Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Models of Human Resource Mangement
Загружено:
mirgasaraИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Models of Human Resource Mangement
Загружено:
mirgasaraАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Models of Human Resource Management
MODELS OF HUMAN RESOURCE MANGEMENT Understanding models in human resource management (HRM) is essential for any human resource practitioner for three reasons. Firstly, it provides a macro perspective of HRM practice in overall organizational set up. Secondly, the unity and diversity of these models serve as vital inputs in drafting tailor made HRM model for organizations. Thirdly, these models offer answers to quite a few dilemmas that practitioners encounter in their mission to pursue an organizationally dovetailed and business aligned human resource function. With these objectives in view, this chapter deals with 30 different models in HRM practice. Each of these models illustrates HRM strategy from a particular perspective, it focus, and the principle elements, the overall philosophy and ultimate objective. These 30 models together enabled HRM, practice that include soft and hard variants of HRM, quality enabled HRM, models drawn from religious scriptures, strategy, structure, process aligned HRM, oriented, profit motivated and sectorial based HRM, thus giving a comprehensive and holistic approach to the subject. BALDRIDGE MODEL OF HRM Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award is regarded as the worlds highest quality award that is given annually to organizations is recognition of its quality standards. HRM practices take a central place in quality movement of organizations. A maximum of 1000 points is allocated to different dimension of quality management for assessment under Baldrige award. Out of these, HRM practices get 150 points. Further, these practices like employee development, involvement and empowerment has potential to influence the other dimensions of the award like customer focus, leadership, and quality planning. Keeping in view its importance, Dr Christopher Hart, president of TQM Group-USA and Prof Leonard Schlesinger of Harvard Business School advocated for application of Baldrige framework to Hr in their paper titled Total Quality Management and the Human Resource Professional: Applying the Baldrige Framework to Human Resources published in HRM in 1991. This orientation may help companies to not only strengthen their quality efforts but also give a purposeful shape to HR function. In quality modeling, HR function needs to develop a new vision for itself as a customer focused service provider, in other words, setting 100 per cent customer satisfaction as HRMs ultimate goal which means, defining who the customers are and determining their precise needs Baldrige award emphasizes the critical role of five HR practices in this endeavor. These are (i) HR planning, (ii) HR education and training, (iii) HR performance and recognition, (iv) HR
involvement, and (v) HR well-being and moral. Again, each of these practices are broken into a number of activities. For example, HR planning practice is sub-divided into redefining job descriptions to increase clarity of job, steps to enrich jobs, lines of authority, organizational structure, etc. Similarly, education and training encompasses activities like leadership training, training in quality, communication, job specific employee training, remedial training for career growth and so on. The quality modeled HRM activities like leadership training in quality, communication, mentoring, job specific employee training for career growth and so on. The quality modeled HRM activities would progress in tandem with quality efforts as illustrated in Table 1.1. TABLE 1.1 Variables Baldrige HRM Outcome Customer focus and satisfaction Employee performance, satisfaction, growth and motivation System Strategic quality planning HR planning Driver Leadership Employee characteristics Managerial Implication Baldrige model of HRM helps organizations in focusing their attention on attaining global standards in quality of products and services. HR managers have to understand quality systems and interlize the philosophy and mechanisms of Malcolm Baldrige award in order to apply the right HR practices. Quality specialists have taken over HR function wherever human resource professionals were not successful in applying quality reinforced HRM model. The lack of basic HRM foundation in quality specialists led to failures in integrating Quality-HRM partnership. Therefore, special attention must be pay to identify an HRM professional with requisites skills who can translate Baldrige HRM Model into practice.
HARVARD MODEL OF HRM The type of HRM policies and practices an organization prefers should be dependent upon its organizational vision, mission, strategy, goals, and objectives. In quite a few cases, such HR practices shall also be devised and adopted in tune with external environment of organizations. In other words, HR policies and practices are subject to be influenced by internal and external environment of organizations. Harvard model of HRM propounded by Michael Beer, Richard
Walton, Quinn Mills, P. Lawrence and Bert Spector highlighted this influence of environment on HRM in their book titled Managing Human Assets published in 1984. This model also know as Soft Model of HRM/Harvard Map of HRM/Multiple Stakeholders Model, argues that human resources policies are to be influenced by two significant considerations: 1. Situational factors. The internal and external environment factors of organizations that include (i) labors market conditions (ii) Social values, (iii) business strategies (iv) technologies, (v) management philosophies, and (vi) market conditions will constrain the formation of HRM polices.
HUMAN RESOURCE MODEL EFFECT ON ORGANIZATION
Abstract: The study is undertaken to assess the major features of the diversified human resource management (HRM) models comprising diagnostic approach, training and development approach and international models and focus in the practical implementation on organizational effectiveness. The study follows mainly textual information to arrive at specific conclusion. Of the 3 Models in HRM, the international Human Resource Management model has the highest coverage in global perspective due to international growth strategies, degree of decentralization, firms size and need for expatriate compensation etc. Keywords: HRM, Training and development, and International HRM. The Cost and Management Vol. 33 No. 4 JulyAugust 2005, pp. 56-62 56 Page 2 and other feed back. Appraisal is important in the sense that unless it is proper, job performance cant be properly diagnosed. Common appraisal methods are objective measures of performance and behaviorally anchored rating scale. The earlier one follows actual output, scrap rate, value of sales etc. Special performance test is made in standard conditions. Judgmental methods follow ranking and rating techniques for measuring performance. The behaviorally anchored rating scale (BARS) provides performance dimensions and fixes anchors viz. behavior of each performance. Objectives The main objective of the study is to make a comparative analysis of the major characteristics of the different human resource management models like diagnostic approach, training and developments approach and international HRM models and assess their impact on organizational effectiveness.
Methodology The study is theoretical in nature based on extensive desk study followed by wide review of relevant research studies done earlier and textual knowledge available in different books and journals. The following analyses have been done: a) Nature of human resource management activities b) Detailed phases of diagnostic approach of HRM comprising human resource conditions, HR objectives, HR activities and evaluation of results. c) Basic features of training and development approach consisting of nine major areas. d) Fundamental characteristics of international HRM model covering six major aspects. e) Attributes of HRM models prescribed by Morgan. f) Factors favoring successful implementation of the different HRM models in global perspectives. Literature Review Ali Ahsan published the article on Use of Markovain Assumption and Efficiency Scale in Human Resource Valuation Model (Ahsan, 1997). The practice of giving value to Human Resource is not new. The concept can be traced back to the early days of slavery. But with the abolition of slavery the practice of valuing Human Resources have been discontinued. Recently, behavioral scientist and financial specialists have questioned the accounting practice of not including value of Human Resource. It is one of the most important resources of an organization and the future of an organization depends to a large extent on systematic 57 The Cost and Management, JulyAugust, 2005 Models of Human Resource Management Page 3 development of such resources. With the view in mind, many Human Resource valuation models have developed to give value to Human Resources of an organization. The author proposes a new Human Resource valuation model to overcome the shortcomings of the previous models. AFM Abdul Moyeen and Afreen Huque authored the article on Human Resource Management Practices in Business Enterprises in Bangladesh(Moyeen and Haq, 2001). This paper explores the human resource management practices in medium and large business enterprises in Bangladesh. Using data from 92 organizations, this study indicates that business enterprises adopt training programs for their employees, a performance appraisal system and a system of rewarding good employees, a policy of job sharing as well as a health and safety plan. The study also examines whether the presence of such practices are related to the firms characteristics. The study finds a positive relationship between a number of HRM
practices, size of firms and union status. The findings of this study have some important implications for business managers, the educators and researchers of HRM. Mohammad Mohiuddin and Monowar Hossain Mahmud made an important study entitled Personnel to Human Resource Management: A Developmental Perspective Analysis (Mohiuddin and Mahmud 2001). This paper reveals that human resource management is sometime thought of as an extended form of personnel management. This is not true. The present paper is an attempt to illustrate the development of HRM as a new dimension as well as a paradigm shift in people management in the organizational context. It has focused on the relevant literature and the dimensional difference among various approaches. This paper will help us to understand the nature and characteristics of the new approach in dealing with human elements of the organization. It will also be useful in designing the competent Human Resource strategies to combat the present day complexities of Human Resource Management and to gain competitive advantages in the world of technological uniformity. Sajid A. Kuraishi made a study on Human Resource Management: Emerging Trends and Policies (Kuraishi, 1990). In his article, he said that innovations in the management of human resources have been taking place over the past decade. These innovations and changes are part of a general shift that will have a great impact on the role and skills and capabilities of the human resources manager.. Yesterdays personnel department has become todays Human Resources Management. HRM now treats seriously the issues of how to attract, develop and motivate people and how to utilize them effectively. Md. Hasibur Rashid and Md. Kismatul Ahsan, in his paper on Privacy in Personnel Management in America: An Ethical Consideration (Rashid and Ahsan, 1997). This paper argues that ethics can play vital role in reducing the attitudinal differences between the personnel manager and employees on the issue of maintaining privacy of employee information. The importance of ethics in personnel management has received inadequate attention in the previous research. The need for employee information for decision making and its disclosures within and outside the organization are examined. On the basis of ethics, 58 The Cost and Management, JulyAugust, 2005 Nawaz Page 4 personnel managers behavior is classified as ethical and unethical. The privacy act of USA, technological development, and absence of appropriate legal framework has put the personnel manager in a paradoxical situation. On the basis of the secondary data and its analysis, this paper concludes that personnel manager should give importance to the ethical side of disclosure of employee information whether that is within or outside the organization and try to avoid unethical side of disclosure of personal information. Possible future researches
on privacy in personnel management are suggested. From the above literature reviewed it is clear that HRM has immense role in developing organizational effectiveness, but no such study has yet been conducted. Keeping this in mind the study is planned to have an in depth analysis of HRM models. Major Characteristics Human Resource Management is a series of decisions that affect the relationship between employees and employers; it affects many constituencies and is intended to influence the effectiveness of employees and employers. Organizational efficiency and equity are the major goals of such efforts. Changing condition expectations of the society technology and employees interest, affect the decision-making. Managing the dynamic process makes the Human Resource decisions more important and challenging. Diagnostic approach Diagnostic approach to HRM have four phases like: Assess Human Resource Conditions, Set Human Resource Objectives, Choose and Apply Human Resource Activities and Evaluation of Results. Human Resource conditions Human Resource conditions comprise external conditions, Organizational conditions & employee conditions. External conditions External conditions cover economic conditions, govt. regulations and union expectations. Economic conditions are employment rates, nature of inflation affect the behavior of the human resources showing reluctance to leave job, demand for overtime etc. Govt. regulation like pension and benefit regulations, health and safety guidelines and immigration provisions etc. affect the Human Resource decisions. The existence or unions prevents the flexibility in designing Human Resource Programs. Union strategies and their negotiation have greater impact on external conditions. Organization Conditions This comprises mainly the internal environment like nature of the organization, nature of the work and employee conditions. 59 The Cost and Management, JulyAugust, 2005 Models of Human Resource Management Page 5 Nature of the organization includes strategies and objectives, financial situation, technology and culture etc. Financial, material and human resources are organized with strategic directions. The work to be performed influences the skill and required training, the compensation and rewards available and manner of job designing.
Employee Conditions Experience, wage, performance lavels i.e. demographics are important. Younger people consider pensions in different ways. Experienced work force prefers less turnover rates. Human Resource Objectives Integrating of efficiency and equity is highly relevant in this context. Efficiency Human Resource efficiency follows market share return on investment and quality of public service influenced by job performance, unit labors cost, attendance, employee separations etc. Equity The decisions about Human Resources involve both process and context. The process refers to how decisions get made and includes human resource conditions, setting objectives, choosing and applying programs and reviewing the available results. The diagnostic model develops an interesting framework blending the content in technical knowledge in the field with the process. The major characteristics of the model are conditions in the external environment, the organization, the nature of the work and that of employees affect human resource decisions and then effectiveness in achieving objectives. Human Resource Activities HRM activities include planning, staffing, development employee union relations, compensation etc. Planning establishes the links between the organizations overall strategies and its human resource strategies. Staffing activities determine the composition of an organizations human resources. Development activities aim to help employees learn new skills or refine existing skills. Employee relations activities promote harmonious relationships among managers and employees. Evaluation of Results Actually evaluation of results determines the effects of Human Resource activities. Manager evaluates ethically by comparing performance ratings or absenteeism rates. To evaluate employees perceptions of equity, managers may examine responses to satisfaction. 60 The Cost and Management, JulyAugust, 2005 Nawaz Page 6 Training and Development Approach American Society for Training and Development prescribes a model comprising following nine major areas of HRM. Training and development, organization and development, organizational job design, human resource planning, selection and staffing, personnel research and information systems, compensation benefits, employee assistance, union relations etc.
The major outputs of human resource areas are quality work life, productivity and readiness for change. This model focuses the major activities grouped into acquisition development, motivation and maintenance. Acquisition covers resource planning, recruiting - internal, external and employee specialization. Development consists of employee training, management development and career development. Motivation follows job design, performance evaluation, rewards, job evaluation, compensation benefits and decipline. Maintenance emphasizes safety and health, employee relations etc. The external influences are govt. regulation labor union management practices and equal employment opportunity. International HRM Model Peter J. Dowling and others prescribe that International HRM refers to those activities undertaken by an organization to utilize its human resources effectively. These activities refer to the following aspects: (a) HR planning (b) Staffing (c) Performance management (d) Training and development (e) Compensation and benefits (f) Labor relations. Morgan presents a model of international HRM having three basic activities like procurement, allocation and utilization. These three activities are scattered over in host, home and other countries. HRM is the interplay among these three dimensions - human resource activities, types of employees and countries of operation. International HRM involves the same activities as domestic HRM (e.g. procurement refers to HR planning and staffing). Domestic HRM is involved with employees within only one national boundary. Practically the complexities of operating in different countries and employing different national categories of workers is a key variable that distinguishes between the two approaches. Dowling states that complexities of International HRM are related to more HR activities, the need for a broader perspective, more involvement in employees personal lives, change in emphasis as the work force mix of expatriates and locals differs, risk exposure and more impact of external influences. Conclusion and Recommendation HRM process is a continuous process. Due to inter relatedness of all the Human Resource functions, more specificity is important. Right number of people insight places in right time 61 The Cost and Management, JulyAugust, 2005 Models of Human Resource Management Page 7
made available through HRM is required to achieve the objectives. Job analysis selection process adapted to the organizations culture and working environment are more helpful for the purpose, with the organizations change over time there must be good matching of individual abilities with organizational needs for the future. Employee training and management development are duly emphasized for the same purpose. Effective performance depends on extrinsic term like, Job design working condition, job security and satisfactory supervision and intrinsic factors of achievement, recognition responsibility from the work etc. While using the different models of HRM in international prospective it is clear that the cultural environment, the nature of the multinational industry, the extent of reliance of the MNCs (multinational companies) on its home country, domestic market and the attitudes of senior management play a significant role in minimizing the human resource activities between domestic and international perspectives. A global perspective in MNCs, degree of centralization or decentralization, limited resources, nature of operations, firms size, professionals with international experience, need for expatriate compensation and international growth strategies etc. have also severe impact on the successful implementation of any of the models of HRM as detailed earlier. Practically HRM output is the central point in selecting the feasible model applicable in the environmental context. Nowadays in competitive global context, introduction of MBO (Management by Objective), Management by Exception, Human Resource Development activities through proper recruitment, selection, training and motivation would facilitate the increasing productivity of the available human resources. All these might be facilitated through application of different human resource models in the context of the environmental strength, opportunity, threat and weakness of the concerned business.
Вам также может понравиться
- HRM and Performance: Achievements and ChallengesОт EverandHRM and Performance: Achievements and ChallengesDavid E GuestОценок пока нет
- Models of Human Resource Management Management EssayДокумент6 страницModels of Human Resource Management Management EssayHND Assignment HelpОценок пока нет
- Abstract - HR ManagementДокумент6 страницAbstract - HR Managementfinal yearОценок пока нет
- Human Resource ManagementДокумент13 страницHuman Resource ManagementKshipra PanseОценок пока нет
- Approaches To Industrial RelationsДокумент39 страницApproaches To Industrial Relationslovebassi86% (14)
- Evaluating A Successful Human Resource Management PlanДокумент18 страницEvaluating A Successful Human Resource Management Plansheebakbs5144Оценок пока нет
- Evolution of HRM PDFДокумент2 страницыEvolution of HRM PDFChad100% (1)
- The Ethical Dimension of Human Resource ManagementДокумент15 страницThe Ethical Dimension of Human Resource ManagementBikash Kumar Shah100% (1)
- Hris ProjectДокумент35 страницHris ProjectAmit Devrukhkar0% (1)
- Human Resources PlanningДокумент9 страницHuman Resources Planningabbast20Оценок пока нет
- Organizational Goals. in An Organization, The Management of Human Resources Means That TheyДокумент129 страницOrganizational Goals. in An Organization, The Management of Human Resources Means That TheyEyaya SISAYОценок пока нет
- HR Metrics - Term PaperДокумент6 страницHR Metrics - Term PaperMalini JayaramanОценок пока нет
- HR Planning Forecasting Module 1 and Half of Module 2Документ12 страницHR Planning Forecasting Module 1 and Half of Module 2Mich Albania100% (1)
- Assessing HRD NeedsДокумент11 страницAssessing HRD NeedsMd.Shakhawat HossainОценок пока нет
- Session 1Документ25 страницSession 1Muhammad NaveedОценок пока нет
- Human Resource Managment (Chapter 1)Документ15 страницHuman Resource Managment (Chapter 1)Praneit Khot100% (1)
- Differnt Definition by Differnt AuthorsДокумент3 страницыDiffernt Definition by Differnt AuthorsRahul Soman100% (1)
- 5 Knowlege Areas in HRMДокумент8 страниц5 Knowlege Areas in HRMjosephtaiwo67% (9)
- Approaches To HR AuditДокумент2 страницыApproaches To HR AuditDsouza W Sharmi100% (1)
- Strategic HRM EvolutionДокумент59 страницStrategic HRM EvolutionRmy Rjdrn100% (1)
- HUMAN RESOURCE AUDIT Assignment 2Документ8 страницHUMAN RESOURCE AUDIT Assignment 2kamauhenryn0% (1)
- HRM Final AssignmentДокумент10 страницHRM Final AssignmentAhmed SharifОценок пока нет
- Manpower Analysis of ONE Bank LTDДокумент7 страницManpower Analysis of ONE Bank LTDNoorullah Patwary ZubaerОценок пока нет
- Changing Role of HRДокумент48 страницChanging Role of HRSandeep Ranjan100% (1)
- Performance ManagementДокумент4 страницыPerformance ManagementTini Dcosta100% (1)
- Bba 301 ModuleДокумент101 страницаBba 301 ModulefinleyОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 SHRM Principles, ConceptsДокумент23 страницыUnit 2 SHRM Principles, ConceptsBhaveshОценок пока нет
- CIPD Factsheet Strategic Human Resource ManagementДокумент6 страницCIPD Factsheet Strategic Human Resource ManagementAlkaAroraОценок пока нет
- Hrdss-Recent Trends in HRD PDFДокумент6 страницHrdss-Recent Trends in HRD PDFyuvrajОценок пока нет
- Evolution of Human Resource ManagementДокумент14 страницEvolution of Human Resource Managementhumanhonest100% (2)
- HR PlanningДокумент26 страницHR PlanningSubodh MayekarОценок пока нет
- Employee Empowerment ProjectДокумент75 страницEmployee Empowerment ProjectAjith KumarОценок пока нет
- Impact of Human Resource ManagementДокумент6 страницImpact of Human Resource ManagementIjaz Bokhari100% (1)
- Microsoft Word - The Human Resource Information SystemДокумент1 страницаMicrosoft Word - The Human Resource Information Systemrajsaroja1988Оценок пока нет
- Challenges in HRPДокумент14 страницChallenges in HRPPrashant GuptaОценок пока нет
- Differences Between Personnel Management vs. Human Resource ManagementДокумент5 страницDifferences Between Personnel Management vs. Human Resource ManagementTH_2014Оценок пока нет
- Models of HRMДокумент16 страницModels of HRMabdullah1996100% (1)
- Human Resource Management (BBS 2nd Year) : Navraj BhusalДокумент64 страницыHuman Resource Management (BBS 2nd Year) : Navraj Bhusalrajesh dhakalОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of HRM ch01Документ17 страницFundamentals of HRM ch01korpseeОценок пока нет
- Reinventing The Wheel at Apex Door CompanyДокумент11 страницReinventing The Wheel at Apex Door Companyjuzzy52100% (1)
- Mba Semester 1: Mb0043 Human Resource Management 3 Credits (Book Id: B0909) Assignment Set - 1Документ17 страницMba Semester 1: Mb0043 Human Resource Management 3 Credits (Book Id: B0909) Assignment Set - 1Mohammed AliОценок пока нет
- Human Resource Function Case StudyДокумент18 страницHuman Resource Function Case StudyabdullahОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 - Intro To HRMДокумент13 страницChapter 1 - Intro To HRMNur FirdausОценок пока нет
- Conventional HRM and E-HrmДокумент19 страницConventional HRM and E-HrmUmair ShabbirОценок пока нет
- Human Resource PlanningДокумент33 страницыHuman Resource PlanningSabila Muntaha Tushi100% (1)
- The Role of Human Resources in SMEsДокумент78 страницThe Role of Human Resources in SMEsdanni1100% (1)
- Case StudyДокумент3 страницыCase Studyruchita1989Оценок пока нет
- Performance AppraisalДокумент85 страницPerformance AppraisalSakhamuri Ram'sОценок пока нет
- EMPLOYEES' PERCEPTION OF TRAINING AND DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMMES IN AN ORGANIZATION: A CASE STUDY OF DELTA STEEL COMPANY (DSC) ALADJA, Nigeria.Документ111 страницEMPLOYEES' PERCEPTION OF TRAINING AND DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMMES IN AN ORGANIZATION: A CASE STUDY OF DELTA STEEL COMPANY (DSC) ALADJA, Nigeria.PROMISE CHIDI-AGBAI IROEGBUОценок пока нет
- Aiou HRM Format NewДокумент3 страницыAiou HRM Format NewSobia NazОценок пока нет
- HRD Learning 3 PDFДокумент45 страницHRD Learning 3 PDFSyafiqah Rusli IV100% (1)
- Training As A Tool For Performance ManagДокумент59 страницTraining As A Tool For Performance ManagSHUBHAM ARORAОценок пока нет
- NRB Syllabus PDFДокумент4 страницыNRB Syllabus PDFnavbhusal100% (11)
- Human Resource Management IntroductionДокумент17 страницHuman Resource Management IntroductionRam AhirОценок пока нет
- Human Resource Management AnswersДокумент6 страницHuman Resource Management AnswerseirulzОценок пока нет
- Chapter 05 - Planning For and Recruiting Human ResourcesДокумент29 страницChapter 05 - Planning For and Recruiting Human ResourcesAmy SyahidaОценок пока нет
- Q.1) Define Human Resource Development? Roles Responsibility and Functions inДокумент36 страницQ.1) Define Human Resource Development? Roles Responsibility and Functions inkaramyi97% (31)
- Human Resource PoliciesДокумент14 страницHuman Resource PolicieselinzolaОценок пока нет
- Performance Management & COmpetency Mapping NotesДокумент93 страницыPerformance Management & COmpetency Mapping NotesSahil Goutham60% (5)
- HR Planning & Development Process of GrameenphoneДокумент28 страницHR Planning & Development Process of GrameenphoneRafi Rabbee73% (11)
- The Phillips Curve: Geoff RileyДокумент2 страницыThe Phillips Curve: Geoff RileymirgasaraОценок пока нет
- Notes of Port Folio ManagemntДокумент3 страницыNotes of Port Folio ManagemntmirgasaraОценок пока нет
- SAARC NRI Feestructure 2013Документ2 страницыSAARC NRI Feestructure 2013mirgasaraОценок пока нет
- Importance of Different Ratios To Different User Groups: Management: Turnover and Operating Performance RatiosДокумент4 страницыImportance of Different Ratios To Different User Groups: Management: Turnover and Operating Performance RatiosmirgasaraОценок пока нет
- Customer Reln MGMTДокумент1 страницаCustomer Reln MGMTmirgasaraОценок пока нет
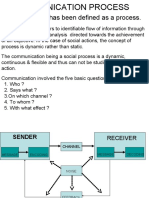
- Communication Has Been Defined As A ProcessДокумент6 страницCommunication Has Been Defined As A ProcessmirgasaraОценок пока нет
- I Believe EssayДокумент2 страницыI Believe Essayapi-532597576Оценок пока нет
- Rubric For GameДокумент2 страницыRubric For GameHanna Regine ValencerinaОценок пока нет
- JP Scopus PublishedДокумент14 страницJP Scopus PublishedAsyraf KassimОценок пока нет
- Outcome Teamwork RubricsДокумент1 страницаOutcome Teamwork RubricsMhaye CendanaОценок пока нет
- There Are Seven Steps To Whole Brain Development in Right Brain EducationДокумент7 страницThere Are Seven Steps To Whole Brain Development in Right Brain EducationSanVyasОценок пока нет
- Midterm Exam For Values EducationДокумент4 страницыMidterm Exam For Values EducationJaymar MagtibayОценок пока нет
- October 24 - Gestalt PsychologyДокумент23 страницыOctober 24 - Gestalt PsychologyEdgar Miralles Inales ManriquezОценок пока нет
- LessonPlan STAFFINGДокумент7 страницLessonPlan STAFFINGElaine EuChan Mendoza Macapagal80% (5)
- Pain - Emotional Body Chart PDFДокумент1 страницаPain - Emotional Body Chart PDFDimitriu Otilia0% (2)
- Language Training For Mining EngineersДокумент6 страницLanguage Training For Mining Engineerscarhuazrca9226Оценок пока нет
- Ologies, Isms, & IcistsДокумент2 страницыOlogies, Isms, & IcistsOmar Alansari-KregerОценок пока нет
- Facilitating Learning 2Документ28 страницFacilitating Learning 2jenniferespanolОценок пока нет
- Focus SystemДокумент10 страницFocus SystemHarthwell CapistranoОценок пока нет
- BurnabycoverletterДокумент1 страницаBurnabycoverletterapi-302222871Оценок пока нет
- Perdev Quarter 1 Module 1 No AnskeyДокумент10 страницPerdev Quarter 1 Module 1 No AnskeyPATRICKJOE PimentelОценок пока нет
- Xie, Et Al (2016) - Linking Calling and Engagement, Role of Career AdaptabilityДокумент9 страницXie, Et Al (2016) - Linking Calling and Engagement, Role of Career AdaptabilitywidyaОценок пока нет
- Duties of A ReporterДокумент3 страницыDuties of A Reportershakeel king0% (1)
- Assessment 1 BX3081 SMMДокумент9 страницAssessment 1 BX3081 SMMYUKI KOОценок пока нет
- Learning 21st Century Skills Requires 21st Century TeachingДокумент7 страницLearning 21st Century Skills Requires 21st Century Teachingapi-285249417Оценок пока нет
- 30 TaskДокумент12 страниц30 TaskAnju DhaubanjarОценок пока нет
- The Four Quadrant Model of The BrainДокумент32 страницыThe Four Quadrant Model of The BrainFeb Namia100% (2)
- Culture & Anarchy NotesДокумент2 страницыCulture & Anarchy NotesArghya Chakraborty50% (2)
- Experiment No: 6 Date: 09/10/2021 Experiment Name: Comprehensive Interest ScheduleДокумент12 страницExperiment No: 6 Date: 09/10/2021 Experiment Name: Comprehensive Interest ScheduleAiswarya Venkataramanan100% (2)
- Ohi 2Документ6 страницOhi 2api-242024640Оценок пока нет
- Group Work in The Classroom: Types of Small GroupsДокумент22 страницыGroup Work in The Classroom: Types of Small GroupsPUJA MANSINGHОценок пока нет
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesДокумент3 страницыDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesJanyn Macapagal MesinaОценок пока нет
- Patient Satisfaction On Square Hospital Service DeliveryДокумент23 страницыPatient Satisfaction On Square Hospital Service DeliveryNir Nishir100% (2)
- End of Year ReflectionДокумент1 страницаEnd of Year Reflectionapi-319999783Оценок пока нет
- Age Is Not MaturityДокумент21 страницаAge Is Not MaturityDr Avitus Leonard100% (1)
- HummsДокумент4 страницыHummsBernard ApuliОценок пока нет
- The Power of People Skills: How to Eliminate 90% of Your HR Problems and Dramatically Increase Team and Company Morale and PerformanceОт EverandThe Power of People Skills: How to Eliminate 90% of Your HR Problems and Dramatically Increase Team and Company Morale and PerformanceРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (22)
- Summary: Who Moved My Cheese?: An A-Mazing Way to Deal with Change in Your Work and in Your Life by Spencer Johnson M.D. and Kenneth Blanchard: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisОт EverandSummary: Who Moved My Cheese?: An A-Mazing Way to Deal with Change in Your Work and in Your Life by Spencer Johnson M.D. and Kenneth Blanchard: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (3)
- The 5 Languages of Appreciation in the Workplace: Empowering Organizations by Encouraging PeopleОт EverandThe 5 Languages of Appreciation in the Workplace: Empowering Organizations by Encouraging PeopleРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (46)
- Scaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0От EverandScaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- Hire With Your Head: Using Performance-Based Hiring to Build Outstanding Diverse TeamsОт EverandHire With Your Head: Using Performance-Based Hiring to Build Outstanding Diverse TeamsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (5)
- The Manager's Path: A Guide for Tech Leaders Navigating Growth and ChangeОт EverandThe Manager's Path: A Guide for Tech Leaders Navigating Growth and ChangeРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (99)
- The Fearless Organization: Creating Psychological Safety in the Workplace for Learning, Innovation, and GrowthОт EverandThe Fearless Organization: Creating Psychological Safety in the Workplace for Learning, Innovation, and GrowthРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (12)
- Getting Along: How to Work with Anyone (Even Difficult People)От EverandGetting Along: How to Work with Anyone (Even Difficult People)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (18)
- Coaching and Mentoring: Practical Techniques for Developing Learning and PerformanceОт EverandCoaching and Mentoring: Practical Techniques for Developing Learning and PerformanceРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (4)
- 12 Habits Of Valuable Employees: Your Roadmap to an Amazing CareerОт Everand12 Habits Of Valuable Employees: Your Roadmap to an Amazing CareerОценок пока нет
- Developing Coaching Skills: A Concise IntroductionОт EverandDeveloping Coaching Skills: A Concise IntroductionРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (5)
- The Fearless Organization: Creating Psychological Safety in the Workplace for Learning, Innovation, and GrowthОт EverandThe Fearless Organization: Creating Psychological Safety in the Workplace for Learning, Innovation, and GrowthРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (101)
- Working with AI: Real Stories of Human-Machine Collaboration (Management on the Cutting Edge)От EverandWorking with AI: Real Stories of Human-Machine Collaboration (Management on the Cutting Edge)Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- The Good Jobs Strategy: How the Smartest Companies Invest in Employees to Lower Costs and Boost ProfitsОт EverandThe Good Jobs Strategy: How the Smartest Companies Invest in Employees to Lower Costs and Boost ProfitsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (16)
- Finding the Next Steve Jobs: How to Find, Keep, and Nurture TalentОт EverandFinding the Next Steve Jobs: How to Find, Keep, and Nurture TalentРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (18)
- Organizational Behaviour: People, Process, Work and Human Resource ManagementОт EverandOrganizational Behaviour: People, Process, Work and Human Resource ManagementОценок пока нет
- Powerful Phrases for Dealing with Difficult People: Over 325 Ready-to-Use Words and Phrases for Working with Challenging PersonalitiesОт EverandPowerful Phrases for Dealing with Difficult People: Over 325 Ready-to-Use Words and Phrases for Working with Challenging PersonalitiesРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (14)
- Giving Effective Feedback (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)От EverandGiving Effective Feedback (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (12)
- The Neurodiversity Edge: The Essential Guide to Embracing Autism, ADHD, Dyslexia, and Other Neurological Differences for Any OrganizationОт EverandThe Neurodiversity Edge: The Essential Guide to Embracing Autism, ADHD, Dyslexia, and Other Neurological Differences for Any OrganizationОценок пока нет
- Goal Setting: How to Create an Action Plan and Achieve Your GoalsОт EverandGoal Setting: How to Create an Action Plan and Achieve Your GoalsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (9)
- The Burnout Epidemic: The Rise of Chronic Stress and How We Can Fix ItОт EverandThe Burnout Epidemic: The Rise of Chronic Stress and How We Can Fix ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (9)
- 101 Tough Conversations to Have with Employees: A Manager's Guide to Addressing Performance, Conduct, and Discipline ChallengesОт Everand101 Tough Conversations to Have with Employees: A Manager's Guide to Addressing Performance, Conduct, and Discipline ChallengesРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (9)
- 50 Top Tools for Coaching, 3rd Edition: A Complete Toolkit for Developing and Empowering PeopleОт Everand50 Top Tools for Coaching, 3rd Edition: A Complete Toolkit for Developing and Empowering PeopleРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (4)
- Scaling Up Compensation: 5 Design Principles for Turning Your Largest Expense into a Strategic AdvantageОт EverandScaling Up Compensation: 5 Design Principles for Turning Your Largest Expense into a Strategic AdvantageРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (4)