Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Study
Загружено:
KathИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Study
Загружено:
KathАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
After turning a patient, the nurse should document the position used, the time that the patient
was turned, and the findings of s in assessment. 2. PERRLA is an abbreviation for normal pupil assessment findings: pupils equal, round, and reactive to light with accommodation. 3. When percussing a patient s chest for postural drainage, the nurse s hands should be cupped. 4. When measuring a patient s pulse, the nurse should assess its rate, rhythm, qua lity, and strength. 5. Before transferring a patient from a bed to a wheelchair, the nurse should pu sh the wheelchair s footrests to the sides and loc its wheels. 6. When assessing respirations, the nurse should document their rate, rhythm, de pth, and quality. 7. For a subcutaneous injection, the nurse should use a 5/8? 25G needle. 8. The notation AA & O 3 indicates that the patient is awa e, alert, and oriented to person ( nows who he is), place ( nows where he is), and time ( nows the date and time). 9. Fluid inta e includes all fluids ta en by mouth, including foods that are liq uid at room temperature, such as gelatin, custard, and ice cream; I.V. fluids; a nd fluids administered in feeding tubes. Fluid output includes urine, vomitus, a nd drainage (such as from a nasogastric tube or from a wound) as well as blood l oss, diarrhea or feces, and perspiration. 10. After administering an intradermal injection, the nurse shouldn t massage the area because massage can irritate the site and interfere with results. 11. When administering an intradermal injection, the nurse should hold the syrin ge almost flat against the patient s s in (at about a 15-degree angle), with the b evel up. 12. To obtain an accurate blood pressure, the nurse should inflate the manometer to 20 to 30 mm Hg above the disappearance of the radial pulse before releasing the cuff pressure. 13. The nurse should count an irregular pulse for 1 full minute. 14. A patient who is vomiting while lying down should be placed in a lateral pos ition to prevent aspiration of vomitus. 15. Prophylaxis is disease prevention. 16. Body alignment is achieved when body parts are in proper relation to their n atural position. 17. Trust is the foundation of a nurse-patient relationship. 18. Blood pressure is the force exerted by the circulating volume of blood on th e arterial walls. 19. Malpractice is a professional s wrongful conduct, improper discharge of duties , or failure to meet standards of care that causes harm to another. 20. As a general rule, nurses can t refuse a patient care assignment; however, in
most states, they may refuse to participate in abortions. 21. A nurse can be found negligent if a patient is injured because the nurse fai led to perform a duty that a reasonable and prudent person would perform or beca use the nurse performed an act that a reasonable and prudent person wouldn t perfo rm. 22. States have enacted Good Samaritan laws to encourage professionals to provid e medical assistance at the scene of an accident without fear of a lawsuit arisi ng from the assistance. These laws don t apply to care provided in a health care f acility. 23. A physician should sign verbal and telephone orders within the time establis hed by facility policy, usually 24 hours. 24. A competent adult has the right to refuse lifesaving medical treatment; howe ver, the individual should be fully informed of the consequences of his refusal. 25. Although a patient s health record, or chart, is the health care facility s phys ical property, its contents belong to the patient. 26. Before a patient s health record can be released to a third party, the patient or the patient s legal guardian must give written consent. 27. Under the Controlled Substances Act, every dose of a controlled drug that s di spensed by the pharmacy must be accounted for, whether the dose was administered to a patient or discarded accidentally. 28. A nurse can t perform duties that violate a rule or regulation established by a state licensing board, even if they are authorized by a health care facility o r physician. 29. To minimize interruptions during a patient interview, the nurse should selec t a private room, preferably one with a door that can be closed. 30. In categorizing nursing diagnoses, the nurse addresses life-threatening prob lems first, followed by potentially life-threatening concerns. 31. The major components of a nursing care plan are outcome criteria (patient go als) and nursing interventions. 32. Standing orders, or protocols, establish guidelines for treating a specific disease or set of symptoms. 33. In assessing a patient s heart, the nurse normally finds the point of maximal impulse at the fifth intercostal space, near the apex. 34. The S1 heard on auscultation is caused by closure of the mitral and tricuspi d valves. 35. To maintain pac age sterility, the nurse should open a wrapper s top flap away from the body, open each side flap by touching only the outer part of the wrapp er, and open the final flap by grasping the turned-down corner and pulling it to ward the body. 36. The nurse shouldn t dry a patient s ear canal or remove wax with a cotton-tipped applicator because it may force cerumen against the tympanic membrane. 37. A patient s identification bracelet should remain in place until the patient h as been discharged from the health care facility and has left the premises.
38. The Controlled Substances Act designated five categories, or schedules, that classify controlled drugs according to their abuse potential. 39. Schedule I drugs, such as heroin, have a high abuse potential and have no cu rrently accepted medical use in the United States. 40. Schedule II drugs, such as morphine, opium, and meperidine (Demerol), have a high abuse potential, but currently have accepted medical uses. Their use may l ead to physical or psychological dependence. 41. Schedule III drugs, such as paregoric and butabarbital (Butisol), have a low er abuse potential than Schedule I or II drugs. Abuse of Schedule III drugs may lead to moderate or low physical or psychological dependence, or both. 42. Schedule IV drugs, such as chloral hydrate, have a low abuse potential compa red with Schedule III drugs. 43. Schedule V drugs, such as cough syrups that contain codeine, have the lowest abuse potential of the controlled substances. 44. Activities of daily living are actions that the patient must perform every d ay to provide self-care and to interact with society. 45. Testing of the six cardinal fields of gaze evaluates the function of all ext raocular muscles and cranial nerves III, IV, and VI. 46. The six types of heart murmurs are graded from 1 to 6. A grade 6 heart murmu r can be heard with the stethoscope slightly raised from the chest. 47. The most important goal to include in a care plan is the patient s goal. 48. Fruits are high in fiber and low in protein, and should be omitted from a lo w-residue diet. 49. The nurse should use an objective scale to assess and quantify pain. Postope rative pain varies greatly among individuals. 50. Postmortem care includes cleaning and preparing the deceased patient for fam ily viewing, arranging transportation to the morgue or funeral home, and determi ning the disposition of belongings. 51. The nurse should provide honest answers to the patient s questions.
53. When caring for an infant, a child, or a confused patient, consistency in nu rsing personnel is paramount. 54. The hypothalamus secretes vasopressin and oxytocin, which are stored in the pituitary gland. 55. The three membranes that enclose the brain and spinal cord are the dura mate r, pia mater, and arachnoid. 56. A nasogastric tube is used to remove fluid and gas from the small intestine preoperatively or postoperatively. 57. Psychologists, physical therapists, and chiropractors aren t authorized to wri te prescriptions for drugs.
52. Mil
shouldn t be included in a clear liquid diet.
58. The area around a stoma is cleaned with mild soap and water. 59. Vegetables have a high fiber content. 60. The nurse should use a tuberculin syringe to administer a subcutaneous injec tion of less than 1 ml. 61. For adults, subcutaneous injections require a 25G 1? needle; for infants, ch ildren, elderly, or very thin patients, they require a 25G to 27G needle. 62. Before administering a drug, the nurse should identify the patient by chec i ng the identification band and as ing the patient to state his name. 63. To clean the s in before an injection, the nurse uses a sterile alcohol swab to wipe from the center of the site outward in a circular motion. 64. The nurse should inject heparin deep into subcutaneous tissue at a 90-degree angle (perpendicular to the s in) to prevent s in irritation. 65. If blood is aspirated into the syringe before an I.M. injection, the nurse s hould withdraw the needle, prepare another syringe, and repeat the procedure. 66. The nurse shouldn t cut the patient s hair without written consent from the pati ent or an appropriate relative. 67. If bleeding occurs after an injection, the nurse should apply pressure until the bleeding stops. If bruising occurs, the nurse should monitor the site for a n enlarging hematoma. 68. When providing hair and scalp care, the nurse should begin combing at the en d of the hair and wor toward the head. 69. The frequency of patient hair care depends on the length and texture of the hair, the duration of hospitalization, and the patient s condition. 70. Proper function of a hearing aid requires careful handling during insertion and removal, regular cleaning of the ear piece to prevent wax buildup, and promp t replacement of dead batteries. 71. The hearing aid that s mar ed with a blue dot is for the left ear; the one wit h a red dot is for the right ear. 72. A hearing aid shouldn t be exposed to heat or humidity and shouldn t be immersed in water. 73. The nurse should instruct the patient to avoid using hair spray while wearin g a hearing aid. 74. The five branches of pharmacology are pharmaco inetics, pharmacodynamics, ph armacotherapeutics, toxicology, and pharmacognosy. 75. The nurse should remove heel protectors every 8 hours to inspect the foot fo r signs of s in brea down. 76. Heat is applied to promote vasodilation, which reduces pain caused by inflam mation. 77. A sutured surgical incision is an example of healing by first intention (hea ling directly, without granulation). 78. Healing by secondary intention (healing by granulation) is closure of the wo
und when granulation tissue fills the defect and allows reepithelialization to o ccur, beginning at the wound edges and continuing to the center, until the entir e wound is covered. 79. Keloid formation is an abnormality in healing that s characterized by overgrow th of scar tissue at the wound site. 80. The nurse should administer procaine penicillin by deep I.M. injection in th e upper outer portion of the buttoc s in the adult or in the midlateral thigh in the child. The nurse shouldn t massage the injection site. 81. An ascending colostomy drains fluid feces. A descending colostomy drains sol id fecal matter. 82. A folded towel (scrotal bridge) can provide scrotal support for the patient with scrotal edema caused by vasectomy, epididymitis, or orchitis. 83. When giving an injection to a patient who has a bleeding disorder, the nurse should use a small-gauge needle and apply pressure to the site for 5 minutes af ter the injection. 84. Platelets are the smallest and most fragile formed element of the blood and are essential for coagulation. 85. To insert a nasogastric tube, the nurse ad bac slightly and then inserts the tube. g at the pharynx, the nurse should tell the close the trachea and open the esophagus by itate this action.) instructs the patient to tilt the he When the nurse feels the tube curvin patient to tilt the head forward to swallowing. (Sips of water can facil
86. Families with loved ones in intensive care units report that their four most important needs are to have their questions answered honestly, to be assured th at the best possible care is being provided, to now the patient s prognosis, and to feel that there is hope of recovery. 87. Double-bind communication occurs when the verbal message contradicts the non verbal message and the receiver is unsure of which message to respond to. 88. A nonjudgmental attitude displayed by a nurse shows that she neither approve s nor disapproves of the patient. 89. Target symptoms are those that the patient finds most distressing. 90. A patient should be advised to ta e aspirin on an empty stomach, with a full glass of water, and should avoid acidic foods such as coffee, citrus fruits, an d cola. 91. For every patient problem, there is a nursing diagnosis; for every nursing d iagnosis, there is a goal; and for every goal, there are interventions designed to ma e the goal a reality. The eys to answering examination questions correctl y are identifying the problem presented, formulating a goal for the problem, and selecting the intervention from the choices provided that will enable the patie nt to reach that goal. 92. Fidelity means loyalty and can be shown as a commitment to the profession of nursing and to the patient. 93. Administering an I.M. injection against the patient s will and without legal a uthority is battery. 94. An example of a third-party payer is an insurance company.
95. The formula for calculating the drops per minute for an I.V. infusion is as follows: (volume to be infused drip factor) time in minutes = drops/minute 96. On-call medication should be given within 5 minutes of the call. 97. Usually, the best method to determine a patient s cultural or spiritual needs is to as him. 98. An incident report or unusual occurrence report isn t part of a patient s record , but is an in-house document that s used for the purpose of correcting the proble m. 99. Critical pathways are a multidisciplinary guideline for patient care. 100. When prioritizing nursing diagnoses, the following hierarchy should be used : Problems associated with the airway, those concerning breathing, and those rel ated to circulation. 101. The two nursing diagnoses that have the highest priority that the nurse can assign are Ineffective airway clearance and Ineffective breathing pattern. 102. A subjective sign that a sitz bath has been effective is the patient s expres sion of decreased pain or discomfort. 103. For the nursing diagnosis Deficient diversional activity to be valid, the p atient must state that he s bored, that he has nothing to do, or words to that effect. 104. The most appropriate nursing diagnosis for an individual who doesn t spea En glish is Impaired verbal communication related to inability to spea dominant la nguage (English). 105. The family of a patient who has been diagnosed as hearing impaired should b e instructed to face the individual when they spea to him. 106. Before instilling medication into the ear of a patient who is up to age 3, the nurse should pull the pinna down and bac to straighten the eustachian tube. 107. To prevent injury to the cornea when administering eyedrops, the nurse shou ld waste the first drop and instill the drug in the lower conjunctival sac. 108. After administering eye ointment, the nurse should twist the medication tub e to detach the ointment. 109. When the nurse removes gloves and a mas , she should remove the gloves firs t. They are soiled and are li ely to contain pathogens. 110. Crutches should be placed 6? (15.2 cm) in front of the patient and 6? to th e side to form a tripod arrangement. 111. Listening is the most effective communication technique. 112. Before teaching any procedure to a patient, the nurse must assess the patie nt s current nowledge and willingness to learn. 113. Process recording is a method of evaluating one s communication effectiveness . 114. When feeding an elderly patient, the nurse should limit high-carbohydrate f oods because of the ris of glucose intolerance.
115. When feeding an elderly patient, essential foods should be given first.
Вам также может понравиться
- Anatomy and PhysiologyДокумент19 страницAnatomy and PhysiologyKathОценок пока нет
- Axillary AnatomyДокумент62 страницыAxillary AnatomyKathОценок пока нет
- Emergency Cart and Code BlueДокумент10 страницEmergency Cart and Code BlueKath100% (1)
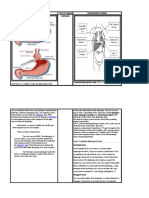
- Gall BladderДокумент1 страницаGall BladderKathОценок пока нет
- DRUg StudyДокумент11 страницDRUg StudyKathОценок пока нет
- DRUg StudyДокумент11 страницDRUg StudyKathОценок пока нет
- ImplementationДокумент2 страницыImplementationKathОценок пока нет
- DEFINITION For GESTATIONAL HYPERTENSION, PREECLAMPSIA, ECCLAMPSIA, AND HELLP SYNDROMEДокумент3 страницыDEFINITION For GESTATIONAL HYPERTENSION, PREECLAMPSIA, ECCLAMPSIA, AND HELLP SYNDROMEKathОценок пока нет
- Patient Rights and ResponsibilitiesДокумент3 страницыPatient Rights and ResponsibilitiesKathОценок пока нет
- NCP: Gestational HTN - Preeclampsiaeclampsia - Hellp SyndromeДокумент23 страницыNCP: Gestational HTN - Preeclampsiaeclampsia - Hellp SyndromeKath100% (2)
- DIPHTHERIAДокумент47 страницDIPHTHERIAKathОценок пока нет
- Overview HerniaДокумент2 страницыOverview HerniaKathОценок пока нет
- Metro Manila Development Screening TestДокумент4 страницыMetro Manila Development Screening TestKath100% (6)
- Nursing Management/Intervention For Ecclampsia, Preeclampsia, PIH.Документ11 страницNursing Management/Intervention For Ecclampsia, Preeclampsia, PIH.KathОценок пока нет
- Antimycobacterial Drug StudyДокумент5 страницAntimycobacterial Drug StudyKathОценок пока нет
- Harmful Effects of Alcohol BeveragesДокумент3 страницыHarmful Effects of Alcohol BeveragesKathОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plans (NCP) of Abruptio PlacentaДокумент13 страницNursing Care Plans (NCP) of Abruptio PlacentaKath76% (21)
- Summary of MineralsДокумент2 страницыSummary of MineralsKathОценок пока нет
- Summary of Vitamins For NutritionДокумент3 страницыSummary of Vitamins For NutritionKathОценок пока нет
- Harmful Effects of Carbonated DrinksДокумент2 страницыHarmful Effects of Carbonated DrinksKathОценок пока нет
- Hiatal and Diaphragmatic HerniaДокумент7 страницHiatal and Diaphragmatic HerniaKathОценок пока нет
- INGUINAL HERNIA and Umbilical HerniaДокумент13 страницINGUINAL HERNIA and Umbilical HerniaKathОценок пока нет
- Circulatory SystemДокумент15 страницCirculatory SystemKathОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (120)
- Periop Lesson PlanДокумент19 страницPeriop Lesson PlanArchana Yadav92% (13)
- Moses Botchway - Area of PracticeДокумент27 страницMoses Botchway - Area of PracticeOtukwor VivianОценок пока нет
- Writing SOAP Notes NYCCДокумент7 страницWriting SOAP Notes NYCCmassagekevin100% (2)
- Workshop Manual Chassis SUPPLEMENT 3000GT 1996 EuroДокумент38 страницWorkshop Manual Chassis SUPPLEMENT 3000GT 1996 Euromb7050Оценок пока нет
- ADVIA Centaur XP Reference Manual PDFДокумент498 страницADVIA Centaur XP Reference Manual PDFVicky100% (1)
- 2005, Vol.23, Issues 4, Psychocutaneous DiseaseДокумент162 страницы2005, Vol.23, Issues 4, Psychocutaneous DiseaseRizweta DestinОценок пока нет
- Case Study #6: TashaДокумент39 страницCase Study #6: Tashaapi-290174387Оценок пока нет
- Medical ErrorДокумент75 страницMedical ErrorVanessa Sugar Syjongtian SiquianОценок пока нет
- Johns Org-Behaviour 10e PPT Ch15Документ155 страницJohns Org-Behaviour 10e PPT Ch15Arvinder WaliaОценок пока нет
- International Connections Paper 1 - HLTH 1050Документ2 страницыInternational Connections Paper 1 - HLTH 1050api-525321076Оценок пока нет
- AlforqueДокумент2 страницыAlforqueDeen Philip OlegarioОценок пока нет
- Ham A PDFДокумент2 страницыHam A PDFHanum Maftukha100% (1)
- 20 MH 8110 Understandpsychosis - 159384Документ3 страницы20 MH 8110 Understandpsychosis - 159384Grace LОценок пока нет
- Clinical Paperwork For StudentsДокумент16 страницClinical Paperwork For StudentsRyanОценок пока нет
- MDM TableДокумент1 страницаMDM TableTsam Choe100% (1)
- Review of Early Intervention For Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder: Focused On Randomized Controlled TrialsДокумент9 страницReview of Early Intervention For Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder: Focused On Randomized Controlled TrialsCristinaОценок пока нет
- Islamic Psychotherapy - Behavior Disorder - Behavior ModificationДокумент48 страницIslamic Psychotherapy - Behavior Disorder - Behavior ModificationNor Anisa MusaОценок пока нет
- Stoma Care AlginateДокумент6 страницStoma Care AlginateWiwit ClimberОценок пока нет
- International Patient Referral - Part 2 - Revised - 29-04-2010 - 2Документ2 страницыInternational Patient Referral - Part 2 - Revised - 29-04-2010 - 2Fatah AssadОценок пока нет
- VygotskyДокумент15 страницVygotskyNawal AhmedОценок пока нет
- Delayed Sleep Phase SyndromeДокумент3 страницыDelayed Sleep Phase Syndromemamero_xxОценок пока нет
- Clinical Decision Making in The ICU Dysphagia Screening Assesment and TreatmentДокумент18 страницClinical Decision Making in The ICU Dysphagia Screening Assesment and TreatmentΜαρία ΧανιωτάκηОценок пока нет
- Duffy 2005Документ6 страницDuffy 2005Dont KnowОценок пока нет
- Guidelines For The Hospital Management of Child Abuse and NeglectДокумент98 страницGuidelines For The Hospital Management of Child Abuse and NeglectsarahanasОценок пока нет
- A Plant Pathologist or A Student Taking Plant Pathology Is Often Asked by Friends or Associates The Following QuestionsДокумент21 страницаA Plant Pathologist or A Student Taking Plant Pathology Is Often Asked by Friends or Associates The Following QuestionsMirza ZiaaОценок пока нет
- Veterinarian Release FormДокумент1 страницаVeterinarian Release FormcrunchymuncheeОценок пока нет
- Essay Research - Cognitive BiasДокумент18 страницEssay Research - Cognitive BiasMatreyi BhambiОценок пока нет
- Unhcr Medevac ProceduresДокумент32 страницыUnhcr Medevac ProceduresharryОценок пока нет
- Assignment On BDIДокумент15 страницAssignment On BDIsushila napitОценок пока нет
- Endo Logbook FormsДокумент3 страницыEndo Logbook FormsAmethystVonОценок пока нет