Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
JPN Pahang Physics Module Form 4chapter 5 Light
Загружено:
Signore MayoreИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
JPN Pahang Physics Module Form 4chapter 5 Light
Загружено:
Signore MayoreАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
JPN Pahang Physics Module Form 4Chapter 5 Light
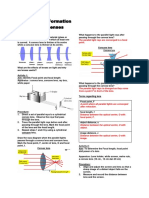
20 Refraction of rays parallel to the principal axis of a convex lens
:Draw in the following diagrams the paths of the rays after passing through the lens.Write in the boxed provided, the name of the
point or line shown.i)ii)iii)iv) Focal planeSecondary focusPrincipal focusPrincipal focusFocal
planeSecondary focus FFFF
JPN Pahang Physics Module Form 4Chapter 5 Light
21 Principles of constructing ray diagrams : Complete the path of each ray after passing through thelensi)
ii) iii)iv) v) vi)vii) viii) Exercise 1 :State the meaning of each of the following terms:i) Focal length ,
f : The distance between optic centre and the principal focus ii)
Object distance,
u : The distance between the object and optic centre iii)
Image distance, v
: The distance between the image and the optic centre
Exercise 2 :Describe how you would
estimate the focal length of a convex lens in the school lab. Place the lens facing the window on the far side of the lab. Adjust the distance of a
screen behind the lens until a sharp image of the window is formed. Measure the focal length (distance betweenthe lens and the image).
FFFFFFFFFFFFF FFF
JPN Pahang Physics Module Form 4Chapter 5 Light
22 Characteristics of image formed by a convex lens : (Construction of ray diagram
method)Construct ray diagrams for each of the following cases and state the characteristics of the imageformed. i)
Case 1 : u >2 f
where u
= object distance ; and f = focal length of lens.Characteristic s of image: Diminished, real and inverted ii)
Case 2 : u =2 f
Characteristics of image:
Same size, real and inverted iii) Case 3 : 2 f
> u > f
Characteristics of image: Magnified, real and inverted
FF2FobjectLensF F2FobjectLensFF 2FobjectLens imageimageimage
Вам также может понравиться
- Answer Scheme-Physics LightДокумент38 страницAnswer Scheme-Physics LightSelva RajОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5: Light: Normal Reflected Angle Incident AngleДокумент13 страницChapter 5: Light: Normal Reflected Angle Incident AngleChristopher AuОценок пока нет
- Topic: Light: Chapter Highlight: 5.4 Lenses Image Form by Convex Lenses Object Distance Ray Diagram Image Distance Image Characte Ristics UsesДокумент14 страницTopic: Light: Chapter Highlight: 5.4 Lenses Image Form by Convex Lenses Object Distance Ray Diagram Image Distance Image Characte Ristics UsesNorhisham Mohamed SobriОценок пока нет
- SMK ALOR PONGSU 34300 BAGAN SERAI, PERAK SCHEME OF WORK FOR FORM 4 PHYSICS YEARLY TEACHING PLAN 2013 SMK ALOR PONGSU 34300 BAGAN SERAI, PERAK SCHEME OF WORK FOR FORM 4 PHYSICS YEARLY TEACHING PLAN 2012 LEARNING AREA: 1. INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICS Week / Date Learning Objective Learning Outcomes Suggested Activities Notes Minimum Requirement & Sources 2/1-4/1 1.1 Understanding Physics A student is able to: • explain what physics is • recognize the physics in everyday objects and natural phenomena Observe everyday objects such as table, a pencil, a mirror etc and discuss hoe they are related to physics concepts. View a video on natural phenomena and discuss how they related to physics concepts. Discuss fields of study in physics such as forces, motion, heta, light etc. JPNP Module Ex: Vernier Callipers And Micrometer Screw Gauge 7/1-11/1 1.2 Understanding base quantities and derived quantities A student is able to: • explain what base quanДокумент48 страницSMK ALOR PONGSU 34300 BAGAN SERAI, PERAK SCHEME OF WORK FOR FORM 4 PHYSICS YEARLY TEACHING PLAN 2013 SMK ALOR PONGSU 34300 BAGAN SERAI, PERAK SCHEME OF WORK FOR FORM 4 PHYSICS YEARLY TEACHING PLAN 2012 LEARNING AREA: 1. INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICS Week / Date Learning Objective Learning Outcomes Suggested Activities Notes Minimum Requirement & Sources 2/1-4/1 1.1 Understanding Physics A student is able to: • explain what physics is • recognize the physics in everyday objects and natural phenomena Observe everyday objects such as table, a pencil, a mirror etc and discuss hoe they are related to physics concepts. View a video on natural phenomena and discuss how they related to physics concepts. Discuss fields of study in physics such as forces, motion, heta, light etc. JPNP Module Ex: Vernier Callipers And Micrometer Screw Gauge 7/1-11/1 1.2 Understanding base quantities and derived quantities A student is able to: • explain what base quanShu85Оценок пока нет
- Form 4 Physics Chapter 5Документ48 страницForm 4 Physics Chapter 5Misratul A'la Mahyuddin100% (4)
- Extra Questions - Refraction - Lens - Answers - 230610 - 042208Документ5 страницExtra Questions - Refraction - Lens - Answers - 230610 - 042208Zoha AzizОценок пока нет
- Laboratory E Thin Lenses: Physics 111: Elementary PhysicsДокумент8 страницLaboratory E Thin Lenses: Physics 111: Elementary PhysicsCraigОценок пока нет
- P F P F: Exercise 1: 5.1 Reflection of LightДокумент2 страницыP F P F: Exercise 1: 5.1 Reflection of LightMohamad Rizal MukhtarОценок пока нет
- Physics 72.1 - E08 Image FormationДокумент9 страницPhysics 72.1 - E08 Image FormationTidal SurgesОценок пока нет
- ELEC4610 Engineering Optics: Mid-Term ExaminationДокумент3 страницыELEC4610 Engineering Optics: Mid-Term ExaminationJohn NgОценок пока нет
- 已編輯 - Ch 19 HW set 2 Harder problem on lensesДокумент4 страницы已編輯 - Ch 19 HW set 2 Harder problem on lenses呆毛是本体Оценок пока нет
- Reflection of Light TestДокумент2 страницыReflection of Light TestVaishnavi RajgopalОценок пока нет
- 10 THДокумент3 страницы10 THRohitОценок пока нет
- Ts - X - Physics - All Chapters Questions - Sa-1 & Pf-1 & 2Документ49 страницTs - X - Physics - All Chapters Questions - Sa-1 & Pf-1 & 2mahadevihusnagare52Оценок пока нет
- Practice QuestionsДокумент4 страницыPractice QuestionsShine BhopalОценок пока нет
- Lecture-3 OMДокумент61 страницаLecture-3 OMarulmuruguОценок пока нет
- Physics CL10 WS 5Документ7 страницPhysics CL10 WS 5vaibhave BhatiaОценок пока нет
- Complete The Ray Diagram Above To Show How The Compound Microscope WorksДокумент3 страницыComplete The Ray Diagram Above To Show How The Compound Microscope WorksSakawi LenОценок пока нет
- 8.focal Length of Convex LensДокумент2 страницы8.focal Length of Convex LensMD. DIDARUL ISLAMОценок пока нет
- Focal Length of Concave MirrorДокумент2 страницыFocal Length of Concave MirrorniteshОценок пока нет
- Lecture and Worksheet - LensesДокумент13 страницLecture and Worksheet - LensesJaymar Dela CruzОценок пока нет
- G-10 Physics Important Questions FinalДокумент29 страницG-10 Physics Important Questions FinalRohan SenapathiОценок пока нет
- Compound MicroscopeДокумент7 страницCompound Microscopeaman100% (1)
- 6.3 Images Formation by Lens Answer PDFДокумент7 страниц6.3 Images Formation by Lens Answer PDFAin NadiaОценок пока нет
- Ray Optics Lect 02 Notes - Ray Optics 02donefinalnotesДокумент35 страницRay Optics Lect 02 Notes - Ray Optics 02donefinalnotesAbhaya RanjanОценок пока нет
- 60686aef887bd50105484aae - ## - Ray Optics Lect 02 Notes PDFДокумент35 страниц60686aef887bd50105484aae - ## - Ray Optics Lect 02 Notes PDFRamesh babu pittalaОценок пока нет
- PPT-3 Chapter 2.2 Concave MirrorsДокумент20 страницPPT-3 Chapter 2.2 Concave MirrorsAreen Alhazaymeh100% (1)
- Light ModuleДокумент38 страницLight ModuleZulhisyam NordinОценок пока нет
- Final Exam Questions #5 - Optical InstrumentsДокумент2 страницыFinal Exam Questions #5 - Optical Instrumentsanonslu2012100% (1)
- S09 P122 - Lenses in CombinationДокумент4 страницыS09 P122 - Lenses in CombinationRA MemijeОценок пока нет
- Object Concave Mirror: Enforcement Exercise Chapter Light For Final Exam Form 5 Semester 1 2010Документ2 страницыObject Concave Mirror: Enforcement Exercise Chapter Light For Final Exam Form 5 Semester 1 2010Mohamad Rizal MukhtarОценок пока нет
- Final Exam Questions #4 - LensДокумент4 страницыFinal Exam Questions #4 - Lensanonslu2012Оценок пока нет
- Lens Lab: Part I: MethodsДокумент4 страницыLens Lab: Part I: MethodsMegan Hayes-GoldingОценок пока нет
- Geometric Optics Exam QuestionsДокумент10 страницGeometric Optics Exam QuestionsMahendra Chouhan100% (3)
- Chapter 5 Light Teacher's GuideДокумент38 страницChapter 5 Light Teacher's GuideFahmi AmiОценок пока нет
- Digital Holographic Microscopy Adjustment For Low-Precision Secondary Optical Mount ManufacturingДокумент10 страницDigital Holographic Microscopy Adjustment For Low-Precision Secondary Optical Mount ManufacturingSena Sukmananda SupraptoОценок пока нет
- Physics Part 2 E.V PDFДокумент5 страницPhysics Part 2 E.V PDFShira YukiОценок пока нет
- Grade 10 Light RevДокумент24 страницыGrade 10 Light RevDanny BlessyОценок пока нет
- Latihan Light f1Документ19 страницLatihan Light f1igori76Оценок пока нет
- Untitled PresentationДокумент13 страницUntitled PresentationsanaОценок пока нет
- Measurement of Focal Length of A Concave Mirror: Experiment-406 FДокумент21 страницаMeasurement of Focal Length of A Concave Mirror: Experiment-406 FSantanuОценок пока нет
- BTL TNVLДокумент8 страницBTL TNVLNguyên Nguyễn XuânОценок пока нет
- Physics XII CH 9 CASE STUDY Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsДокумент15 страницPhysics XII CH 9 CASE STUDY Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsNjan KL16么PorottaОценок пока нет
- Spherical Mirrors: Concave MirrorДокумент3 страницыSpherical Mirrors: Concave MirrorLeah ClovisОценок пока нет
- Documents - MX Chapter 5 Light Teachers Guide 558445afb6f9eДокумент38 страницDocuments - MX Chapter 5 Light Teachers Guide 558445afb6f9eMK Joey ThamОценок пока нет
- TS Physics DCEB QuestionsДокумент16 страницTS Physics DCEB QuestionsKrishna KishoreSarvaОценок пока нет
- Q On LensesДокумент3 страницыQ On Lenseszendaya alisiaОценок пока нет
- Sains Chapter 7 ModuleДокумент15 страницSains Chapter 7 ModuleRosalmi AyuОценок пока нет
- Ashadeep Iit: Chapter: 09 - Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsДокумент3 страницыAshadeep Iit: Chapter: 09 - Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsPurab PatelОценок пока нет
- Implementing Light Field Image Refocusing Algorithm: Wenxingfu@nwpu - Edu.cnДокумент8 страницImplementing Light Field Image Refocusing Algorithm: Wenxingfu@nwpu - Edu.cnWafa BenzaouiОценок пока нет
- SEMESTER 2 Practical Science 1Документ2 страницыSEMESTER 2 Practical Science 1are_mine90Оценок пока нет
- Autonomous Robot OperationДокумент16 страницAutonomous Robot OperationDiego CorreaОценок пока нет
- A Level Physics 2 QuestionsДокумент43 страницыA Level Physics 2 QuestionsTRIPPLE KAYZ UGОценок пока нет
- Qty Items Part Numbers: D D D D Object TelescopeДокумент7 страницQty Items Part Numbers: D D D D Object TelescopekamdidoelОценок пока нет
- Report V1.1.4.finalДокумент17 страницReport V1.1.4.finalDiego CorreaОценок пока нет