khanОценок пока нет
- De g3-5 Staticelectricity GTKДокумент2 страницыDe g3-5 Staticelectricity GTKapi-560457996Оценок пока нет
- What Is ElectricityДокумент7 страницWhat Is ElectricityArjhay GironellaОценок пока нет
- OpenStax 118 Notes ProbsДокумент88 страницOpenStax 118 Notes ProbsPeter NardiОценок пока нет
- 8th Physics U3 Some Natural Phenomenon FДокумент10 страниц8th Physics U3 Some Natural Phenomenon FWorld WarriorОценок пока нет
- Static ElectricityДокумент4 страницыStatic ElectricityMuhammad Wasil KhanОценок пока нет
- ETM 10 Basic Electricity: Engr. Romano A. Pimentel InstructorДокумент17 страницETM 10 Basic Electricity: Engr. Romano A. Pimentel InstructorWynne LiОценок пока нет
- Electricity 01 - Electric ChargeДокумент16 страницElectricity 01 - Electric ChargeAli SalamehОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of ElectricityДокумент9 страницFundamentals of Electricityjohn kevin pascuaОценок пока нет
- Contact-Induced Charge SeparationДокумент2 страницыContact-Induced Charge SeparationMohanie D SudamaОценок пока нет
- Electric ChargesДокумент31 страницаElectric ChargesJeorge QuiboyОценок пока нет
- The Cause of Car ShockДокумент11 страницThe Cause of Car ShockManoj JainОценок пока нет
- Electrostatics 2022 KatikamuДокумент24 страницыElectrostatics 2022 KatikamuWAFULA BRIAN OKANYAОценок пока нет
- Electricity - Misconceptions Spread by K-6 TextbooksДокумент32 страницыElectricity - Misconceptions Spread by K-6 Textbookszezo478Оценок пока нет
- Lecture - Electric Force and Electric FieldДокумент58 страницLecture - Electric Force and Electric FieldnafsОценок пока нет
- ElectrostaticsДокумент51 страницаElectrostaticsdebarshi12Оценок пока нет
- Physics ProjectДокумент44 страницыPhysics ProjectAvnish TewariОценок пока нет
- Physics AssignmentДокумент3 страницыPhysics AssignmentHussein BoffuОценок пока нет
- Electricity - Misconceptions Spread by K-6 TextbooksДокумент28 страницElectricity - Misconceptions Spread by K-6 TextbooksBraulio IrrutiaОценок пока нет
- Electron Theory DAE 1st Year ElectricalДокумент21 страницаElectron Theory DAE 1st Year ElectricalBakhtawar KhanОценок пока нет
- What Is An Electrostatic Force?Документ3 страницыWhat Is An Electrostatic Force?Carlton GrantОценок пока нет
- Some Natural Phenomena Lesson 1Документ20 страницSome Natural Phenomena Lesson 1rajesh duaОценок пока нет
- Electric Charge and Electric FieldДокумент3 страницыElectric Charge and Electric FieldAhmet UlusoyОценок пока нет
- ElectricДокумент318 страницElectricdenokОценок пока нет
- Nature is a Powerhouse of Electricity! Physics Books for Kids | Children's Physics BooksОт EverandNature is a Powerhouse of Electricity! Physics Books for Kids | Children's Physics BooksОценок пока нет
- 9 - Static Electricity CombinedДокумент57 страниц9 - Static Electricity CombinedAli khan7Оценок пока нет
- ELECTROSTATICS 1 - Form 1 Physics Notes: Positive ChargeДокумент6 страницELECTROSTATICS 1 - Form 1 Physics Notes: Positive Chargecatherine SitatiОценок пока нет
- Electrostatics SS1Документ6 страницElectrostatics SS1OlusolaОценок пока нет
- SKMJ - Static ElectricityДокумент18 страницSKMJ - Static Electricitykhumaira.jamariОценок пока нет
- Faculty of Civil Engineering and Architecture: Kaunas University of TechnologyДокумент8 страницFaculty of Civil Engineering and Architecture: Kaunas University of TechnologyDar MudasirОценок пока нет
- Chapter 02Документ14 страницChapter 02Sujoy BanikОценок пока нет
- KS3 Static Electricity Gap-FillДокумент1 страницаKS3 Static Electricity Gap-FillSophie Wyatt-SmithОценок пока нет
- Ch-Electric charges:-Le-Static ElectricityДокумент34 страницыCh-Electric charges:-Le-Static ElectricityZeedan MohammedОценок пока нет
- Science A-Z Book MidДокумент13 страницScience A-Z Book Midapi-313935494Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 22 Notes and WorksheetsДокумент8 страницChapter 22 Notes and WorksheetscelinelizabethОценок пока нет
- Electrophysical Agent 1Документ209 страницElectrophysical Agent 1syammptОценок пока нет
- Physics ResearchДокумент4 страницыPhysics ResearchYzza Veah EsquivelОценок пока нет
- Static Electricity: An Interactive Module For BGSCE Physics Created by Mrs. C. Saunders - NeelyДокумент18 страницStatic Electricity: An Interactive Module For BGSCE Physics Created by Mrs. C. Saunders - NeelyChristanique McIntoshОценок пока нет
- Atomic StructureДокумент19 страницAtomic StructureElmarОценок пока нет
- Q3 - Lesson 1 PDFДокумент85 страницQ3 - Lesson 1 PDFTimothy Francisco100% (1)
- "Elektron" This Is The Origin of The Terms Electricity andДокумент7 страниц"Elektron" This Is The Origin of The Terms Electricity andstudy for KNOWLEDGEОценок пока нет
- Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering MT-144-NSU (Theory)Документ39 страницBasic Electrical & Electronics Engineering MT-144-NSU (Theory)Asad KhokharОценок пока нет
- Chemical Bond: What Is Electricity?Документ2 страницыChemical Bond: What Is Electricity?JohnОценок пока нет
- Electric ChargeДокумент4 страницыElectric ChargeDis DoodОценок пока нет
- Intro To Electrical Technology EditedДокумент60 страницIntro To Electrical Technology Editedmae OrgayaОценок пока нет
- Homework 1 Phys 212 Dr. AmirДокумент6 страницHomework 1 Phys 212 Dr. AmirAldo Novaz CostradaОценок пока нет
- Optical Properties of Nanomaterials: Roopavath Uday KiranДокумент30 страницOptical Properties of Nanomaterials: Roopavath Uday KiranFlorin AndreiОценок пока нет
- BIOLOGYДокумент2 страницыBIOLOGYChristine Joy MolinaОценок пока нет
- Physical Science (PHSC-112) Week 11-20 Grade 11 Week 11-19 Kuya PioloДокумент11 страницPhysical Science (PHSC-112) Week 11-20 Grade 11 Week 11-19 Kuya Piolokyle bryan paul100% (2)
- RDT 112 Prelim SummaryДокумент26 страницRDT 112 Prelim SummaryJian SolimanОценок пока нет
- Photoelectric Effect Problems AnswersДокумент1 страницаPhotoelectric Effect Problems AnswersLuisa Gardênia Farias100% (2)
- ECT1026 Field Theory - 2007 - Lecture 3-8RДокумент23 страницыECT1026 Field Theory - 2007 - Lecture 3-8RteressanathanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 23: Electric Field: 23-3 Coulomb's Law 23-4 Electric Field 23-6 Electric Field LinesДокумент41 страницаChapter 23: Electric Field: 23-3 Coulomb's Law 23-4 Electric Field 23-6 Electric Field LinesDavid ZamudioОценок пока нет
- Dynamics Newton'S Laws of Motion Intended Learning Outcomes (Ilo) 2. Field ForcesДокумент5 страницDynamics Newton'S Laws of Motion Intended Learning Outcomes (Ilo) 2. Field ForcesRALPH ANDREW ESPERONОценок пока нет
- Intro Physics 2.a4Документ643 страницыIntro Physics 2.a4JakeОценок пока нет
- FAQ-How NGWDM Amplifier Works and How To Calculate The OSNRДокумент11 страницFAQ-How NGWDM Amplifier Works and How To Calculate The OSNRThunder-Link.comОценок пока нет
- Work, Power & Energy (Practice Questions)Документ20 страницWork, Power & Energy (Practice Questions)SakshamОценок пока нет
- Surface RoughnessДокумент8 страницSurface RoughnessMahmoud S NasereddinОценок пока нет
- RM 5Документ46 страницRM 5soumengoswami10Оценок пока нет
- An Infrared Light Emitting DiodeДокумент3 страницыAn Infrared Light Emitting DiodeMansur0% (1)
- Chapter 4 (Work, Power and Energy)Документ39 страницChapter 4 (Work, Power and Energy)Prakas PalanychamyОценок пока нет
- Newton's Third LawДокумент69 страницNewton's Third LawJhen IvyОценок пока нет
- Chapter 15Документ32 страницыChapter 15GauravОценок пока нет
- Theodolite InstructionsДокумент6 страницTheodolite InstructionsAnonymous kRuU3IjZEОценок пока нет
- 2201 Chapter 7Документ18 страниц2201 Chapter 7Roy VeseyОценок пока нет
- XII - Physics - Chapter 4 - Moving Charges - Magnetism - Saju - Hsslive PDFДокумент15 страницXII - Physics - Chapter 4 - Moving Charges - Magnetism - Saju - Hsslive PDFMariyam FarhanaОценок пока нет
- How To Use The GPR Calculator and Why Even Bother ?Документ7 страницHow To Use The GPR Calculator and Why Even Bother ?zallpallОценок пока нет
- Cisco DWDM OverviewДокумент87 страницCisco DWDM OverviewRishi NandwanaОценок пока нет
- Electric Charge: Conservation and Quantization Conductors, Insulators, and Induced ChargesДокумент21 страницаElectric Charge: Conservation and Quantization Conductors, Insulators, and Induced ChargesAcadGucciManeОценок пока нет
- VIC-3D Testing GuideДокумент57 страницVIC-3D Testing GuidemeatymealОценок пока нет
- InVia Raman Microscope - Excitation Wavelength OptionsДокумент4 страницыInVia Raman Microscope - Excitation Wavelength OptionsSindhuraj MukherjeeОценок пока нет
- C V RamanДокумент8 страницC V RamanJayesh KomalwarОценок пока нет
- Chapter 25 Modern Optics and Matter Waves: Physics For Scientists and Engineers, 2e (Knight)Документ16 страницChapter 25 Modern Optics and Matter Waves: Physics For Scientists and Engineers, 2e (Knight)Nicole LopezОценок пока нет
- JC PhysicsДокумент1 страницаJC Physicsterrygoh6972Оценок пока нет
- 01 DM - bt1001 - E01 DWDM Principles 62pДокумент62 страницы01 DM - bt1001 - E01 DWDM Principles 62phammadОценок пока нет