Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Pump Training Slides Slides 1 - 20
Загружено:
Jegede OluwaseunИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Pump Training Slides Slides 1 - 20
Загружено:
Jegede OluwaseunАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Pump Design Part I
Engr. Bolakale Uthman
This document is for exclusive use only. Copying without permission of DeltaAfrik is not permitted
Page 1
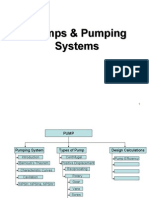
Training Agenda: Pumps
Introduction Type of pumps Assessment of pumps Energy efficiency opportunities
This document is for exclusive use only. Copying without permission of DeltaAfrik is not permitted
Page 2
Common Pump Terminology
Capacity Total Head (H) Shutoff Head Rise to Shutoff Minimum Recirculation Best Efficiency Point Runout Net Positive Suction Head (NPSH) Brake Horsepower
This document is for exclusive use only. Copying without permission of DeltaAfrik is not permitted
Page 3
Introduction
What are Pumping Systems?
Objective of pumping system Transfer liquid from source to destination Circulate liquid around a system
This document is for exclusive use only. Copying without permission of DeltaAfrik is not permitted
Page 4
Introduction
What are Pumping Systems
Main pump components
Pumps Prime movers: electric motors, diesel engines, air system Piping to carry fluid Valves to control flow in system Other fittings, control, instrumentation
End-use equipment
Heat exchangers, tanks, hydraulic machines
This document is for exclusive use only. Copying without permission of DeltaAfrik is not permitted
Page 5
Introduction
Pumping System Characteristics
Head
Resistance of the system Two types: static and friction
source Static head destination
Static head
Difference in height between source and destination Independent of flow
Static head
Flow
This document is for exclusive use only. Copying without permission of DeltaAfrik is not permitted Page 6
Introduction
Pumping System Characteristics
Static head consists of
Static suction head (hS): lifting liquid relative to pump center line Static discharge head (hD) vertical distance between centerline and liquid surface in destination tank
Static head at certain pressure
Head (in feet) = Pressure (psi) X 2.31 Specific gravity
This document is for exclusive use only. Copying without permission of DeltaAfrik is not permitted Page 7
Introduction
Pumping System Characteristics
Friction head
Resistance to flow in pipe and fittings Depends on size, pipes, pipe fittings, flow rate, nature of liquid Proportional to square of flow rate Closed loop system only has friction head (no static head)
Friction head
Flow
Page 8
This document is for exclusive use only. Copying without permission of DeltaAfrik is not permitted
Introduction
Pumping System Characteristics
In most cases: Total head = Static head + friction head
System curve System curve
System head
Static head
Friction head
System head
Friction head Static head
Flow
Flow
This document is for exclusive use only. Copying without permission of DeltaAfrik is not permitted
Page 9
Introduction
Pumping System Characteristics
Pump performance curve Relationship between head and flow
Flow increase System resistance increases Head increases Flow decreases to zero
Flow Head
Performance curve for centrifugal pump
Zero flow rate: risk of
pump burnout
This document is for exclusive use only. Copying without permission of DeltaAfrik is not permitted Page 10
Introduction
Pumping System Characteristics
Pump operating point
Duty point: rate of flow at certain head Pump operating point: intersection of pump curve and system curve
Head
Pump performance curve
System curve
Pump operating point
Static head
Flow
This document is for exclusive use only. Copying without permission of DeltaAfrik is not permitted Page 11
Introduction
Pumping System Characteristics
Pump suction performance (NPSH)
Cavitation or vaporization: bubbles inside pump If vapor bubbles collapse Erosion of vane surfaces Increased noise and vibration Choking of impeller passages Net Positive Suction Head NPSH Available: how much pump suction exceeds liquid vapor pressure NPSH Required: pump suction needed to avoid cavitation
This document is for exclusive use only. Copying without permission of DeltaAfrik is not permitted Page 12
Typical Pump Curve
Shutoff Head
Best Efficiency Point
Brake Horsepower Rise to Shutoff
System Curve
Runout
Minimum Recirculation
This document is for exclusive use only. Copying without permission of DeltaAfrik is not permitted Page 13
NPSH required
Hf
Hs NPSHr at runout NPSHr at rated condition
This document is for exclusive use only. Copying without permission of DeltaAfrik is not permitted Page 14
Fundamental Types of Pumps
Types of Pumps Centrifugal Pumps
Steam Pumps Any of the pumps can have one or several impellers, which may be; Power Pumps Metering Pumps Diaphragm Pumps Simplex, with single cylinder Duplex, with two cylinders Triplex, with three cylinders Quadruplex, with four cylinders Quintuplex, with five cylinders Multiplex, with many cylinders Gear Pumps Vane Pumps Screw Pumps Progressive Cavity Pumps Lobe Pumps
PD Pumps
Axial Flow
Reciprocating Pumps
Mixed Flow
Open Closed Semi-Open Single Suction Double Suction
Rotary Pumps
Radial Flow
End Suction Pumps In-line Pumps Vertical Volute Pumps Axially (Horizontally) Split Pumps Multi-staged Centrifugal Pumps Vertical Turbine Pumps
This document is for exclusive use only. Copying without permission of DeltaAfrik is not permitted
Page 15
Approximate Upper limit of Pressure and Capacity by Pump Class
This document is for exclusive use only. Copying without permission of DeltaAfrik is not permitted
Page 16
Type of Pumps
Positive Displacement Pumps
For each pump revolution
Fixed amount of liquid taken from one end Positively discharged at other end
If pipe blocked
Pressure rises Can damage pump
Used for pumping fluids other than water
This document is for exclusive use only. Copying without permission of DeltaAfrik is not permitted
Page 17
Type of Pumps
Positive Displacement Pumps
Reciprocating pump
Displacement by reciprocation of piston plunger Used only for viscous fluids and oil wells
Rotary pump
Displacement by rotary action of gear, cam or vanes Several sub-types Used for special services in industry
This document is for exclusive use only. Copying without permission of DeltaAfrik is not permitted Page 18
Type of Pumps
Dynamic pumps
Mode of operation
Rotating impeller converts kinetic energy into pressure or velocity to pump the fluid
This document is for exclusive use only. Copying without permission of DeltaAfrik is not permitted
Page 19
Type of Pumps
Centrifugal Pumps
How do they work?
Liquid forced into impeller Vanes pass kinetic energy to liquid: liquid rotates and leaves impeller Volute casing converts kinetic energy into pressure energy
(Sahdev M)
This document is for exclusive use only. Copying without permission of DeltaAfrik is not permitted Page 20
Вам также может понравиться
- Basic Pump FundamentalДокумент99 страницBasic Pump FundamentalJimit Shah100% (1)
- Pump Installation & MaintenanceДокумент116 страницPump Installation & MaintenanceMohammed El-Shahat100% (9)
- PumpДокумент40 страницPumpbabulu175% (4)
- PumpsДокумент80 страницPumpsMuhammad Nursalam100% (1)
- Course2a-Energy Efficiency PDFДокумент59 страницCourse2a-Energy Efficiency PDFNazaruddin SinagaОценок пока нет
- Troubleshooting PumpДокумент54 страницыTroubleshooting PumpM.nour El-din100% (3)
- Presentation On Centrifugal PumpsДокумент27 страницPresentation On Centrifugal PumpsPiyush MalviyaОценок пока нет
- Centrifugal Pump PDFДокумент20 страницCentrifugal Pump PDFSumedh Singh100% (1)
- Pump TheoryДокумент23 страницыPump TheoryYeahkevinrocksОценок пока нет
- Mechanical SealsДокумент2 страницыMechanical Sealscuraaj100% (1)
- Training PumpДокумент52 страницыTraining Pumparis mulyana100% (1)
- Problem Solving - Centrifugal PumpsДокумент40 страницProblem Solving - Centrifugal PumpsEtemadiОценок пока нет
- Maintenance of PumpsДокумент22 страницыMaintenance of PumpsBhaumik Bhuva100% (2)
- Centrifugal Pump ImpellerДокумент4 страницыCentrifugal Pump ImpellerKrunal Patil100% (1)
- Pump FinalДокумент84 страницыPump Finalpowergops100% (2)
- Pump Maintenance Procedures 1Документ7 страницPump Maintenance Procedures 1Shraddha Raut100% (1)
- Centrifugal PumpsДокумент24 страницыCentrifugal PumpsHari Babu DharmavarapuОценок пока нет
- Principle of Centrifugal PumpsДокумент13 страницPrinciple of Centrifugal Pumpsvisitabhinav100% (3)
- On-Line Duralobe Classic SQ RTP Sterilobe Acculobe Tra10 Tra20Документ173 страницыOn-Line Duralobe Classic SQ RTP Sterilobe Acculobe Tra10 Tra20kamchorepkОценок пока нет
- Centrifugal Pump Troubleshooting ChecklistДокумент8 страницCentrifugal Pump Troubleshooting Checklistab_s5036Оценок пока нет
- Pump TrainingДокумент15 страницPump TrainingdalayeliОценок пока нет
- MBN - E00657 Multistage Pump PDFДокумент8 страницMBN - E00657 Multistage Pump PDFAlfonso BlancoОценок пока нет
- Centrifugal Pump OverloadingДокумент2 страницыCentrifugal Pump OverloadingAbdul AlimОценок пока нет
- Study of A Centrifugal Pump, Pipe Fittings and Valves - Ch.E 206Документ30 страницStudy of A Centrifugal Pump, Pipe Fittings and Valves - Ch.E 206Synthia100% (1)
- Mechanical Interview Questions and Answers Fluid MechanicsДокумент2 страницыMechanical Interview Questions and Answers Fluid Mechanicsjk50% (2)
- Pump Motor TripДокумент4 страницыPump Motor TripKamal UddinОценок пока нет
- Pump System CurveДокумент6 страницPump System CurveMohan MalavОценок пока нет
- Pumps Centrifugal and ReciprocatingДокумент24 страницыPumps Centrifugal and ReciprocatingumarОценок пока нет
- Pump Training 2Документ5 страницPump Training 2kevinGojiОценок пока нет
- Centrifugal PumpsДокумент138 страницCentrifugal PumpsNikhil MalhotraОценок пока нет
- Submersible PumpДокумент15 страницSubmersible Pumpnwright_besterОценок пока нет
- Mechanical SealsДокумент9 страницMechanical SealsAbubakar Siddiq100% (1)
- Filter Press 1Документ7 страницFilter Press 1lutexgadsonОценок пока нет
- PumpДокумент34 страницыPumpsoha89100% (1)
- Dorner 3200 Vacuum ConveyorДокумент8 страницDorner 3200 Vacuum ConveyorBobKatОценок пока нет
- Centrifugal Pump MaintenanceДокумент32 страницыCentrifugal Pump MaintenancemersiumОценок пока нет
- PUMP TrainingДокумент130 страницPUMP TrainingTirta Budiawan100% (4)
- 2,4 Pipes&PumpsДокумент226 страниц2,4 Pipes&PumpsShankar Angappan100% (1)
- Classification of PumpsДокумент7 страницClassification of PumpsJoanna Marie100% (1)
- Top Entry Mixer Features For EkatoДокумент2 страницыTop Entry Mixer Features For EkatoShankarОценок пока нет
- Centrifugal Pump VibrationДокумент4 страницыCentrifugal Pump Vibrationzhangj5Оценок пока нет
- NPSH Calculating ItДокумент6 страницNPSH Calculating ItJerry MateoОценок пока нет
- Mechanical SealДокумент15 страницMechanical SealTinu Paul Jepin100% (2)
- Vertical Sump PumpДокумент6 страницVertical Sump Pumpsahildhingra100% (1)
- AgitatorДокумент8 страницAgitatorMugesh KannaОценок пока нет
- Submersible PumpДокумент3 страницыSubmersible Pumpeddy brachoОценок пока нет
- 12 Pump Sizing Example 1 & 2AДокумент37 страниц12 Pump Sizing Example 1 & 2AMohamed Abd El-MoniemОценок пока нет
- Training of API PumpsДокумент52 страницыTraining of API PumpsMas Bagus100% (2)
- Pumps - Centrifugal vs. Positive Displacement: Instructor: Edward P. Brunet, JR., PEДокумент11 страницPumps - Centrifugal vs. Positive Displacement: Instructor: Edward P. Brunet, JR., PEyogachemОценок пока нет
- Pump Troubleshooting: Ahmed Abdullah ZayedДокумент514 страницPump Troubleshooting: Ahmed Abdullah Zayedاشرينكيل مسونكيل0% (1)
- Al-Salam Higher Institute For: by Abdelaal Mohamed Khttap Cairo 2014Документ28 страницAl-Salam Higher Institute For: by Abdelaal Mohamed Khttap Cairo 2014عبدوخطابОценок пока нет
- 3 Scribd 001 PumpsДокумент38 страниц3 Scribd 001 PumpsJames WattersonОценок пока нет
- Pumps Training Very BasicДокумент38 страницPumps Training Very Basicprashant mishraОценок пока нет
- Pumps & Pumping Systems-GeneralДокумент349 страницPumps & Pumping Systems-GeneralKondala RaoОценок пока нет
- Flow More Pumps LTD: Industrial Training ReportДокумент40 страницFlow More Pumps LTD: Industrial Training ReportAbu Obaidah Khan100% (1)
- Pumps and Pumping SystemsДокумент40 страницPumps and Pumping SystemsMohamed Elshahat Badr100% (1)
- Pumps and Pumping SystemsДокумент40 страницPumps and Pumping SystemsRendy Andromeda100% (6)
- Pumps & Pumping Systems: Training Session On Energy EquipmentДокумент40 страницPumps & Pumping Systems: Training Session On Energy EquipmentAmir Chip100% (1)
- Rotary PumpsДокумент31 страницаRotary PumpsalbertОценок пока нет
- Lab Exercises: ObjectivesДокумент2 страницыLab Exercises: ObjectivesIdris Khan PathanОценок пока нет
- Cyber Law IntroductionДокумент4 страницыCyber Law IntroductionVENKAT SОценок пока нет
- 69-343-136 Operator's and Maintenance Manual 14 Sandvik-PDF en-USДокумент86 страниц69-343-136 Operator's and Maintenance Manual 14 Sandvik-PDF en-USrobОценок пока нет
- Free Water Knock Out Summary Sheet PDFДокумент1 страницаFree Water Knock Out Summary Sheet PDFAbdullah FathanОценок пока нет
- S.No. Name of The Agency Contact Details: M/s M.P. PrintersДокумент3 страницыS.No. Name of The Agency Contact Details: M/s M.P. PrintersVIKKAS AGARWALОценок пока нет
- Ankit Singh Kandari: SkillsДокумент1 страницаAnkit Singh Kandari: SkillsSravani RajuОценок пока нет
- Type V Sheet - Light Frame ConstructionДокумент3 страницыType V Sheet - Light Frame ConstructionIonFlorentaОценок пока нет
- Lab 7: 802.1X: Wireless NetworksДокумент13 страницLab 7: 802.1X: Wireless NetworksJosel ArevaloОценок пока нет
- Monopoly Nes CheatsДокумент3 страницыMonopoly Nes CheatsAlfieGle123Оценок пока нет
- Digital Marketing 101 - QuizДокумент54 страницыDigital Marketing 101 - QuizAsep Andi0% (2)
- Dagupan Lights Photo Contest Guides & Registration 2020Документ3 страницыDagupan Lights Photo Contest Guides & Registration 2020MjhayОценок пока нет
- En 9 8 001 BSP HoseДокумент11 страницEn 9 8 001 BSP HosePaulo YorgosОценок пока нет
- SAP-C01 Dumps - Pass Your Exam by DumpshqДокумент3 страницыSAP-C01 Dumps - Pass Your Exam by Dumpshqsap-c01dumps0% (1)
- Unit 1 Assignment in ResearchДокумент3 страницыUnit 1 Assignment in ResearchJovzОценок пока нет
- Pipes Selection Chart - Modified-1Документ3 страницыPipes Selection Chart - Modified-1Eslam ElsayedОценок пока нет
- (I) No. Name Stipend Stream Avgmark Grade Class: Create The Table Givem Below With Name and StiudentДокумент1 страница(I) No. Name Stipend Stream Avgmark Grade Class: Create The Table Givem Below With Name and StiudentUdit JunejaОценок пока нет
- Account Statement For Account:3869000100750616: Branch DetailsДокумент4 страницыAccount Statement For Account:3869000100750616: Branch DetailsUddeshya SrivastavaОценок пока нет
- Operational ManagementДокумент12 страницOperational ManagementArgaw DagneОценок пока нет
- 5.3 Organisational Roles, Responsibilities and AuthoritiesДокумент1 страница5.3 Organisational Roles, Responsibilities and AuthoritiesAnabela GibraltarОценок пока нет
- Pore-Water Pressures Defined Using A Finite Element AnalysisДокумент5 страницPore-Water Pressures Defined Using A Finite Element AnalysisPuspa ChandОценок пока нет
- Grammarly Score and Plagiarism Check PercentageДокумент24 страницыGrammarly Score and Plagiarism Check PercentageSABS RIDES AND LIFEОценок пока нет
- Volumes by Sections Using Prismoidal FormulasДокумент4 страницыVolumes by Sections Using Prismoidal FormulasfaizalprbwОценок пока нет
- Argosy Professional Ethics Class FAQsДокумент38 страницArgosy Professional Ethics Class FAQsDavid Moore, PhD CDP100% (1)
- Led DMX Decoder User Manual PDFДокумент4 страницыLed DMX Decoder User Manual PDFjaziel daitОценок пока нет
- CS 584Документ8 страницCS 584Yasir MirzaОценок пока нет
- How To Install ManualДокумент6 страницHow To Install ManualAmunindrahnat RaОценок пока нет
- Digital Media Project Proposal: Submitted To: DR Sawera ShamiДокумент3 страницыDigital Media Project Proposal: Submitted To: DR Sawera ShamiJaveria JanОценок пока нет
- Dhemaji: Dhemaji District (Assam E-District Project)Документ1 страницаDhemaji: Dhemaji District (Assam E-District Project)Boishal Bikash BaruahОценок пока нет
- FiCEB Spreadsheet V01Документ49 страницFiCEB Spreadsheet V01Kutty MansoorОценок пока нет
- PUMPS and CALCULATIONSДокумент7 страницPUMPS and CALCULATIONSkenoly123Оценок пока нет