Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Naloxone (Narcan)
Загружено:
Adrianne BazoИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Naloxone (Narcan)
Загружено:
Adrianne BazoАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
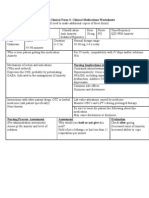
NURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications Worksheets
(You will need to make additional copies of these forms)
Generic Name Trade Name Classification Dose Route Time/frequency
Naloxone Narcan Antidotes (for 0.2 IVP PRN
opioids)
Peak Onset Duration Normal dosage range
1-2 min 45 min 0.02-0.2 mg q 2-3 min until response obtained; repeat q 1-2
Unknown hr if needed
Why is your patient getting this medication For IV meds, compatibility with IV drips and/or
Reversal of CNS depression and respiratory solutions
depression because of suspected opioid overdosage Administer undiluted for suspected opioid overdoseFor
patients with opioid-induced respiratory depression, dilute 0.4
mg of naloxone in 10 ml of sterile water or 0.9% NaCl for
injection. Rate: Administer at a rate of 0.1-0.4 mg over 15
seconds in patients with suspected opioid overdose
Mechanism of action and indications Nursing Implications (what to focus on)
(Why med ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactions
Competitively blocks the effects of opioids, including Hypersensitivity
CNS and respiratory depression, without producing any Resuscitation equipment, oxygen, vasopressors, and
agonist (opioid-like) effects mechanical ventilation should be available to supplement
Reversal of signs of opioid excess naloxone therapy as needed
Common side effects
none
Interactions with other patient drugs, OTC or Lab value alterations caused by medicine
herbal medicines (ask patient specifically) none
None for this pt
Be sure to teach the patient the following about this
medication
As medication becomes effective, explain purpose and
effects of naloxone to patient
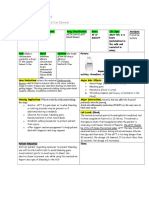
Nursing Process- Assessment Assessment Evaluation
(Pre-administration assessment) Why would you hold or not give this Check after giving
Monitor respiratory rate, rhythm, and depth; med? Alertness without significant
pulse, ECG, blood pressure; and level of Only give for suspected opioid pain or withdrawal
consciousness frequently for 3-4 hr after the symptoms
expected peak of blood concentrations.
overdose/toxicity
After a moderate overdose of a short half-
life opioid, physical stimulation may be
enough to prevent significant
hypoventilation. The effects of some opioids
may last longer than the effects of
naloxone, and repeat doses may be
necessary
Assess patient for level of pain after
administration when used to treat
postoperative respiratory depression.
Naloxone decreases respiratory depression
but also reverses analgesia
Вам также может понравиться
- Zofran Drug CardДокумент1 страницаZofran Drug CardSheri4900% (1)
- NarcanДокумент1 страницаNarcanKatie McPeekОценок пока нет
- Valium Drug AnalysisДокумент1 страницаValium Drug AnalysisFerdinand Sherwin MorataОценок пока нет
- AdenosineДокумент2 страницыAdenosinejdmedicОценок пока нет
- Name of Drugs Indications Contraindications ADVERSE Reactions To Watch Out For Drug Interactions Nursing ConsiderationsДокумент2 страницыName of Drugs Indications Contraindications ADVERSE Reactions To Watch Out For Drug Interactions Nursing ConsiderationsAlexis SilvestreОценок пока нет
- Nalbuphine (Nubain)Документ2 страницыNalbuphine (Nubain)Adrianne Bazo100% (1)
- DORMICUMДокумент1 страницаDORMICUMArian Rose100% (1)
- Morphine SulfateДокумент5 страницMorphine Sulfateapi-3797941100% (4)
- Drug Card BenadrylДокумент1 страницаDrug Card BenadrylAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Enoxaparin (Lovenox)Документ1 страницаEnoxaparin (Lovenox)EОценок пока нет
- VancomycinДокумент1 страницаVancomycinE100% (2)
- DexmedetomidineДокумент2 страницыDexmedetomidineapt48 ukwmsОценок пока нет
- Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseДокумент1 страницаMedication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseMarina Wasem NetzlaffОценок пока нет
- Drug Study of AminophyllineДокумент6 страницDrug Study of AminophyllineFrancis CorpuzОценок пока нет
- Atropine Drug ProfileДокумент2 страницыAtropine Drug ProfileShahpmdОценок пока нет
- LisinoprilДокумент1 страницаLisinoprilKatie McPeekОценок пока нет
- Oxazepam (Serax)Документ1 страницаOxazepam (Serax)CassieОценок пока нет
- Imipenem Cilastatin (Primaxin)Документ1 страницаImipenem Cilastatin (Primaxin)EОценок пока нет
- Buspar (Buspirone)Документ1 страницаBuspar (Buspirone)EОценок пока нет
- Cefazolin (Ancef)Документ1 страницаCefazolin (Ancef)Adrianne BazoОценок пока нет
- DocetaxelДокумент4 страницыDocetaxelfnurdiansah002Оценок пока нет
- Effects of Midazolam and Diazepam drug studyДокумент10 страницEffects of Midazolam and Diazepam drug studyAbie Jewel Joy Roque100% (1)
- AeknilДокумент2 страницыAekniljaycey24Оценок пока нет
- Atropine SulfateДокумент2 страницыAtropine SulfateMae Ann Bueno CastillonОценок пока нет
- Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: ALEXA MURIEL L. MOZAR Section: BLOCK 261Документ2 страницыMindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: ALEXA MURIEL L. MOZAR Section: BLOCK 261Alexandra AntondyОценок пока нет
- Phenylephrine HydrochlorideДокумент5 страницPhenylephrine HydrochlorideSean Amir S. Savellano100% (1)
- DiazepamДокумент1 страницаDiazepamStephanie PeОценок пока нет
- Drug Card for Heparin (HEP-LOCKДокумент1 страницаDrug Card for Heparin (HEP-LOCKTee WoodОценок пока нет
- PropofolДокумент2 страницыPropofolFarkhanОценок пока нет
- MIDAZOLAM DRUG STUDYДокумент5 страницMIDAZOLAM DRUG STUDYShara Lailanie A. AzisОценок пока нет
- AcarboseДокумент1 страницаAcarboseHanna SeОценок пока нет
- Fluticasone Flovent HFA asthma inhaler guideДокумент1 страницаFluticasone Flovent HFA asthma inhaler guideKevin Nelson0% (1)
- Epinephrine Drug Name Dosages Therapeutic ActionsДокумент4 страницыEpinephrine Drug Name Dosages Therapeutic ActionsAxl Rose R. ArnejoОценок пока нет
- OPIOID OVERVIEWДокумент3 страницыOPIOID OVERVIEWGerrahОценок пока нет
- LidocaineДокумент4 страницыLidocaineAhmad Fauzi100% (1)
- Effects of atracurium besylateДокумент3 страницыEffects of atracurium besylateWidya WidyariniОценок пока нет
- NaloxoneДокумент3 страницыNaloxoneTracyОценок пока нет
- DRUG STUDY: MORPHINE SULFATE AND ITS USES, MECHANISM OF ACTION, EFFECTS, AND INTERACTIONSДокумент8 страницDRUG STUDY: MORPHINE SULFATE AND ITS USES, MECHANISM OF ACTION, EFFECTS, AND INTERACTIONSShara Lailanie A. Azis100% (1)
- Nursing Classification, Actions, Indications and Contraindications of CiticolineДокумент1 страницаNursing Classification, Actions, Indications and Contraindications of CiticolineHarvey BanagОценок пока нет
- DRUG NAME: Hydroxyurea: Synonym (S) : Common Trade Name (S) : ClassificationДокумент7 страницDRUG NAME: Hydroxyurea: Synonym (S) : Common Trade Name (S) : ClassificationDewinta AbutОценок пока нет
- VancomycinДокумент2 страницыVancomycinRye AnchОценок пока нет
- IsoketДокумент2 страницыIsoketJaessa FelicianoОценок пока нет
- PrednisoloneДокумент2 страницыPrednisoloneKatie McPeekОценок пока нет
- Generic Name: Brand Name:: ClassificationsДокумент2 страницыGeneric Name: Brand Name:: ClassificationsbillyktoubattsОценок пока нет
- RocephinДокумент1 страницаRocephinCassieОценок пока нет
- DiazepamДокумент1 страницаDiazepamkualamonkey100% (1)
- AmiodaroneДокумент2 страницыAmiodaronekumaninaОценок пока нет
- Novolog (Insulin Aspart)Документ3 страницыNovolog (Insulin Aspart)EОценок пока нет
- XopenexДокумент1 страницаXopenexKatie McPeekОценок пока нет
- Morphine (Astramorph)Документ1 страницаMorphine (Astramorph)Adrianne BazoОценок пока нет
- Hydro Cod One Acetaminophen (Lortab)Документ1 страницаHydro Cod One Acetaminophen (Lortab)EОценок пока нет
- Ativan (Lorazepam) 08Документ1 страницаAtivan (Lorazepam) 08CassieОценок пока нет
- Morphine (Astramorph) PCAДокумент2 страницыMorphine (Astramorph) PCAAdrianne Bazo100% (3)
- Oxycodone Acetaminophen PercocetДокумент1 страницаOxycodone Acetaminophen PercocetEОценок пока нет
- Corrected MB MED LIST 2008Документ2 страницыCorrected MB MED LIST 2008tennillegoreОценок пока нет
- MorphineДокумент1 страницаMorphineCassie100% (3)
- Drug Card AcetaminophenДокумент1 страницаDrug Card AcetaminophenAdrianne Bazo100% (3)
- Makalah SGD 1 Skenario 2 Blok 22Документ80 страницMakalah SGD 1 Skenario 2 Blok 22Dea Intania DewiОценок пока нет
- AcetaminophenДокумент1 страницаAcetaminophenKatie McPeek100% (1)
- Merperidine (Demerol)Документ1 страницаMerperidine (Demerol)EОценок пока нет
- Zoloft SertralineДокумент1 страницаZoloft SertralineAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Zofran IVPДокумент1 страницаZofran IVPAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- ZithromycinДокумент1 страницаZithromycinAdrianne BazoОценок пока нет
- Vitamin EДокумент1 страницаVitamin EAdrianne BazoОценок пока нет
- Temazepam (Restoril)Документ1 страницаTemazepam (Restoril)Adrianne BazoОценок пока нет
- ToradolДокумент2 страницыToradolAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Thyroid Preparations (Thyrar)Документ1 страницаThyroid Preparations (Thyrar)Adrianne BazoОценок пока нет
- Zocor (Simvastin)Документ3 страницыZocor (Simvastin)Adrianne BazoОценок пока нет
- Levalbuterol XopenexДокумент2 страницыLevalbuterol XopenexCassie100% (1)
- Vitamin DДокумент2 страницыVitamin DAdrianne BazoОценок пока нет
- Theragran (Multiple Vitamins)Документ3 страницыTheragran (Multiple Vitamins)Adrianne BazoОценок пока нет
- Tamoxifen NolvadexДокумент1 страницаTamoxifen NolvadexAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- ValiumДокумент2 страницыValiumAdrianne BazoОценок пока нет
- Tim OpticДокумент2 страницыTim OpticAdrianne BazoОценок пока нет
- TumsДокумент2 страницыTumsAdrianne BazoОценок пока нет
- Dulcolax SuppositoryДокумент1 страницаDulcolax SuppositoryAdrianne BazoОценок пока нет
- RisperdalДокумент2 страницыRisperdalAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Seroquel (Quetiapine)Документ1 страницаSeroquel (Quetiapine)Adrianne BazoОценок пока нет
- SinacДокумент2 страницыSinacEОценок пока нет
- Protonix IVДокумент1 страницаProtonix IVAdrianne BazoОценок пока нет
- Prozac FluoxetineДокумент2 страницыProzac FluoxetineEОценок пока нет
- Reglan Drug CardДокумент4 страницыReglan Drug CardAdrianne BazoОценок пока нет
- ProtonixДокумент1 страницаProtonixAdrianne BazoОценок пока нет
- Quest RanДокумент2 страницыQuest RanAdrianne BazoОценок пока нет
- Potassium ChlorideДокумент2 страницыPotassium ChlorideAdrianne BazoОценок пока нет
- Predacot PrednisoneДокумент1 страницаPredacot PrednisoneAdrianne BazoОценок пока нет
- Promethazine (Phenergan)Документ1 страницаPromethazine (Phenergan)Adrianne BazoОценок пока нет
- Prinivil (Lisinapril)Документ2 страницыPrinivil (Lisinapril)Adrianne BazoОценок пока нет
- Pepcid IV FamotidineДокумент2 страницыPepcid IV FamotidineAdrianne BazoОценок пока нет
- Plavix ClopidogrelДокумент2 страницыPlavix ClopidogrelAdrianne Bazo50% (2)
- Guillane - Barre SyndromeДокумент16 страницGuillane - Barre SyndromeMarivic DianoОценок пока нет
- Minimally Invasive Dentistry: Paradigm Shifts in Preparation DesignДокумент7 страницMinimally Invasive Dentistry: Paradigm Shifts in Preparation DesignArtit SongwatcharapornОценок пока нет
- Brief-Depot-Bupe-Interim-Guidelines For South Australia Community Prescribers 2020 11 24Документ16 страницBrief-Depot-Bupe-Interim-Guidelines For South Australia Community Prescribers 2020 11 24maco6708Оценок пока нет
- 24 Doctors With The Courage To Tell The Truth About Distilled WaterДокумент22 страницы24 Doctors With The Courage To Tell The Truth About Distilled WaterEnglishTutr100% (5)
- Ayurveda Today IndexДокумент9 страницAyurveda Today IndexSurya Ppvv100% (1)
- Mandatory Problem ReportingДокумент24 страницыMandatory Problem ReportingTZ LABОценок пока нет
- Chap 18 Musculoskeletal SystemДокумент29 страницChap 18 Musculoskeletal SystemAna Dominique Espia100% (1)
- Blood Glucose MonitoringДокумент13 страницBlood Glucose MonitoringPopiОценок пока нет
- Journal Pneumonia 1Документ1 страницаJournal Pneumonia 1dwi-148502Оценок пока нет
- Diuretics Pharmacology 79 88Документ6 страницDiuretics Pharmacology 79 88Neha RoyОценок пока нет
- ALINA COMBINE PHARMACEUTICALS (PVT) LTD. Product ListДокумент5 страницALINA COMBINE PHARMACEUTICALS (PVT) LTD. Product ListaoryaОценок пока нет
- Heart Failure by IvsДокумент66 страницHeart Failure by IvsArianne LasamОценок пока нет
- Psychiatric Assessment FormДокумент6 страницPsychiatric Assessment Formapi-309279404Оценок пока нет
- Chest Pain.Документ53 страницыChest Pain.Shimmering MoonОценок пока нет
- Care Pathways Early Diagnosis PrintДокумент5 страницCare Pathways Early Diagnosis PrintiannikkiОценок пока нет
- Practical Guideline in Office Hysteroscopy SEGiДокумент95 страницPractical Guideline in Office Hysteroscopy SEGiMarcus MenezesОценок пока нет
- The Mechanism of Letting GoДокумент8 страницThe Mechanism of Letting GoFilipe Rovarotto100% (6)
- Manufacturer of Implant and Surgical InstrumentДокумент15 страницManufacturer of Implant and Surgical InstrumentGeorge.gescoworldОценок пока нет
- Review of The Biological Response To A Novel Bone Cement PEMA and PBMAДокумент8 страницReview of The Biological Response To A Novel Bone Cement PEMA and PBMAReem MohammedОценок пока нет
- Prof. Eman Rushdy Sulphonylurea A Golden Therapy For DiabetesДокумент51 страницаProf. Eman Rushdy Sulphonylurea A Golden Therapy For Diabetestorr123Оценок пока нет
- Meridian Therapy Extra Vessels 2-12-EVДокумент22 страницыMeridian Therapy Extra Vessels 2-12-EVDontcho Lissiyski100% (14)
- Msds Barrier 77 B JotunДокумент13 страницMsds Barrier 77 B JotuncrysОценок пока нет
- How To Work With The Sprays PDFДокумент32 страницыHow To Work With The Sprays PDFrosaflimaОценок пока нет
- Rediscovering Rogers's Self Theory and Personality: December 2015Документ9 страницRediscovering Rogers's Self Theory and Personality: December 2015Clorence John Yumul FerrerОценок пока нет
- Voutour v. Pfizer Canada Inc. - SettlementДокумент15 страницVoutour v. Pfizer Canada Inc. - SettlementOmar Ha-RedeyeОценок пока нет
- Ijpp 2006Документ356 страницIjpp 2006G Venkatesh100% (1)
- Bio-Filtration For Air Pollution Control: M.Tech. Environmental Engineering Seminar - IiДокумент25 страницBio-Filtration For Air Pollution Control: M.Tech. Environmental Engineering Seminar - IiKaushal PatelОценок пока нет
- Marie Mongan HypnoBirthingДокумент2 страницыMarie Mongan HypnoBirthingkpantelov0% (2)
- Healthcare System in MexicoДокумент2 страницыHealthcare System in MexicoMariana MartínezОценок пока нет
- Psychometrics and Scale DevelopmenyДокумент4 страницыPsychometrics and Scale DevelopmenySumaira ManzoorОценок пока нет