Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Chapter 4
Загружено:
Sujit KumarИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chapter 4
Загружено:
Sujit KumarАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chapter 4
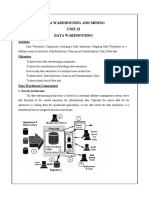
Data and Knowledge Management
1. Recognize the importance of data, the issues involved in managing these data, and the data life cycle. 2. Describe the sources of data and explain how data are collected. 3. Explain the advantages of the database approach. 4. Explain the operation of data warehousing and its role in decision support. 5. Explain data governance and how it helps to produce high-quality data. 6. Define knowledge and describe the different types of knowledge.
Lesson 4 Managing Data Resources
Learning Objectives
To analyse the reasons for organisations having trouble in finding their required information. To understand the benefits of database management system in .improving the organisation of information To learn the various types of database models affecting the way a business can access and use information To know about the requirements of a database environment
4.1 Introduction
Effective use of information depends on how data are stored, organised and accessed in an organisation. Proper delivery of information not only depends upon the capabilities of computer hardware and software but also on the organisations ability to manage data as an important resource. After seeing the unwilling to make the requisite organisational changes. Moving to database environment can be a costly long-term process. In addition to the cost of DBMS Software, related hardware, and data modeling, organizations should anticipate heavy expenditure for integrating, merging and standardizing their data that will populate their database to eliminate inconsistencies, redundancies and errors that typically arise when overlapping data are stored and maintained by different systems and different functional areas. You should understand the managerial and organisational requirements as well as the technologies for managing data as a resource. Organizations need to manage their data assets very carefully to make sure that the data can be easily accessed and managed by the managers and employees across the organisation. First, we describe the typical challenges facing business trying to access information using traditional file management technologies. Then we describe the technology of database management systems, which can overcome many of the drawbacks of traditional file management systems and provide the firm wide integration of information required for digital firm applications.
4.2 Organizing Data in a Traditional File Environment
Information is becoming as important a business resource as money, material, and people. Businesses are realizing the competitive advantage they can gain over their competition through useful information, not just data. Why should you know about organizing data? Because it's almost inevitable that some day you'll be establishing or at least working with a database of some kind. As with anything else, understanding the lingo
11.602 Copy Right: Rai University 65
Chapter 6
Foundations of Business Intelligence: Databases and Information Management
Вам также может понравиться
- Database Approach Organizes Data for Easy AccessДокумент21 страницаDatabase Approach Organizes Data for Easy AccessRodel Novesteras ClausОценок пока нет
- Unit 1Документ9 страницUnit 120ACS45 Jeevan rajОценок пока нет
- Management Information Systems Managing The Digital Firm Canadian 5th Edition Laudon Solutions ManualДокумент36 страницManagement Information Systems Managing The Digital Firm Canadian 5th Edition Laudon Solutions Manualgregoryfinnzvpvga100% (34)
- Management Information Systems Managing The Digital Firm Canadian 5Th Edition Laudon Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFДокумент57 страницManagement Information Systems Managing The Digital Firm Canadian 5Th Edition Laudon Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFelizabethciaraqdcank100% (9)
- Managing Data Resources and Business IntelligenceДокумент2 страницыManaging Data Resources and Business IntelligenceGraciella AudreyОценок пока нет
- Itm Mod 3Документ25 страницItm Mod 3SHARMIKA SINGHОценок пока нет
- Basic of Intelligence BusinessДокумент5 страницBasic of Intelligence BusinessDhivena JeonОценок пока нет
- LESSON 1 Information ManagementДокумент5 страницLESSON 1 Information ManagementvenusdoradoОценок пока нет
- Module 5: Data Management: RequiredДокумент7 страницModule 5: Data Management: RequiredasimОценок пока нет
- CS403 Courtney Paradice Database Systems For Management CCBY Chapter1Документ31 страницаCS403 Courtney Paradice Database Systems For Management CCBY Chapter1Aamir HanifОценок пока нет
- Using A Machine Learning Data Catalog To Reboot Data GovernanceДокумент14 страницUsing A Machine Learning Data Catalog To Reboot Data GovernancerammandoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5: Data Resource Management: Ææñ, Æ Ææ and Ææthese DatabasesДокумент4 страницыChapter 5: Data Resource Management: Ææñ, Æ Ææ and Ææthese DatabasesNaiha AbidОценок пока нет
- Unit 3 NotesДокумент52 страницыUnit 3 NotesShivam PalОценок пока нет
- Info Sys Challenges in Management - Exam Question NotesДокумент7 страницInfo Sys Challenges in Management - Exam Question NotesDionОценок пока нет
- Lesson 04 - Databases and Information Management (Handout 2021)Документ17 страницLesson 04 - Databases and Information Management (Handout 2021)AnuОценок пока нет
- Chapter5-DATA AND KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENTДокумент39 страницChapter5-DATA AND KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENTyoshellyОценок пока нет
- Information System Management Meeting 1Документ35 страницInformation System Management Meeting 1Anggraeni TriОценок пока нет
- Lecture Week: 3 Chapter 3: Database Concepts: Tutorial: Bap 71 AisДокумент7 страницLecture Week: 3 Chapter 3: Database Concepts: Tutorial: Bap 71 AisOdria ArshianaОценок пока нет
- Reporter Group 2 Module6Документ5 страницReporter Group 2 Module6maangela TangcoОценок пока нет
- Organizing Data and InformationДокумент11 страницOrganizing Data and InformationAditya Singh100% (1)
- Book Governanca - Kymberly - ResumoДокумент10 страницBook Governanca - Kymberly - ResumoSabrina Lameiras Germano SilvaОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Is Week 2Документ19 страницFundamentals of Is Week 2vmera23Оценок пока нет
- Contemporary Approach To MISДокумент11 страницContemporary Approach To MISshailendrashakya001Оценок пока нет
- Unit III MisДокумент27 страницUnit III MisTanya MalviyaОценок пока нет
- Information Management: By: Karl Steven A. Maddela InstructorДокумент33 страницыInformation Management: By: Karl Steven A. Maddela InstructorKarl Steven Adalem Maddela100% (4)
- Module-1 BSAIS3B LUMAPAYROSALIEДокумент10 страницModule-1 BSAIS3B LUMAPAYROSALIEAlyssaОценок пока нет
- Mis Chapt5Документ19 страницMis Chapt5Yajie LiОценок пока нет
- Ess8 Im ch05Документ19 страницEss8 Im ch05Sammy Acquah100% (1)
- Mysql Workbench: Database Design. Development. Administration. MigrationДокумент16 страницMysql Workbench: Database Design. Development. Administration. MigrationManuel I. Lantigua DíazОценок пока нет
- List Problems of Traditional File Environment and Explain TWO of ThemДокумент4 страницыList Problems of Traditional File Environment and Explain TWO of ThemHidayahJohariОценок пока нет
- Ringkasan Chapter 3Документ3 страницыRingkasan Chapter 3rismawatyОценок пока нет
- DBMS Study Material-1Документ10 страницDBMS Study Material-1Jayant RanaОценок пока нет
- E-Commerce Note BBA 7th Semester Unit V Business InteligenceДокумент5 страницE-Commerce Note BBA 7th Semester Unit V Business InteligenceSant Kumar YadavОценок пока нет
- Organizing Data and InformationДокумент11 страницOrganizing Data and InformationAditya SinghОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Tutorial SolutionsДокумент8 страницChapter 3 Tutorial SolutionsChand DivneshОценок пока нет
- Unit 01Документ9 страницUnit 01harsh hariharnoОценок пока нет
- Database Management NOTESДокумент15 страницDatabase Management NOTESFouzian PashaОценок пока нет
- Manual Approach: Chapter OneДокумент10 страницManual Approach: Chapter OneBlack PandaОценок пока нет
- ISP500 Topic 3 Data and Knowledge Management - ch5Документ23 страницыISP500 Topic 3 Data and Knowledge Management - ch5Mr. NОценок пока нет
- Implementation of Data WarehouseДокумент11 страницImplementation of Data WarehouseSHITAL SUMANОценок пока нет
- Module 1 Bsais3b GasconalyssamarieДокумент10 страницModule 1 Bsais3b GasconalyssamarieAlyssaОценок пока нет
- Data Management ChallengesДокумент9 страницData Management Challengesdatateam0% (1)
- ISP500 Topic 3 Data and Knowledge Management - ch5Документ23 страницыISP500 Topic 3 Data and Knowledge Management - ch5Stärk 10Оценок пока нет
- Data and Database Administration With Focus On Data QualityДокумент35 страницData and Database Administration With Focus On Data QualityMaria AftabОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 Data Resource ManagementДокумент6 страницChapter 5 Data Resource ManagementAmanda Wijaya100% (1)
- Summary Chapter 6 Foundations of Business Intelligence: Databases and Information ManagementДокумент2 страницыSummary Chapter 6 Foundations of Business Intelligence: Databases and Information ManagementNiswatun Chaira50% (2)
- Data Warehousing AssignmentДокумент9 страницData Warehousing AssignmentRushil Nagwan100% (2)
- Foundations of Business Intelligence: Databases and Data ManagementДокумент21 страницаFoundations of Business Intelligence: Databases and Data ManagementDane ParochaОценок пока нет
- IPM Individual AssignmentДокумент7 страницIPM Individual AssignmentMikealayОценок пока нет
- 12 01 09 10 32 12 1287 Sindhujam PDFДокумент23 страницы12 01 09 10 32 12 1287 Sindhujam PDFPrasad DhanikondaОценок пока нет
- CT 3Документ8 страницCT 3Rahat fahimОценок пока нет
- Unit-3 MISДокумент14 страницUnit-3 MISDivyaОценок пока нет
- IT's Strategic Role in BPR & TQMДокумент18 страницIT's Strategic Role in BPR & TQMalokthakurОценок пока нет
- NC Software Engineering: Database ConceptsДокумент102 страницыNC Software Engineering: Database ConceptsMelusi DemademaОценок пока нет
- DBMS (R20) Unit - 1Документ14 страницDBMS (R20) Unit - 1MOHANKRISHNACHAITANYA KОценок пока нет
- Using Information Technology 10th Edition Williams Solutions ManualДокумент44 страницыUsing Information Technology 10th Edition Williams Solutions Manuallloydkieran71epfi100% (20)
- Lct1 - Introduction To Database&DBMSДокумент20 страницLct1 - Introduction To Database&DBMSJackton BrianОценок пока нет
- The Case for the Chief Data Officer: Recasting the C-Suite to Leverage Your Most Valuable AssetОт EverandThe Case for the Chief Data Officer: Recasting the C-Suite to Leverage Your Most Valuable AssetРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (2)
- Data-Driven Business Strategies: Understanding and Harnessing the Power of Big DataОт EverandData-Driven Business Strategies: Understanding and Harnessing the Power of Big DataОценок пока нет
- Managing Data in Motion: Data Integration Best Practice Techniques and TechnologiesОт EverandManaging Data in Motion: Data Integration Best Practice Techniques and TechnologiesОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4Документ3 страницыChapter 4Sujit KumarОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4Документ3 страницыChapter 4Sujit KumarОценок пока нет
- E-commerce DBMS MS Access Lesson on DSSДокумент1 страницаE-commerce DBMS MS Access Lesson on DSSSujit KumarОценок пока нет
- Communication FinalДокумент31 страницаCommunication FinalSujit KumarОценок пока нет
- Industrial Relations & Labor Laws: BY: Prof. V.P.KAKKARДокумент62 страницыIndustrial Relations & Labor Laws: BY: Prof. V.P.KAKKARNishant KhattwaniОценок пока нет
- BBA SyllabusДокумент1 страницаBBA SyllabusSujit KumarОценок пока нет
- PIBM closed 21 Nov, reopens 22 NovДокумент1 страницаPIBM closed 21 Nov, reopens 22 NovSujit KumarОценок пока нет
- Available BooklistДокумент3 страницыAvailable BooklistSujit KumarОценок пока нет
- Business LawДокумент6 страницBusiness LawSujit KumarОценок пока нет
- Group 2: I Made Niken Novianti Ida Wayan Reddya Baswara Audrey Celestino Aaron AgasДокумент2 страницыGroup 2: I Made Niken Novianti Ida Wayan Reddya Baswara Audrey Celestino Aaron AgasAudrey CeeОценок пока нет
- Serverless Computing: Need, Impact and ChallengesДокумент257 страницServerless Computing: Need, Impact and ChallengesNikita MalikОценок пока нет
- Chapter-11& 12 File SystemДокумент52 страницыChapter-11& 12 File SystemKarthik KaranthОценок пока нет
- Storage Structure and RelationshipsДокумент25 страницStorage Structure and RelationshipswendaОценок пока нет
- What Is NormalizationДокумент2 страницыWhat Is NormalizationAkaylia WilsonОценок пока нет
- BIДокумент18 страницBIshawonОценок пока нет
- Module 4Документ7 страницModule 4Abigail MendezОценок пока нет
- CHP 19Документ63 страницыCHP 19mona yadvОценок пока нет
- The CREATE TABLE Statement Is Used To Create A Table in A DatabaseДокумент17 страницThe CREATE TABLE Statement Is Used To Create A Table in A DatabaseRitu KapurОценок пока нет
- Solution Manual Chemical Process Control George StephanopoulosДокумент3 страницыSolution Manual Chemical Process Control George StephanopoulosSatish KumarОценок пока нет
- Web Browsing - G5 (Edited)Документ25 страницWeb Browsing - G5 (Edited)jonny lêОценок пока нет
- Database System Architecture: Kamran Dahri Lecturer, IICTДокумент13 страницDatabase System Architecture: Kamran Dahri Lecturer, IICTrashidОценок пока нет
- MUHAMMAD SYAFI B. YUSOP Computer Based Information SystemДокумент10 страницMUHAMMAD SYAFI B. YUSOP Computer Based Information SystemMuhd Syafi100% (1)
- Data Vault SeriesДокумент10 страницData Vault SeriesHarish NagappaОценок пока нет
- Relevance Feedback & Query ExpansionДокумент4 страницыRelevance Feedback & Query ExpansionMi YaОценок пока нет
- Art Gallery ReportДокумент45 страницArt Gallery Reportchala pathiОценок пока нет
- Visualizing Data in Oracle Analytics ServerДокумент537 страницVisualizing Data in Oracle Analytics ServerDeivis CampoОценок пока нет
- Difference Between RAM and ROMДокумент2 страницыDifference Between RAM and ROMMaricar Dela Cruz VLOGSОценок пока нет
- ISM ProjectДокумент11 страницISM ProjectJatin SinghОценок пока нет
- The Cassandra Data ModelДокумент4 страницыThe Cassandra Data ModelJorge IvannОценок пока нет
- Select Char (65) : Declare @start Int Set @start 65 While (@start 90) Begin Print Char (@start) Set @start @start+1 ENDДокумент17 страницSelect Char (65) : Declare @start Int Set @start 65 While (@start 90) Begin Print Char (@start) Set @start @start+1 ENDVasu Dev RaoОценок пока нет
- Data Warehousing and Mining Lecture OverviewДокумент12 страницData Warehousing and Mining Lecture OverviewRahul BansalОценок пока нет
- DBДокумент59 страницDBshahbazОценок пока нет
- 2020 Ryu JMedInternetResДокумент9 страниц2020 Ryu JMedInternetResEAPОценок пока нет
- Course 20339-1A - Planning and Administering SharePoint 2016Документ8 страницCourse 20339-1A - Planning and Administering SharePoint 2016Ashish Kolambkar0% (1)
- Ms-Access NotesДокумент28 страницMs-Access NotesMbugua MainaОценок пока нет
- George Lahovari - Marele Dictionar Geografic Al Romaniei - Vol 3 PDFДокумент777 страницGeorge Lahovari - Marele Dictionar Geografic Al Romaniei - Vol 3 PDFRoxana Aldea-CiaciruОценок пока нет
- Mineshbhai To Know MeДокумент13 страницMineshbhai To Know MeMinesh ChunaraОценок пока нет
- Cultura InglesaДокумент12 страницCultura InglesaSinai SanchezОценок пока нет
- Class Comparison Methods in Data Mining - JavatpointДокумент3 страницыClass Comparison Methods in Data Mining - JavatpointRavindra Kumar PrajapatiОценок пока нет