Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Newtons 1st and 2nd
Загружено:
Jun ShimИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Newtons 1st and 2nd
Загружено:
Jun ShimАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
1.
Three forces of magnitude F1 = 3.0 N, F2 = 4.0 N and F3 = 6.0 N act at a point. The point is in
equilibrium. The magnitude of the resultant of F1 and F2 is
A.
1.0 N.
B.
5.0 N.
C.
6.0 N.
D.
7.0 N.
(1)
2.
Which of the following quantities must be zero for a particle in equilibrium?
A.
Kinetic energy
B.
Acceleration
C.
Velocity
D.
Momentum
(1)
3.
A fire-fighting helicopter is flying at constant speed along a horizontal straight-line carrying a
bucket of water as shown in the diagram below. The rope to the bucket makes a fixed angle with
the vertical.
constant speed
rope
bucket of water
Which of the following diagrams is the correct free body diagram of the forces acting on the
bucket?
A.
B.
C.
D.
(1)
4.
This question is about a balloon used to carry scientific equipment.
The diagram below represents a balloon just before take-off. The balloons basket is attached to
the ground by two fixing ropes.
balloon
basket
fixing rope
50
fixing rope
50
ground
There is a force F vertically upwards of 2.15 103 N on the balloon. The total mass of the
balloon and its basket is 1.95 102 kg.
(a)
State the magnitude of the resultant force on the balloon when it is attached to the ground.
...................................................................................................................................
(1)
(b)
Calculate the tension in either of the fixing ropes.
...................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
(3)
(c)
The fixing ropes are released and the balloon accelerates upwards. Calculate the magnitude
of this initial acceleration.
...................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
(2)
(d)
The balloon reaches a terminal speed 10 seconds after take-off. The upward force F
remains constant. Describe how the magnitude of air friction on the balloon varies during
the first 10 seconds of its flight.
...................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 8 marks)
5.
A block of mass m is pulled along a horizontal, frictionless surface by a force of magnitude F.
The force makes an angle with the vertical.
F
block
The magnitude of the acceleration of the block in the horizontal direction produced by the force F
is
A.
F
.
m
B.
F sin
.
m
C.
F cos
.
m
D.
F tan
.
m
(1)
6.
A frictionless trolley of mass m moves down a slope with a constant acceleration a. A second
similar frictionless trolley has mass 2m. The acceleration of the second trolley as it moves down
the slope is
A.
1
a.
2
B.
a.
C.
2a.
D.
4a.
(1)
7.
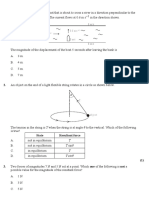
A block of mass M is held at rest on a horizontal table. A heavy chain is attached to the block
with part of the chain hanging over the table. The block and the chain can slide without friction.
block
table
chain
The block is released. Which one of the following graphs best represents the variation with time t
of the speed v of the block as it moves on the table?
A.
C.
B.
D.
(1)
8.
A small boat in still water is given an initial horizontal push to get it moving. The boat gradually
slows down. Which of the following statements is true for the forces acting on the boat as it slows
down?
A.
There is a forward force that diminishes with time.
B.
There is a backward force that diminishes with time.
C.
There is a forward force and a backward force both of which diminish with time.
D.
There is a forward force and a backward force that are always equal and opposite.
(1)
9.
A block on a frictionless horizontal table is attached by a light, inextensible string to an object P
of mass m that hangs vertically as shown below.
pulley
M
P
mass m
The pulley has zero friction and the acceleration of free fall is g. The acceleration of the block
and object P is
A.
g.
B.
m g.
M
C.
m g.
m+M
D.
m+M
g.
m
(1)
10.
A ball of weight W is dropped on to the pan of a top pan weighing balance and rebounds off the
pan.
pan
00.00
At the instant that the ball has zero velocity when in contact with the pan, the scale will read
A.
zero.
B.
a value less than W but greater than zero.
C.
W.
D.
a value greater than W.
(1)
11.
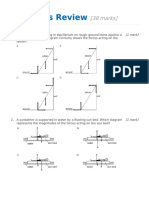
The diagram below shows five wooden blocks joined by inelastic strings. A constant force
accelerates the blocks to the right on a frictionless horizontal table.
W
accelerating
force
table
In which string is the tension the greatest?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Z
(1)
12.
A general expression for Newtons second law of motion is
F=
p
t
What condition is applied so that the law may be expressed in the form F = ma?
A.
The mass m is constant.
B.
The acceleration a is constant.
C.
The force F is constant.
D.
The direction of the force F is constant.
(1)
13.
A trolley of mass 1.5 kg is pulled along a horizontal table by a force of 5.0N.
force 5.0N
The frictional force acting on the trolley is 0.50N.
The acceleration of the trolley is
A.
0.30 m s2.
B.
0.33 m s2.
C.
3.0 m s2.
D.
3.3 m s2.
(1)
14.
A frictionless trolley of mass m moves down a slope with a constant acceleration a. A second
similar frictionless trolley has mass 2m. The acceleration of the second trolley as it moves down
the slope is
A.
1
a.
2
B.
a.
C.
2a.
D.
4a.
(1)
Вам также может понравиться
- As Newtons Laws and Momentum QuestionsДокумент61 страницаAs Newtons Laws and Momentum Questionshasan_shahryar2008Оценок пока нет
- Newtons LawsДокумент110 страницNewtons LawsTenisha CastilloОценок пока нет
- Linear DynamicsДокумент11 страницLinear DynamicsInfrion MatiqueonОценок пока нет
- 2a-Dynamics MC Practice ProblemsДокумент26 страниц2a-Dynamics MC Practice Problemsruuki25Оценок пока нет
- Mechanics Paper 1 Study GuideДокумент6 страницMechanics Paper 1 Study GuideJi Jing MengОценок пока нет
- 2a Dynamics MCNДокумент17 страниц2a Dynamics MCNSnowy JiangОценок пока нет
- Dynamics Practice Problems-2011!09!28Документ21 страницаDynamics Practice Problems-2011!09!28Lester CabungcalОценок пока нет
- AJC TutorialДокумент4 страницыAJC TutorialYong Ming HengОценок пока нет
- Chapter Questions Newton S LawsДокумент8 страницChapter Questions Newton S LawsJunLi CaiОценок пока нет
- Dynamics-Ramps and InclinesДокумент2 страницыDynamics-Ramps and InclinesEyob YimerОценок пока нет
- Reinforcement Exercise Chapter 3Документ3 страницыReinforcement Exercise Chapter 3Noratiqah Binti Mohd AminОценок пока нет
- 2.2 Forces ReviewДокумент17 страниц2.2 Forces ReviewAmrit sharmaОценок пока нет
- Multiple Choice Review - DynamicsДокумент10 страницMultiple Choice Review - DynamicsPremkumar NaikarОценок пока нет
- 50Документ22 страницы50rockingjoeОценок пока нет
- PSI AP Physics I Dynamics Multiple-Choice QuestionsДокумент10 страницPSI AP Physics I Dynamics Multiple-Choice QuestionsKarla PereraОценок пока нет
- Mechanics Baseline Test Questions and DiagramsДокумент8 страницMechanics Baseline Test Questions and DiagramsWanMohdAimranОценок пока нет
- AP Physics 1 - Test 05 - Force and Motion Score:: A B C D EДокумент6 страницAP Physics 1 - Test 05 - Force and Motion Score:: A B C D ESTОценок пока нет
- College Physics A Strategic Approach 3Rd Edition Knight Test Bank Full Chapter PDFДокумент36 страницCollege Physics A Strategic Approach 3Rd Edition Knight Test Bank Full Chapter PDFmaureen.cerza655100% (11)
- 1d Forces Concepts Practice TestДокумент9 страниц1d Forces Concepts Practice TestNütella VallejosОценок пока нет
- Practice Physics TestДокумент7 страницPractice Physics Testthey12Оценок пока нет
- Mechanics SummaryДокумент27 страницMechanics Summaryuse otherОценок пока нет
- College Physics 1St Edition Freedman Test Bank Full Chapter PDFДокумент36 страницCollege Physics 1St Edition Freedman Test Bank Full Chapter PDFmaureen.cerza655100% (12)
- 2.4 2.6 Newtons Laws and Momentum PDFДокумент10 страниц2.4 2.6 Newtons Laws and Momentum PDFAZTonseОценок пока нет
- Vectors and Scalars in MechanicsДокумент18 страницVectors and Scalars in Mechanicsmardel11Оценок пока нет
- Ap Physc M - Dynamics Free Response - 2023 09 09Документ18 страницAp Physc M - Dynamics Free Response - 2023 09 09Abdullah MalikОценок пока нет
- Lom TopicwiseДокумент35 страницLom Topicwisedd100% (1)
- Physics I Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenОценок пока нет
- As Work Energy and Power QuestionsДокумент35 страницAs Work Energy and Power Questionstougao222Оценок пока нет
- AP Physics 1 Algebra Based Unit 2 DynamicsДокумент10 страницAP Physics 1 Algebra Based Unit 2 DynamicsNikhita RajeshОценок пока нет
- CH 4-5 AP Problems All-1Документ21 страницаCH 4-5 AP Problems All-1Christian ChiuОценок пока нет
- Dynamics-Newton's 2nd LawДокумент8 страницDynamics-Newton's 2nd LawEyob YimerОценок пока нет
- Dynamics Multiple Choice QuestionsДокумент8 страницDynamics Multiple Choice QuestionsPaola Rafaela FacchineiОценок пока нет
- WPEДокумент6 страницWPESanjeev KumarОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 4Документ4 страницыTutorial 4Farah HananiОценок пока нет
- 2023 - Part 1 - 2nd LawДокумент7 страниц2023 - Part 1 - 2nd LawMary GinetaОценок пока нет
- FrictionsДокумент2 страницыFrictionsPei YunОценок пока нет
- Test 2 (August) Physics Form 4Документ5 страницTest 2 (August) Physics Form 4Macita KaoruОценок пока нет
- 1993 MC MechДокумент7 страниц1993 MC MechryumiloveОценок пока нет
- Edumantra: Physics DPPДокумент4 страницыEdumantra: Physics DPPNikhil PanigrahiОценок пока нет
- Friction Level1Документ6 страницFriction Level1BОценок пока нет
- Newtons Law Force & Friction WA (English)Документ19 страницNewtons Law Force & Friction WA (English)Swarnlata MishraОценок пока нет
- FORCESДокумент73 страницыFORCESMaria BhaijiОценок пока нет
- Physics I Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenОценок пока нет
- Physics Paper PDFДокумент18 страницPhysics Paper PDFRana IrfanОценок пока нет
- Friction: Section - I: Straight Objective Type 5.1Документ9 страницFriction: Section - I: Straight Objective Type 5.1rashidОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 - ReviewPackage Multiple ChoiceSolutionДокумент16 страницUnit 2 - ReviewPackage Multiple ChoiceSolutionThuran NathanОценок пока нет
- Momentum&CollisionsДокумент12 страницMomentum&CollisionsGia GavicaОценок пока нет
- 2012 Lecture Revision QN (Forces) 19 July NgLT1Документ11 страниц2012 Lecture Revision QN (Forces) 19 July NgLT1timchanymОценок пока нет
- Inclined plane unit end questions mechanicsДокумент4 страницыInclined plane unit end questions mechanicsNaresh JonnaОценок пока нет
- Paper 1 Fizik PAT 2016Документ15 страницPaper 1 Fizik PAT 2016Junaidah Mohamad RamliОценок пока нет
- A of Block Is P. of For WhichДокумент1 страницаA of Block Is P. of For Whichmohapatramugdha99Оценок пока нет
- End of Year AP Problems - 4 - Momentum CДокумент4 страницыEnd of Year AP Problems - 4 - Momentum CChristina ZhangОценок пока нет
- (106 Marks) : 4 Kinetic Energy of The Object at Gravitational Potential Energy of The Object at H 3 4 4 3 9 16 16 9Документ25 страниц(106 Marks) : 4 Kinetic Energy of The Object at Gravitational Potential Energy of The Object at H 3 4 4 3 9 16 16 9Skruzdelyte MielaОценок пока нет
- PHY5113 TUTORIAL N0 3 Questions PDFДокумент9 страницPHY5113 TUTORIAL N0 3 Questions PDFAlbertОценок пока нет
- Assignment # 4 MomentsДокумент9 страницAssignment # 4 MomentsKalidОценок пока нет
- Particle Dynamics (11th JK) WAДокумент48 страницParticle Dynamics (11th JK) WAParijat SutradharОценок пока нет
- Physics 201 Exam StudyДокумент8 страницPhysics 201 Exam StudytomvalixОценок пока нет
- Motion Physics ProblemsДокумент9 страницMotion Physics ProblemsChinny SabadoОценок пока нет
- FRICTION Class Notes Free Full SyllabusДокумент2 страницыFRICTION Class Notes Free Full Syllabuskrahul39896666Оценок пока нет
- Thermal Arc 161 STL 201 Ts Inverter Welder SM PDFДокумент96 страницThermal Arc 161 STL 201 Ts Inverter Welder SM PDFduyОценок пока нет
- MSDS 42935Документ3 страницыMSDS 42935EliasОценок пока нет
- Payables Open Interface Import in Oracle Apps R12Документ11 страницPayables Open Interface Import in Oracle Apps R12sudharshan79Оценок пока нет
- EMB 20100301 Mar 2010Документ156 страницEMB 20100301 Mar 2010agnithiumОценок пока нет
- 9040 - User ManualДокумент236 страниц9040 - User ManualWallie Billingsley77% (13)
- Astm-A707 CS As LTS PDFДокумент5 страницAstm-A707 CS As LTS PDFGoutam Kumar DebОценок пока нет
- Life Pixel - Nikon D5500 DIY Digital Infrared Conversion TutorialДокумент6 страницLife Pixel - Nikon D5500 DIY Digital Infrared Conversion TutorialCОценок пока нет
- What Is Physical GeologyДокумент25 страницWhat Is Physical GeologyMelanyОценок пока нет
- ZMD402AT-CT Technical DataДокумент7 страницZMD402AT-CT Technical DataCarlos SandersОценок пока нет
- CoP Fo Petroleum Road Tanker Vapour Collection Systems and Equipment Used in Unloading OperationsДокумент29 страницCoP Fo Petroleum Road Tanker Vapour Collection Systems and Equipment Used in Unloading OperationsMuhammad Ibad AlamОценок пока нет
- Combination Woodworking Machine Quotation PDFДокумент2 страницыCombination Woodworking Machine Quotation PDFAlunel TapuОценок пока нет
- Iec 62097-2009Документ170 страницIec 62097-2009luis.alvaradoОценок пока нет
- Load Case CombinationsДокумент5 страницLoad Case CombinationsFrancisco UgarteОценок пока нет
- EC2151 Electric Circuit Important QuestionsДокумент47 страницEC2151 Electric Circuit Important QuestionschitragowsОценок пока нет
- Engineering Drawing Solution All Year First Part Ioe NotesДокумент31 страницаEngineering Drawing Solution All Year First Part Ioe Notesई. सन्तोष शर्माОценок пока нет
- Regional Contest Package in EIM NC IIДокумент3 страницыRegional Contest Package in EIM NC IIAlОценок пока нет
- Software MetricsДокумент253 страницыSoftware MetricsAditya ChourasiyaОценок пока нет
- Magic Quadrant For Identity Governance and AdministrationДокумент18 страницMagic Quadrant For Identity Governance and AdministrationmilosvblОценок пока нет
- Arduino Uno Schematic Annotated1Документ1 страницаArduino Uno Schematic Annotated1matthewwu2003100% (1)
- Ijso 2012Документ5 страницIjso 2012bhaskarОценок пока нет
- TNK500P Taneko Industrial Generator (TNK JKT)Документ2 страницыTNK500P Taneko Industrial Generator (TNK JKT)Rizki Heru HermawanОценок пока нет
- Alcatel U3 - Alcatel U3 User GuideДокумент53 страницыAlcatel U3 - Alcatel U3 User Guideoswaldomarangoni5295100% (11)
- Manual de TallerДокумент252 страницыManual de TallerEdison RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Abs/Tcs/Esp Training GuideДокумент136 страницAbs/Tcs/Esp Training GuideKatapangTkrОценок пока нет
- DIN EN 10213 - 2008 - Fundidos em AçoДокумент29 страницDIN EN 10213 - 2008 - Fundidos em AçoLeonardo MartinsОценок пока нет
- RDSS L2 Pert Chart - PKG-04 - Joynagar.... 21082023Документ5 страницRDSS L2 Pert Chart - PKG-04 - Joynagar.... 21082023sourish69Оценок пока нет
- Design of Connetiomn Chankara AryaДокумент21 страницаDesign of Connetiomn Chankara AryaMohamed AbdОценок пока нет
- Ci-2001 Ab OmДокумент30 страницCi-2001 Ab OmEnrique FlowersОценок пока нет
- CST Design Studio - WorkflowДокумент102 страницыCST Design Studio - WorkflowHeber Bustos100% (7)
- Quality Management Project On Quality Tools of "Ford Motors"Документ6 страницQuality Management Project On Quality Tools of "Ford Motors"Anuj SharmaОценок пока нет