Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Length Units of Work
Загружено:
Shabnam SulimanИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Length Units of Work
Загружено:
Shabnam SulimanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Length Units of Work
Length is a one-dimensional concept related to the geometric concepts of direction and line. Put more simply length is usually thought of as the extent of line. Length measures need to be investigated in the many practical situations in which they occur, for example, as length, width, depth, height, thickness or closeness of objects. Most initial experiences relate to straight lines, but distances along curves or around plane shapes are also relevant. See the links in the "Learning Sequence" column for more detail on the steps in the sequence. Learning Sequence Identifying the attribute Comparing and ordering Exemplar Link Exemplar Link Non-standard units Exemplar Link Level 1 Measurement AO1 compare a group of objects by length measure length with non-standard units use measuring language to compare length, width, and height demonstrate a personal benchmark for 1 metre, 1/2 metre identify and use external benchmarks to carry out practical measuring tasks discuss the need for having and using standard measures of length make sensible estimates about the lengths of given objects recognise the need for a standard unit of length recognise a metre length estimate and measure to the nearest metre carry out practical measuring tasks using appropriate metric units. make measurement estimates using appropriate metric units pose measurement questions recognise the need for a standard unit of length recognise a centimetre length estimate and measure to the nearest centimetre estimate using metres amd centimetres measure to the nearest metre and centimetre Teddy Bears and Friends Taller, Wider, Longer Making Benchmarks Curriculum Achievement Objectives Level 1 Measurement AO1 Specific Learning Outcomes The students will be able to: Compare lengths from the same starting point Use materials to make a long or short construction Use materials to compare large and small areas compare the length of two objects select objects which are about the same length as a given object order three or more objects by length Units of Work Worms and more
Level 1 Measurement AO1
Time capsule Gingerbread Man
Standard units Exemplar Link Link to Learning Objects Level 2 Link to Learning Objects Level 3
Level 2 Measurement AO1
Level 2 Measurement AO1
Pirate Plays
Level 2 Measurement AO1
Make a measurement trail
Level 2 Measurement AO1
All About Me
Level 2 Measurement AO1 Level 2 Measurement AO2 Level 2 Measurement AO1 Level 2 Measurement AO2
Paper Planes L2
find objects that they estimate to be a 1cm, 10cm, 50cm and one metre long measure lengths of approximately one metre to the nearest cm
Scavenger Hunt
Area Units of Work
Area is a two-dimensional concept related to the geometric concept of an enclosed region. It is defined in the maths curriculum as the size of a surface expressed as a number of square units. Investigations of the size of an area should begin with comparisons between different surfaces and progress to the use of non-standard, and then standard, units. The use of formulae to calculate the areas of common polygons is the final stage of the learning sequence. Learning Sequence Identifying the attribute Curriculum Achievement Objectives Level 1 Measurement AO1 Specific Learning Outcomes The students will be able to: compare lengths from the same starting point use materials to make a long or short construction use materials to compare large and small areas directly compare the area of 2 objects by superimposing cover a shape with smaller shapes cover a shape with non-standard area units and count the number used compare and order areas of shapes using nonstandard area units recognise the need for a standard unit of area measure surfaces using square centimetres estimate the measure of surfaces using square centimetres Units of Work Worms and more
Comparing and ordering Non-standard units
Level 1 Measurement AO1 Level 1 Measurement AO1
Prints and Outlines Great cover up
Standard units Link to Learning Objects Level 2 Link to Learning Objects Level 3
Level 2 Measurement AO1
Outlining area
Volume and Capacity Units of Work
Volume is the measure of space taken up by a three-dimensional object. The space within a container is known as its capacity but as the thickness of many containers is negligible, it has become acceptable to refer to the space inside as volume too. (The terms volume and capacity are used interchangeably throughout the measurement strand of the NZ curriculum document although the glossary defines capacity as the interior volume of an object.) Two different practical situations need to be experienced by students as they learn about volume. One relates to experiences involving "how much space does a three-dimensional object occupy?" which eventually leads to measures of volume derived from measuring the length of the objects dimensions. The other set of experiences relates to measures of fluids. Learning Sequence Identifying the attribute Curriculum Achievement Objectives Level 1 Measurement AO1 Specific Learning Outcomes The students will be able to: push, pull, lift and handle objects in order to become aware of mass compares 2 masses by pushing and lifting pack materials and fill containers pour liquids from and into containers compare the volume of two containers by packing or pouring order the volume of three or more containers by packing or pouring recognise that two matched amounts of liquid remain the same when one amount is poured into a container of a different shape. use non-standard volume units (cups, spoons, bottles) to fill a container and count the number used build with blocks and count the number of blocks used compare and order volumes of containers using non-standard volume units use non standard units to measure the volume of a container accurately count a set of up to 20 objects Units of Work
Tricky Bags
Comparing and ordering Level 1 Measurement AO1
Three Bears
Non-standard units
Level 1 Measurement AO1
Spoonfuls, Cupfuls and Handfuls
Level 1 Measurement AO1
Level 1 Number knowledge AO1
Dino Cylinders
Level 1 Measurement develop an understanding of 100 and the quantity for which it stands AO1 understand the relationship between 100 and 10
Level 1 Number knowledge AO1 Standard units Link to Learning Objects Level 2 Link to Learning Objects Level 3 Level 2 Measurement AO1 use non-standard volume units (cups, spoons, bowls) to fill a container and count the number used recognise the need for a standard unit of volume measure to the nearest litre and half litre by using litre containers to fill and count accurately measure volume using standard kitchen measuring cups
Counting on Measurement
Popcorn
Level 2 Measurement AO1
How Much Cereal? Party Volumes
Level 2 Measurement estimate volume using litres and millilitres accurately measure volume using litres and millilitres AO1
Level 2 Measurement
AO2 Level 2 Measurement AO1 use objects of 1 litre volume to estimate the volume of other objects discuss the need for having and using standard measures of volume make sensible estimates about the volume of given objects carry out conversions between basic standard measures of volume (millilitres to litres) explain the meaning of metric prefix terminology (e.g kilo) Making Benchmarks
Mass Units of Work
The mass of an object is a measure of the amount of matter in it. Weight is the force that gravity exerts on an object and so can vary from place to place. The terms mass and weight are used loosely, and inaccurately, in everyday speech to mean the same thing. The NZ curriculum document reflects the correct use of the terminology and uses the term mass not weight. Learning Sequence Curriculum Achievement Objectives Level 1 Measurement AO1 Specific Learning Outcomes The students will be able to: push, pull, lift and handle objects in order to become aware of mass compares 2 masses by pushing and lifting pack materials and fill containers pour liquids from and into containers compare a 2 objects by weight order 3 or more objects by weight describe the weight of objects using comparative language, for example, heavier, lighter compare a group of 3 or more objects by mass measure mass with non-standard units Units of Work
Identifying the Attribute
Tricky Bags
Comparing and Ordering Level 1 Measurement AO1
Seesaws
Non-standard units
Level 1 Measurement AO1 Level 1 Number strategies AO1 Level 1 Number knowledge AO2
Measuring beads
Standard Units Link to Learning Objects Level 2 Link to Learning Objects Level 3
Level 2 Measurement AO1 Level 2 Measurement AO1
estimate weight in kilograms and grams measure accurately using kilograms and grams recognise a 100 gram mass record measurements in kg and g using decimal notation accurately measure specific amounts of materials use objects of 1kg mass to estimate the mass of other objects discuss the need for having and using standard measures of mass make sensible estimates about the mass of given objects explain the meaning of metric prefix terminology (e.g kilo)
Weighing Stations Great Grams
Level 2 Measurement
AO1 Level 2 Measurement AO2
Making benchmarks mass
Angle Units of Work Angle is the measure of turn. An understanding of angle begins with students exploring turning left and right, clockwise and anticlockwise. Students move on to measure angles and construct angles and shapes using protractors. Learning Sequence Curriculum Achievement Objectives Specific Learning Outcomes The students will be able to: Units of Work
Identifying the attribute Comparing and ordering
Level 1 Measurement AO1
show a quarter turn and a half turn in a number of situations see that to quarter turns equals on half turn recognise the corner of a shape that is equivalent to a quarter turn
Turns
Level 1 Position Link to Learning and orientation Objects Level 2 AO1 Level 2 Measurement AO1
understand clockwise and anticlockwise Clockwise directions understand that quarter half turns may be begun from any direction and not just from lines parallel to the classroom walls or other fixed lines estimate and measure angles using other angles Angles
Non-standard units
Level 2 Measurement AO1
Temperature Units of Work
Temperature is the measure of how hot or cold things are. Students can perceive large differences in temperature and are exposed everyday to wide ranges in the temperature of objects, for example, cold drinks and hot showers. However our perception of temperature is affected by an immediately prior experience, for example the bedroom feels "freezing" if you have been seated in front of a fire. Important applications include temperature; cooking; planning picnics. Learning Sequence Identifying the attribute Comparing and Ordering Non-Standard Units Standard Units Level 3 Measurement AO1 Curriculum Achievement Objectives Level 1 Measurement AO1 Specific Learning Outcomes The students will be able to: describe objects as hot or cold describe the day as hot or cold compare the temperature of two objects order a group of 2 or more objects by temperature Not applicable for temperature recognise the need for a standard unit of temperature measure temperature (degrees Celcius) with a thermometer calculate changes in temperatures use thermometers to measure temperature in degrees Celsius investigate factors that influence temperatures Weather dot com Units of Work I'm Freezing
Applying and Interpreting
Level 4 Measurement AO1
Level 4 Measurement AO4
Cool times with heat
Stage One: Identifying the Attribute
Early temperature experiences must develop an awareness of what temperature is, and of the range of words that can be used to discuss temperature. The use of words such as hot, cold, warm and freezing, focuses attention on the attribute of temperature. Students need to experience a variety of temperatures by touching warm and cold objects. They can also observe the effects of heating and cooling objects. Discussing the daily temperature and the variation that can occur within a day extends students awareness of temperature. A daily weather chart where the students record their observations about the weather is a useful activity.
Stage Two: Comparing and Ordering
Comparing the temperatures of objects is the second stage in developing an understanding of temperature. Students can begin by touching two objects and determining which is warmer. They can then move to comparing and ordering three or more objects. Students need also to experience the impact that heat has on an object. For example, butter melts when it is heated and ice-cream melts when it is taken out of the freezer. In addition to ordering objects that they can touch, students need to discuss and observe features of hotter and colder days. They can then order pictures or photographs of hot and cold climates
Time Units of Work
Time is a measure but it is a different from the other measures in that it cannot be seen or touched. However, we are surrounded by the effect of time passing, for example, day to night and one season to another. There are two aspects of time students must develop:
time as an instant which can be named, for example, 6:15; time as a duration which describes an amount of time that has passed, for example, a minute, the afternoon, the year. Learning Sequence Curriculum Achievement Objectives Level 1 Measurement AO1 Specific Learning Outcomes The students will be able to: sequence events within a day describe a duration as long or short name and order the days of the week directly compares the duration of two events uses non-standard units to compare the duration of two or more events tell time to the hour and half hour using analogue clocks recognise the length of a minute recognise the length of a second tell time after the hour by counting minutes tell time to the hour and half hour using analogue clocks tell time to the hour and half hour using digital clocks solve time problems involving hours and half hours estimate the time taken for daily activities in hours and minutes use advanced counting or partitioning strategies to solve problems involving minutes and hours check the reasonableness of answers obtained using a calculator measure time in periods of up to 15 minutes compare non standard and standard measurements for time Units of Work
Identifying the attribute
Passing time
Comparing and Ordering Non-standard units Standard units Link to Learning Objects Level 2 Link to Learning Objects Level 3
Level 1 Measurement AO1
How long now
Level 2 Measurement AO1
Just a minute
Level 2 Measurement AO1
Clock wise
Level 2 Measurement AO1 Level 2 Number strategies AO1
How Long Does it Take?
Level 2 Measurement AO1
Calibrating Clocks
Вам также может понравиться
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Cold Bending FdatДокумент1 страницаCold Bending FdatAnonymous AdofXEYAgE100% (1)
- Math CurДокумент46 страницMath CurAA MMОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 5 - SolutionsДокумент22 страницыTutorial 5 - SolutionsjunedrkaziОценок пока нет
- U4 TestДокумент5 страницU4 Test1jerushaОценок пока нет
- Worksheet TRGO NB8 Without AnswersДокумент2 страницыWorksheet TRGO NB8 Without AnswersathulОценок пока нет
- Method of ReiterationДокумент2 страницыMethod of ReiterationParamveer Sharma100% (2)
- Traverse SurveyДокумент33 страницыTraverse SurveyAtikah Nasrudin95% (44)
- 6 Uniform Circular MotionДокумент83 страницы6 Uniform Circular MotionRamachandranPerumal0% (1)
- (Mai 3.5) Arcs and SectorsДокумент16 страниц(Mai 3.5) Arcs and SectorsJuhi KastiyaОценок пока нет
- Quarter 2 Week 2Документ10 страницQuarter 2 Week 2Estela Joy A. SolОценок пока нет
- Flashcards Quantitative Aptitude Revision Maths ShortcutsДокумент108 страницFlashcards Quantitative Aptitude Revision Maths Shortcutskvdheerajkumar100% (1)
- Aim: What Are Cofunctions?: Do NowДокумент5 страницAim: What Are Cofunctions?: Do NowbwlomasОценок пока нет
- List of Class 11 Trigonometry FormulasДокумент2 страницыList of Class 11 Trigonometry FormulasRohit Kumar SharmaОценок пока нет
- Lesson 1.1 E: XercisesДокумент21 страницаLesson 1.1 E: XercisesBob JohnsonОценок пока нет
- Elements of Plane TrigonometryДокумент275 страницElements of Plane TrigonometryMannyОценок пока нет
- Mathematics 6 Quarter 4 Week 4: NAME: - GRADE & SECTIONДокумент9 страницMathematics 6 Quarter 4 Week 4: NAME: - GRADE & SECTIONUnavailable ThingsОценок пока нет
- Self Study Materials For Pre Sea Deck Rev0.16 PDFДокумент302 страницыSelf Study Materials For Pre Sea Deck Rev0.16 PDFNiña Antonette Lorenzo100% (1)
- AC Fundamentals (PART 2)Документ29 страницAC Fundamentals (PART 2)Fasih Ul HaqОценок пока нет
- GeometryДокумент37 страницGeometryKasie SobremisanaОценок пока нет
- 3 - Trigonometric FunctionsДокумент26 страниц3 - Trigonometric FunctionsZamanoden D. UndaОценок пока нет
- ES8 Exp 1 - Inclined Plane - 1012Документ6 страницES8 Exp 1 - Inclined Plane - 1012Nicholas klassОценок пока нет
- CulvertДокумент5 страницCulvertFauzankalibata100% (1)
- A11 Trigonometrical GraphsДокумент3 страницыA11 Trigonometrical GraphsVarshLokОценок пока нет
- GE MMW ShortДокумент6 страницGE MMW Shortrhizelle19100% (2)
- 3D Geometry Lines SolutionsДокумент9 страниц3D Geometry Lines Solutionskcani7129Оценок пока нет
- ASNA2041Документ18 страницASNA2041BorjaОценок пока нет
- Flipgrid Lesson Plan - GibbsДокумент2 страницыFlipgrid Lesson Plan - Gibbsapi-596273912Оценок пока нет
- 2) Cyclic QuadrilateralДокумент11 страниц2) Cyclic QuadrilateralRedzuan SaidiОценок пока нет
- Cree Dictionary of Mathematical Terms With Visual Examples 1695333093Документ72 страницыCree Dictionary of Mathematical Terms With Visual Examples 1695333093api-704912609Оценок пока нет
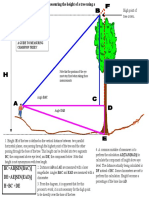
- Tree Measuring GuideДокумент7 страницTree Measuring GuideAlinaADОценок пока нет