Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Two Broad Strategies:: Segmentation of Rural Market
Загружено:
kapooranukaran3493Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Two Broad Strategies:: Segmentation of Rural Market
Загружено:
kapooranukaran3493Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
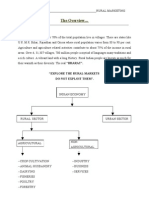
SEGMENTATION OF RURAL MARKET Two broad strategies: Mass market strategy-targeting the total market as potential buyers of a brand
nd in a product category with one marketing mix Market segmentation strategy-it is the process of identifying small markets that exist within a large market and are similar in terms of criteria by which they choose a product within a product category but act differently across the groups. A segment represents a set of consumers who respond in a similar way to a given marketing mix and marketing stimuli.
Segmentation variables : Geographic-region, state, district, village Demographic-age, gender, occupation Psychographic-social class, personality and lifestyle Product related variables-types of usage, amount of usage and benefit sought
While segmenting a market , organizations can opt for a single variable or a combination of variables(multivariate segmentation) Conditions for effective market segmentation : Measurable-to calculate the market potential Accessible-in a financially viable manner Profitable-large enough Data availability-on segmentation variables
Benefits of market segmentation : Customer oriented philosophy-in an optimum manner Enables tailoring of marketing program-customized for delight Enables development of strong positioning of brand-
Approaches for segmenting the rural market of India : Based on size of village population-13% villages having population of >2000 you can tap 50% of the rural population that possesses 60% of rural wealth
ORG MARG classification :
1|Page
Class I ->5000 Class II-1000 to 5000 Class III-<1000 Population single most important variable for segmentation Based on location with respect to nearby town 1. Villages near urban centres-purchase from nearby towns 2. Villages in developing districts-potential market for branded goods as income profile is good 3. Immobile and self sufficient Asiatic villages-they are media dark Based on size of farmland-land holding pattern can be a basis for segmentation of the rural market 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Marginal farmer<1 hectare Small farmer 1-2 hectare Semi medium farmer 2-4 hectare Medium farmer 4-10 hectare Large farmer > 10 hectares
This basis is more appropriate for marketing of agricultural inputs. The weakness are : -based on land owned and not on its fertility level -silent about other occupations -silent about attitude -silent about non-agricultural activities Based on sociological characteristics
-proprietors of land like zamindars -rich farmers-dominant caste of the area -small peasants or marginal farmers-1 to 2 hectares ownership -tenant farmers-rented lands
2|Page
-agricultural labourers-daily wage basis -artisans and others-unemployed In India there are 56 distinct socio-cultural regions A. Based on income Rural rich consumer -concentrated rich consumers-punjab, Haryana, AP, Gujarat and Karnataka -scattered rich consumers-money lenders and zamindars Rural consumers around urban area-akin to urban consumers Rural consumers above poverty line-purchase manufactured goods in addition to agro products Rural consumers below poverty line-26% of population and is not of interest to marketers. NCAER has also classified : -destitutes-<Rs 16000 per annum(essential) -aspirants-16-22000(basic durables) -climbers-22-45000(consumables and consumer durables) -Consumers-45-215000(consumables and consumer durables) -Very rich>215000(market for international brands) B. Based on development level-developed, developing and underdeveloped rural Punjab, Haryana, Gujarat, Maharashtra, goa, Karnataka. Kerala, TN are considered developed C. Based on age group perspectives -pre inidependence -pain of nation building>1947 -pain of liberalization>1985 -liberalization children>1990
3|Page
-millenium children >1997
>35 laggards as influenced by beliefs and customs D. Based on distribution and internal structure of villages -nuclear -linear villages -irregularly clustered villages -scattered homesteads This classification is for the use of sales staff who are operating in the rural market to plan and execute their route to tap different retailers in villages Rural market segmentation tools-Thompson rural market index Developing a targeted marketing strategy Define relevant market Analysis of potential customers Basis for segmentation Define market segments Analyse competitors position Evaluate market segments Select market segments Finalise marketing mix
Criteria for segmentation Environment of different districts Density of population Heterogeneity Mobility, media availability and cost of access to the area System of interaction
4|Page
Вам также может понравиться
- Market SegmentationДокумент18 страницMarket SegmentationAbhinav JayabalanОценок пока нет
- 1 Rural - Marketing - S.T.PДокумент11 страниц1 Rural - Marketing - S.T.PShahrukh Pathan100% (1)
- Presentation On Rural MarketingДокумент11 страницPresentation On Rural Marketingjatish sharmaОценок пока нет
- Marketing Strategy of ParleДокумент62 страницыMarketing Strategy of Parlesagar puranik80% (5)
- Marketing Strategy of ParleДокумент59 страницMarketing Strategy of Parlesagarkhedekar999Оценок пока нет
- Rural MarketingДокумент22 страницыRural MarketingasfastasitgetsОценок пока нет
- Variables That Differentiate Rural From UrbanДокумент22 страницыVariables That Differentiate Rural From UrbanAditi ChandraОценок пока нет
- Rural Marketing: An OverviewДокумент64 страницыRural Marketing: An OverviewRajesh VallilathОценок пока нет
- Project Report On Rural Marketing at ParleДокумент33 страницыProject Report On Rural Marketing at ParleMamta MalviОценок пока нет
- Project Report On Rural Marketing at ParleДокумент33 страницыProject Report On Rural Marketing at ParleBrijesh Kumar Singh50% (2)
- Rural MKT 2Документ65 страницRural MKT 2DivaxОценок пока нет
- Rural MarketingДокумент14 страницRural MarketingDani. YОценок пока нет
- Rural Marketing in Doc.2Документ8 страницRural Marketing in Doc.2Vinay Prateek BansriyarОценок пока нет
- Rural Marketing M1M3Документ18 страницRural Marketing M1M3Priya ChaudharyОценок пока нет
- Rural Marketing - MMS & PGDMДокумент30 страницRural Marketing - MMS & PGDMDhananjay KumarОценок пока нет
- Rural Marketing inДокумент9 страницRural Marketing inVinay Prateek BansriyarОценок пока нет
- Rural HaatДокумент20 страницRural HaatkanchanОценок пока нет
- Relevance & Importance Problems in Rural MarketingДокумент35 страницRelevance & Importance Problems in Rural MarketingAmitPandiaОценок пока нет
- Rural Marketing of ParleДокумент58 страницRural Marketing of ParleSagar KapoorОценок пока нет
- Rural Marketing StrategiesДокумент23 страницыRural Marketing StrategiesPraveen KumarОценок пока нет
- Challenges, Opportunitie S and StrategiesДокумент30 страницChallenges, Opportunitie S and StrategiesGaurav DagaОценок пока нет
- Rural Marketing in Terms of STPДокумент33 страницыRural Marketing in Terms of STPKamal Deep Choudhary100% (1)
- Rural MarketingДокумент258 страницRural MarketingPriyanka ChoudharyОценок пока нет
- Rural Marketing Management by Prof Dharmendra PandeyДокумент88 страницRural Marketing Management by Prof Dharmendra Pandeydpandey82Оценок пока нет
- Segment Indian Rural Market: Presented BY Ashvin 15MBA1383Документ14 страницSegment Indian Rural Market: Presented BY Ashvin 15MBA1383Ash Vin RajputОценок пока нет
- Rural Marketing Is Necessary For Developing India Defining Rural MarketingДокумент9 страницRural Marketing Is Necessary For Developing India Defining Rural MarketingAshish PareekОценок пока нет
- 5692 6458 05Документ19 страниц5692 6458 05Ankit SachdevaОценок пока нет
- RuralmarketingpptДокумент50 страницRuralmarketingpptKamalDeepKaurОценок пока нет
- Rajat Rural MarketingДокумент7 страницRajat Rural MarketingPrakash KcОценок пока нет
- Rural Marketing Strategy: STP Strategies atДокумент38 страницRural Marketing Strategy: STP Strategies atAmitPandiaОценок пока нет
- Rural Marketing Research PaperДокумент8 страницRural Marketing Research PaperShazia JamalОценок пока нет
- Rural Marketing - An Insight: Prof. Aparna KanchanДокумент50 страницRural Marketing - An Insight: Prof. Aparna KanchanMaitry PatelОценок пока нет
- Rural ManagementДокумент168 страницRural ManagementPrasanjeet Bhattacharjee90% (10)
- Mba IV Rural Marketing (12mbamm415) Notes - UnlockedДокумент121 страницаMba IV Rural Marketing (12mbamm415) Notes - UnlockedJohn Patterson100% (1)
- Introduction To Rural Marketing: Module-1Документ20 страницIntroduction To Rural Marketing: Module-1deepakanjanОценок пока нет
- Rural MarketingДокумент16 страницRural Marketing720 Manvir SinghОценок пока нет
- Submitted To: Sunny Dawar Submitted By: Satish, Saurav, Ramratan, Ravis Hankar & RishikeshДокумент10 страницSubmitted To: Sunny Dawar Submitted By: Satish, Saurav, Ramratan, Ravis Hankar & Rishikeshrkjain90Оценок пока нет
- Distribution Strategy in Rural MarketingДокумент89 страницDistribution Strategy in Rural Marketingm_dattaias100% (6)
- Rural MarketingДокумент40 страницRural MarketingBARKHA TILWANIОценок пока нет
- Rural Marketing FinaldocДокумент26 страницRural Marketing FinaldocPraNita AmbavaneОценок пока нет
- Rural Marketing 3Документ12 страницRural Marketing 3ankitamittal12_88552Оценок пока нет
- R.M.-5 - S.T.P. - Rural MarketsДокумент33 страницыR.M.-5 - S.T.P. - Rural MarketsSayan SethОценок пока нет
- Future of Rural Marketing in IndiaДокумент8 страницFuture of Rural Marketing in IndiaPrashant Dabral0% (1)
- Rural MarketingДокумент30 страницRural MarketingNaveenОценок пока нет
- Rural Marketing in India: By-Ankit Pawar (5) Astha Savyasachi (7) Mba (Gen), Sec-A, Sem-2Документ30 страницRural Marketing in India: By-Ankit Pawar (5) Astha Savyasachi (7) Mba (Gen), Sec-A, Sem-2asthasachiОценок пока нет
- North Maharashtra University, Jalgaon Department of Management StudiesДокумент14 страницNorth Maharashtra University, Jalgaon Department of Management StudiesTushar PatilОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 Introduction To Rural MarketingДокумент25 страницUnit 1 Introduction To Rural MarketingSufyan ShaikhОценок пока нет
- Amravati: Presented By: Sushant S. Tantarpale Mba 2 YearДокумент11 страницAmravati: Presented By: Sushant S. Tantarpale Mba 2 YearSushantОценок пока нет
- Rural Marketing in India Economy: '''Building Sustainable Market Linkages For Rural Products: Industry'sДокумент15 страницRural Marketing in India Economy: '''Building Sustainable Market Linkages For Rural Products: Industry'seyecandy123Оценок пока нет
- Rural RetailingДокумент18 страницRural RetailingAmyra Johnson100% (1)
- Champi ShampooДокумент42 страницыChampi ShampooPradip VishwakarmaОценок пока нет
- Concept of Rural MarketingДокумент10 страницConcept of Rural MarketinggeetapurshotamaniОценок пока нет
- Rural Management 2014 (Intro)Документ20 страницRural Management 2014 (Intro)Rashmi HulsurkarОценок пока нет
- Rural Marketing-An OverviewДокумент13 страницRural Marketing-An Overviewgarvit0% (1)
- "Rural Marketing For FMCG": Project OnДокумент74 страницы"Rural Marketing For FMCG": Project OnAshish Anil MataiОценок пока нет
- Rural Marketing - An Insight: Presented byДокумент50 страницRural Marketing - An Insight: Presented byDeeplakhan BhanguОценок пока нет
- Unit 1Документ47 страницUnit 110A akash ranaОценок пока нет
- Agribusiness Management : Strategies for Successful Farming EnterprisesОт EverandAgribusiness Management : Strategies for Successful Farming EnterprisesОценок пока нет
- Introduction to Marketing - Principles of Wholesale and Retail DistributionОт EverandIntroduction to Marketing - Principles of Wholesale and Retail DistributionРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (2)
- Electrocomponents - RS Group - Investor - Event - 2022 - Presentation - 30.03.2022Документ105 страницElectrocomponents - RS Group - Investor - Event - 2022 - Presentation - 30.03.2022sydubh72Оценок пока нет
- Case Study (Solved)Документ10 страницCase Study (Solved)Aditya DsОценок пока нет
- Sharda dss10 PPT 04Документ38 страницSharda dss10 PPT 04Abdulmajeed AlshehriОценок пока нет
- BNI Bank StatementДокумент1 страницаBNI Bank Statementelisio.silvaОценок пока нет
- A No BS Guide To Become A Professional Day Trader Trading TuitionsДокумент17 страницA No BS Guide To Become A Professional Day Trader Trading Tuitionsshivam100% (2)
- Worlducation Team Performance Plan: BSBTWK502 Manage Team EffectivenessДокумент10 страницWorlducation Team Performance Plan: BSBTWK502 Manage Team Effectivenessstar trendzОценок пока нет
- Compensation Management at Tata Consultancy Services LTDДокумент4 страницыCompensation Management at Tata Consultancy Services LTDNishaant S Prasad0% (2)
- The Future of FinanceДокумент30 страницThe Future of FinanceRenuka SharmaОценок пока нет
- Acct Statement - XX7977 - 21042023Документ13 страницAcct Statement - XX7977 - 21042023Ashish kumarОценок пока нет
- Od Intervention With Case StudiesДокумент13 страницOd Intervention With Case StudiesArushi Kaul75% (8)
- Designing Successful Go To Market SrategiesДокумент21 страницаDesigning Successful Go To Market Srategiessaurav_edu67% (3)
- Models of InternationaisationДокумент8 страницModels of InternationaisationShreyas RautОценок пока нет
- Impact of E-Commerce in The Philippines in The Time of PandemicДокумент9 страницImpact of E-Commerce in The Philippines in The Time of PandemicAngelica Beatriz L. Benecen100% (1)
- Settlement CaseДокумент14 страницSettlement CaseSsseven GODОценок пока нет
- Comparison of Consumer BehaviorДокумент15 страницComparison of Consumer BehaviorSubhayu MajumdarОценок пока нет
- Virtusa Pegasystems Engagement Success StoriesДокумент20 страницVirtusa Pegasystems Engagement Success StoriesEnugukonda UshasreeОценок пока нет
- Iii. The Sales Presentation Ben Feldman: The Package Concept RevisitedДокумент12 страницIii. The Sales Presentation Ben Feldman: The Package Concept RevisitedCherryber Urdaneta100% (2)
- With Effect From The Academic Year 2009-2010Документ2 страницыWith Effect From The Academic Year 2009-2010Joseph George KonnullyОценок пока нет
- Request For Redemption or Fund Switch - DES VersionДокумент2 страницыRequest For Redemption or Fund Switch - DES VersionAvillz Mar LeeОценок пока нет
- Internship Reflective ReportДокумент26 страницInternship Reflective ReportTan C Chi0% (1)
- Marketing Strategy of NestléДокумент27 страницMarketing Strategy of Nestléshami00992Оценок пока нет
- Eae 7501-Msc Entrepreneurship & Innovation Assignment Guidance NotesДокумент5 страницEae 7501-Msc Entrepreneurship & Innovation Assignment Guidance Notesknowledge factory0% (1)
- From Renter To OwnerДокумент21 страницаFrom Renter To OwnerAllen & UnwinОценок пока нет
- Mankiw10e Lecture Slides Ch04Документ43 страницыMankiw10e Lecture Slides Ch04Anggi YudhaОценок пока нет
- The Supply Chain Management Concept 1aДокумент20 страницThe Supply Chain Management Concept 1aMRK466100% (1)
- Accounting Quizbowl QuestionsДокумент7 страницAccounting Quizbowl QuestionsChabby ChabbyОценок пока нет
- Management 111204015409 Phpapp01Документ12 страницManagement 111204015409 Phpapp01syidaluvanimeОценок пока нет
- A Review On Julie's Manufactring SDN BHD - Chika OgbuehiДокумент8 страницA Review On Julie's Manufactring SDN BHD - Chika OgbuehiChika100% (2)
- Assignment 2Документ27 страницAssignment 2Amisha SinghОценок пока нет
- EY Further Expansion On Per 22 in New Transfer Pricing Audit GuidanceДокумент4 страницыEY Further Expansion On Per 22 in New Transfer Pricing Audit GuidanceRizky Hd-rОценок пока нет