Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
LRFD Design Spreadsheet
Загружено:
wgao2010Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
LRFD Design Spreadsheet
Загружено:
wgao2010Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Tensile Rupture (Sections D2 & J4.
1b)
Pn = AeFu = AnUFu
Fu = Ag = tpl = # members db = Connecting Element? Net Area Determination
58ksi 4.5in2 0.5in 1 0.75in N (Y or N)
failure path #1 s (in) 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 g (in) 1.500 3.000 3.000 1.500 s2/4g 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 Total width (in) 1.500 3.000 3.000 1.500 -0.875 -0.875 0.000 tpl (in) 0.500 0.500 0.500 0.500 0.500 0.500 0.500 Area (in2) 0.750 1.500 1.500 0.750 -0.438 -0.438 0.000 3.625
width segment 1 width segment 2 width segment 3 width segment 4 hole 1 hole 2 hole 3 Net Area failure path #2
width segment 1 width segment 2 width segment 3 width segment 4 hole 1 hole 2 hole 3 Net Area 0.85Ag = Controlling An = U= Ae = Pn = Determine Capacity LRFD t= 0.75 3.825in2
s (in) 0.000 3.000 3.000 0.000
g (in) 1.500 3.000 3.000 1.500
s2/4g 0.000 0.750 0.750 0.000
Total width (in) 1.500 3.750 3.750 1.500 -0.875 -0.875 -0.875
tpl (in) 0.500 0.500 0.500 0.500 0.500 0.500 0.500
Area (in2) 0.750 1.875 1.875 0.750 -0.438 -0.438 -0.438 3.938
3.625in2 1.000 3.625in2 210.3kips
ASD t = 2
t Pn = CLF Ps,eq = Check Capacity LRFD t= t Pn = Pu Pu/ tPn =
158kips 1.40 112.6kips
Pn / t = CLF Ps,eq =
105kips 0.90 116.8kips
ASD 0.75 158kips 50.00kips 31.7%kips Okay t = Pn / t = Pa Pa / (Pn / t ) = 2 105kips 35.00kips 33.3%kips Okay
Tensile Yielding (Sections D2 & J4.1a) Ag Fy = Pn = 2in2 50ksi 100kips
Pn = AgFy
IF you need to determine capacity: LRFD t= t Pn = CLF Ps,eq = 0.9 90kips 1.40 64.3kips
ASD t = Pn / t = CLF Ps,eq = 1.67 60kips 0.90 66.5kips
IF you need to check capacity: LRFD t= t Pn = Pu Pu/ tPn = 0.9 90kips 50.00kips 55.6%kips Okay
ASD t = Pn / t = Pa Pa / (Pn / t ) = 1.67 60kips 35.00kips 58.5%kips Okay
Bolt Bearing (J3.10) deformation at bolt hole IS a design consideration: Rn = min[1.2LctFu, 2.4dtFu] deformation at bolt hole IS NOT a design consideration: Rn = min[1.5LctFu, 3.0dtFu] long slotted holes perpendicular to force: Rn = min[1.0LctFu, 2.0dtFu] Deformation at the bolt hole is not a design consideration Use Equation J3-6b tpl = db = 0.5in 0.75in End dist Lc = 1.5in 1.0625in
Fu =
65ksi
num bolts
12bolts/connection Use (k) 621.6
Tear Bearing Use Out Deformation (k/bolt) (k/bolt) (k/bolt) Fu factor Rn Controlling Rn = IF you need to determine capacity: LRFD t= t Pn = CLF Ps,eq = 0.75 466kips 1.40 333.0kips 1.5 51.8 621.6k 3.0 73.1 51.8
ASD t = Pn / t = CLF Ps,eq = 2 311kips 0.90 345.3kips
IF you need to check capacity: LRFD t= t Pn = Pu Pu/ tPn = 0.75 466kips 50.00kips 10.7%kips Okay
ASD t = Pn / t = Pa Pa / (Pn / t ) = 2 311kips 50.00kips 16.1%kips Okay
Block Shear (Section J4.3) Fy = Fu = tpl = db = 36ksi 58ksi 1in 0.75in
Rn = min[0.6FuAnv + UbsFuAnt, 0.6FyAgv + UbsFuAnt]
Failure Path #1
gross path length (in) Agv Anv1 10.500 10.500
number holes/path 0.000 3.500
net path length (in) 10.500 7.438
# paths 2.000 1.000
Area (in^2) 21.000 7.438
Anv2 Ant Ubs
10.500 6.000 1.0 Shear Fracture (k)
3.500 1.000
7.438 5.125
1.000 1.000
5.578 5.125
Shear Yield (k) 750.9 number holes/path 0.000 3.500 1.500
Use (k) 750.2 net path length (in) 10.500 7.438 6.188
Rn Failure Path #2
750.2 gross path length (in)
# paths 1.000 1.000 1.000
Area (in^2) 10.500 7.438 6.188
Agv Anv Ant Ubs
10.500 10.500 7.500 0.5 Shear Fracture (k)
Shear Yield (k) 406.2
Use (k) 406.2
Rn Controlling Rn = IF you need to determine capacity: LRFD t= t Pn = CLF Ps,eq = 0.75
438.3 406.2k
ASD t = Pn / t = CLF Ps,eq = 2 203kips 0.90 225.7kips
305kips 1.40 217.6kips
If you need to check capacity: LRFD t= t Pn = Pu Pu/ tPn = 0.75 305kips 50.00kips 16.4%kips Okay Pa / (Pn / t ) =
ASD t = Pn / t = Pa 2 203kips 50.00kips 24.6%kips Okay
Tension Limit State Summary
Last Revised:
Serviceability Limit States: Limit State Slenderness Specification D1 Limit L/r < 300 or r > L/300
Strength Limit States: All strength limit states take the form: LRFD Pu < tPn Req'd Pn = Pu/ t < Pn Pu / ( tPn) < 1.00 ASD Pa < Pn/t Req'd Pn = Pa t < Pn Pa / (Pn/t) < 1.00
Rn (nominal resistance) is often used in place of Pn (nominal axial strength) in the equations above. Typical Design Variables Stl Type, Section
Limit State Specification Tensile Yielding
Nominal Capacity Member Capacity: FyAg Member Capacity: FuAe Capacity per connection:
D2(a)/J4.1(a)
0.90
1.67
Tensile Rupture
D2(b)/J4.1(b)
Stl Type, Section, Bolt size, Bolt 0.75 Layout, Section modifications
2.00
Block Shear
J4.3
Stl Type, 0.75 Section, Bolt min(0.6FuAnv + UbsFuAnt, Size, Bolt 0.6FyAgv + UbsFuAnt) Layout,
2.00
Section modifications Stl Type, Section, Bolt Std Holes, Defl an issue: Size, Bolt min(1.2 Lct Fu, 2.4 dt Fu) 0.75 Layout, Section Std Holes, Defl not issue: modifications min(1.5 Lct Fu, 3.0 dt Fu) Capacity per bolt hole:
Bolt Bearing
J3.10
2.00
Notes: 1. See SCM specification D3 for requirements for computing An, and Ae. 2. SCM specification J4.1(b) places an upper limit of 0.85Ag on An for connecting elements. 3. Multiple failure paths may need to be considered for Tensile Rupture and Block Shear. 4. The least bolt bearing value in a connection controls the bolt bearing strength of the member.
Bolt Summary
Last Revised:
Strength Limit States: All strength limit states take the form: LRFD Ru < tRn Req'd Rn = Ru/ t < Rn Ru / ( tRn) < 1.00 ASD Ra < Rn/t Req'd Rn = Ra t < Rn Ra / (Rn/t) < 1.00
Which is: FORCE on a bolt < STRENGTH of a bolt The STRENGTH of a bolt is computed by:
Simple Tension or Shear
Limit State Specification Nominal Capacity Typical
Design Variables Tensile Rupture Shear Rupture Slip Capacity J3.6 Single Bolt Capacity: FntAb Single Shear Plane: FnvAb Single Shear Plane: DuhscTb Bolt Material, Bolt Size Bolt Material, Bolt Size Bolt Material, Bolt Size 0.75 2.00
J3.6
0.75
2.00
J3.8
0.75
2.00
Combined Shear and Tension: Bearing Type Fasteners (-X or -N bolts):
Modify the nominal tensile rupture capacity for the presence of shear (SCM J3.7) Apply the shear rupture limit state without modification Typical Design Variables Bolt Material, Bolt Size Bolt Material, Bolt Size
Limit State Specification Nominal Capacity, R n Tensile Rupture Shear Rupture Single Bolt Capacity: F'ntAb Single Shear Plane: FnvAb
J3.7
0.75
2.00
J3.6
0.75
2.00
Slip Critical Type Fasteners (-SC bolts):
Modify the nominal slip capacity for the presence of tension (SCM J3.9) Apply the tensile rupture limit state without modification Typical Design Variables Bolt Material, Bolt Size
Limit State Specification Nominal Capacity, R n Tensile Rupture Single Bolt Capacity: FntAb
J3.6
0.75
2.00
Slip Capacity
J3.9
Single Shear Plane: DuhscTbks
Bolt Material, Bolt Size
0.75
2.00
The FORCE on a bolt is computed by:
Forces Concentric with the Bolt Group at the Faying Surface:
All bolts are assumed to be equally stressed in tension. All shear planes are assumed to be equally stressed in shear.
Eccentricity in the Plane of the Faying Surface:
Elastic Vector Method: See SCM pg 7-8. Computes shear in the bolts. Direct method that is conservative and has an inconsistent factor of safety. Instantaneous Center of Rotation Method: See SCM pg 7-6. Computes the relationship between the applied load and the shear load in the worst case bolt. Iterative method that is more consistent with test results and not as conservative as the Elastic Method.
Eccentricity out of the Plane of the Faying Surface:
Case I Method: See SCM pg 7-10. Basic mechanics (Mc/I) using the compression contact area to find the tension in the worst case bolt. Finding Ix may be iterative. If the shear is concentric with the bolt group it is equally divided among the shear planes otherwise use either the elastic vector or IC method to find the bolt shear forces. Case II Method: See SCM pg 7-12. Uses basic statics (Applied Moment = Pe = rat n' dm= Internal Moment) without considering the contact area to find the tension in the worst case bolt. If the shear is concentric with the bolt group it is equally divided among the shear planes otherwise use either the elastic vector or IC method to find the bolt shear forces.
Вам также может понравиться
- Casing Types, Functions, and ClassificationsДокумент71 страницаCasing Types, Functions, and ClassificationsPeterMarkОценок пока нет
- Inertia Base FrameДокумент2 страницыInertia Base FrameLasandu WanniarachchiОценок пока нет
- Australian Standard: Steel StructuresДокумент11 страницAustralian Standard: Steel StructuresRadu BalabanОценок пока нет
- 1554.1-2011 Structural Steel Welding - Part 1. Welding of Steel StrucutresДокумент8 страниц1554.1-2011 Structural Steel Welding - Part 1. Welding of Steel Strucutreskaramullahrasheed50% (2)
- SPACE SHUTTLE CRITERIAДокумент38 страницSPACE SHUTTLE CRITERIAffontanaОценок пока нет
- Torque Tightening E411 GBДокумент76 страницTorque Tightening E411 GBRoberto UrrutiaОценок пока нет
- Assess Structural Condition & Risk FactorsДокумент23 страницыAssess Structural Condition & Risk FactorsYudi Agung NugrohoОценок пока нет
- Bolting NewДокумент6 страницBolting Newsam_roy124Оценок пока нет
- Bou Stead 2012Документ16 страницBou Stead 2012huynhvanchauОценок пока нет
- C P & C I .: Cema B4, B5, C5, C6, D6 & E7 Class IdlersДокумент20 страницC P & C I .: Cema B4, B5, C5, C6, D6 & E7 Class IdlersArdian20Оценок пока нет
- Anchor HiltiДокумент324 страницыAnchor HiltiRuben GutierrezОценок пока нет
- Civil Design Help - Foundation For Rotating Equipment PDFДокумент31 страницаCivil Design Help - Foundation For Rotating Equipment PDFoluomo1Оценок пока нет
- Jurnal Dowel PDFДокумент5 страницJurnal Dowel PDFLukmanHakimОценок пока нет
- AISC 360-05 Fillet Weld Capacity TableДокумент1 страницаAISC 360-05 Fillet Weld Capacity TablejxsnyderОценок пока нет
- HILTI Technology Manual PDFДокумент210 страницHILTI Technology Manual PDFRoger Yan100% (1)
- Anclajes Red HeadДокумент8 страницAnclajes Red HeadLeonardo AvilaОценок пока нет
- A Practical Design Guide For Welded Connections Analysis and Design of Welded ConnectionsДокумент22 страницыA Practical Design Guide For Welded Connections Analysis and Design of Welded Connectionssherif ashrafОценок пока нет
- TN005 - Guidelines For Designing To As 4100 When Imported Materials Are InvolvedДокумент7 страницTN005 - Guidelines For Designing To As 4100 When Imported Materials Are InvolvedAndy AcousticОценок пока нет
- Inch Series Dowel Pins: Mechanical PropertiesДокумент2 страницыInch Series Dowel Pins: Mechanical PropertieswilliaqОценок пока нет
- Ucs TestingДокумент4 страницыUcs TestingkmandisodzaОценок пока нет
- Wall Structures: After The Foundations Have Been Completed The Walls Are Set Out and Construction CommencesДокумент16 страницWall Structures: After The Foundations Have Been Completed The Walls Are Set Out and Construction CommencesMirza Waqar BaigОценок пока нет
- Steel Connection DesignДокумент115 страницSteel Connection DesignPratikto WibowoОценок пока нет
- 40 Ton Crane Tender DocumentДокумент12 страниц40 Ton Crane Tender DocumentJaay VelОценок пока нет
- Nuts&Bolts SignedДокумент13 страницNuts&Bolts SignedMomchil YordanovОценок пока нет
- G DavitarmsДокумент30 страницG Davitarmsosvald97Оценок пока нет
- Pav Man Texas 2018Документ480 страницPav Man Texas 2018Helio de AlmeidaОценок пока нет
- Designing HSS Connections PDFДокумент4 страницыDesigning HSS Connections PDF112160rbcОценок пока нет
- Csa-G40 350WLRДокумент2 страницыCsa-G40 350WLRMario VenturaОценок пока нет
- Design Analysis of Top Lid Transportation Frame for ITER CryostatДокумент18 страницDesign Analysis of Top Lid Transportation Frame for ITER Cryostatmaulik gajjarОценок пока нет
- API 5CT P110 7Документ2 страницыAPI 5CT P110 7rageshmv100% (1)
- AIMS Design ManualДокумент76 страницAIMS Design ManualDavid RochaОценок пока нет
- Architecture Design Handbook - Flashings and Copings - Coping CoversДокумент5 страницArchitecture Design Handbook - Flashings and Copings - Coping CoversDukeОценок пока нет
- Shear Lug DesignДокумент19 страницShear Lug DesignariyaОценок пока нет
- Deco Heavy Duty Adjustable Anchors Sales SheetsДокумент2 страницыDeco Heavy Duty Adjustable Anchors Sales SheetsPete SwiftОценок пока нет
- Column SpliceДокумент1 страницаColumn SpliceBun KunОценок пока нет
- 18 - FastenersДокумент25 страниц18 - FastenersSameOldHat100% (1)
- Mathcad - Grout Connection HSE RulesДокумент3 страницыMathcad - Grout Connection HSE RulesRayodcОценок пока нет
- Discussion - Yield Line Analysis of Bolted Hanging ConnectionsДокумент1 страницаDiscussion - Yield Line Analysis of Bolted Hanging ConnectionsRob TamaccioОценок пока нет
- The Development of A New Design Procedure For Conventional Single-Plate Shear ConnectionsДокумент12 страницThe Development of A New Design Procedure For Conventional Single-Plate Shear ConnectionsMiguelОценок пока нет
- LUSAS Verification Manual Linear Static AnalysisДокумент364 страницыLUSAS Verification Manual Linear Static Analysisellyot22Оценок пока нет
- Bolting and WeldingДокумент73 страницыBolting and Weldinggerrydimayuga100% (2)
- Chapter 5CДокумент6 страницChapter 5Cnishant361Оценок пока нет
- Design Procedure For Concrete AnchorДокумент36 страницDesign Procedure For Concrete AnchorYan Yan100% (1)
- Bolted Connections LectureДокумент65 страницBolted Connections Lecturerghazzaoui1793100% (1)
- Flowjet Valves Product BrochureДокумент18 страницFlowjet Valves Product BrochureUday GokhaleОценок пока нет
- Finite Element Analysis of Engine Mounting Bracket by Considering Pretension Effect and Service LoadДокумент7 страницFinite Element Analysis of Engine Mounting Bracket by Considering Pretension Effect and Service LoadDevendra Kumar KumawatОценок пока нет
- Discussion - Steel Column Base Plate Design PDFДокумент4 страницыDiscussion - Steel Column Base Plate Design PDFOtto A. CobeñaОценок пока нет
- SteelWise Specifying MaterialsДокумент6 страницSteelWise Specifying Materialsv100% (1)
- SteelwiseДокумент5 страницSteelwiseΈνκινουαν Κόγκ ΑδάμουОценок пока нет
- Fortress Timber & Metal SDS Screws 2017 WebДокумент36 страницFortress Timber & Metal SDS Screws 2017 WebGabriel MacedoОценок пока нет
- SKF Pillow Block HousingsДокумент64 страницыSKF Pillow Block HousingsJulio Deyvis Ayala Gutierrez100% (1)
- Buckling Behaviour of Cylindrical Shells With Stepwise Wall ThicknessДокумент33 страницыBuckling Behaviour of Cylindrical Shells With Stepwise Wall ThicknessGogyОценок пока нет
- The Consequence of Bolt FailuresДокумент4 страницыThe Consequence of Bolt FailuresasdfgaОценок пока нет
- An Article On Tank Bulging Effect or Bulging Effect of Tank ShellsДокумент3 страницыAn Article On Tank Bulging Effect or Bulging Effect of Tank ShellsSNDОценок пока нет
- Introduction To The Economics of Structural SteelworkДокумент156 страницIntroduction To The Economics of Structural SteelworkCharles AjayiОценок пока нет
- Tension Member LRFDДокумент9 страницTension Member LRFDgullipalliОценок пока нет
- AISC Tension MemberДокумент3 страницыAISC Tension Membermodulor3dОценок пока нет
- IicДокумент58 страницIicAUNGPSОценок пока нет
- Steel Tension Member Design GuideДокумент20 страницSteel Tension Member Design Guide201087Оценок пока нет
- Chapter J Design of ConnectionsДокумент16 страницChapter J Design of Connectionsghosh73Оценок пока нет
- Design Air SystemsДокумент41 страницаDesign Air Systemssmacna100% (12)
- Pid Legend PDFДокумент1 страницаPid Legend PDFSocMed Dtk UI0% (1)
- Pid Legend PDFДокумент1 страницаPid Legend PDFSocMed Dtk UI0% (1)
- Databook PreviousДокумент87 страницDatabook PreviousGiovaniTorcadaОценок пока нет
- Camlock CatalogoДокумент12 страницCamlock CatalogoPascualSalvador100% (1)
- Pid Legend PDFДокумент1 страницаPid Legend PDFSocMed Dtk UI0% (1)
- PFD&PID With AUtoCAD P&ID PDFДокумент7 страницPFD&PID With AUtoCAD P&ID PDFihllhmОценок пока нет
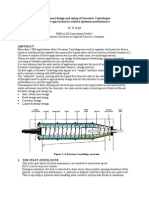
- Decanter CentrifugeДокумент10 страницDecanter Centrifugewgao201067% (3)
- Are You Properly Specifying Materials - Part 1Документ4 страницыAre You Properly Specifying Materials - Part 1wgao2010100% (1)
- Property ZokДокумент7 страницProperty Zokvmangione77Оценок пока нет
- STEEL INDUSTRY EMBRACES A992Документ6 страницSTEEL INDUSTRY EMBRACES A992Jagadeesh Nandam100% (1)
- 800 Cranes, Rigging and LiftingДокумент43 страницы800 Cranes, Rigging and LiftingLm Imran100% (5)
- PDFДокумент3 страницыPDFINAP 0Оценок пока нет
- CHALMERS (Fibre-Reinforced Concrete For Industrial Construction PDFДокумент162 страницыCHALMERS (Fibre-Reinforced Concrete For Industrial Construction PDFsochiva pramestiОценок пока нет
- Shell Momentum Balances for Pipe and Annular FlowДокумент15 страницShell Momentum Balances for Pipe and Annular FlowPatricia de LeonОценок пока нет
- Air Ejector Selection PDFДокумент9 страницAir Ejector Selection PDFmyungkwan haОценок пока нет
- 2 Lec2Документ25 страниц2 Lec2Armando FaríasОценок пока нет
- SIMONE (Equations and Methods)Документ65 страницSIMONE (Equations and Methods)Amine DoumiОценок пока нет
- Thermo Lab Write UpДокумент5 страницThermo Lab Write Upspoons5550% (2)
- Bearing Failure Analysis-V2Документ9 страницBearing Failure Analysis-V2Anonymous omGSHUEQОценок пока нет
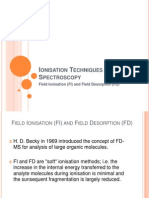
- Field Desorption, Field IonisationДокумент13 страницField Desorption, Field Ionisationhey80milionОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 - Crystal Structure - Part 1 PDFДокумент45 страницChapter 1 - Crystal Structure - Part 1 PDFGoh boon tongОценок пока нет
- Boltzmann's and Saha's EquationsДокумент22 страницыBoltzmann's and Saha's Equationssujayan2005Оценок пока нет
- Mass Transfer Operations: Gate PyqДокумент62 страницыMass Transfer Operations: Gate PyqChandrashekharCSKОценок пока нет
- Torque Values for Spiral Wound GasketsДокумент11 страницTorque Values for Spiral Wound GasketsloqОценок пока нет
- Maintenance SchedulingДокумент18 страницMaintenance Schedulingfadhil barОценок пока нет
- Fluid Mechanics SyllabusДокумент4 страницыFluid Mechanics Syllabusjohn@gmail.com0% (1)
- GALATIANSДокумент2 страницыGALATIANSFuckyouuОценок пока нет
- Lecture 6 Zeta PotentialДокумент12 страницLecture 6 Zeta PotentialPenny Yap100% (2)
- Lubricants For The Textile IndustryДокумент44 страницыLubricants For The Textile IndustryMario MullerОценок пока нет
- PaperchinaДокумент10 страницPaperchinaRAM KUMARОценок пока нет
- Urban Planning Students Report On Sustainable Development Plan For Tsunami Affected Cuddlore, Tamil Nadu, IndiaДокумент83 страницыUrban Planning Students Report On Sustainable Development Plan For Tsunami Affected Cuddlore, Tamil Nadu, Indiaravi shankarОценок пока нет
- Astm E1220Документ6 страницAstm E1220Gerardo Mediavilla100% (1)
- Chapter 11: Reactions of Alkyl HalidesДокумент34 страницыChapter 11: Reactions of Alkyl HalidesHeena DuaОценок пока нет
- CHEM 381-Introduction To Chemical Engeneering-Salman Ahmad PDFДокумент2 страницыCHEM 381-Introduction To Chemical Engeneering-Salman Ahmad PDFHashmi AshmalОценок пока нет
- Magnetism and Matter - 5 (I) Multiple Choice QuestionsДокумент8 страницMagnetism and Matter - 5 (I) Multiple Choice QuestionsFact's FactoryОценок пока нет
- D 3032 - 98 - RdmwmzitotgДокумент42 страницыD 3032 - 98 - RdmwmzitotgPrakash MakadiaОценок пока нет
- Ideal GasДокумент60 страницIdeal Gas68zrvtr9bfОценок пока нет
- Light Properties and Interactions in 40Документ3 страницыLight Properties and Interactions in 40Rhonoelle Reevenujlah100% (1)
- Introduction To Molecular Spectros PDFДокумент333 страницыIntroduction To Molecular Spectros PDFmekoki86% (7)
- Drill Pipe Eng PDFДокумент8 страницDrill Pipe Eng PDFTariq ChagouriОценок пока нет
- Material Balance Equations PresentationДокумент9 страницMaterial Balance Equations PresentationDeddy NurfaqihОценок пока нет