Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Formula Booklet
Загружено:
Robin D'ArcyИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Formula Booklet
Загружено:
Robin D'ArcyАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
OCR 2010
GCE Physics B (Advancing Physics)
*
O
C
E
/
2
6
2
9
1
*
Data, Formulae and Relationships Booklet
(Revised Version 2.2)
GCE Advanced Level and Advanced Subsidiary
Physics B (Advancing Physics)
Physics units G491, G492, G494, G495
These data, formulae and relationships are for the use of candidates
following the Physics B (Advancing Physics) specification.
Clean copies of this booklet must be available in the examination room, and
must be given up to the invigilator at the end of the examination.
Copies of this booklet may be used for teaching.
DC (SLM) 26291/9
CST254
Instructions to Exams Officer/Invigilator
Do not send this Data Sheet for marking; it should be retained in the centre or destroyed.
CST254
OCR 2010
GCE Physics B (Advancing Physics)
Data
Values are given to three significant figures, except where more or fewer are useful.
Physical constants
speed of light c 3.00 10
8
ms
1
permittivity of free space c
0
8.85 10
12
C
2
N
1
m
2
(or F m
1
)
electric force constant k =
1
4c
0
8.98 10
9
N m
2
C
2
( 9 10
9
N m
2
C
2
)
permeability of free space a
0
4 10
7
N A
2
(or H m
1
)
charge on electron e 1.60 10
19
C
mass of electron m
e
9.11 10
31
kg = 0.000 55 u
mass of proton m
p
1.673 10
27
kg = 1.007 3 u
mass of neutron m
n
1.675 10
27
kg = 1.008 7 u
mass of alpha particle m
6.646 10
27
kg = 4.001 5 u
Avogadro constant L, N
A
6.02 10
23
mol
1
Planck constant h 6.63 10
34
J s
Boltzmann constant k 1.38 10
-23
J K
1
molar gas constant R 8.31 J mol
1
K
1
gravitational force constant G 6.67 10
11
N m
2
kg
2
CST254
OCR 2010
GCE Physics B (Advancing Physics)
Other data
standard temperature and pressure (stp) 273 K (0C), 1.01 10
5
Pa (1 atmosphere)
molar volume of a gas at stp V
m
2.24 10
2
m
3
gravitational field strength at the Earths
surface in the UK g 9.81 N kg
1
Conversion factors
unified atomic mass unit 1u = 1.661 10
27
kg
1 day = 8.64 10
4
s
1 year 3.16 10
7
s
1 light year 10
16
m
Mathematical constants and equations
e = 2.72 = 3.14 1 radian = 57.3
arc = r0 circumference of circle = 2r
sin0 tan 0 0
and cos 0 1 for small 0
area of circle = r
2
curved surface area of cylinder = 2rh
ln(x
n
) = n lnx volume of cylinder = r
2
h
ln(e
kx
) = kx surface area of sphere = 4r
2
volume of sphere =
4
3
r
3
Prefixes
10
12
p
10
9
n
10
6
10
3
m
10
3
k
10
6
M
10
9
G
CST254
OCR 2010
GCE Physics B (Advancing Physics)
Formulae and relationships
Imaging and Signalling
focal length
1
v
=
1
u
+
1
f
Cartesian convention
(object distance u,
image distance v, focal length f)
refractive index
n =
speed of light in vacuo
speed of light in medium
(refractive index n)
Noise limitation on maximum
bits per sample
b = log
2
V
total
V
noise
or 2
b
=
V
total
V
noise
(maximum bits per sample b,
total voltage variation V
total
,
noise voltage V
noise
)
Electricity
current
I =
Q
t
(current I, charge flow Q,
time interval t)
potential difference
V =
E
Q
(potential difference V, energy E,
charge Q)
power P = IV = I
2
R (power P, potential difference V,
current I)
V
load
= c Ir (emf c, internal resistance r)
resistance and conductance R =
V
I
G =
I
V
(resistance R, conductance G,
potential difference V, current I )
G = G
1
+ G
2
+ ....... (conductors in parallel)
resistance R = R
1
+ R
2
+ ....... (resistors in series)
conductivity and resistivity G =
oA
l
, R =
pl
A
(conductivity o, resistivity p,
cross section A, length l )
capacitance C =
Q
V
energy stored =
1
2
QV =
1
2
CV
2
(potential difference V, charge Q,
capacitance C)
discharge of capacitor Q = Q
0
e
t
/
RC
(initial charge Q
0
,
time constant RC)
t = RC (time constant t)
Materials
density p =
M
V
(density p, mass M, volume V )
Hookes law F = kx (tension F, spring constant k,
extension x)
stress, strain and
the Young modulus
stress =
tension
cross-sectional area
strain =
extension
original length
Young modulus =
stress
strain
elastic strain energy =
1
2
kx
2
CST254
OCR 2010
GCE Physics B (Advancing Physics)
Gases
ideal gas equation pV = nRT (pressure p, volume V, number of
moles n, molar gas constant R)
pV = NkT (number of molecules N,
Boltzmann constant k)
kinetic theory of gases pV =
1
3
Nmc
2
(pressure p, volume V, number of
molecules N, mass of molecule m,
mean square speed c
2
)
Motion and forces
momentum p = mv (momentum p, mass m, velocity v )
force = rate of change of momentum
impulse = Ft (force F)
components of a vector in two perpendicular directions
Fsin0
Fcos0
0
F
work = Fx (force F, component of displacement
in the direction of the force x)
power = Fv (speed v)
equations for uniformly accelerated motion s = ut +
1
2
at
2
(initial speed u, final speed v,
time taken t, acceleration a,
distance travelled s)
v = u + at
v
2
= u
2
+ 2as
for circular motion
a =
v
2
r
,
F =
mv
2
r
(radius of circle r)
Energy and thermal effects
efficiency
efficiency =
useful energy output
energy input
energy E = mc0 (change in energy E, mass m,
specific thermal capacity c,
temperature change 0)
Boltzmann factor
e
(E
/kT
)
CST254
OCR 2010
GCE Physics B (Advancing Physics)
Waves
nz = dsin0 (on a distant screen from a diffraction
grating or double slit; order n, wavelength z,
angles of maxima 0)
v = fz (wave speed v, frequency f, wavelength z)
Oscillations
d
2
x
dt
2
= a =
[
k
m
]
x = (2f)
2
x (acceleration a,
force per unit displacement k, mass m,
displacement x, frequency f)
x = A cos 2 ft (amplitude A, time t)
x = A sin 2 ft
T = 2
m
k
(periodic time T)
f =
1
T
total energy E =
1
2
kA
2
=
1
2
mv
2
+
1
2
kx
2
Atomic and nuclear physics
radioactive decay
N
t
= zN
(number N, decay constant z)
N = N
0
e
zt
(initial number N
0
)
T
1
2
=
ln2
z
(half-life T
1
2
)
absorbed dose = energy deposited per unit mass
dose equivalent = absorbed dose quality factor
risk = probability consequence
expected random variation in N random counts is of the order N
mass-energy relationship E
rest
= mc
2
(energy E, mass m, speed of light c)
relativistic factor
=
l
1 v
2
/c
2
(speed of object v, speed of light c)
relativistic energy E
total
= E
rest
(total energy E
total
, rest energy E
rest
,
relativistic factor )
energy-frequency relationship for photons E = hf (photon energy E, Planck constant h,
frequency f)
z =
h
p
(wavelength z, Planck constant h,
momentum p (= mv for slow moving
particles))
CST254
OCR 2010
GCE Physics B (Advancing Physics)
Field and potential
for all fields
field strength =
dV
dr
V
r
(potential gradient dV/dr)
gravitational fields g =
F
m
(gravitational field strength g,
gravitational force F, mass m)
V
grav
=
GM
r
,
F =
GMm
r
2
(gravitational potential V
grav
, force F,
gravitational constant G, mass M, distance r)
Electric fields
E =
F
q
(electric field strength E, electric force F,
charge q)
V
elec
=
kQ
r
F =
kQq
r
2
(electric potential V
elec
, force F, electric force
constant k, charge Q, distance r)
Electromagnetism
force on a current carrying conductor F = ILB (flux density B, current I, length L)
force on a moving charge F = qvB (charge q, velocity perpendicular to field v)
c =
d(N1)
dt
(induced emf c, flux 1, number of turns
linked N)
ideal transformer
V
1
V
2
=
N
1
N
2
I
2
I
1
=
N
1
N
2
CST254
OCR 2010
GCE Physics B (Advancing Physics)
BLANK PAGE
Copyright Information
OCR is committed to seeking permission to reproduce all third-party content that it uses in its assessment materials. OCR has attempted to identify and contact all copyright holders
whose work is used in this paper. To avoid the issue of disclosure of answer-related information to candidates, all copyright acknowledgements are reproduced in the OCR Copyright
Acknowledgements Booklet. This is produced for each series of examinations and is freely available to download from our public website (www.ocr.org.uk) after the live examination series.
If OCR has unwittingly failed to correctly acknowledge or clear any third-party content in this assessment material, OCR will be happy to correct its mistake at the earliest possible
opportunity.
For queries or further information please contact the Copyright Team, First Floor, 9 Hills Road, Cambridge CB2 1GE.
OCR is part of the Cambridge Assessment Group; Cambridge Assessment is the brand name of University of Cambridge Local Examinations Syndicate (UCLES), which is itself a
department of the University of Cambridge.
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- High-Resolution Micromachined Interferometric AccelerometerДокумент75 страницHigh-Resolution Micromachined Interferometric AccelerometerjitendraОценок пока нет
- Physics For Entertainment Volume 1 (Yakov Perelman)Документ211 страницPhysics For Entertainment Volume 1 (Yakov Perelman)snath7800Оценок пока нет
- Evaluasi Mutu Fisik, Total Bakteri, Dan Sensori Minuman Sari Tempe Dengan Penambahan Bunga KecombrangДокумент12 страницEvaluasi Mutu Fisik, Total Bakteri, Dan Sensori Minuman Sari Tempe Dengan Penambahan Bunga KecombrangJosua PakpahanОценок пока нет
- Questions Bank On ElectrostaticsДокумент2 страницыQuestions Bank On Electrostaticsashok PradhanОценок пока нет
- Induction - George Ricarrson 2501987261Документ11 страницInduction - George Ricarrson 2501987261George RYОценок пока нет
- Magic The Gathering - Masquerade Cycle 2 - NemesisДокумент386 страницMagic The Gathering - Masquerade Cycle 2 - Nemesisapi-3804457100% (4)
- External DC fuse board for Sunny Island battery invertersДокумент2 страницыExternal DC fuse board for Sunny Island battery invertersrhadammantysОценок пока нет
- ZTE NODE-B ConnectivityДокумент19 страницZTE NODE-B ConnectivitySanjeet Doodi100% (7)
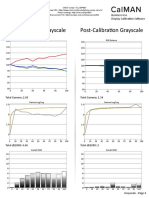
- TCL 55P607 CNET Review Calibration ResultsДокумент3 страницыTCL 55P607 CNET Review Calibration ResultsDavid KatzmaierОценок пока нет
- Seguridad Electrica 4Документ28 страницSeguridad Electrica 4salo081018Оценок пока нет
- Holiday Assignment XДокумент2 страницыHoliday Assignment XMonis ShaikhОценок пока нет
- High Performance Techniques For Microsoft SQL Server PDFДокумент307 страницHigh Performance Techniques For Microsoft SQL Server PDFmaghnus100% (1)
- Check List For Overall Piping Plot PlanДокумент3 страницыCheck List For Overall Piping Plot PlankamleshyadavmoneyОценок пока нет
- Manual Fx2n 485 BDДокумент8 страницManual Fx2n 485 BDaxo_vfrОценок пока нет
- PD05P XXX XXX B SeДокумент2 страницыPD05P XXX XXX B SemaaoeОценок пока нет
- UNAVCO 2008 LiDAR Campaign Processing ReportДокумент23 страницыUNAVCO 2008 LiDAR Campaign Processing ReportLina Xiomara SierraОценок пока нет
- GGGДокумент3 страницыGGGAnkitОценок пока нет
- Various Types of Steering System, Steering GeometryДокумент32 страницыVarious Types of Steering System, Steering GeometrySumit Choudhary100% (1)
- BasrahДокумент19 страницBasrahDurban Chamber of Commerce and IndustryОценок пока нет
- SM 1201r9 UsxrayДокумент500 страницSM 1201r9 UsxrayMurat KaanОценок пока нет
- PSE YRC1000micro 00Документ25 страницPSE YRC1000micro 00LiemОценок пока нет
- Adiabatic Logic: An Alternative Approach To Low Power Application CircuitsДокумент6 страницAdiabatic Logic: An Alternative Approach To Low Power Application CircuitsBibartan DasОценок пока нет
- Blockchain Unconfirmed Transaction Hack Script Docx PDF FreeДокумент2 страницыBlockchain Unconfirmed Transaction Hack Script Docx PDF FreeHealing Relaxing Sleep Music100% (1)
- Ups Lyonn Modelo: Ult St5-100 KS: 10KVA A 120KVAДокумент1 страницаUps Lyonn Modelo: Ult St5-100 KS: 10KVA A 120KVASebastian Matias CruzОценок пока нет
- Powerfactory 2020: Technical ReferenceДокумент13 страницPowerfactory 2020: Technical ReferenceDaniel ManjarresОценок пока нет
- Appendix B DAX ReferenceДокумент174 страницыAppendix B DAX ReferenceTomislav Mališ100% (1)
- Project PBLДокумент19 страницProject PBLAdam LuqmanОценок пока нет
- Confined SpacesДокумент27 страницConfined SpacesDivya RastogiОценок пока нет
- Session5 Automotive PackagingДокумент72 страницыSession5 Automotive PackagingShivprasad Savadatti100% (1)
- Libro de FLOTACIÓN-101-150 PDFДокумент50 страницLibro de FLOTACIÓN-101-150 PDFIsaias Viscarra HuizaОценок пока нет