Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
GE 13 Diuretics Drug Table
Загружено:
hidayah BorhanudinИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
GE 13 Diuretics Drug Table
Загружено:
hidayah BorhanudinАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
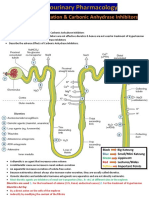
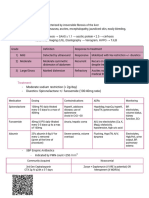
GE 13: DIURETIC DRUGS
Definition: drugs that induce a state of increased urine flow Classes of diuretics Example of drugs Mechanism of action - Inhibits the enzyme carbonic anhydrase in proximal tubular epithelial cells - the enzyme catalyses the reaction between CO2 and H2O to produce H+ and HCO3Inihibits the Na+/K+/Clcarrier in the luminal membrane Site of action Proximal tubule Therapeutics uses - treatment of chronic glaucoma - prophylaxis of acute mountain sickness Pharmacokinetics Adverse effects
Carbonic Acetazolamide anhydrase inhibitor
Loop/high-ceiling diuretics
Bumetanide Furosemide
Ascending loop of Henle
- reduce acute pulmonary edema due to congestive heart failure - stimulate tubular Ca2+ secretion in hypercalcemia condition - reduce intracranial pressure in patients with severe traumatic brain injury
- administered orally or parentally - duration of action about 1 6 hours - the most effective diuretic
- potassium depletion (hypokalaemia), high concentration of Na+ in distal tubule results in increase exchange of Na+ for K+ - acute hypovolemia (decrease in volume of blood plasma) - hyperuricaemia, blocking of uric acid secretion causing attacks of gouts - ototoxicity,
permanent hearing damage with continued treatment (worse with aminoglycoside antibiotics) Thiazides and related agents Chlorothiazide - decrease the Na+ Hydrochlorothiazide reabsorption by binding Chlorthalidone to the Cl- site of Na+/Clcontransporter on luminal membrane & inhibiting its action Chlorothiazide actions: - increase excretion of Na+ and Cl- loss of K+ - decrease urinary calcium excretion - reduced peripheral vascular resistance with continued use Distal tubule
Distal tubule
Potassium-sparing diuretics
Spironolactone - a synthetic aldosterone antagonist
- competes with aldosterone for intracellular receptors prevent translocation of receptor complex to
- reduce systolic and diastolic bp for extended periods in the treatment of hypertension - reduce extracellular volume in mild/moderate congestive HF - prevent recurrent kidney stone formation in idiopathic calciuria - distal tubule - diuretic - collecting - treatment of tubule secondary hyperaldosteronism
- administered orally - taken 1 -3 weeks for stable reduction in bp
- potassium depletion - hyperuricaemia - volume depletion which can cause dizziness - hypercalcemia - hyperglycaemia - hypersensistivity
- completely absorbed orally - rapidly converted to active metabolite
- disturbance in hormonal activity, may induce gynaecomastia in male and irregular
- amiloride - triamterene
Osmotic diuretics
- mannitol - urea
the nucleus prevent transcription and translation of mediator protein - these mediators normally stimulate Na+/K+ exchanger - prevent Na+ reabsorption and secretion of K+ and H+ - blocks Na+ luminal channels (act independently of aldosterone) - inhibit reabsorption of Na+ - reduce secretion of K+ and H+ - act indirectly by modifying the content of filtrate by increasing the osmolarity
menstruation in female - hyperkalaemia, nausea, lethargy, confusion
- distal tubule - collecting tubule
- glomerulus
- reduce intracranial pressure - treatment of acute renal failure
Вам также может понравиться
- DiureticsДокумент4 страницыDiureticsBill John100% (1)
- Lecture 6-1Документ50 страницLecture 6-1Vijita PriyaОценок пока нет
- Diuretics MergedДокумент727 страницDiuretics MergedRinkiОценок пока нет
- Diuretic Drugs Dr. DarmawanДокумент54 страницыDiuretic Drugs Dr. DarmawanEdi KurniadiОценок пока нет
- GRP 6.pharmaДокумент29 страницGRP 6.pharmaLjc JaslinОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент59 страницUntitledSafayet HossainОценок пока нет
- 6.1. AntihipertensiДокумент52 страницы6.1. AntihipertensiDada DoniОценок пока нет
- 1 DiurethicsДокумент8 страниц1 DiurethicsMoataz TrabehОценок пока нет
- Electrolyte Imbalance - Handout PDFДокумент23 страницыElectrolyte Imbalance - Handout PDFFaisal Ridho SaktiОценок пока нет
- Diuretics Lec.11Документ12 страницDiuretics Lec.11alhsnawybyshwОценок пока нет
- Diuretics - : Five Major Classes of Diuretics AreДокумент6 страницDiuretics - : Five Major Classes of Diuretics AreVaishali PrasharОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular PharmacologyДокумент61 страницаCardiovascular PharmacologyTeeOne920% (1)
- Kee: Pharmacology, 8th Edition: Chapter 43: Diuretics Downloadable Key PointsДокумент3 страницыKee: Pharmacology, 8th Edition: Chapter 43: Diuretics Downloadable Key PointsLondera BainОценок пока нет
- Beige Brown Vintage Group Project Presentation - 20230922 - 184226 - 0000Документ25 страницBeige Brown Vintage Group Project Presentation - 20230922 - 184226 - 0000Mercurio AysonОценок пока нет
- Diuretics: Class of Drug Actions Uses Side Effects Nursing ImplicationsДокумент1 страницаDiuretics: Class of Drug Actions Uses Side Effects Nursing ImplicationsRaju NiraulaОценок пока нет
- Diuretics 1Документ34 страницыDiuretics 1ياسمين مجديОценок пока нет
- Ph'cology of Diuretics (RZH)Документ48 страницPh'cology of Diuretics (RZH)beby febyola siagianОценок пока нет
- DrugsДокумент116 страницDrugsRyan FlahertyОценок пока нет
- Diuretics: Sumolly Anak DavidДокумент29 страницDiuretics: Sumolly Anak Davidfarmasi_hmОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular For PharmacologДокумент134 страницыCardiovascular For Pharmacologephremtigabie7Оценок пока нет
- Genitourinary PharmacologyДокумент11 страницGenitourinary PharmacologySadia YousafОценок пока нет
- Lecture+24 +25+diureticsДокумент69 страницLecture+24 +25+diureticsGhina RizwanОценок пока нет
- Pharmacology of Diuretics: DR - Datten Bangun MSC, SPFKДокумент46 страницPharmacology of Diuretics: DR - Datten Bangun MSC, SPFKRizky Pramata Simamora 19000029Оценок пока нет
- Cirrhosis SBPДокумент9 страницCirrhosis SBPapi-690342013Оценок пока нет
- Diuretics: Professor C. B. Choudhary Department of Pharmacology NMCTH, BiratnagarДокумент52 страницыDiuretics: Professor C. B. Choudhary Department of Pharmacology NMCTH, BiratnagarKulgaurav RegmiОценок пока нет
- Diuretics: Chris Hague, PHDДокумент29 страницDiuretics: Chris Hague, PHDranachamanОценок пока нет
- Lecture 04 - 306Документ16 страницLecture 04 - 306ShAkil AhmedОценок пока нет
- Drug Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesДокумент8 страницDrug Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesKhim CaronanОценок пока нет
- Diuretics: DR Mozna TalpurДокумент33 страницыDiuretics: DR Mozna TalpurShahid HameedОценок пока нет
- Diuretics: BY-DR. Saurabh Kansal Dept. of Pharmacology Msy Medical College MeerutДокумент33 страницыDiuretics: BY-DR. Saurabh Kansal Dept. of Pharmacology Msy Medical College MeerutPrakhar GoelОценок пока нет
- VasopressinДокумент2 страницыVasopressinKim LompotОценок пока нет
- Pharmacology RCR1 RenalДокумент6 страницPharmacology RCR1 RenaleamcrawleyОценок пока нет
- Renal UWДокумент7 страницRenal UWridin007Оценок пока нет
- Renal Drugs Diuretics Agents: by Desalegn Chilo (B.Pharm, MSC)Документ54 страницыRenal Drugs Diuretics Agents: by Desalegn Chilo (B.Pharm, MSC)Remedan TahaОценок пока нет
- Drug Study - CholangioДокумент10 страницDrug Study - CholangioClaireMutiaОценок пока нет
- Drugs Affecting Renal SystemДокумент44 страницыDrugs Affecting Renal SystemRwapembe StephenОценок пока нет
- Pharm - Pure & SimpleДокумент33 страницыPharm - Pure & SimpleBlake FarberОценок пока нет
- 5 Hypertension Handout PDFДокумент20 страниц5 Hypertension Handout PDFMd Sakil AminОценок пока нет
- Dr. Prajogo - PharmacologyДокумент144 страницыDr. Prajogo - Pharmacologydelia rahmaОценок пока нет
- Management of Acute Kidney InjuryДокумент31 страницаManagement of Acute Kidney InjurysumitОценок пока нет
- Cardio Lab MedsДокумент11 страницCardio Lab MedsDianne Erika MeguinesОценок пока нет
- Topic - Diuretics: Submitted By, Group - 07Документ28 страницTopic - Diuretics: Submitted By, Group - 07Arvi KhanОценок пока нет
- DiureticsДокумент12 страницDiureticslandita683Оценок пока нет
- Diabetes Insipidus: Nitha K 2 Year MSC NursingДокумент47 страницDiabetes Insipidus: Nitha K 2 Year MSC NursingNITHA K100% (1)
- Drugs Acting On The KidneysДокумент56 страницDrugs Acting On The Kidneysbetu tufaОценок пока нет
- 09 Diuretics UpdДокумент42 страницы09 Diuretics UpdYeni Chie Aneuk TuleutОценок пока нет
- DiureticsДокумент3 страницыDiureticsarshu98172Оценок пока нет
- Meds #1 NotesДокумент4 страницыMeds #1 NotesAnh TrinhОценок пока нет
- Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Lec 3 and 4 LatestДокумент37 страницAnti-Inflammatory Drugs Lec 3 and 4 Latests.nilormee1201Оценок пока нет
- Cardiotonic DrugsДокумент67 страницCardiotonic DrugsLady Mae Ramos100% (1)
- Dehydration PresentationДокумент3 страницыDehydration PresentationAhsan KhanОценок пока нет
- Diuretic Agents: Dept. of Pharmacology & TherapeuticДокумент44 страницыDiuretic Agents: Dept. of Pharmacology & Therapeuticangelica gloryОценок пока нет
- Gagal Jantung "Manajemen Iskemik Vs Non Iskemik: DR - Tengku M Budiansyah, SP - JP Siloam Hospitals BogorДокумент76 страницGagal Jantung "Manajemen Iskemik Vs Non Iskemik: DR - Tengku M Budiansyah, SP - JP Siloam Hospitals BogorIndahnvkОценок пока нет
- Chronic Renal FailureДокумент54 страницыChronic Renal FailureAkia Cayasan BayaОценок пока нет
- HypercalcemiaДокумент50 страницHypercalcemiaEvelyn EdgarОценок пока нет
- PharmacologyДокумент23 страницыPharmacologyAbhisek ChatterjeeОценок пока нет
- Drug Study (MS)Документ9 страницDrug Study (MS)Kristine GallardoОценок пока нет
- Diuretics: Diuretics Are Drugs That Increase The Volume of Urine FlowДокумент35 страницDiuretics: Diuretics Are Drugs That Increase The Volume of Urine FlowAmanuel Maru100% (1)
- Physiology for General Surgical Sciences Examination (GSSE)От EverandPhysiology for General Surgical Sciences Examination (GSSE)S. Ali MirjaliliОценок пока нет
- New Document (116) New Document (115) New Document (1Документ9 страницNew Document (116) New Document (115) New Document (1Manav PARMARОценок пока нет
- Adolescent Violence Towards Parents Myths and RealitiesДокумент25 страницAdolescent Violence Towards Parents Myths and RealitiesJoão D C MendonçaОценок пока нет
- Marketing Plan For Paraiso Islet ResortДокумент25 страницMarketing Plan For Paraiso Islet ResortEllaine Claire Lor100% (1)
- Financial Crisis Among UTHM StudentsДокумент7 страницFinancial Crisis Among UTHM StudentsPravin PeriasamyОценок пока нет
- Acidity (As Acetic Acid) On Undenatured and Denatured EthanolДокумент10 страницAcidity (As Acetic Acid) On Undenatured and Denatured EthanolVinh NguyenОценок пока нет
- 1999, 2003 - Purple Triangles - BrochureДокумент32 страницы1999, 2003 - Purple Triangles - BrochureMaria Patinha100% (2)
- Schiffman Cb09 PPT 06Документ49 страницSchiffman Cb09 PPT 06Parth AroraОценок пока нет
- Institute of Actuaries of India: Subject CT3-Probability and Mathematical Statistics May 2008 ExaminationДокумент10 страницInstitute of Actuaries of India: Subject CT3-Probability and Mathematical Statistics May 2008 ExaminationeuticusОценок пока нет
- Afia Rasheed Khan V. Mazharuddin Ali KhanДокумент6 страницAfia Rasheed Khan V. Mazharuddin Ali KhanAbhay GuptaОценок пока нет
- Units 6-10 Review TestДокумент20 страницUnits 6-10 Review TestCristian Patricio Torres Rojas86% (14)
- INTRODUCTIONДокумент1 страницаINTRODUCTIONNabila Gaming09Оценок пока нет
- Electronic Load FundamentalsДокумент16 страницElectronic Load FundamentalsMiguel PenarandaОценок пока нет
- PsychFirstAidSchools PDFДокумент186 страницPsychFirstAidSchools PDFAna ChicasОценок пока нет
- Hard Soft Acid Base TheoryДокумент41 страницаHard Soft Acid Base TheorythinhbuОценок пока нет
- Defending A Dogma: Between Grice, Strawson and Quine: Elvis ImafidonДокумент10 страницDefending A Dogma: Between Grice, Strawson and Quine: Elvis ImafidonYang Wen-LiОценок пока нет
- ACT December 2018 Form B05 PDFДокумент54 страницыACT December 2018 Form B05 PDFPranav ChatiОценок пока нет
- Rizal ExaminationДокумент3 страницыRizal ExaminationBea ChristineОценок пока нет
- Midterm Decision Analysis ExercisesДокумент5 страницMidterm Decision Analysis ExercisesAYLEN INJAYAОценок пока нет
- Improving Self-Esteem - 08 - Developing Balanced Core BeliefsДокумент12 страницImproving Self-Esteem - 08 - Developing Balanced Core BeliefsJag KaleyОценок пока нет
- Ross, D. (2013) - Field Guide To Jumping Spiders of Southeast Idaho.Документ4 страницыRoss, D. (2013) - Field Guide To Jumping Spiders of Southeast Idaho.Dave RossОценок пока нет
- Practice Makes Perfect Basic Spanish Premium Third Edition Dorothy Richmond All ChapterДокумент67 страницPractice Makes Perfect Basic Spanish Premium Third Edition Dorothy Richmond All Chaptereric.temple792100% (3)
- Southeast Asian Fabrics and AttireДокумент5 страницSoutheast Asian Fabrics and AttireShmaira Ghulam RejanoОценок пока нет
- Biblehub Com Commentaries Matthew 3 17 HTMДокумент21 страницаBiblehub Com Commentaries Matthew 3 17 HTMSorin TrimbitasОценок пока нет
- Friedman LawsuitДокумент12 страницFriedman LawsuitChris GothnerОценок пока нет
- CV AmosДокумент4 страницыCV Amoscharity busoloОценок пока нет
- Gothic Revival ArchitectureДокумент19 страницGothic Revival ArchitectureAlexandra Maria NeaguОценок пока нет
- Dopamine What It Is, Function & SymptomsДокумент7 страницDopamine What It Is, Function & SymptomsRaj KumarОценок пока нет
- JURDING (Corticosteroids Therapy in Combination With Antibiotics For Erysipelas)Документ21 страницаJURDING (Corticosteroids Therapy in Combination With Antibiotics For Erysipelas)Alif Putri YustikaОценок пока нет
- DUN Bukit Lanjan CNY Sponsorship Form2Документ1 страницаDUN Bukit Lanjan CNY Sponsorship Form2alamsekitarselangorОценок пока нет
- A Tool For The Assessment of Project Com PDFДокумент9 страницA Tool For The Assessment of Project Com PDFgskodikara2000Оценок пока нет