Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Brain Tumor Types
Загружено:
husravИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Brain Tumor Types
Загружено:
husravАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Brain Tumor Types (http://www.braintumor.
org/patients-family-friends/about-brain-tumors/tumor-types/)
There are more than 120 types of brain tumors. Today, most medical institutions use the World Health Organization (WHO) classification system to identify brain tumors. The WHO classifies brain tumors by cell origin and how the cells behave, from the least aggressive (benign) to the most aggressive (malignant). Some tumor types are assigned a grade, ranging from Grade I (least malignant) to Grade IV (most malignant), which signifies the rate of growth. There are variations in grading systems, depending on the tumor type. The classification and grade of an individual tumor help predict its likely behavior. This section describes the most frequently diagnosed types. Click on the links below for more information on specific tumor types.
Acoustic Neuroma Astrocytoma:
o o o o
Grade I - Pilocytic Astrocytoma Grade II - Low-grade Astrocytoma Grade III - Anaplastic Astrocytoma Grade IV - Glioblastoma (GBM)
Chordoma CNS Lymphoma Craniopharyngioma Other Gliomas:
o o o o o
Brain Stem Glioma Ependymoma Mixed Glioma Optic Nerve Glioma Subependymoma
Medulloblastoma Meningioma Metastatic Brain Tumors Oligodendroglioma Pituitary Tumors Primitive Neuroectodermal (PNET) Other Brain-Related Conditions Schwannoma
The following tumor types are more common in children than in adults:
Brain Stem Glioma Craniopharyngioma Ependymoma Juvenile Pilocytic Astrocytoma (JPA) Medulloblastoma Optic Nerve Glioma Pineal Tumor Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumors (PNET) Rhabdoid Tumor
Keep in mind that many tumors have different subtypes; for example, an astrocytoma can be a juvenile pilocytic astrocytoma, an anaplastic astrocytoma or a glioblastoma. In addition, the same tumors sometimes have different names; even pathologists are not always consistent in what they call them. Finally, it is important to note that nonmalignant, or benign, brain tumors can be just as difficult to treat as malignant brain tumors.
Brain Tumor Types (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brain_tumor)
Tumors can be benign or malignant, can occur in different parts of the brain, and may or may not be primary tumors. A primary tumor is one that has started in the brain, as opposed to a metastatictumor, [4] which is something that has spread to the brain from another part of the body. Tumors may or may not be symptomatic: some tumors are discovered because the patient has symptoms, others show up incidentally on an imaging scan, or at an autopsy. The most common primary brain tumors are: Gliomas (50.3%) Meningiomas (20.9%) Pituitary adenomas (15%) Nerve sheath tumors (8%)
[5]
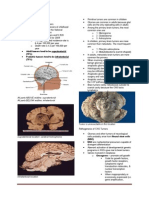
(World Health Organization grading system)
Grade I tumor
Benign = non-cancerous Slow growing Cells look almost normal under a microscope Usually associated with long-term survival Rare in adults
Grade II tumor
Relatively slow growing Sometimes spreads to nearby normal tissue and comes back (recurs) Cells look slightly abnormal under a microscope Sometimes comes back as a higher grade tumor
Grade III tumor
Malignant = cancerous Actively reproduces abnormal cells Tumor spreads into nearby normal parts of the brain Cells look abnormal under a microscope Tends to come back, often as a higher grade tumor
Grade IV tumor
Most malignant Grows fast Easily spreads into nearby normal parts of the brain Actively reproduces abnormal cells Cells look very abnormal under a microscope Tumor forms new blood vessels to maintain rapid growth Tumors have areas of dead cells in their center (called necrosis)
Вам также может понравиться
- Label KuningДокумент2 405 страницLabel KuningAll Malik Ha100% (4)
- Brain CancerДокумент24 страницыBrain CancerJohn Lester FernandezОценок пока нет
- Skeletal and Skin TractionДокумент38 страницSkeletal and Skin TractionCORROS JASMIN MARIEОценок пока нет
- Johann On Cancer - Instruction Manual - Healing Cancer With RifeДокумент17 страницJohann On Cancer - Instruction Manual - Healing Cancer With RifeThomas PhoenixОценок пока нет
- Brain CancerДокумент33 страницыBrain Cancermynoidanh19Оценок пока нет
- Brain Cancer (Tumors) : Jinu Janet Varghese Group: 4 Year: 5 Tbilisi State Medical UniversityДокумент35 страницBrain Cancer (Tumors) : Jinu Janet Varghese Group: 4 Year: 5 Tbilisi State Medical UniversityPPDSNeuroUnsri RSMHОценок пока нет
- Brain CancerДокумент29 страницBrain CancerMaria VisitacionОценок пока нет
- Diagnostic Imaging - Abdomen PDFДокумент1 017 страницDiagnostic Imaging - Abdomen PDFLucian Vintila67% (3)
- Brain TumorДокумент30 страницBrain TumorRushdaОценок пока нет
- Brain TumorsДокумент78 страницBrain Tumorsnarswiponshistoryan100% (3)
- The Radiology Assistant Brain Tumor - Systematic Approach PDFДокумент29 страницThe Radiology Assistant Brain Tumor - Systematic Approach PDFMichael DeanОценок пока нет
- Iscador EBM91 PDFДокумент208 страницIscador EBM91 PDFJose CaceresОценок пока нет
- Brain TumorsДокумент19 страницBrain TumorsNavjot BrarОценок пока нет
- Exploring Medical Language 10th Brooks Test BankДокумент16 страницExploring Medical Language 10th Brooks Test BankRaadqqqОценок пока нет
- Lung CancerДокумент25 страницLung CancerCarla Mae Guillermo NavarroОценок пока нет
- NCM 104 Cellular Aberration Lecture 2007Документ104 страницыNCM 104 Cellular Aberration Lecture 2007Kris TejereroОценок пока нет
- Living with a Brain Tumor: Dr. Peter Black's Guide to Taking Control of Your TreatmentОт EverandLiving with a Brain Tumor: Dr. Peter Black's Guide to Taking Control of Your TreatmentРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- Klasifikasi Tumor OtakДокумент81 страницаKlasifikasi Tumor Otaknovy rosalia chandraОценок пока нет
- Brain Cancer ReportДокумент5 страницBrain Cancer ReportCrisantaCasliОценок пока нет
- LP Brain TumorДокумент20 страницLP Brain TumorMuhammad PanduОценок пока нет
- BRAIN TUMOR-Online Learning 1Документ11 страницBRAIN TUMOR-Online Learning 1エルミタ ジョイ ファティマОценок пока нет
- Brain TumorДокумент7 страницBrain TumorPintu Kumar100% (1)
- Brain TumorsДокумент34 страницыBrain TumorsbenedictusОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology: Gliomas Meningiomas Pituitary Adenomas Acoustic NeuromasДокумент7 страницPathophysiology: Gliomas Meningiomas Pituitary Adenomas Acoustic NeuromasWira Febrisandi IrsanОценок пока нет
- Brain Tumors - Classifications, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentsДокумент10 страницBrain Tumors - Classifications, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentsshamimОценок пока нет
- Brain CancerДокумент3 страницыBrain CancerSamuel CamoronganОценок пока нет
- Brain CancerДокумент74 страницыBrain CancerDan EvanzОценок пока нет
- TUMOURS IN PAED-WPS OfficeДокумент6 страницTUMOURS IN PAED-WPS OfficePraise ToluwalaseОценок пока нет
- CNS Tumor Classification (Full)Документ21 страницаCNS Tumor Classification (Full)borstОценок пока нет
- Brain TumorДокумент9 страницBrain TumorSara SabirОценок пока нет
- Seminar On Brain TumorДокумент26 страницSeminar On Brain TumorawasthiphothocopyОценок пока нет
- AstrositomaДокумент29 страницAstrositomaFitria NurulfathОценок пока нет
- Brain TumorsДокумент30 страницBrain TumorsDagmawi BahiruОценок пока нет
- Brain Tumor FactsДокумент1 страницаBrain Tumor FactsfranОценок пока нет
- Risk Factors: Brain TumorДокумент49 страницRisk Factors: Brain Tumoryan04Оценок пока нет
- Artikel Tumor Otak (Bahasa Inggris)Документ13 страницArtikel Tumor Otak (Bahasa Inggris)Lindan NagaОценок пока нет
- CNS Tumors: Adult Tumors Tend To Be Supratentorial (70%) Pediatric Tumors Tend To Be Infratentorial (70%)Документ8 страницCNS Tumors: Adult Tumors Tend To Be Supratentorial (70%) Pediatric Tumors Tend To Be Infratentorial (70%)Jessica Febrina WuisanОценок пока нет
- CNS Lymphoma: Background of The Case Definition of The Case: Brain MassДокумент1 страницаCNS Lymphoma: Background of The Case Definition of The Case: Brain MassMercicae AОценок пока нет
- Braiin CancerДокумент6 страницBraiin CancerTia RamadhanyОценок пока нет
- AstrocytomaДокумент3 страницыAstrocytomaShamae PatalinjugОценок пока нет
- L 4 - Brain TumorsДокумент117 страницL 4 - Brain TumorsDiana PopoviciОценок пока нет
- Primary Tumors of The Central Nervous System, and The Major Factors That Influence Patient Outcomes.Документ4 страницыPrimary Tumors of The Central Nervous System, and The Major Factors That Influence Patient Outcomes.bobo lenneОценок пока нет
- Anaplastic AstrocytomaДокумент9 страницAnaplastic AstrocytomaputsaputraОценок пока нет
- Brain Tumor ICP Head and Neck CA TracheostomyДокумент11 страницBrain Tumor ICP Head and Neck CA TracheostomyWincy Faith SalazarОценок пока нет
- Al Waqi'Ah Aks WWW - Alkalam.pkДокумент20 страницAl Waqi'Ah Aks WWW - Alkalam.pkSyeda Sakina NaqviОценок пока нет
- Doctors CallДокумент1 страницаDoctors CallNGUYỄN THỊ THIОценок пока нет
- Brain Tumors: What You Need To Know AboutДокумент51 страницаBrain Tumors: What You Need To Know AboutIndahОценок пока нет
- Brain Tumor-1Документ56 страницBrain Tumor-1Sadab AlamОценок пока нет
- 2017 - Paul Tahalele - Brain TumourДокумент49 страниц2017 - Paul Tahalele - Brain TumourVincentius Michael WilliantoОценок пока нет
- Glioblastoma BrochureДокумент24 страницыGlioblastoma Brochuresdifghweiu wigufОценок пока нет
- Brain Tumor (Group B)Документ29 страницBrain Tumor (Group B)Srush AliОценок пока нет
- Astrocytic Tumours: Related ArticlesДокумент6 страницAstrocytic Tumours: Related Articlesroni pahleviОценок пока нет
- Astrocytoma: Insights Into Risk Factors, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and ManagementДокумент4 страницыAstrocytoma: Insights Into Risk Factors, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and ManagementIndah Nevhita LОценок пока нет
- Tumor OtakДокумент17 страницTumor Otakmona030988Оценок пока нет
- Brain Tumors: Primary BTДокумент5 страницBrain Tumors: Primary BTMohamed Al-zichrawyОценок пока нет
- In Braunds Clinical Neurology in Small Animals LoДокумент24 страницыIn Braunds Clinical Neurology in Small Animals LoNxyz GxyzОценок пока нет
- Anaplastic Astrocytoma - Know The Brain Cancer SystemsДокумент3 страницыAnaplastic Astrocytoma - Know The Brain Cancer Systemsluna_AlmeyerОценок пока нет
- Brain TumorsДокумент1 страницаBrain Tumorskaplan abateОценок пока нет
- Brain Cancer: by Cara KlingamanДокумент16 страницBrain Cancer: by Cara Klingamanrenu_gang1552Оценок пока нет
- Lymphoblastic Leukemia: This MRI Shows A Juvenile Pilocytic Astrocytoma of The CerebellumДокумент1 страницаLymphoblastic Leukemia: This MRI Shows A Juvenile Pilocytic Astrocytoma of The CerebellumMohammadAwitОценок пока нет
- Symptoms of A Brain TumourДокумент5 страницSymptoms of A Brain TumournandaОценок пока нет
- Brain Tumors: Special Characters For Research and Banking: Review ArticleДокумент9 страницBrain Tumors: Special Characters For Research and Banking: Review Articledmandatari7327Оценок пока нет
- Neuropathology: Dr. Siddaganga S MДокумент29 страницNeuropathology: Dr. Siddaganga S Msiddaganga sigiОценок пока нет
- Group 5 - Brain CancerДокумент32 страницыGroup 5 - Brain CancerShiangОценок пока нет
- Sol IntracranialДокумент76 страницSol IntracranialPanduRespatiОценок пока нет
- IBM System x3500 M4: IBM Redbooks Product GuideДокумент54 страницыIBM System x3500 M4: IBM Redbooks Product GuidehusravОценок пока нет
- Com536 MV ReportДокумент10 страницCom536 MV ReporthusravОценок пока нет
- Com528 Pic ReportДокумент37 страницCom528 Pic Reporthusrav100% (1)
- Presentation TopicsДокумент1 страницаPresentation TopicshusravОценок пока нет
- Bone: Cystic & Neoplastic LesionsДокумент83 страницыBone: Cystic & Neoplastic LesionsPuspita PrihatiniОценок пока нет
- Medical-Surgical Nursing Assessment and Management of Clinical Problems 9e Chapter 16Документ15 страницMedical-Surgical Nursing Assessment and Management of Clinical Problems 9e Chapter 16sarasjunk100% (1)
- NCP Cervical Final)Документ4 страницыNCP Cervical Final)Theresa Abrillo83% (6)
- Brain TumorДокумент9 страницBrain TumorSara SabirОценок пока нет
- Malignant Myopericytoma: Report of A New Case and Review of The LiteratureДокумент6 страницMalignant Myopericytoma: Report of A New Case and Review of The LiteratureRachel AutranОценок пока нет
- 36 Critical Illnesses in MalaysiaДокумент1 страница36 Critical Illnesses in Malaysiawan_andyОценок пока нет
- Benign Liver Tumors: HemangiomaДокумент6 страницBenign Liver Tumors: HemangiomaEnricoSetiawanОценок пока нет
- 01 Cancer NoteДокумент4 страницы01 Cancer NoteDerrick liОценок пока нет
- Exam 4Документ10 страницExam 4pauchanmnlОценок пока нет
- Oralpatho SEQДокумент16 страницOralpatho SEQKhushboo e ZehraОценок пока нет
- MEN1 PPДокумент15 страницMEN1 PPAaron D. PhoenixОценок пока нет
- Brain Tumor New 1Документ6 страницBrain Tumor New 1Tiiffanyy Faiith PadillaОценок пока нет
- DataДокумент207 страницDatamikhael muaneoОценок пока нет
- Prostate Cancer Treatment in India Detailed InformationДокумент3 страницыProstate Cancer Treatment in India Detailed InformationinadorОценок пока нет
- Septic Arthritis: Briones, Hershey C. BSN - IiiДокумент8 страницSeptic Arthritis: Briones, Hershey C. BSN - IiiHershey Cordero BrionesОценок пока нет
- Chapter 16 Reducing Your Cancer Risk Study GuideДокумент3 страницыChapter 16 Reducing Your Cancer Risk Study GuideMichael Smith IIОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 Tissues Glands and MembranesДокумент84 страницыChapter 4 Tissues Glands and MembranesSofia MorenoОценок пока нет
- The Selfish Cell - An Evolutionary Defeat Springer 2008)Документ97 страницThe Selfish Cell - An Evolutionary Defeat Springer 2008)Pablo HenrriquezОценок пока нет
- About Thyroid Cancer: Overview and TypesДокумент12 страницAbout Thyroid Cancer: Overview and Typesumaima rizwanОценок пока нет
- A Rare Case of Colon Cancer in A Young Patient: A Case Report and Literature ReviewДокумент5 страницA Rare Case of Colon Cancer in A Young Patient: A Case Report and Literature ReviewIJAR JOURNALОценок пока нет
- LiposarcomaДокумент9 страницLiposarcomaFano Fahad TaihuttuОценок пока нет
- Benign Lung TumorДокумент16 страницBenign Lung TumorAbdul Mubdi ArdiansarОценок пока нет