Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Cues Nursing DX Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale
Загружено:
Jamie IcabandiИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Cues Nursing DX Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale
Загружено:
Jamie IcabandiАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
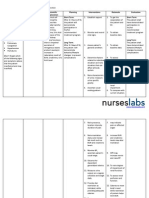
CUES SUBJECTIVE: Gapinandiho ako it mabasa. Pilang beses eot-a., as verbalized by the patient.
OBJECTIVE: Frequent passage of watery stools (4-6 times a day) Hyperactive bowel sounds(72cpm) Abdominal guarding due to cramping pain weakness
NURSING DX Fluid volume deficit related to damage and loss of epithelial cells due to inflammation as evidenced by increased bowel sounds, passage of watery stools, and cramping abdominal pain
OBJECTIVES General: To provide nutrition to all body cells. Specific: After 8 hours of effective nursing interventions, the patient will be able to: >decrease frequency of defecation in a range of 1-3 times a day. >decrease bowel sounds to the acceptable range of 335cpm to be assessed via auscultation >be free of evidence of pain: facial grimace and guarding
NURSING INTERVENTIONS INDEPENDENT: Obtain the patients initial vital signs. Observe and record stool frequency, characteristics, amounts and precipitating factors. Promote bed rest, provide bedside commode.
RATIONALE
To provide baseline data for monitoring the patient. A thorough and good assessment is vital for carrying out correct interventions to correct the patients current condition Rest decreases intestinal motility and reduces the metabolic rate when infection or hemorrhage is a complication. Urge to defecate may occur without warning and be uncontrollable, increasing the risk for incontinence and falls if facilities are not close at hand. Reduce noxious odors to avoid undue client embarrassment, and to provide an environment conducive for rest. Avoiding intestinal irritants promotes intestinal rest.
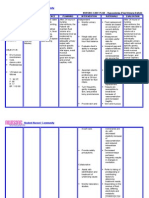
Remove stool properly. Provide room deodorizers.
Identify foods and fluids that precipitate diarrhea.
Encourage to eat foods like banana and apple. Avoid foods that are oily, spicy and caffeine. Encourage and offer fluids gradually. Offer clear liquids hourly; avoid cold fluids.
Fruits that are stool former.
Foods that may precipitate gastric cramping.
Provides colon rest by omitting or decreasing the stimulus of foods/fluids. Gradual resumption of fluids may prevent cramping and recurrence of diarrhea; however, cold fluids can increase intestinal motility. Presence of disease with unknown cause that is difficult to cure and that ma require surgical intervention can lead to stress reactions that may aggravate condition. May signify that toxic megacolon or perforation and peritonitis are imminent/have occurred, necessitating immediate medical intervention.
Encourage or provide opportunity for patient to verbalize or discuss feelings related to the disease process. Monitor and observe for fever, lethargy, leukocytosis, decreased serum protein, anxiety, and
prostration. Provide good perianal care.
Diarrheal stool is oftentimes highly acidic. This causes anal soreness and irritation in the perianal area Used to decrease acute inflammatory process when symptoms are refractory to sulfasalazine and 5-aminosalicylic acids, or for a sudden flare-ups of the disease process. Immunosuppresant may be given to block inflammatory response, decrease steroid requirements, promote healing of fistulas. Used for treatment and maintenance of moderate to severe refractory or fistulizing CD. Drug blocks the inflammatory agents activity, leading to decreased inflammation and promoting intestinal healing. Used when exacerbation is caused by or accompanied by infection, or may be part of a long-term treatment regimen.
COLLABORATIVE: STEROIDS (hydrocortisone, prednisolone, prednisone, butesonide)
IMMUNE-MODULATING AGENTS(azathioprine, 6mercaptorurine, methotrexate, cyclosporine) BIOLOGIC RESPONSE MODIFIERS (monoclonal antibodies such as IV infliximab)
ANTI-INFECTIVES (metronidazole, ciprofloxacin)
ANTIDIARRHEALS (diphenoxylate, loperamide, anodyne suppositories)
Decreases GI motility/propulsion(peristalsis) and diminishes digestive secretions to relieve cramping and diarrhea Used with caution in ulcerative colitis because they may precipitate toxic megacolon and are contraindicated in the presence of infection. May be useful for clients who do not respond to standard interventions.
ANTISPASMODIC (Lhoscyamine, dicyclomine, hyoscamine/atropine/scopola mine/phenobarbital) Assist with/prepare for surgical intervention---ileostomy, total colostomy, percutaneous abcess drainage
May be necessary if perforation or vowel obstuction occurs or disease is unresponsive to medical treatment. Total colectomy is considered curative for UC (which affects only the colon). However, it may not resolve extraintestinal manifestations. In Crohns disease, surgery may be performed to remove a diseased
section of bowel, but is not curative, as inflammation can occur anywhere in the GI tract. The client ma require a temporary or permanent colostomy.
Вам также может понравиться
- Diarrhea Care PlanДокумент2 страницыDiarrhea Care Planzepoli_zepoly6232100% (1)
- Assessment Objectives: "Masakit Lagi Yung Lalamunan NyaДокумент3 страницыAssessment Objectives: "Masakit Lagi Yung Lalamunan Nyaangel_pearl413100% (2)
- Acc Phu Case NCP HyperthermiaДокумент1 страницаAcc Phu Case NCP Hyperthermiamacy_bautistaОценок пока нет
- NCP Making (Ulcerative Colitis & Crohn's Disease)Документ2 страницыNCP Making (Ulcerative Colitis & Crohn's Disease)R Hornilla ArcegaОценок пока нет
- Compartment Syndrome NCP (PAIN)Документ2 страницыCompartment Syndrome NCP (PAIN)eunica16Оценок пока нет
- Tachycardia NCPДокумент2 страницыTachycardia NCPRemita Hutagalung50% (4)
- Aguinaldo Nursing Care Plan Ulcerative ColitisДокумент3 страницыAguinaldo Nursing Care Plan Ulcerative ColitisSophia Kaye Aguinaldo100% (1)
- Aiza NCPДокумент6 страницAiza NCPponponolmedoОценок пока нет
- Assessment Healt H Patte RN Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome (Edit) Intervention (Edit) Evaluation (EDIT) Rema RKSДокумент3 страницыAssessment Healt H Patte RN Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome (Edit) Intervention (Edit) Evaluation (EDIT) Rema RKStflorenzОценок пока нет
- NCP Gastric CancerДокумент6 страницNCP Gastric Cancerhayascent hilarioОценок пока нет
- NCPДокумент7 страницNCPJo Chiko FlorendoОценок пока нет
- Ca6 NCP Pain - NinaДокумент6 страницCa6 NCP Pain - NinaNinaОценок пока нет
- Glaucoma NCPДокумент4 страницыGlaucoma NCPChantal CaraganОценок пока нет
- Nutrition Imbalance NCPДокумент1 страницаNutrition Imbalance NCPmawelОценок пока нет
- NCP Crohn'sДокумент2 страницыNCP Crohn'sJanice Marco100% (1)
- Disturbed Sleeping Pattern NCPДокумент4 страницыDisturbed Sleeping Pattern NCPSamVelascoОценок пока нет
- NCP GastroenteritisДокумент1 страницаNCP GastroenteritisFranchesca PaunganОценок пока нет
- 7 Hyperthyroidism Nursing Care Plan (NCP)Документ1 страница7 Hyperthyroidism Nursing Care Plan (NCP)Apol PenОценок пока нет
- NCP - Diabetes Mellitus Type IIДокумент10 страницNCP - Diabetes Mellitus Type IIChristine Karen Ang SuarezОценок пока нет
- San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesДокумент3 страницыSan Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, Philippineskuro hanabusaОценок пока нет
- NCP PancreatitisДокумент2 страницыNCP PancreatitisJeanelle Generoso100% (1)
- NCP Acute Pain RT CancerДокумент3 страницыNCP Acute Pain RT CancerCharissa Magistrado De LeonОценок пока нет
- NCP For COLON Cancer PatientДокумент4 страницыNCP For COLON Cancer PatientCarolina Tardecilla100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Risk For InjuryДокумент1 страницаNursing Care Plan Risk For InjuryAce Dioso TubascoОценок пока нет
- NCP For MGДокумент1 страницаNCP For MGSandra MedinaОценок пока нет
- NURSING CARE PLAN For TB 2003Документ6 страницNURSING CARE PLAN For TB 2003Princess Andrea Bulatao100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: IndependentДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan: IndependentAdhaОценок пока нет
- NCP AidsДокумент16 страницNCP AidstferdianingsihОценок пока нет
- NCP 1 Addisons DiseaseДокумент5 страницNCP 1 Addisons DiseaseRenee RoSeОценок пока нет
- NCP - Deficient Fluid VolumeДокумент2 страницыNCP - Deficient Fluid VolumerobbychuaОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care PlanДокумент11 страницNursing Care Planaycee0316100% (1)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluation S: Patient Was SeenДокумент3 страницыAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluation S: Patient Was Seenkaren kate ablesОценок пока нет
- NCP - Acute PainДокумент2 страницыNCP - Acute PainsAm_300% (1)
- Thyroidectomy NCPДокумент1 страницаThyroidectomy NCPkzbreakerrОценок пока нет
- New DS3Документ3 страницыNew DS3dakieОценок пока нет
- "Nagtatae Siya 4 Days Na" As Verbalized by The Mother. Inatake of Causative Agents Irritation of The Stomach Inflammation of The Stomach Increase GI Motility DiarrrheaДокумент4 страницы"Nagtatae Siya 4 Days Na" As Verbalized by The Mother. Inatake of Causative Agents Irritation of The Stomach Inflammation of The Stomach Increase GI Motility DiarrrheaMelissa MhelОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan: Pulmonary EbolismДокумент5 страницNursing Care Plan: Pulmonary EbolismneuronurseОценок пока нет
- Altered Renal Perfusion CRFДокумент4 страницыAltered Renal Perfusion CRFKristel Anne Nillo ZepolОценок пока нет
- NCP 4Документ1 страницаNCP 4marohunkОценок пока нет
- Ncp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasДокумент4 страницыNcp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasFran LanОценок пока нет
- NCP-fluid Volume DeficitДокумент4 страницыNCP-fluid Volume DeficitChrissa Mae Aranilla MayoОценок пока нет
- Deficit)Документ2 страницыDeficit)Lee DeeОценок пока нет
- COLCHICINE pptx1800128929Документ15 страницCOLCHICINE pptx1800128929April Mergelle LapuzОценок пока нет
- Care Plan ExampleДокумент2 страницыCare Plan Exampleincess27100% (1)
- NCP PTBДокумент2 страницыNCP PTBMack Jhed AnarconОценок пока нет
- NCP (Riskforimpairedskinintegrity)Документ3 страницыNCP (Riskforimpairedskinintegrity)Ma Kaye Gelizabeth Corpuz-DauloОценок пока нет
- HoplessnessДокумент16 страницHoplessnessHamza IshtiaqОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan For Tissue InjuryДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan For Tissue InjuryJobelle AcenaОценок пока нет
- NCP PryllДокумент6 страницNCP PryllpjcolitaОценок пока нет
- Com/4-Cholecystitis - Cholelithiasis - Nursing-Care - Plans/2/ 6-OverviewДокумент2 страницыCom/4-Cholecystitis - Cholelithiasis - Nursing-Care - Plans/2/ 6-OverviewCharles Belonio Dorado100% (1)
- Activity IntoleranceДокумент2 страницыActivity IntolerancedohbleОценок пока нет
- NCP (Or) ThyroidectomyДокумент3 страницыNCP (Or) ThyroidectomyChiz CorreОценок пока нет
- NCPДокумент4 страницыNCPAndrea BroccoliОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan For AIDS HIVДокумент3 страницыNursing Care Plan For AIDS HIVFARAH MAE MEDINA100% (2)
- NCPДокумент7 страницNCPMarius Clifford BilledoОценок пока нет
- NCP PSHДокумент17 страницNCP PSHMargareth OrtizОценок пока нет
- NCPsДокумент13 страницNCPsRocel DevillesОценок пока нет
- Intestinal Obstraction MajДокумент44 страницыIntestinal Obstraction MajHamss AhmedОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan - Using NandaДокумент16 страницNursing Care Plan - Using NandaWardinatul ImanОценок пока нет
- CASE STUDIES L3 A Group 3Документ10 страницCASE STUDIES L3 A Group 3Doneva Lyn MedinaОценок пока нет
- Allergic RhinitisДокумент2 страницыAllergic RhinitisJamie IcabandiОценок пока нет
- Schizophrenia Tied To Teen Brain ChangesДокумент5 страницSchizophrenia Tied To Teen Brain ChangesJamie IcabandiОценок пока нет
- Ciprofloxacin Drug StudyДокумент1 страницаCiprofloxacin Drug StudyJamie IcabandiОценок пока нет
- Child - Cerebral PalsyДокумент3 страницыChild - Cerebral PalsyJamie Icabandi67% (3)
- Philippines)Документ8 страницPhilippines)Jamie IcabandiОценок пока нет
- Neuro AssessmentДокумент13 страницNeuro Assessmentyassyrn100% (2)
- NCP FeverДокумент2 страницыNCP FeverJamie IcabandiОценок пока нет
- CATL 34189-20AH Low Temperature Cell SpecificationДокумент17 страницCATL 34189-20AH Low Temperature Cell Specificationxueziying741Оценок пока нет
- Bashar CitateДокумент7 страницBashar CitateCristiana ProtopopescuОценок пока нет
- Graphs in ChemДокумент10 страницGraphs in Chemzhaney0625Оценок пока нет
- Hal Foster Vision and Visuality Discussions in Contemporary Culture PDFДокумент75 страницHal Foster Vision and Visuality Discussions in Contemporary Culture PDFEd GomesОценок пока нет
- Perfil Clinico de Pacientes Con Trastornos de La Conducta AlimentariaДокумент44 страницыPerfil Clinico de Pacientes Con Trastornos de La Conducta AlimentariaFrida PandoОценок пока нет
- Newsite KPI Check. - Ver2Документ4 183 страницыNewsite KPI Check. - Ver2nasircugaxОценок пока нет
- Somanabolic+Muscle+Maximizer+PDF+ +eBook+Free+Download+Kyle+LeonДокумент34 страницыSomanabolic+Muscle+Maximizer+PDF+ +eBook+Free+Download+Kyle+LeonAaron BarclayОценок пока нет
- ESUR Guidelines 10.0 Final VersionДокумент46 страницESUR Guidelines 10.0 Final Versionkon shireОценок пока нет
- Shower Tapware: For More Information and Detailed Specifications Please Refer To Our Website: WWW - Plumbline.co - NZДокумент11 страницShower Tapware: For More Information and Detailed Specifications Please Refer To Our Website: WWW - Plumbline.co - NZNoman KhanОценок пока нет
- 160 78-m1Документ70 страниц160 78-m1George100% (7)
- IGCSE Religious Studies (Edexcel - 2009 - Be Careful Not To Choose The New' IGCSE)Документ8 страницIGCSE Religious Studies (Edexcel - 2009 - Be Careful Not To Choose The New' IGCSE)Robbie TurnerОценок пока нет
- Reading The Bible From Feminist, Dalit, Tribal and Adivasi Perspectives (Course Code: BC 107)Документ8 страницReading The Bible From Feminist, Dalit, Tribal and Adivasi Perspectives (Course Code: BC 107)Arun Stanley100% (2)
- Andre Bazin, The Ontology of The Photographic Image From His Book What Is Cinema Vol. IДокумент8 страницAndre Bazin, The Ontology of The Photographic Image From His Book What Is Cinema Vol. IAnkit LadiaОценок пока нет
- Education and Its LegitimacyДокумент4 страницыEducation and Its LegitimacySheila G. Dolipas100% (6)
- Baptismal DelayДокумент20 страницBaptismal DelayfiohdiohhodoОценок пока нет
- 02 Height and Distance - NIMCET Free Study MatrerialДокумент2 страницы02 Height and Distance - NIMCET Free Study MatrerialIshang VashishthaОценок пока нет
- Chem 152 Lab ReportДокумент21 страницаChem 152 Lab Reportapi-643022375Оценок пока нет
- Engine Interface ModuleДокумент3 страницыEngine Interface ModuleLuciano Pereira0% (2)
- The Effect of Realistic Mathematics Education Approach On Students' Achievement and Attitudes Towards MathematicsДокумент9 страницThe Effect of Realistic Mathematics Education Approach On Students' Achievement and Attitudes Towards MathematicsyusfazilaОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент45 страницUntitledjemОценок пока нет
- Vertical Transportation: Commercial, Hotel, Hospital, Etc)Документ5 страницVertical Transportation: Commercial, Hotel, Hospital, Etc)fdarchitectОценок пока нет
- VisualizationДокумент2 страницыVisualizationKIRAN H SОценок пока нет
- Gunnar Fischer's Work On Ingmar Bergman's The Seventh Seal and Wild StrawberriesДокумент6 страницGunnar Fischer's Work On Ingmar Bergman's The Seventh Seal and Wild StrawberriesSaso Dimoski100% (1)
- Australia Harvesting Rainwater For Environment, Conservation & Education: Some Australian Case Studies - University of TechnologyДокумент8 страницAustralia Harvesting Rainwater For Environment, Conservation & Education: Some Australian Case Studies - University of TechnologyFree Rain Garden ManualsОценок пока нет
- Free Vibration of SDOFДокумент2 страницыFree Vibration of SDOFjajajajОценок пока нет
- IELTS Materials ReadingДокумент9 страницIELTS Materials ReadingßläcklìsètèdTȜè0% (1)
- Pre-Socratic Pluralism AtomismДокумент1 страницаPre-Socratic Pluralism AtomismpresjmОценок пока нет
- Risk Factors of Oral CancerДокумент12 страницRisk Factors of Oral CancerNauman ArshadОценок пока нет
- Effect of Social Economic Factors On Profitability of Soya Bean in RwandaДокумент7 страницEffect of Social Economic Factors On Profitability of Soya Bean in RwandaMarjery Fiona ReyesОценок пока нет
- K. Subramanya - Engineering Hy-Hill Education (India) (2009) 76Документ1 страницаK. Subramanya - Engineering Hy-Hill Education (India) (2009) 76ramsinghmahatОценок пока нет