Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Creating A Simple PHP and MySQL-Based Login System
Загружено:
buulaaatОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Creating A Simple PHP and MySQL-Based Login System
Загружено:
buulaaatАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Creating a Simple PHP and MySQL-Based Login System
Contents:
Ctrl+clink on a item to read
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9.
Files Step 1 - Creating the Users Table & Adding a User Step 2 - Create the Database Configuration File (includes/config.inc.php) Step 3 - Create the Functions (includes/functions.inc.php) Step 4 - Create the Login Script (includes/login.inc.php) Step 5 - Create the Log Out Script (includes/logout.inc.php) Step 6 - Create the Login Page (login.php) Step 7 - Creating the Login Screen CSS File (css/login.css) Step 8 - Creating the Admin Page (index.php)
Files
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. /login.php - Front-facing login screen /index.php - Password-protected page /css/login.css - CSS file for login screen /includes/config.inc.php - Database configuration file /includes/function.inc.php - Core functions /includes/login.inc.php - Login script /includes/logout.inc.php - Logout script
Step 1 - Creating the Users Table & Adding a User
The following MySQL query will create the users table we will need to create the login system:
CREATE TABLE `tpc_tutorials`.`users` ( `id` INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY , `username` VARCHAR( 20 ) NOT NULL , `password` VARCHAR( 32 ) NOT NULL , UNIQUE ( `username` ) ) ENGINE = MYISAM
id - Each user is assigned a unique ID, AUTO_INCREMENT ensures that this automatically increases with each user that is added. username - Each username must be unique and no greater than 20 characters. password - Because we will be using MD5 encryption, which produces unique strings with a length of 32 characters, we have allowed this field a maximum of 32 characters.
Next, we will add a user to the users table:
INSERT INTO `tpc_tutorials`.`users` ( `id` , `username` , `password` ) VALUES ( NULL , 'admin', MD5( 'password' )
);
The MySQL statement above creates a user with admin as the username, and password as the password. The MD5 command will encrypt the password in a 32-character string. If all is working properly, you should end up with 5f4dcc3b5aa765d61d8327deb882cf99 in the password field.
Step 2 - Create the Database Configuration File
(includes/config.inc.php)
In this step, we will create a configuration file that stores our MySQL database connection settings. Creating a separate file for database settings helps if you have to change your MySQL username, password, server, or database. Otherwise, you may end up having to make the same change over and over again, which can be quite time-consuming. (I learned this the hard way!)
<?php /** * MySQL Database Configuration * * @file /includes/config.inc.php * @note Replace the settings below with those for your MySQL database. */ define('DB_HOSTNAME', 'database_hostname'); define('DB_USERNAME', 'database_username'); define('DB_PASSWORD', 'database_password'); define('DB_DATABASE', 'database_name'); ?>
Step 3 - Create the Functions
(includes/functions.inc.php)
The functions file includes those functions frequently used, and consolidating these help save time and reduce code clutter. The key concepts illustrated in this part of the tutorial are: Functions & function commenting Use of header() for redirection
<?php /** * Crucial Functions for Application * * @package tpc_tutorials * @file */ /includes/functions.inc.php
/** * Redirects to specified page
* * @param string $page Page to redirect user to * @return void */ function redirect($page) { header('Location: ' . $page); exit(); }
/** * Check login status * * @return boolean Login status */ function check_login_status() { // If $_SESSION['logged_in'] is set, return the status if (isset($_SESSION['logged_in'])) { return $_SESSION['logged_in']; } return false; }
Step 4 - Create the Login Script
(includes/login.inc.php)
The script we create during this step will be executed after we submit a username and password via the login screen. Several key concepts will be illustrated in this step: Sanitizing data (making sure data is safe for database) Simple MySQL queries using the object-oriented MySQLi extension Including an external PHP file Use of $_SESSION variables
<?php // Include required MySQL configuration file and functions require_once('config.inc.php'); require_once('functions.inc.php');
// Start session session_start();
// Check if user is already logged in if ($_SESSION['logged_in'] == true) { // If user is already logged in, redirect to main page redirect('../index.php'); } else { // Make sure that user submitted a username/password and username only consists of alphanumeric chars
if ( (!isset($_POST['username'])) || (! isset($_POST['password'])) OR (!ctype_alnum($_POST['username'])) ) { redirect('../login.php'); }
// Connect to database $mysqli = @new mysqli(DB_HOSTNAME, DB_USERNAME, DB_PASSWORD, DB_DATABASE);
// Check connection if (mysqli_connect_errno()) { printf("Unable to connect to database: %s",
mysqli_connect_error());
exit(); }
// Escape any unsafe characters before querying database $username = $mysqli->real_escape_string($_POST['username']); $password = $mysqli->real_escape_string($_POST['password']);
// Construct SQL statement for query & execute $sql = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = '" . $username . "' AND password = '" . md5($password) . "'"; $result = $mysqli->query($sql);
// If one row is returned, username and password are valid if (is_object($result) && $result->num_rows == 1) {
// Set session variable for login status to true $_SESSION['logged_in'] = true; redirect('../index.php'); } else { // If number of rows returned is not one, redirect back to login screen redirect('../login.php'); } } ?>
Step 5 - Create the Log Out Script
(includes/logout.inc.php)
There are two new PHP features introduced in this script: unset() and session_destroy().
<?php // Start session session_start();
unset() - Unsets specified variable session_destroy() - Destroys all data registered to a session
// Include required functions file require_once('functions.inc.php');
// If not logged in, redirect to login screen // If logged in, unset session variable and display logged-out message
if (check_login_status() == false) { // Redirect to redirect('login.php'); } else { // Kill session variables unset($_SESSION['logged_in']); unset($_SESSION['username']);
// Destroy session session_destroy(); } ?> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Strict//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-strict.dtd"> <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xml:lang="en" lang="en"> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-type" content="text/html;charset=utf-
8" />
<title>Creating a Simple PHP and MySQL-Based Login System dev.thatspoppycock.com</title> </head> <body> <h1>Logged Out</h1> <p>You have successfully logged out. Back to <a href="../login.php">login</a> screen.</p> </body> </html>
Step 6 - Create the Login Page
(login.php)
The following HTML page is one example of how you can style and layout your login screen. The CSS will be created in the next step, which can be edited to suit your needs.
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Strict//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-strict.dtd"> <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xml:lang="en" lang="en"> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-type" content="text/html;charset=utf-8" /> <title>Creating a Simple PHP and MySQL-Based Login System dev.thatspoppycock.com</title> <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="css/login.css" /> </head> <body> <form id="login-form" method="post" action="includes/login.inc.php"> <fieldset> <legend>Login to Web Site</legend> <p>Please enter your username and password to access the administrator's panel</p> <label for="username"> <input type="text" name="username" id="username" />Username: </label> <label for="password"> <input type="password" name="password" id="password" />Password:
</label> <label for="submit"> <input type="submit" name="submit" id="submit" value="Login" /> </label> </fieldset> </form> </body> </html>
Step 7 - Creating the Login Screen CSS File
(css/login.css)
Create a new directory called css, and save the following in a file called login.css.
body { font-family: 'Trebuchet MS', Verdana, Arial, sans-serif; font-size: 10pt; }
#login-form { width: 300px; margin: 0 auto; }
#login-form fieldset { padding: 10px; }
#login-form legend { font-weight: bold; font-size: 9pt; }
#login-form label { display: block; height: 2em; background-color: #e7e7e7; padding: 10px 10px 0; }
#login-form input { margin-right: 20px; border: 1px solid #999; float: right; clear: right; background: #ccc; }
#login-form input:focus, #login-form input-hover { border: 1px solid #333; }
Step 8 - Creating the Admin Page
(index.php)
The first instruction we pass is session_start(), which allows us to use the $_SESSION variable to access information. After that, we bring our library of functions so we can use the check_login_status() and redirect() functions. The if statement in the code block redirects the user back to the login screen if he/she is not logged in.
<?php // Start session session_start();
// Include required functions file require_once('includes/functions.inc.php');
// Check login status... if not logged in, redirect to login screen if (check_login_status() == false) { redirect('login.php'); } ?> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Strict//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-strict.dtd"> <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xml:lang="en" lang="en"> <head>
8" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-type" content="text/html;charset=utf-
<title>Creating a Simple PHP and MySQL-Based Login System dev.thatspoppycock.com</title> </head> <body> <h1>Administration Panel</h1> <p>You are currently logged in. You may log out using the button below.</p> <p><a href="includes/logout.inc.php">Log Out</a></p> </body> </html>
Вам также может понравиться
- Making Login Menu With PHP and mySQLДокумент38 страницMaking Login Menu With PHP and mySQLDidi HaryadiОценок пока нет
- Routing, Controllers, Acti Ons, Views, Areas : Softuni TeamДокумент53 страницыRouting, Controllers, Acti Ons, Views, Areas : Softuni TeamGrig MărcușОценок пока нет
- Lab - 02 - Building Websites Using ASP - NET Core Razor PagesДокумент27 страницLab - 02 - Building Websites Using ASP - NET Core Razor PagesTran Khai Minh KhoiОценок пока нет
- Lab01 Mars PDFДокумент7 страницLab01 Mars PDFAna LigiaОценок пока нет
- Capstone Final PresentationДокумент18 страницCapstone Final Presentationhimanshu guptaОценок пока нет
- SSD ForensicДокумент101 страницаSSD ForensicFebrian SubagiyoОценок пока нет
- Lecture 02 ASP - NET MVC RazorДокумент23 страницыLecture 02 ASP - NET MVC Razorchea soksanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 (w6) ASP - NET OverviewДокумент41 страницаChapter 7 (w6) ASP - NET Overviewmuhammedsavas799Оценок пока нет
- Capstone Proposal - Project Part 3 - Rev 3Документ15 страницCapstone Proposal - Project Part 3 - Rev 3api-446537001Оценок пока нет
- Red October. Detailed Malware DescriptionДокумент114 страницRed October. Detailed Malware DescriptionYury ChemerkinОценок пока нет
- Learn ASP - NET: ASP - NET: Razor Syntax CheatsheetДокумент8 страницLearn ASP - NET: ASP - NET: Razor Syntax CheatsheetKarthik BachawalaОценок пока нет
- Network Administration and Management: Prepared By: Inocencio, Rose MДокумент92 страницыNetwork Administration and Management: Prepared By: Inocencio, Rose MJermyn G EvangelistaОценок пока нет
- Towards Network Automation - A Multi-Agent Based Intelligent Networking SystemДокумент220 страницTowards Network Automation - A Multi-Agent Based Intelligent Networking SystemvanndaОценок пока нет
- Par T A - Multiple Choice Questions: Total 10 Mar KsДокумент15 страницPar T A - Multiple Choice Questions: Total 10 Mar KsyawahabОценок пока нет
- Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) : Web Based System DevelopmentДокумент48 страницCascading Style Sheets (CSS) : Web Based System DevelopmentNur MahirahОценок пока нет
- Final Digital Forensic Small Devices ReportДокумент21 страницаFinal Digital Forensic Small Devices ReportMithilesh PatelОценок пока нет
- Aprisa SR+ User Manual 1.11.1 EnglishДокумент492 страницыAprisa SR+ User Manual 1.11.1 EnglishErica PereiraОценок пока нет
- Assg1 Sol PDFДокумент3 страницыAssg1 Sol PDFkartikalindaОценок пока нет
- P17173392 FinalYearProject ReportДокумент91 страницаP17173392 FinalYearProject ReportBen HarkerОценок пока нет
- Lecture5 PHP MysqlДокумент66 страницLecture5 PHP MysqlSusha PОценок пока нет
- MipsДокумент46 страницMipsAjay RoopeshОценок пока нет
- Dynamic Malware AnalysisДокумент6 страницDynamic Malware AnalysisBik AshОценок пока нет
- 4 Step Mitigation For Log4j AttacksДокумент3 страницы4 Step Mitigation For Log4j Attackskarthikp86Оценок пока нет
- Exploit Attack: Shaunak Joshi (Roll No:43162)Документ7 страницExploit Attack: Shaunak Joshi (Roll No:43162)Shaunak JoshiОценок пока нет
- Malware Analysis and Classification SurveyДокумент9 страницMalware Analysis and Classification SurveyHendreson KafodyaОценок пока нет
- Elster As300p Profiles 2011 02 Smart MeteringДокумент3 страницыElster As300p Profiles 2011 02 Smart MeteringnscacОценок пока нет
- 4 - MySQL & PHP PDFДокумент62 страницы4 - MySQL & PHP PDFNiko NazaroffОценок пока нет
- Apache Friends - Xampp For WindowsДокумент11 страницApache Friends - Xampp For WindowsLalatendu SwainОценок пока нет
- Lab9 - NessusДокумент11 страницLab9 - NessusSaw GyiОценок пока нет
- FYP PresentationДокумент14 страницFYP PresentationNasrul SultanОценок пока нет
- Computer Organization LabДокумент19 страницComputer Organization LabKowsik_JSОценок пока нет
- 1.bitwise OperatorsДокумент2 страницы1.bitwise OperatorsPaul kollamОценок пока нет
- PHP Basics 2020Документ16 страницPHP Basics 2020Jaye 99Оценок пока нет
- MIPS Assembly Language Programming: Computer Organization and AssemblyДокумент33 страницыMIPS Assembly Language Programming: Computer Organization and AssemblySardar IrfanullahОценок пока нет
- 2019ibmSecCombatingDestructiveMalwareReport Final6 PDFДокумент20 страниц2019ibmSecCombatingDestructiveMalwareReport Final6 PDFfabianrh2009Оценок пока нет
- HTMLДокумент14 страницHTMLGear Arellano IIОценок пока нет
- Final ReportДокумент22 страницыFinal ReportSitansu Sekhar MohantyОценок пока нет
- Basic Computer Organization and Design-IДокумент54 страницыBasic Computer Organization and Design-IchodarОценок пока нет
- PHP Final Exam ReviewerДокумент3 страницыPHP Final Exam ReviewerBeth JacintoОценок пока нет
- Lifecycle of An Aspnet MVC 5 ApplicationДокумент2 страницыLifecycle of An Aspnet MVC 5 ApplicationLincoln BurrowsОценок пока нет
- Web Pages With MVC3 and Razor SyntaxДокумент282 страницыWeb Pages With MVC3 and Razor Syntaxozamaro100% (1)
- Shamoon Malware Attacks Aramco: Who, What, When, Where?Документ3 страницыShamoon Malware Attacks Aramco: Who, What, When, Where?zahra alsayedОценок пока нет
- CPP Project ReportДокумент18 страницCPP Project ReportCM5I101ONKAR KANKIОценок пока нет
- How To Use ProDiscover, ProDiscover ForensicsДокумент13 страницHow To Use ProDiscover, ProDiscover Forensicsgkpalok100% (1)
- Lecture 2 - SecSDLCДокумент10 страницLecture 2 - SecSDLCKing KongОценок пока нет
- ICT ReportДокумент3 страницыICT ReportHemavathiОценок пока нет
- Cisco AAVID Enterprise VPN DesignДокумент76 страницCisco AAVID Enterprise VPN Designwctang888Оценок пока нет
- PCSpim TutorialДокумент5 страницPCSpim Tutorialsimona13Оценок пока нет
- Lab1 2019Документ24 страницыLab1 2019Ching Fung KwokОценок пока нет
- Malware AnalysisДокумент5 страницMalware AnalysisRavi KumarОценок пока нет
- Computer Security: Identifying Malicious PatternsДокумент31 страницаComputer Security: Identifying Malicious PatternsMahmoudОценок пока нет
- ClearSky-End of Year Report-2018Документ120 страницClearSky-End of Year Report-2018Luis SosaОценок пока нет
- Research ProposalДокумент3 страницыResearch Proposalapi-460973473Оценок пока нет
- Lazarus Under The Hood PDF Final PDFДокумент58 страницLazarus Under The Hood PDF Final PDFCristobal CordobaОценок пока нет
- SQL SynopsisДокумент8 страницSQL SynopsisAnthati KumarОценок пока нет
- Developing ASP - Net MVC 4 Web ApplicationsДокумент585 страницDeveloping ASP - Net MVC 4 Web ApplicationsJOAQUIN ENRIQUE LEALОценок пока нет
- SecurityДокумент28 страницSecurityapi-19796528Оценок пока нет
- Analizador de Combustion Kigaz 310 Manual EngДокумент60 страницAnalizador de Combustion Kigaz 310 Manual EngJully Milagros Rodriguez LaicheОценок пока нет
- WEB DESIGN WITH AUSTINE-converted-1Документ9 страницWEB DESIGN WITH AUSTINE-converted-1JayjayОценок пока нет
- Pivot TableДокумент19 страницPivot TablePrince AroraОценок пока нет
- Excon2019 ShowPreview02122019 PDFДокумент492 страницыExcon2019 ShowPreview02122019 PDFSanjay KherОценок пока нет
- Digital MetersДокумент47 страницDigital MetersherovhungОценок пока нет
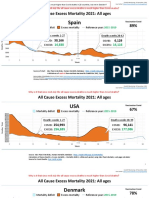
- Countries EXCESS DEATHS All Ages - 15nov2021Документ21 страницаCountries EXCESS DEATHS All Ages - 15nov2021robaksОценок пока нет
- Leigh Shawntel J. Nitro Bsmt-1A Biostatistics Quiz No. 3Документ6 страницLeigh Shawntel J. Nitro Bsmt-1A Biostatistics Quiz No. 3Lue SolesОценок пока нет
- The Homework Song FunnyДокумент5 страницThe Homework Song Funnyers57e8s100% (1)
- Famous Russian PianoДокумент10 страницFamous Russian PianoClara-Schumann-198550% (2)
- The JHipster Mini Book 2Документ129 страницThe JHipster Mini Book 2tyulist100% (1)
- Functional DesignДокумент17 страницFunctional DesignRajivSharmaОценок пока нет
- Obesity - The Health Time Bomb: ©LTPHN 2008Документ36 страницObesity - The Health Time Bomb: ©LTPHN 2008EVA PUTRANTO100% (2)
- Post Appraisal InterviewДокумент3 страницыPost Appraisal InterviewNidhi D100% (1)
- Movie Piracy in Ethiopian CinemaДокумент22 страницыMovie Piracy in Ethiopian CinemaBehailu Shiferaw MihireteОценок пока нет
- UC 20 - Produce Cement Concrete CastingДокумент69 страницUC 20 - Produce Cement Concrete Castingtariku kiros100% (2)
- DNA ReplicationДокумент19 страницDNA ReplicationLouis HilarioОценок пока нет
- PLC Laboratory Activity 2Документ3 страницыPLC Laboratory Activity 2Kate AlindajaoОценок пока нет
- Computing of Test Statistic On Population MeanДокумент36 страницComputing of Test Statistic On Population MeanKristoffer RañolaОценок пока нет
- Corrosion Fatigue Phenomena Learned From Failure AnalysisДокумент10 страницCorrosion Fatigue Phenomena Learned From Failure AnalysisDavid Jose Velandia MunozОценок пока нет
- Gods Omnipresence in The World On Possible MeaninДокумент20 страницGods Omnipresence in The World On Possible MeaninJoan Amanci Casas MuñozОценок пока нет
- Linguistics Is Descriptive, Not Prescriptive.: Prescriptive Grammar. Prescriptive Rules Tell You HowДокумент2 страницыLinguistics Is Descriptive, Not Prescriptive.: Prescriptive Grammar. Prescriptive Rules Tell You HowMonette Rivera Villanueva100% (1)
- Marketing FinalДокумент15 страницMarketing FinalveronicaОценок пока нет
- Chapter13 PDFДокумент34 страницыChapter13 PDFAnastasia BulavinovОценок пока нет
- RSA - Brand - Guidelines - 2019 2Документ79 страницRSA - Brand - Guidelines - 2019 2Gigi's DelightОценок пока нет
- Agco Serie 800 PDFДокумент24 страницыAgco Serie 800 PDFJohnny VargasОценок пока нет
- MRBR ATR 72 Rev18Документ424 страницыMRBR ATR 72 Rev18Juan Forero OrtizОценок пока нет
- Wilcoxon Matched Pairs Signed Rank TestДокумент3 страницыWilcoxon Matched Pairs Signed Rank TestDawn Ilish Nicole DiezОценок пока нет
- School of Mathematics 2021 Semester 1 MAT1841 Continuous Mathematics For Computer Science Assignment 1Документ2 страницыSchool of Mathematics 2021 Semester 1 MAT1841 Continuous Mathematics For Computer Science Assignment 1STEM Education Vung TauОценок пока нет
- Partes de La Fascia Opteva Y MODULOSДокумент182 страницыPartes de La Fascia Opteva Y MODULOSJuan De la RivaОценок пока нет
- Human EpigenomicsДокумент234 страницыHuman EpigenomicsHeron HilárioОценок пока нет
- Blockchain Basics: A Non-Technical Introduction in 25 StepsОт EverandBlockchain Basics: A Non-Technical Introduction in 25 StepsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (24)
- Optimizing DAX: Improving DAX performance in Microsoft Power BI and Analysis ServicesОт EverandOptimizing DAX: Improving DAX performance in Microsoft Power BI and Analysis ServicesОценок пока нет
- Grokking Algorithms: An illustrated guide for programmers and other curious peopleОт EverandGrokking Algorithms: An illustrated guide for programmers and other curious peopleРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (16)
- SQL QuickStart Guide: The Simplified Beginner's Guide to Managing, Analyzing, and Manipulating Data With SQLОт EverandSQL QuickStart Guide: The Simplified Beginner's Guide to Managing, Analyzing, and Manipulating Data With SQLРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (46)
- Fusion Strategy: How Real-Time Data and AI Will Power the Industrial FutureОт EverandFusion Strategy: How Real-Time Data and AI Will Power the Industrial FutureОценок пока нет
- ITIL 4 : Drive Stakeholder Value: Reference and study guideОт EverandITIL 4 : Drive Stakeholder Value: Reference and study guideОценок пока нет
- Business Intelligence Strategy and Big Data Analytics: A General Management PerspectiveОт EverandBusiness Intelligence Strategy and Big Data Analytics: A General Management PerspectiveРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- The Future of Competitive Strategy: Unleashing the Power of Data and Digital Ecosystems (Management on the Cutting Edge)От EverandThe Future of Competitive Strategy: Unleashing the Power of Data and Digital Ecosystems (Management on the Cutting Edge)Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Relational Database Design and ImplementationОт EverandRelational Database Design and ImplementationРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (5)
- High-Performance Oracle: Proven Methods for Achieving Optimum Performance and AvailabilityОт EverandHigh-Performance Oracle: Proven Methods for Achieving Optimum Performance and AvailabilityОценок пока нет
- Oracle Database 12c Backup and Recovery Survival GuideОт EverandOracle Database 12c Backup and Recovery Survival GuideРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- Agile Metrics in Action: How to measure and improve team performanceОт EverandAgile Metrics in Action: How to measure and improve team performanceОценок пока нет
- Microsoft Access Guide to Success: From Fundamentals to Mastery in Crafting Databases, Optimizing Tasks, & Making Unparalleled Impressions [III EDITION]От EverandMicrosoft Access Guide to Success: From Fundamentals to Mastery in Crafting Databases, Optimizing Tasks, & Making Unparalleled Impressions [III EDITION]Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (8)















































































































![Microsoft Access Guide to Success: From Fundamentals to Mastery in Crafting Databases, Optimizing Tasks, & Making Unparalleled Impressions [III EDITION]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/610686937/149x198/9ccfa6158e/1714467780?v=1)

