Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Design of Bridge
Загружено:
dsanandaАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Design of Bridge
Загружено:
dsanandaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
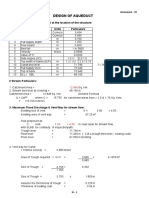
Total width of the bridge = Clear span of the bridge = No.
of main Girders = Spacing of the T-beams/main girders(c/c) Thickness of kerb Width of kerb(including parapet wall) Width of parapet wall Width of the bearing Effective span of the bridge = spacing of the cross beam Provide one at each end of the span, total no. of cross beams= No.of cross beams provided= Spacing of beams
7.000 15.000 3 2.250 0.300 0.300 0.150 1.000 16.000 4.050 6.704 7 2.667 2.600 0.800 21 7.6 2400 2200 120 30 1.450 2.300 1.586 0.850
m m m m m m m m m
say Thickness of girder Thickness of deck slab Thickness of wearing coat unit weight of concrete Unit weight of wearing coat Depth of cross beams Thickness of cross beam Effective span of cross beams in transverse direction Effective span of cross beams in longitudinal direction Ratio of long span to short span L/B= Length of catelever portion CALCULATION OF DEAD LOAD Dead load due to wearing coat Dead load due to deck slab
m c/c m m cm cm kg/cum kg/cum cm cm m m m
THE SLAB IS DESIGNED AS TWO WAY
167.200 kg/sq.m 504.000 kg/sq.m 671.200 kg/sq.m
Slab supported on all four sides and continuous. From Pigaud's curve, for k= m1= Total dead weight of panel Moment due along short span Moment due along long span Live load Placing the track symentrically Impact Load: Give type of vehicle (1 for wheeled, 2 for tracked) span= 15.000 m I= 21.44 % 1 0.630 for 1/k= 1.586207 0.049 m2= 0.018 2238.452 kg 5674.476 kg-cm 11572.8 kg-cm =
DESIGN OF CANTELEVER PORTION
Thickness of slab at the end Thicknes of slab at girder sl.no Item 1 2 3 4 parapet kerb weraing coat Slab(rect.) 15 cm 36 cm L m 0.300 0.076 0.150 B m 1.00 1.00 1.00 D m unit wt.t load dist. Moment kg/cum kg m kg-m 174.00 0.775 134.85 0.30 2400 216.00 0.700 151.20 0.55 2200 91.96 0.275 25.29 0.85 2400 306.00 0.425 130.05
Slab(triangular)
0.105
1.00
0.85
2400
214.20 1002.16
0.283
60.69 502.079
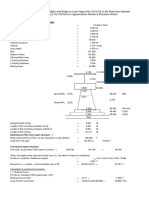
Momenyt due to live load For Class AA loading, the minimum clearence shall be 1.2 m for carriage width of 5.5 m and above In the present case the cantelever width excluding the kerb works out 0.550 m Hence IRC Class A loading shall be considered The loading will be as shown in the fig 1. Effective width of dispersion 'e' is computed by Code clause 305.13.2 be=1.2x+bw where be=effective width x=dist. of the C.G. of conc. Load from the face of the the support= 0.150 m bw=breadth of concentration area of the laod= 0.402 m Therefore effective width= 0.582 m When the wheel load is at the edge of the slab near abutment, the net effective width of dispersion= 0.416 m Live load/m width including impact= Wl x100x(1+I)/be 20552.9 kg Maximum moment due to live load 3082.93 kg-m
4372.677
Reinforcement Total moment due to dead load and live load= Effective depth required Cover to reinforcement Dia of main steel 20 mm a_st= 3.14 Provide overall depth of D= 36.00 Effective depth provided =d= 30.00 Area of steel=Ast=[ M/t jd]= 7.07 spacing 44.47 Provide spacing of 30 Area of steel providede= 10.47 Bending moment for distribution steel:
3585.012 kg-m 18.69 cm 5.00 cm sq.cm cm cm sq.cm cm c/c cm c/c sq.cm
=0.2 Mw + 0.3 Ml
1025.296 kg-m
Dia of bar 12 mm a_st= Effective depth =de= Area of steel=Ast=[ M/t jd]= spacing Provide spacing of Area of steel providede=
1.13 30.40 2.02 55.97 30 3.77
sq.cm cm sq.cm cm c/c cm c/c sq.cm
DESIGN OF INTERMEDIATE LONGITUDINAL GIRDER
Bending moment due to dead load: sl.no 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 Item weraing coat Deck Slab T-Rib Bottom flange Top fillet Cross beams Fillets No. 1 1 1 2 2 2 7 32 Factor 1.00 1.00 1.00 0.50 1.00 0.50 1.00 0.50 L m 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.45 1.45 B m 2.25 2.25 0.80 0.15 0.15 0.15 0.30 0.15 D unit wt.t load m kg/cum kg 0.076 2200 376.20 0.21 2400 1134.00 1.71 2400 3290.88 0.15 2400 54.00 0.30 2400 216.00 0.15 2400 54.00 1.20 2400 548.10 *Divided by total length 0.15 2400 78.30 *Divided by total length 5673.18
a b
Maximum bending moment =WL^2/8=
181542 kg-m
Bending moment due to Live load Maximum live load B.M would occur under Class A two lane loading Impact factor fraction=A/[B+L] Where A=constant factor= B=constant factor= L=Span in metres=
4.5 For RCC bridges 6 For RCC bridges 16.000 m
Therefore I= P
20.5% P
1800 1700
('g+w)
P
1800
P
700
w
950
550
1250
1000
2250 Transverse disposition of two trains of Class A loading for determination of reactions on longitudinal beam Rx=SW[1+SI dx e/(Sdx^2I)]
As per IRC f= g= w=
150 1200 500
Live load B.M. by Courbons method C.G of load from kerb C.G of of bridge Eccentricity of loading= n= SW=n x W =where n=
3050 3200 150 mm 3 4
axle load 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
P=W/2 wheel Location Total load Dist. To axis from girder SP Load of first 1 2 3 P wheel 1.35 1 4 2.25 0.00 2.25 1.35 1 4 2.25 0.00 2.25 5.7 1 4 2.25 0.00 2.25 5.7 1 4 2.25 0.00 2.25 3.4 1 4 2.25 0.00 2.25 3.4 1 4 2.25 0.00 2.25 3.4 1 4 2.25 0.00 2.25
Ra
Rb
Rc Ra
with impact factor Rb Rc 1.61 1.61 1.61 1.61 1.61 1.61 1.61 1.45 1.45 1.45 1.45 1.45 1.45 1.45
1.467P 1.467P 1.467P 1.467P 1.467P 1.467P 1.467P
1.333P 1.333P 1.333P 1.333P 1.333P 1.333P 1.333P
1.200P 1.200P 1.200P 1.200P 1.200P 1.200P 1.200P
1.77 1.77 1.77 1.77 1.77 1.77 1.77
70 For tracked wheels For outer girder 1.625 2050
0.55
3600 Rp Rq 0.95 Ra 2.25
Rb Rc
intensity of load=
19.44444 t/sq.m
Rx=(SP/n){1+SI/[SX2 I] X e} Minimum clereance required between the road face of the kerb and outer edge of the track = 1.2+width of track/2 e= 0.55 = 1.625 m Ra= Rb= Rc= 0.9111 0.455556 0.6667 0.333333 0.4222 0.211111
Maximum bending moment at the centre of the span
Вам также может понравиться
- Design of Backing Wall & Bed BlockДокумент4 страницыDesign of Backing Wall & Bed BlocksantkabirОценок пока нет
- Design of Double Lane Road Bridge: 1. Hydraulic Particulars Sno. Description Units ParticularsДокумент4 страницыDesign of Double Lane Road Bridge: 1. Hydraulic Particulars Sno. Description Units ParticularsPurdiansyah100% (1)
- Idge ManagulliДокумент63 страницыIdge ManagulliHemant SonawadekarОценок пока нет
- 7-3 Culvert Design PDFДокумент16 страниц7-3 Culvert Design PDFSed BeelzeОценок пока нет
- COUNTERFORTДокумент2 страницыCOUNTERFORTMALAY MRIDHAОценок пока нет
- Catchment Area CalculationДокумент6 страницCatchment Area CalculationSoham SantraОценок пока нет
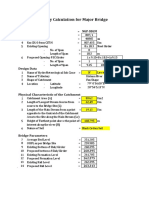
- Hydraulic Analysis of Major BridgeДокумент10 страницHydraulic Analysis of Major BridgeUmar KarimiОценок пока нет
- MIB KM 170+915-Riv-Hfl From DeptДокумент6 страницMIB KM 170+915-Riv-Hfl From DeptVB665Оценок пока нет
- Drain Capacity DesignДокумент10 страницDrain Capacity DesignWan Imran Hasif100% (1)
- 14 C - BridgesДокумент4 страницы14 C - Bridgesgurumurthy38Оценок пока нет
- CD WorkДокумент4 страницыCD Workale hopeju2009Оценок пока нет
- 184 907Документ40 страниц184 907Ankur DubeyОценок пока нет
- Pier Cap Plan: Project:-Client: - ConsultantsДокумент1 страницаPier Cap Plan: Project:-Client: - ConsultantsShaileshRastogiОценок пока нет
- Positioning of Irc Live Loads:: Coventions Used Below Are in Reference With The Above FigureДокумент4 страницыPositioning of Irc Live Loads:: Coventions Used Below Are in Reference With The Above FigureBensingh DhasОценок пока нет
- Part 3 Abut - Well Foundation DesignДокумент46 страницPart 3 Abut - Well Foundation Designshashi rajhansОценок пока нет
- RCC Retaining Wall DesignДокумент12 страницRCC Retaining Wall DesignifylasyОценок пока нет
- Hydrology ReportДокумент9 страницHydrology ReportamitОценок пока нет
- Project Structure: Providing Bridge For Colony Approach Road Under SC/ST Grant 2018-2019Документ3 страницыProject Structure: Providing Bridge For Colony Approach Road Under SC/ST Grant 2018-2019Seph RjyОценок пока нет
- Box CanalДокумент43 страницыBox CanalRaviTejaОценок пока нет
- DLB @4.465 On Kollimerla DrainfinalДокумент55 страницDLB @4.465 On Kollimerla Drainfinalrvkumar3619690Оценок пока нет
- DESIGN AqueductДокумент89 страницDESIGN AqueductmukhleshОценок пока нет
- Capacity of Tank 3000 KL Location Bagri District Rajgarh 18 M Nagar Palika, RajrahДокумент6 страницCapacity of Tank 3000 KL Location Bagri District Rajgarh 18 M Nagar Palika, Rajrahankkeshmundra1Оценок пока нет
- 60m Span DesignДокумент131 страница60m Span DesignPhanindra NathОценок пока нет
- RCC Counterfort WallДокумент20 страницRCC Counterfort Wallalok jhaОценок пока нет
- Bridge Analysis and Design v1.1Документ132 страницыBridge Analysis and Design v1.1cengiz100% (1)
- Design Lined CanalsДокумент2 страницыDesign Lined CanalsUttam Kumar GhoshОценок пока нет
- Computation of Wind Force On Superstructure For PierДокумент2 страницыComputation of Wind Force On Superstructure For Piervasu7900Оценок пока нет
- Design of Fall at RD 29.250 of RB Upper/DyДокумент13 страницDesign of Fall at RD 29.250 of RB Upper/Dyshweta0% (1)
- Sdsadsadw DweasdДокумент44 страницыSdsadsadw DweasdChandan SharmaОценок пока нет
- Hydraulic Particulars: 1) - CANAL 2) - DrainageДокумент4 страницыHydraulic Particulars: 1) - CANAL 2) - DrainageMohammed Quadir KhanОценок пока нет
- Slab Culvert Irc 21 Irc 112Документ5 страницSlab Culvert Irc 21 Irc 112imamtaОценок пока нет
- Hydraulic Calculation For TANDULA RIVERДокумент12 страницHydraulic Calculation For TANDULA RIVERgagajainОценок пока нет
- Br.927-1 Ch.169.821 - NewДокумент11 страницBr.927-1 Ch.169.821 - Newsabir aliОценок пока нет
- Upper Mai Hydroelectric Project: SUPPORT PIERS Dimension DGN Chainage: 0+668.40Документ49 страницUpper Mai Hydroelectric Project: SUPPORT PIERS Dimension DGN Chainage: 0+668.40MohanSharmaОценок пока нет
- Hydraulic Calculation of Box Culvert: Wlu HC Hu C HLB Blu BLC WLCДокумент1 страницаHydraulic Calculation of Box Culvert: Wlu HC Hu C HLB Blu BLC WLCIwanTiaraMotorОценок пока нет
- 16.6m Superstructure Design TgirderДокумент58 страниц16.6m Superstructure Design TgirderEngineeri TadiyosОценок пока нет
- Rigid Pavement DesignДокумент2 страницыRigid Pavement DesignGautam DuttaОценок пока нет
- Hydraulic CalculationДокумент7 страницHydraulic Calculationsanjay vermaОценок пока нет
- Footing BiaxialДокумент22 страницыFooting Biaxialvimal patelОценок пока нет
- BR. No. 232Документ17 страницBR. No. 232SM ConsultantsОценок пока нет
- R.C.C Pier Design of BridgeДокумент42 страницыR.C.C Pier Design of BridgeMd BIN HASAN100% (1)
- Hydraulic Cal Saudatti R1Документ5 страницHydraulic Cal Saudatti R1Hemant SonawadekarОценок пока нет
- DLRB DESN PROC Ver.1-5.11.2020Документ11 страницDLRB DESN PROC Ver.1-5.11.2020S N satyanarayanaОценок пока нет
- Design of Pier PDFДокумент4 страницыDesign of Pier PDFChManikumarОценок пока нет
- Retaining Wall DesignДокумент126 страницRetaining Wall DesignSeph RjyОценок пока нет
- Design of R.C.C Tee Beam Bridge 5.1 Design of Deck Slab 5.1.1 DATAДокумент24 страницыDesign of R.C.C Tee Beam Bridge 5.1 Design of Deck Slab 5.1.1 DATANithin M.TОценок пока нет
- 1 - Slab Bridge Final April23 - 2014Документ11 страниц1 - Slab Bridge Final April23 - 2014teweldeОценок пока нет
- Canal Trough Slab Trough Side Wall Road Slab Concrete Steel: Design of Pier With Pier Footing For Canal TroughДокумент15 страницCanal Trough Slab Trough Side Wall Road Slab Concrete Steel: Design of Pier With Pier Footing For Canal TroughSandip UpОценок пока нет
- Waterway Calculation For Major BridgeДокумент8 страницWaterway Calculation For Major BridgeAnonymous cYcLLOmmk8Оценок пока нет
- Bridge Design Using STAADДокумент38 страницBridge Design Using STAADZair LópezОценок пока нет
- UT - 25.509 - DEPR RevisedДокумент102 страницыUT - 25.509 - DEPR Revisedp_ignatiusОценок пока нет
- Design of Drain at KM. 0.600Документ5 страницDesign of Drain at KM. 0.600Sameer AhmadОценок пока нет
- Design Calculation of AbutmentДокумент53 страницыDesign Calculation of AbutmentSreeraja SreevilasanОценок пока нет
- Tunnel PortalДокумент7 страницTunnel PortaldsanandaОценок пока нет
- Adit Portal DesignДокумент7 страницAdit Portal DesigndsanandaОценок пока нет
- Bridge DesignДокумент33 страницыBridge DesignMaiwand KhanОценок пока нет
- Composite Steel GirderДокумент10 страницComposite Steel GirdersorowareОценок пока нет
- Hydraulic and Structural Design of Super PassageДокумент25 страницHydraulic and Structural Design of Super PassageCPK100% (2)
- AbutmentДокумент31 страницаAbutmenthrpinfra100% (1)
- Sump Design Chas 5.10.09Документ22 страницыSump Design Chas 5.10.09battulas1953Оценок пока нет
- Lattice Girder DesignДокумент3 страницыLattice Girder DesigndsanandaОценок пока нет
- Deflection - Steelcolumn STORYEY DRIFTДокумент30 страницDeflection - Steelcolumn STORYEY DRIFTdsanandaОценок пока нет
- Nof - To Staad Stability AnalysisДокумент3 страницыNof - To Staad Stability AnalysisdsanandaОценок пока нет
- Stability of Stack: Node L/C Force-X KNДокумент4 страницыStability of Stack: Node L/C Force-X KNdsanandaОценок пока нет
- Computation of Idc PDFДокумент1 страницаComputation of Idc PDFdsanandaОценок пока нет
- Wind Temp Load - CalculationДокумент5 страницWind Temp Load - CalculationdsanandaОценок пока нет
- Thermal Expansion CalculatorДокумент3 страницыThermal Expansion CalculatordsanandaОценок пока нет
- Book1staad Solid ModellingДокумент10 страницBook1staad Solid ModellingdsanandaОценок пока нет
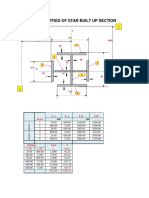
- Properties of Star Built Up Section: X-Dir y - Dir A KG/MДокумент3 страницыProperties of Star Built Up Section: X-Dir y - Dir A KG/Mdsananda100% (1)
- Pier DesignДокумент1 страницаPier DesigndsanandaОценок пока нет
- Volume Calculatorv 2Документ2 страницыVolume Calculatorv 2dsanandaОценок пока нет
- Design of Aquaduct Portal by Staad ModelДокумент8 страницDesign of Aquaduct Portal by Staad ModeldsanandaОценок пока нет
- Book1staad Solid ModellingДокумент10 страницBook1staad Solid ModellingdsanandaОценок пока нет
- Broad Vrested WeirДокумент5 страницBroad Vrested WeirdsanandaОценок пока нет
- Embankments PART 1Документ5 страницEmbankments PART 1dsanandaОценок пока нет
- Flood Hydrology FrequencyДокумент3 страницыFlood Hydrology FrequencydsanandaОценок пока нет
- View Flow-Duration Curve Go To Inputs: Log Log Chart For Data AnalysysДокумент2 страницыView Flow-Duration Curve Go To Inputs: Log Log Chart For Data AnalysysdsanandaОценок пока нет
- Pitching 3Документ4 страницыPitching 3dsanandaОценок пока нет
- Design of Ogee SpillwayДокумент4 страницыDesign of Ogee Spillwaydsananda100% (3)
- Filter - Text File AaДокумент4 страницыFilter - Text File AadsanandaОценок пока нет
- Aquaduct STAAD MODEL PDFДокумент3 страницыAquaduct STAAD MODEL PDFdsanandaОценок пока нет
- Staad Listing: Analysis of Aquaduct Portal by Staad ModelДокумент3 страницыStaad Listing: Analysis of Aquaduct Portal by Staad ModeldsanandaОценок пока нет
- StabilityДокумент26 страницStabilitydsanandaОценок пока нет
- Back Water Profile Computations: at WeirДокумент4 страницыBack Water Profile Computations: at WeirdsanandaОценок пока нет
- Design of Embankment DamДокумент5 страницDesign of Embankment DamdsanandaОценок пока нет
- 2way Wall Table53 ReynoldsДокумент2 страницы2way Wall Table53 Reynoldsdsananda100% (1)
- Oh - Tank - Foundation As Per Indian Standard CodeДокумент7 страницOh - Tank - Foundation As Per Indian Standard Codedsananda100% (1)
- Water Profile ComputationДокумент3 страницыWater Profile ComputationdsanandaОценок пока нет
- Gate GrooveДокумент1 страницаGate GroovedsanandaОценок пока нет
- Solution of Equation by Matrix MetodДокумент2 страницыSolution of Equation by Matrix MetoddsanandaОценок пока нет
- Lampiran IIb Perbup Nomor 4 Tahun 2019 Tentang Kebijakan Akuntansi Pemerintah Kabupaten BanjarДокумент154 страницыLampiran IIb Perbup Nomor 4 Tahun 2019 Tentang Kebijakan Akuntansi Pemerintah Kabupaten BanjarIsro MОценок пока нет
- A Brief History of PLU Crew - by Jim OjalaДокумент9 страницA Brief History of PLU Crew - by Jim OjalaRoger ShanafeltОценок пока нет
- Rig Move Procedures DevelopmentДокумент31 страницаRig Move Procedures DevelopmentCarlos Santos100% (1)
- Kongo Class Guided Missile Destroyers - The King KongoДокумент18 страницKongo Class Guided Missile Destroyers - The King KongohindujudaicОценок пока нет
- A Matter of Balance: How Heeling Affects SteeringДокумент2 страницыA Matter of Balance: How Heeling Affects SteeringSF ghhgОценок пока нет
- Install Torque Strut at Front AxleДокумент4 страницыInstall Torque Strut at Front AxleNoir OctobreОценок пока нет
- Filter Cross RefferenceДокумент2 страницыFilter Cross RefferenceVicente TanОценок пока нет
- Deed of Sale of Motor VehicleДокумент2 страницыDeed of Sale of Motor VehicleMarvinОценок пока нет
- Q1.Part of A Bus Route Is Along A High Street.: Motion Graphs QsДокумент18 страницQ1.Part of A Bus Route Is Along A High Street.: Motion Graphs QsAnushka NairОценок пока нет
- 14 CFR Part 1Документ15 страниц14 CFR Part 1AngeloRofelTabundaNavaОценок пока нет
- CH6 - MiscellaneousДокумент111 страницCH6 - Miscellaneoussujan pokhrelОценок пока нет
- Works & Head Office:: Lifting SolutionsДокумент8 страницWorks & Head Office:: Lifting SolutionsFiroz PawaskarОценок пока нет
- Disconnected Streets and The Effect On Walkability in LiverpoolДокумент59 страницDisconnected Streets and The Effect On Walkability in LiverpoolJared AlvesОценок пока нет
- Grumman AA-5B 1977-79 POH SearchableДокумент192 страницыGrumman AA-5B 1977-79 POH Searchablesplyn100% (1)
- The Introduction of Refusal Density Test On Asphalt Mixture DesignДокумент8 страницThe Introduction of Refusal Density Test On Asphalt Mixture DesignDheeraj senОценок пока нет
- PC300 8M0 PDFДокумент12 страницPC300 8M0 PDFDin Udin0% (1)
- Volvo Group KPMG True Value Case StudyДокумент8 страницVolvo Group KPMG True Value Case Studyaa1122Оценок пока нет
- BPW Trailer Axles Series H K N With Drum BrakesДокумент108 страницBPW Trailer Axles Series H K N With Drum Brakesruman214Оценок пока нет
- CMD Fahrzeugliste 09 2017Документ27 страницCMD Fahrzeugliste 09 2017greemaxОценок пока нет
- Auto Repair Technician Home: Home BMW Coding Auto Key Program Download & Installation DPF Tpms Shop Contact UsДокумент12 страницAuto Repair Technician Home: Home BMW Coding Auto Key Program Download & Installation DPF Tpms Shop Contact UsStefBeck BeckОценок пока нет
- XC40 2018Документ8 страницXC40 2018Najib JonОценок пока нет
- ExxonMobil VOY2012 - FINAL (Feb 8 2012 Ver 1.0)Документ12 страницExxonMobil VOY2012 - FINAL (Feb 8 2012 Ver 1.0)Sumeet SudОценок пока нет
- Analytical-Empirical Pavement Evaluation Using The FWD PDFДокумент9 страницAnalytical-Empirical Pavement Evaluation Using The FWD PDFGang Liu100% (1)
- THE Bicicle Effect: Juan Carlos KreimerДокумент5 страницTHE Bicicle Effect: Juan Carlos KreimerPatriciaОценок пока нет
- ICAO Self Audit Checklist For AirportsДокумент23 страницыICAO Self Audit Checklist For Airportsnimsv1980100% (1)
- Procedures For Approval of Service Suppliers v2.9 June 2021Документ72 страницыProcedures For Approval of Service Suppliers v2.9 June 2021Cleverson SchmidtОценок пока нет
- Gandhinagar Thermal PowerplantДокумент46 страницGandhinagar Thermal PowerplantniravОценок пока нет
- Civil Aviation Regulations 2016 ENGLISHДокумент160 страницCivil Aviation Regulations 2016 ENGLISHSaran RamanОценок пока нет
- Gambar KenderaanДокумент170 страницGambar KenderaanMohd Hazril HarunОценок пока нет
- Cma-Cgm Taxas Detetion PDFДокумент2 страницыCma-Cgm Taxas Detetion PDFmarcelloairesОценок пока нет