Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
2 G 3 G 4 G
Загружено:
Charu PandeyИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
2 G 3 G 4 G
Загружено:
Charu PandeyАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
http://indianblogger.
com/understanding-the-generations1g-2g-3g-and-4g/
With the advent of generations after generation of mobile networks it has become important to understand the concept behind each. The evolution of the three generations has been explained in one of my previous blog. Please refer my previous article on how the 1g, 2g and 3g evolved. In this article the focus would be more on understanding the subtle differences between the four generations. Let us start with the first two wireless generations first. Analysis of 1g & 2g:
In 1G, narrow band analogue mobile network is used. This facilitates the voice calls and sending text messages. These services are provided with circuit switching. Today the usual call starts from the beginning pulse to rate to the final rate. Then in case of 2G Narrow Band Wireless Digital Network is used. It brings more clarity to the conversation and both these circuit-switching model. Both the 1G and 2G deals with voice calls and has to utilize the maximum bandwidth as well as a limited till sending messages i.e. SMS. The latest technologies such as GPRS, is not available in these generations. But the greatest disadvantage as concerned to 1G is that with this we could contact with in the premises of that particular nation, where as in case of 2G the roaming facility a semi-global facility is available. 1G networks (NMT, C-Nets, AMPS, TACS) are considered to be the first analog cellular systems, which started early 1980s. There were radio telephone systems even before that. 2G networks (GSM, CDMA, DAMPS) are the first digital cellular systems launched early 1990s.
Some of the advantages that 2G had over 1G are:
The lower powered radio signals require less battery power, so phones last much longer between charges, and batteries can be smaller. The digital voice encoding allowed digital error checking which could increase sound quality by increasing dynamic range and lowering the noise floor. The lower power emissions helped address health concerns. Going all-digital allowed for the introduction of digital data services, such as SMS and email. Greatly reduced fraud. With analog systems it was possible to have two or more cloned handsets that had the same phone number.
Enhanced privacy. A key digital advantage not often mentioned is that digital cellular calls are much harder to eavesdrop on by use of radio scanners. While the security algorithms used have proved not to be as secure as initially advertised, 2G phones are immensely more private than 1G phones, which have no protection against eavesdropping.
The intermediate generation: In between 2G and 3G there is another generation called 2.5G. The intermediate mobile generation if we can call it that. Firstly, this mid generation was introduced mainly for involving latest bandwidth technology in addition to the existing 2G generation. But this had not brought out any new evolution and so had not became critical enough to be recognized as a standalone generation. Arrival of 3G: To overcome the shortcomings of 2G and 2.5G, the 3G had been introduced. In 3G Wide
Brand Wireless Network is used with which the clarity increases and gives the perfection similar to that of a real conversation. The data are sent through the technology called Packet Switching .Voice calls are interpreted through Circuit Switching. What is Packet Switching? This is actually done by supplying various addressed packets, which will be interconnected to have the conversation. It is not necessary to create a new dedicated path for sending the data. It had been modified in such a way that the data can be send through any path and hence this data will be received in less time as compared to that of voice calls. Main features of 3G Wireless Network: The features and services of 3G are as follows: 1. With the help of 3G, we can access many new services like global roaming. 2. 3G also have Wide Band Voice Channel, by this the world has been contracted to a little village because a person can contact with other person located in any part of the world and can even send messages too. 3. Then the point to be noted is that 3G gives clarity of voice as well can talk with out any disturbance.
4. In addition to that 3G also have entertainments such as Fast Communication, Internet, Mobile T.V, Video Conferencing, Video Calls, Multi Media Messaging Service (MMS), 3D gaming, Multi-Gaming etc are also available with 3G phones. 5. 3G networks (UMTS FDD and TDD, CDMA2000 1x EVDO, CDMA2000 3x, TDSCDMA, Arib WCDMA, EDGE, IMT-2000 DECT) are the latest cellular networks that have data rates 384 KB/s and more. 6. The bandwidth and location information available to 3G devices gives rise to applications not previously available to mobile phone users. Some of the applications are: o Mobile TV a provider redirects a TV channel directly to the subscribers phone where it can be watched. o Video on demand a provider sends a movie to the subscribers phone. o Video conferencing subscribers can see as well as talk to each other. o Tele-medicine a medical provider monitors or provides advice to the potentially isolated subscriber. o Location-based services a provider sends localized weather or traffic conditions to the phone, or the phone allows the subscriber to find nearby businesses or friends.
Main aspects of 4G Networks: The Forth Generation could be ready for implementation around 2012.
Then with the case of Fourth Generation that is 4G in addition to that of the services of 3G have some additional features such as Multi-Media Newspapers, You can also watch T.V programs with the clarity that of an ordinary T.V. In addition, we can send Data much faster that that of the previous generations A 4G cellular system must have target peak data rates of up to approximately 100 Mbit/s for high mobility such as mobile access and up to approximately 1 Gbit/s for low mobility such as nomadic/local wireless access, according to the ITU requirements. Scalable bandwidths up to at least 40 MHz should be provided. A 4G system is expected to provide a comprehensive and secure all-IP based solution where facilities such as IP telephony, ultra-broadband Internet access, gaming services and HDTV streamed multimedia may be provided to users. Although legacy systems are in place to adopt existing users, the infrastructure for 4G will be only packet-based (all-IP). Some proposals suggest having an open Internet platform. Technologies considered to be early 4G include: Flash-OFDM, the 802.16e mobile version of WiMax (also known as WiBro in South Korea), and HC-SDMA.
Indian market still awaits the full implementation of 3G and there are lot of issues relating to its availability. When 4G comes along it will also be seen whether it succeeds in the Indian context or not.
http://blog.tincg.com/blog/wireless-wonders/2g-vs-3g-vs4g-whats-it-all-mean
Being curious about the new 4G network that is being boasted over the airwaves by Sprint, I decided to do a little research about the differences of the G-World and what it means. It's really pretty simple when you know the basic history of the words and the types of networks they refer to. 1st generation (1G) refers to the Analog System which was the first in wireless telecommunications. This network was not capable of handling the overwhelming response to the many users of cell phones today. 2nd-generation (2G) referred to the new world of Digital wireless telecommunications. This type of network allows more users simultaneous access to the network. Along with 2G networks came the age of cell phones that were capable of sending data as well as voice. 3rd generation (3G) generally refers to higher data speeds, always-on data and even greater voice capacity than previous generations. This type of network has helped increase productivity in the work force and allows users to do even more multi-tasking. 4th generation (4G) is somewhat vague and suggests even higher data speeds. These types of networks are more data-centric and based on standard Internet technologies. Often voice services are provided through a special form of VoIP. If you are using your cell service to meet the demands of remote worker solutions, then most likely you've already experienced the improvements that 3G networks bring with regards to data speeds. The 4G systems through the use of WiMAX boast speeds in the 3 Mbps down and 1 Mbps up range. Once the 4G systems in wide spread usage, we can only hope that it will benefit small business telecommunications as much if not greater than the move to 3G did.
http://hubpages.com/hub/3G-and-4GMobile-Services Analysis and Comparison of 1G , 2G , 3G ,4G and 5G Telecom Services
94 rate or flag this page By Kevin Peter
Present Status of Telecom Services
The telecommunication service in World had a great leap within a last few year. . 6 billion people own a mobile phones so we are going to analyze the various generations of cellular systems as studied in the evolution of mobile communications from 1st generation to 5th generation .Now almost all the service providers as well as the customers seek for availing these 3G and 4G services. We can analyze that this could be due to increase in the telecoms customers day by day. In the present time, there are four generations in the mobile industry. These are respectively 1G the first generation, 2G the second generation, 3G the third generation, and then the 4G the forth generation. Ericson a Swedish company is launching this high tech featured mobile into the market. It is being first introduced in the Swedish Capital city, Stockholm.
Present Status of Telecommunication Services in Asian Countries
Now we are in the midst of 4G. In China, the 3G service came into existence only by last February. Therefore, that it may take time for exposing to other states. But we should also realize many other countries such as the Asian countries were using these services since last decade. Due to these reasons, we can hope that the 4G may enter within a few years. The 3G (Third Generation) had also reached India recently. There is no doubt that within a few years India will be the first in telecom users also.
What's 4G Mobile Technology by Prof. Willie Lu, HubPoll: 5G Wireless Systems What are 5G Wireless Systems?
Intelligence in handset WWW (World Wide Wireless Forum) Integration of space systems with 4G wireless systems Can't Say
See results without voting
Analysis of Telecom Services
Let us examine what these 3G & 4G have rather than that of 1G and 2G.
Analysis of 1G and 2G services
In 1G, Narrow band analogue wireless network is used, with this we can have the voice calls and can send text messages. These services are provided with circuit switching. Todays the usual call starts from the beginning pulse to rate to the final rate. Then in case of 2G Narrow Band Wireless Digital Network is used. It brings more clarity to the conversation and both these circuit-switching model. Both the 1G and 2G deals with voice calls and has to utilize the maximum bandwidth as well as a limited till sending messages i.e. SMS. The latest technologies such as GPRS, is not available in these generations. But the greatest disadvantage as concerned to 1G is that with this we could contact with in the premises of that particular nation, where as in case of 2G the roaming facility a semi-global facility is available.
2.5 Generation
In between 2G and 3G there is another generation called 2.5G. Firstly, this mid generation was introduced mainly for involving latest bandwidth technology with addition to the existing 2G generation. To be frank but this had not brought out any new evolution and so had not clicked to as much to that extend.
Interesting applications of 4G Mobile Phone What is 3G Generation
But to overcome the limitations of 2G and 2.5G the 3G had been introduced. In this 3G Wide Brand Wireless Network is used with which the clarity increases and gives the perfection as like that of a real conversation. The data are sent through the technology called Packet Switching .Voice calls are interpreted through Circuit Switching.
What is Packet Switching
This is actually done by supplying various addressed packets, which will be interconnected to have the conversation. It is not necessary to create a new dedicated path for sending the data.
It had been modified in such a way that the data can be send through any path; hence, this data will be received at a less time as compared to that of voice calls.
Packet Switching in Computer networks
The data packs are also used in computer that is when we connected with internet this data pack helps to download the web pages that is being displayed in the monitor. For a Data Pack it does not need any separate path for downloading or displaying any objects in the computer or any other equipment. This is due to the reason that by networking, separate paths are being created and after analyzing each, the data are being transferred to the correct access point.
Hub Challenge 18 out of 30 : Analysis and Comparison of 1G , 2G , 3G ,4G and 5G Telecom Services
3G and 4G Featuress Main 3G Services
With the help of 3G, we can access many new services too. One such service is the GLOBAL ROAMING. Another thing to be noted in case of 3G is that Wide Band Voice Channel that is by this the world has been contracted to a little village because a person can contact with other person located in any part of the world and can even send messages too. Then the point to be noted is that 3G gives clarity of voice as well can talk with out any disturbance. Not only these but also have entertainments such as Fast Communication, Internet, Mobile T.V, Video Conferencing, Video Calls, Multi Media Messaging Service (MMS), 3D gaming, Multi-Gaming etc are also available with 3G phones.
Main 4G Features
Then with the case of Fourth Generation that is 4G in addition to that of the services of 3G some additional features such as Multi-Media Newspapers, also to watch T.V programs with the clarity as to that of an ordinary T.V. In addition, we can send Data much faster that that of the previous generations.
What is the reason for delay in implementing 3G and 4G Mobile services?
It is very sad to say that the 3G services had only reached with in some towns of china, so that it may take time to reach to Other countries. Another major defect of this is that Wide Band Frequency Spectrum, which is needed for 3G, is lacking. Another reason for this is that it a cost bearing item especially for sending data. So for us it is a higher one which could be used only by upper classes. If it should be accepted among all customers, firstly it should be availed at a lower rate, for which the rate of spectrum should be declined.
http://www.teknocrat.com/1g-vs-2g-vs-3g-vs-4g-vs-5gcomparison-differences-and-analysis.html
Generation Definition Throughput Technology When was it around What it offers
1G
Analog
14.4 Kbps (peak)
AMPS,NMT,TACS 1970 1980 TDMA,CDMA 1990 to 2000
Wireless phones are used for voice only. This is achieved by allowing multiple users on a single channel via multiplexing. Cellular phones are used for data also along with voice. The Internet becomes popular and data becomes more relevant. Multimedia services and streaming starts to show growth. Phones start supporting web browsing though limited and very few phones have that. Multimedia
2G
Digital 9.6/14.4 Narrow Kbps band circuit data
2.5G
Packet Data
171.2 GPRS Kbps(peak) 20-40 Kbps
20012004
3G
Digital
3.1 Mbps
CDMA 2000
2004-
Broadband (peak) Packet 500-700 Data Kbps
(1xRTT, EVDO) UMTS, EDGE
2005
services support along with streaming are more popular. Universal access and portability across different device types are made possible. (Telephones, PDAs, etc.) Higher throughput to support higher data needs of the consumers Speeds are further increased to keep up with data access demand used by various services. High definition streaming is now supported. New phones with HD capabilities surface. It gets pretty cool. Portability is increased further. World-wide roaming is not a distant dream.
3.5G
Packet Data
14.4 Mbps (peak) 1-3 Mbps 100-300 Mbps (peak) 3-5 Mbps 100 Mbps (Wi-Fi)
HSPA
2006 2010
4G
Digital Broadband Packet All IP Very high throughput
WiMax LTE Wi-Fi
Now
5G
Not Yet
Probably gigabits
Not Yet
Soon
http://www.facebook.com/topic.php?uid=20959235574097 6&topic=421
how 2 g works?
How 2G works, Uses of 2G technology (Second Generation technology)
2G network allows for much greater penetration intensity. 2G technologies enabled the various mobile phone networks to provide the services such as text messages, picture messages and MMS (multi media messages). 2G technology is more efficient. 2G technology holds sufficient security for both the sender and the receiver. All text messages are digitally encrypted. This digital encryption allows for the transfer of data in such a way that only the intended receiver can receive and read it.
2G Technologies (Second Generation Technologies)
Second generation technologies are either time division multiple access (TDMA) or code division multiple access (CDMA). TDMA allows for the division of signal into time slots. CDMA allocates each user a special code to communicate over a multiplex physical channel. Different TDMA technologies are GSM, PDC, iDEN, iS-136.CDMA technology is IS-95. GSM has its origin from the Group special Mobile, in Europe. GSM (Global system for mobile communication) is the most admired standard of all the mobile technologies. Although this technology originates from the Europe, but now it is used in more than 212 countries in the world. GSM technology was the first one to help establish international roaming. This enabled the mobile subscribers to use their mobile phone connections in many different countries of the worlds is based on digital signals ,unlike 1G technologies which were used to transfer analogue signals. GSM has enabled the users to make use of the short message services (SMS) to any mobile network at any time. SMS is a cheap and easy way to send a message to anyone, other than the voice call or conference. This technology is beneficial to both the network operators and the ultimate users at the same time.
Another use of this technology is the availability of international emergency numbers, which can be used by international users anytime without having to know the local emergency numbers. PDC or personal digital cellular technology was developed in Japan, and is exclusively used in JAPAN as well. PDC uses 25 KHz frequency. Docomo launched its first digital service of PDC in 1993.integrated digital enhanced network (iDEN) was developed by MOTOROLA, as a major mobile technology. It enabled the mobile users to make use of complex trunked radio and mobile phones. iDEN has a frequency of about 25Khz.i DEN allows three or six user per mobile channel.iS-136 is a second generation cellular phone
system. It is also known as digital AMPS. D-AMPS were widely popular in America and Canada. However now it is in the declining phase. This technology is facing a strong competition by GSM technologies. Now the network carriers have adopted GSM and other CDMA 2000 technologies at large. Interim standard 95 is a first and the foremost CDMA cellular technology. It is most famous by its brand name known as cdmaOne. It makes use of the CDMA to transfer the voice signals and data signals from cellular phones to cell sites (cell sites is cellular network).
Benefits of 2G technology (Second Generation)
Digital signals require consume less battery power, so it helps mobile batteries to last long. Digital coding improves the voice clarity and reduces noise in the line. Digital signals are considered environment friendly. The use of digital data service assists mobile network operators to introduce short message service over the cellular phones. Digital encryption has provided secrecy and safety to the data and voice calls. The use of 2G technology requires strong digital signals to help mobile phones work. If there is no network coverage in any specific area, digital signals would be weak.
How does 3 g work?
3G is the short form used for third-generation technology. There are few technologies in the history of mankind where there has been so much hype, followed by so much dissapointment, but it looks like the 3G providers have finally got their act together in 2008, and have started delivering the 3G mobile broadband services that we have all been waiting for. According to wikipedia definition: 3G is the third generation of mobile phone standards and technology, superseding 2G. It is based on the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) family of standards under the International Mobile Telecommunications programme, IMT-2000. 3G technologies enable network operators to offer users a wider range of more advanced services while achieving greater network capacity through improved spectral efficiency. Services include wide-area wireless voice telephony, video calls, and broadband wireless data, all in a mobile environment. Additional features also include HSPA data transmission capabilities able to deliver speeds up to 14.4Mbit/s on the downlink and 5.8Mbit/s on the uplink. The first country to start 3G service on a great scale was Japan where by 2005 nearly 40% of consumers used 3G network only. With 2G technology becoming outdated in Japan,almost all the 2G networks have now been shifted to 3G networks. 3G gives the ability to transfer both voice as well as non-voice based Data at a much faster level. While marketing 3G services, video telephony is famously referred as a killer
application. 3G networks have not been upgraded from 2G networks and do not function on the same frequency spectrum. For 3G services new networks need to be fitted and new frequencies are allocated to the mobile operators. When you sign up for a mobile broadband deal, you will usually be provided with a USB 'dongle' and a sim card. You will need to insert the SIM card into the dongle and then, when you plug it into your laptop it should self-install. The good thing about the USB dongle solution is that you can install it in a number of machines, so you could take it with you to a meeting and then give it to your partner when they are heading out to a meeting with their own laptop.
http://www.wisegeek.com/what-are-3g-networks.htm
Third generation or 3G networks represent an international standard for wide-area cellular networks that are replacing 2G networks. The main advantage of 3G networks is use of a wider radio spectrum resulting in faster data transmission for advanced multimedia services and a larger network capacity. Carriers can deliver these advantages at a reduced cost compared to 2G network technologies, though physical implementation of a 3G network can be expensive in some cases. 3G networks represent the natural evolution from previous standards. Increasingly cellular phones and handheld mobile devices have incorporated additional services to telephony. Todays mobile devices offer high-speed World Wide Web access, emailing, messaging, video phone and multimedia services. People want to be able to watch streaming movies on their cellular phones, download and play music, store data and share files with other cellular users. 3G networks offer faster, slicker ways to do this. 3G networks have been in operation globally since December 2005 and are continuing to spread. Some telecommunication companies in the U.S., Canada, Asia and Europe use a flavor of 3G called W-CDMA (Wideband Code Division Multiple Access). Others use CDMA2000, a non-compatible, competing 3G standard that includes a small family of protocols. These are known as CDMA2000 1xRTT (1 times Radio Transmission Technology), CDA2000 EV-DO (Evolution Data Only), and CDMA EV-DV (Evolution Data/Voice). Two popular mobile carries that use CDMA technology are Sprint and Verizon. If your mobile phone utilizes a subscriber identity module or SIM card, your carrier is using a GSM (Global System for Mobile communications) network. GSM networks make the switch to 3G networks by first incorporating a General Packet Radio Service (GPRS). From here the network can be converted to a Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS), a 3G standard sometimes referred to as 3GSM. Alternately the network can incorporate an Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution (EDGE) system, though some people consider EDGE a 2.75G system since it is slightly slower than other 3G networks.
In practical terms, if you are looking for a GSM mobile phone carrier and that carrier offers UMTS or EDGE, you know you are getting a 3G network. Alternately, if considering CDMA carriers, look for one of the CDMA2000 flavors mentioned earlier. Be alert for newer technologies as well. As you might have expected, there is already talk of 4G networks, and protocols will continue to evolve with time to define newer standards.
http://www.articlealley.com/what-is-3g-and-how-does-itwork-807522.html
Many people have asked me over the last 12 months, "What is 3G?" So I've decided to write an article on how this great technology works and how it can benefit the users of it! Telecommunications and electronics manufacturing giants made the news as they battled to be the first in what was hoped would be a huge market for a new era of mobile communication, and then when 3G was actually set up, mobile phone companies tried to convince consumers to upgrade to the new services. Despite all the talk, a lot of people still don't know what 3G really means. What follows is a brief guide to 3G mobile phone communication. What is it? 3G means that the new generation of mobile phones now have the capacity to hook up to wireless broadband services. The connection speed is 144 kbps and which is roughly three times the speed of a 56K dial up modem connection. Some services offer higher connection speeds. You will be able to surf the net from a mobile or cell phone, enjoy real music video streaming wirelessly. And even 3D games, videoconferencing is all part of the 3G technology.
Laptop users also can take advantage of 3G networks for mobile broadband without a Wi-Fi network; basically you'll just have to have a network supplied computer card and a simple data plan. What kinds of 3G networks exist? There are two main varieties of 3G: UMTS (Universal Mobile Telephone Service), which uses W-CDMA as its underlying standard, and CDMA2000 1xEV-DO (Evolution-Data Optimised. now 1xEV-DO and even W-CDMA are located in all major capital cities all over Australia and ofcourse growing all the time. Speeds for both should be about entry-level ADSL quality. Which Companies provide 3G services? In Australia, The big four mobile phone networks / carriers all have 3G services, but they each have different plans, services and coverage areas. Presently the service of these carriers is not provided in all localities, and when a user goes
outside the 3G supported areas, the phones fall back on the normal GSM/ GPRS system enabling users to reach approximately 95% of the mobile phone population. these plans from all networks and providers start from a low $20 per month and up. What Kinds of Phones Support 3G? If you want to take advantage of 3G you not only have to subscribe to a new service plan, but you need a new phone.
Third-generation handsets offer video calls, music downloads and streaming services. They're generally a bit bigger than their 2G predecessors but offer a whole lot more multimedia capacity. All the major manufacturers (Nokia, Sony Ericsson, Motorola, Sharp, NEC, Samsung) sell models with 3G capacity. Check with your service provider to find out which handsets are suitable for the plan that you wish to sign up for. More About 3G With the advert of 3G technology your options related to services you wouldn't even imagine previously can now be available. There's no doubt 3G and with handset manufactures creating more phones to handle it, it will open the doors to wireless communications you previously thought was not possible! Each network provider will have their own spin on how their 3G system works and it might be good to review all 3G networks before signing up on a lengthy contract! It's all about speed and coverage. If the network provider has good 3G speed and coverage for the areas you are mainly located in, you're on a winner. The future looks bright for wireless high-speed communication systems like 3G. Soon you'll have one wireless device in your hands that will pretty much be able to do everything you need. You'll be able to even watch VIDEO calls, download anything you want at high wireless download speeds as well as even paying your accounts with one mobile device! What's coming next? In the near future the connection speeds of 144kbps will be increased to 30-100 Mbps in the so-called 4G networks. These speeds will allow users to enjoy highquality streaming video, high-quality videoconferencing and voice-over-IP mobile communication. If you enjoy the services that you get on a broadband Internet connection and would like to have them in your pocket, then the time is right to take a close look at 3G mobile phones.
------
How 4g works? http://ezinearticles.com/?Understanding-Exactly-How-4GNetworks-Really-Work&id=3110713
Perhaps most people don't realize that the internet and cell phones are about to have a lot more in common than they already do. Yes, you can access email on both the internet and cell phones at this point, and some cell phones are even fast enough that they can handle simple streaming audio. But there's a much more monumental shift that's about to take place in the world of wireless internet, and that's going to shake things up for a very long time. Currently, most people connect to the internet through wires, even when they technically are wireless. Routers plug into a cable, which is the exact same kind of ethernet cable that plugs directly into laptops and personal computers to offer cable, DSL, T1, or T3 internet. Most offices have upgraded to the speedier T1 and T3, but even those aren't particularly fast compared with what's about to happen to the internet. Consider how easy it is to turn on a cell phone, get a signal, and make a call. Gigantic towers spread out all over the country go ahead and send the information you need to do this, and those collections of towers all over the place are formally known as networks. Until very recently, in the world of cell phones, the quickest and most efficient network type was 3G. With the invention of 4G, there's a huge advantage not just for cell phone users, but for laptop owners, too. Cell phone users will be excited because it means a more efficient network and the capability to see faster, less choppy video. Most of them will also be able to enjoy higher quality streaming music, and occasionally, even high quality streaming games. But the most important thing that will happen is that computers, finally, will be able to act more like cell phones in all of the best ways. Right now, even wireless internet depend on wires, with most networks only covering a single room or restaurant. With a new development in internet that moves things a step forward, some brave companies are seeing the future of communications and planning accordingly. Alongside those cell phone towers are towers dedicated to providing internet signal all over the country. Now, thanks to that network, it is possible to turn on a laptop or a personal computer anywhere, whether it's a hotel room that promised Wi-Fi but didn't deliver or the middle of nowhere in snowstorm, and get internet. The part where 4G comes in is the part where computer users are going to need a network that can scoot along millions and millions of bytes of fast-moving technology, from video to songs. Without the new network, which is already wowing customers on both coasts who use Verizon for their mobile service, it just wouldn't be possible to get the same quality of internet with the simple click of a button. The combination of a new and unique way of providing internet service with a network that can handle the load of data being transferred is the only way to move the internet along in its evolution. The future is now, and it's never looked so bright.
Now that 4G Wireless makes a little more sense, it's time to make the leap to the new version of the world wide web. Clear internet makes the transition a whole lot easier.
Article Source: http://EzineArticles.com/3110713
http://wiki.answers.com/Q/How_will_4G_technology_wor k_and_How_the_network_will_be_installed_and_be_used
4G is being developed to accommodate the quality of service (QoS) and rate requirements set by forthcoming applications like wireless broadband access, Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS), video chat, mobile TV, HDTV content, Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB), minimal service like voice and data, and other streaming services for "anytime-anywhere". The 4G working group has defined the following as objectives of the 4G wireless communication standard: * A spectrally efficient system (in bits/s/Hz and bits/s/Hz/site),[2] * High network capacity: more simultaneous users per cell,[3] * A nominal data rate of 100 Mbit/s while the client physically moves at high speeds relative to the station, and 1 Gbit/s while client and station are in relatively fixed positions as defined by the ITU-R,[1] * A data rate of at least 100 Mbit/s between any two points in the world,[1] * Smooth handoff across heterogeneous networks,[4] * Seamless connectivity and global roaming across multiple networks,[5] * High quality of service for next generation multimedia support (real time audio, high speed data, HDTV video content, mobile TV, etc)[5] * Interoperability with existing wireless standards,[6] and * An all IP, packet switched network.[5] In summary, the 4G system should dynamically share and utilise network resources to meet the minimal requirements of all the 4G enabled users. According to the 4G working groups, the infrastructure and the terminals of 4G will have almost all the standards from 2G to 4G implemented. Although legacy systems are in place to adopt existing users, the infrastructure for 4G will be only packet-based (all-IP). Some proposals suggest having an open platform where the new innovations and evolutions can fit. The technologies which are being considered as pre-4G are the following: Flash-OFDM, WiMax, WiBro, iBurst, 3GPP Long Term Evolution and 3GPP2 Ultra Mobile Broadband. One of the first technology really fullfilling the 4G requirements as set by the ITU-R will be LTE Advanced as currently standardized by 3GPP. LTE Advanced will be an evolution of the 3GPP Long Term Evolution. Higher data rates are for instance achieved by the aggregation of multiple LTE carriers that are currently limited to 20MHz bandwidth. s."
http://communication.howstuffworks.com/convergence/4g -networks.htm
how 4g will change business?
Today's cell phones are generally great at what they were originally intended to do -- make calls, send text messages, that sort of thing. But with an ever-growing amount of Internetrelated activity taking place on modern mobile phones, the current networks can't keep up. They have a knack for becoming completely swamped whenever too many people try to update their Twitter account, download music, watch videos, check traffic reports or do whatever other online activities they're burning to do while away from their traditional computers. Just as mainstream cell-users have started to get more comfortable with the term 3G, the third-generation technology that supports "smartphones," whispers of a mythical 4G on the horizon have already started to spread. In a basic sense, 4G (fourth-generation wireless communications) will involve settling mobile communications firmly and fully into the realm of Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP). Although 4G technology will eventually be implemented in a variety of mobile gadgets, such as laptops and gaming devices, it will have the most noticeable impact in the case of mobile phones since they still deal with voice data differently. In essence, cell phones will use the same basic VoIP system that computer softphone software programs and many long-distance carriers do now. They'll transfer all the information they have to send over a wireless Internet connection in a manner conforming to various Internet Protocols (IP). This will enable them to more completely maximize on packet switching, which is a great way to send information quickly -- and at a much lower cost -- from one destination to another.
When 4G networks become standard, users should notice a difference. 4G technology has some persuasive benefits, which are helping accelerate the industry's push in its direction. Peak times might still be a little pokey (by the standards of people spoiled by superfast Internet service), but overall, it should be a step up from the service most cell phone users are familiar with today. If you're a little rusty on the ins and outs of cell phone technology and VoIP, you can brush up on the basics by checking out How Cell Phones Work and How VoIP Works. For more on the future that's fast approaching and the fiscal benefits it could herald for businesses, continue to the next page.
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Product Service Manual - Level 2: Applicable Country & RegionsДокумент125 страницProduct Service Manual - Level 2: Applicable Country & RegionsRobson LuizОценок пока нет
- Ghép nối qua cổng-ghép nối kênh 1. Ghép nối bộ nhớДокумент139 страницGhép nối qua cổng-ghép nối kênh 1. Ghép nối bộ nhớBùi Việt ĐứcОценок пока нет
- L Completely Fair Scheduler PDFДокумент10 страницL Completely Fair Scheduler PDFpelao321Оценок пока нет
- Relais FANOX SIL-B PDFДокумент311 страницRelais FANOX SIL-B PDFcalidadОценок пока нет
- Codes and Standards - Cable Tray InstituteДокумент5 страницCodes and Standards - Cable Tray InstituteRajamanickam Kalavathi SubramanianОценок пока нет
- Bloch. Nuclear Induction Experiment 1946 PDFДокумент16 страницBloch. Nuclear Induction Experiment 1946 PDFEdward Ventura BarrientosОценок пока нет
- 079c PDFДокумент6 страниц079c PDFmohanОценок пока нет
- Signal TransmissionДокумент25 страницSignal TransmissionKumbati SupertiksОценок пока нет
- Xilinx XC 3000Документ21 страницаXilinx XC 3000shabbir470100% (1)
- Rfid Reader Rs 232Документ11 страницRfid Reader Rs 232Varun Sankar SОценок пока нет
- Introduction To IR SpectrosДокумент119 страницIntroduction To IR SpectrosAvinash100% (3)
- PC Parts RecomendedДокумент220 страницPC Parts RecomendedAhmad Bik ElhaysОценок пока нет
- Sajhani Grid Station (Pakistan) ReportДокумент9 страницSajhani Grid Station (Pakistan) ReportAsad KhanОценок пока нет
- ASBU Catalog 2016 V1.0Документ139 страницASBU Catalog 2016 V1.0Sandu Andrei100% (2)
- Update 201409Документ4 062 страницыUpdate 201409NguyễnThạchОценок пока нет
- 0417 w16 QP 13 PDFДокумент16 страниц0417 w16 QP 13 PDFHan SungОценок пока нет
- Control SystemДокумент215 страницControl SystemRyan Tuyan100% (1)
- Neema Daneshvar ResumeДокумент1 страницаNeema Daneshvar Resumeneema762Оценок пока нет
- Valleylab ForceTriad - User Manual PDFДокумент100 страницValleylab ForceTriad - User Manual PDFPaulina LekszyckaОценок пока нет
- Plus Elite Cabin Regatta: User and Installation Guide Manuel D'emploi Et D'installationДокумент85 страницPlus Elite Cabin Regatta: User and Installation Guide Manuel D'emploi Et D'installationmansoorОценок пока нет
- BD 10032015Документ2 страницыBD 10032015Syaribul ManapОценок пока нет
- DP9127V DPДокумент11 страницDP9127V DPGustavo AlonsoОценок пока нет
- Infineon Bts3408g Ds v01 05 enДокумент14 страницInfineon Bts3408g Ds v01 05 enblessingj19it018Оценок пока нет
- FlowChart SymbolsДокумент5 страницFlowChart SymbolskalubandihariОценок пока нет
- AVSU Area ValveДокумент2 страницыAVSU Area ValveRobert_Hegedus_1642Оценок пока нет
- NJM5534 - 2 22 11Документ6 страницNJM5534 - 2 22 11Hoàng ĐìnhОценок пока нет
- Arteche CT Tripping Relays Catalog PDFДокумент28 страницArteche CT Tripping Relays Catalog PDFtamky SubstationОценок пока нет
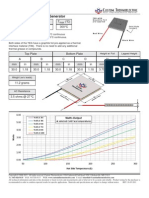
- Mina TEG SpecДокумент3 страницыMina TEG SpecPamela SandersinОценок пока нет
- BSSPAR1: Chapter 10 Multi-BCF and Common BCCH: 1 © Nokia Siemens NetworksДокумент22 страницыBSSPAR1: Chapter 10 Multi-BCF and Common BCCH: 1 © Nokia Siemens NetworksJunaidОценок пока нет
- Distance Learning Programme: Test Type: UNIT - 9 & 10Документ60 страницDistance Learning Programme: Test Type: UNIT - 9 & 10Crazy ChallengeОценок пока нет