Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
CHM113 CH 1 (Chang) Handouts
Загружено:
Hsiung Wei WeiИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CHM113 CH 1 (Chang) Handouts
Загружено:
Hsiung Wei WeiАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
10/20/2011
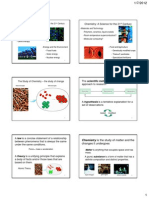
Chemistry: A Science for the 21st Century
Health and Medicine Sanitation systems
Chemistry: The Study of Change
Chapter 1
Surgery with anesthesia Vaccines and antibiotics Gene therapy Energy and the Environment Fossil fuels Solar energy Nuclear energy
2
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Chemistry: A Science for the 21st Century
Materials and Technology Polymers, ceramics, liquid crystals Room-temperature superconductors? Molecular computing?
Macroscopic
The Study of Chemistry
Microscopic
Food and Agriculture Genetically modified crops Natural pesticides Specialized fertilizers
3 4
10/20/2011
The scientific method is a systematic approach to research
A law is a concise statement of a relationship between phenomena that is always the same under the same conditions.
Force = mass x acceleration
A hypothesis is a tentative explanation for a set of observations
tested modified
5
A theory is a unifying principle that explains a body of facts and/or those laws that are based on them.
Atomic Theory
Chemistry In Action:
Primordial Helium and the Big Bang Theory In 1940 George Gamow hypothesized that the universe began with a gigantic explosion or big bang.
Chemistry is the study of matter and the changes it undergoes
Matter i anything that occupies space and M is hi h i d has mass. A substance is a form of matter that has a definite composition and distinct properties.
Experimental Support expanding universe cosmic background radiation primordial helium
liquid nitrogen
gold ingots
silicon crystals
10/20/2011
A mixture is a combination of two or more substances in which the substances retain their distinct identities. 1. Homogenous mixture composition of the mixture is the same throughout throughout. soft drink, milk, solder 2. Heterogeneous mixture composition is not g uniform throughout.
Physical means can be used to separate a mixture into its pure components.
magnet
cement, iron filings in sand
9
distillation
10
An element is a substance that cannot be separated into simpler substances by chemical means. 114 elements have been identified
82 elements occur naturally on Earth gold, aluminum, lead, oxygen, carbon, sulfur
32 elements have been created by scientists technetium, americium, seaborgium
11 12
10/20/2011
A compound is a substance composed of atoms of two or more elements chemically united in fixed proportions. Compounds can only b separated i t th i C d l be t d into their pure components (elements) by chemical means.
Classifications of Matter
lithium fluoride
quartz
dry ice carbon dioxide
13 14
A Comparison: The Three States of Matter
The Three States of Matter: Effect of a Hot Poker on a Block of Ice
gas
liquid
15
solid
16
10/20/2011
Types of Changes
A physical change does not alter the composition or identity of a substance. sugar di dissolving l i ice melting in water A chemical change alters the composition or identity of the substance(s) involved.
Extensive and Intensive Properties
An extensive property of a material depends upon how much matter is is being considered.
mass length volume
An intensive property of a material does not depend upon how much matter is is being considered. considered
density temperature
hydrogen burns in air to form water
17
color
18
Matter - anything that occupies space and has mass.
mass measure of the quantity of matter SI unit of mass is the kilogram (kg) 1 kg = 1000 g = 1 x 103 g weight force that gravity exerts on an object weight = c x mass
on earth, c = 1.0 on moon, c ~ 0.1
International System of Units (SI)
A 1 kg bar will weigh
1 kg on earth 0.1 kg on moon
19 20
10/20/2011
Volume SI derived unit for volume is cubic meter (m3) 1 cm3 = (1 x 10-2 m)3 = 1 x 10-6 m3 1 dm3 = (1 x 10-1 m)3 = 1 x 10-3 m3 1 L = 1000 mL = 1000 cm3 = 1 dm3 1 mL = 1 cm3
21
22
Density SI derived unit for density is kg/m3 1 g/cm3 = 1 g/mL = 1000 kg/m3 density = mass volume m d= V
A piece of platinum metal with a density of 21.5 g/cm3 has a volume of 4.49 cm3. What is its mass? m d= V m = d x V = 21.5 g/cm3 x 4.49 cm3 = 96.5 g
23 24
10/20/2011
A Comparison of Temperature Scales
Convert 172.9 0F to degrees Celsius. = 9 x 0C + 32 5 0F 32 = 9 x 0C 5
0F
K = 0C + 273.15
273 K = 0 0C 373 K = 100 0C
0F
= 9 x 0C + 32 5
32 0F = 0 0C 212 0F = 100 0C
25
5 x (0F 32) = 0C 9 0C = 5 x (0F 32) 9 0C = 5 x (172 9 32) = 78 3 (172.9 78.3 9
26
Chemistry In Action
On 9/23/99, $125,000,000 Mars Climate Orbiter entered Mars atmosphere 100 km (62 miles) lower than planned and was destroyed by heat. 1 lb = 1 N 1 lb = 4.45 N This is going to be the cautionary tale that will be embedded into introduction to the metric system in elementary school, high school, and college science courses till the end of time.
27
Scientific Notation
The number of atoms in 12 g of carbon: 602,200,000,000,000,000,000,000 6.022 6 022 x 1023 The mass of a single carbon atom in grams: 0.0000000000000000000000199 1.99 x 10-23 N x 10n
N is a number between 1 and 10 n is a positive or negative integer
28
10/20/2011
Scientific Notation
568.762 move decimal left n>0 568.762 = 5.68762 x 102 0.00000772 move decimal right n<0 0.00000772 = 7.72 x 10-6
Scientific Notation
Multiplication
1. Multiply N1 and N2 2. Add exponents n1 and n2 (4.0 x 10-5) x (7.0 x 103) = (4.0 x 7.0) x (10-5+3) = 2 28 x 10-2 = 2.8 x 10-1 8.5 x 104 5.0 x 109 = (8.5 5.0) x 104-9 = 1.7 1 7 x 10-5
Addition or Subtraction
1. Write each quantity with the same exponent n 2. Combine N1 and N2 3. The exponent, n, remains the same 4.31 x 104 + 3.9 x 103 = 4.31 4 31 x 104 + 0.39 x 104 = 0 39 4.70 x 104
Division
1. Divide N1 and N2 2. Subtract 2 S bt t exponents n1 and n2 t d
29
30
Significant Figures
Any digit that is not zero is significant 1.234 kg 606 m 0.08 L 4 significant figures Zeros between nonzero digits are significant 3 significant figures 1 significant figure Zeros to the left of the first nonzero digit are not significant
How many significant figures are in each of the following measurements?
24 mL 3001 g 0.0320 m3 6.4 x 104 molecules 560 kg 2 significant figures 4 significant figures 3 significant figures 2 significant figures 2 significant figures
If a number is greater than 1, then all zeros to the right of the decimal point are significant 2.0 mg 2 significant figures If a number is less than 1, then only the zeros that are at the end and in the middle of the number are significant 0.00420 g 3 significant figures
31
32
10/20/2011
Significant Figures
Addition or Subtraction
The answer cannot have more digits to the right of the decimal p point than any of the original numbers. y g 89.332 +1.1 90.432 3.70 3 70 -2.9133 0.7867 one significant figure after decimal point round off to 90.4 two significant figures after decimal point round off to 0.79
Significant Figures
Multiplication or Division
The number of significant figures in the result is set by the original g g number that has the smallest number of significant figures 4.51 x 3.6666 = 16.536366 = 16.5 3 sig figs round to 3 sig figs
6.8 112.04 = 0.0606926 = 0.061 2 sig figs round to 2 sig figs
34
33
Significant Figures
Exact Numbers
Numbers from definitions or numbers of objects are considered to have an infinite number of significant figures
Accuracy how close a measurement is to the true value Precision how close a set of measurements are to each other
The average of three measured lengths; 6.64, 6.68 and 6.70? 6.64 + 6.68 + 6.70 = 6.67333 = 6.67 = 7 3 Because 3 is an exact number
35
accurate & precise
precise but not accurate
not accurate & not precise
36
10/20/2011
Dimensional Analysis Method of Solving Problems Dimensional Analysis Method of Solving Problems
1. Determine which unit conversion factor(s) are needed 2. Carry units through calculation 3. 3 If all units cancel except for the desired unit(s) then the unit(s), problem was solved correctly. Conversion Unit 1 L = 1000 mL given quantity x conversion factor = desired quantity 1.63 L x given unit x desired unit given unit = desired unit 1000 mL = 1630 mL 1L 1.63 L x 1L L2 = 0.001630 mL 1000 mL
How many mL are in 1.63 L?
37
38
The speed of sound in air is about 343 m/s. What is this speed in miles per hour? conversion units meters to miles seconds to hours 1 mi = 1609 m 1 min = 60 s 1 hour = 60 min
343
1 mi 60 s m x x s 1609 m 1 min
60 min mi = 767 hour 1 hour
39
10
Вам также может понравиться
- Chmstry 123Документ229 страницChmstry 123Bxhsh HdhshsshОценок пока нет
- Blended-Learning-Plan-Form (Mathematics 7)Документ2 страницыBlended-Learning-Plan-Form (Mathematics 7)KarlzОценок пока нет
- The Study of Chemistry - The Study of ChangeДокумент6 страницThe Study of Chemistry - The Study of Changeasianpanda14Оценок пока нет
- Chem Chapter 1Документ38 страницChem Chapter 1Madison WalkerОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Chemistry The Study of ChangeДокумент60 страницChapter 1 Chemistry The Study of ChangeAbdelrahmanJamalОценок пока нет
- Chap 1Документ35 страницChap 1RF PopeXian100% (1)
- Chemistry: An Introduction To MatterДокумент27 страницChemistry: An Introduction To MatterMohd NubliОценок пока нет
- Kimia 1Документ44 страницыKimia 1hasan ashariОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1-Unit of MeasurementsДокумент60 страницChapter 1-Unit of MeasurementsNajma AqilahОценок пока нет
- CHEM 111-2: General Chemistry I: Instructor: Dr. Fatma Melis ÇağdaşДокумент50 страницCHEM 111-2: General Chemistry I: Instructor: Dr. Fatma Melis ÇağdaşjalepeОценок пока нет
- Chemistry: A Science For The 21 CenturyДокумент36 страницChemistry: A Science For The 21 CenturyCristian MitraОценок пока нет
- b7XVBu-GC - Chapter 1Документ26 страницb7XVBu-GC - Chapter 1Christella LuyeyeОценок пока нет
- ChemistryДокумент30 страницChemistryAravindОценок пока нет
- Chemistry LectureДокумент47 страницChemistry LectureDuchess DianalanОценок пока нет
- 2 MeasurementsДокумент32 страницы2 MeasurementsCarl Jervin ReyesОценок пока нет
- CHE1010 Lec 1&2Документ10 страницCHE1010 Lec 1&2Charlotte ChamaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1wДокумент26 страницChapter 1wShelley HernandezОценок пока нет
- Basic Principle of ChemistryДокумент31 страницаBasic Principle of ChemistrybybmaishanuОценок пока нет
- Units of MeasurementДокумент36 страницUnits of MeasurementHafiz HamidiОценок пока нет
- 1 Chemistry For Engineers Chemistry and Measurement 2023Документ38 страниц1 Chemistry For Engineers Chemistry and Measurement 2023Hanzly AurellanoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Study of ChangeДокумент36 страницChapter 1 Study of ChangeArlan BartolomeОценок пока нет
- Orca Share Media1581597155263Документ40 страницOrca Share Media1581597155263Richmond VillasisОценок пока нет
- Chemistry 1411Документ83 страницыChemistry 1411AliciaTorresОценок пока нет
- MODULES-IN-PHYSICAL-SCIENCE WithnyouuuДокумент10 страницMODULES-IN-PHYSICAL-SCIENCE WithnyouuuHesoyam HesoyamОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 MeasurementsДокумент77 страницChapter 1 MeasurementsESPALMADO, Dianne N.Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Matter & Energy AssignmentДокумент37 страницChapter 2 Matter & Energy Assignmentragingpheonix87Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Units of MeasurementДокумент23 страницыChapter 1 Units of MeasurementNurul Asyiqin JihanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ43 страницыChapter 1Romeo Charlie AlphaОценок пока нет
- Chemistry in Our LivesДокумент44 страницыChemistry in Our LivesmorganОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Intro To ChemistryДокумент47 страницChapter 1 Intro To Chemistrykumutha100% (1)
- Chemistry SM XI 2021-22Документ154 страницыChemistry SM XI 2021-22SHRUTI AGARWALAОценок пока нет
- CHEM 121 - General Chemistry Chapter 1Документ14 страницCHEM 121 - General Chemistry Chapter 1kingdom12828Оценок пока нет
- Unit One ChemistryДокумент31 страницаUnit One Chemistrybruck simenehОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 NotesДокумент5 страницChapter 1 NotesErin olinoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Chemistry The Study of ChangeДокумент62 страницыChapter 1 Chemistry The Study of ChangeDoom RefugeОценок пока нет
- 01 Lecture KMДокумент44 страницы01 Lecture KMUday Prakash SahuОценок пока нет
- Inogranic Chem 11TДокумент116 страницInogranic Chem 11T0.1hacker0123Оценок пока нет
- M1 IntroductionДокумент14 страницM1 IntroductionG02 - BALACANAO JHERICE A.Оценок пока нет
- Physical Quantities, Units and DimensionsДокумент15 страницPhysical Quantities, Units and DimensionsAmelia OwensОценок пока нет
- MeasurementДокумент61 страницаMeasurementHannah CorpuzОценок пока нет
- Brown Lemay Chap 1Документ38 страницBrown Lemay Chap 1Alex AlexanderОценок пока нет
- Chapter 01 Brown Reyes1Документ13 страницChapter 01 Brown Reyes1Shreyas BhargavОценок пока нет
- Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryДокумент57 страницSome Basic Concepts of ChemistryAshutosh KunduОценок пока нет
- Chemistry - A.A. 2021-2022Документ32 страницыChemistry - A.A. 2021-2022Ridwan MugdhaОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 Basic Concepts of Chemistry 1Документ33 страницыUnit 1 Basic Concepts of Chemistry 1naveedОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Chemistry The Study of ChangeДокумент62 страницыChapter 1 Chemistry The Study of ChangeFABIO DE LIMAОценок пока нет
- CHM 1045 Chapter 1 PrasadДокумент62 страницыCHM 1045 Chapter 1 PrasadBobОценок пока нет
- Class Xi MaterialДокумент316 страницClass Xi MaterialShlok MishraОценок пока нет
- Chemistry: The Study of ChangeДокумент24 страницыChemistry: The Study of ChangeAhamed AfshanОценок пока нет
- Lect 2 MeasurementsДокумент73 страницыLect 2 MeasurementsRogerine RoyОценок пока нет
- Chemistry: The Study of ChangeДокумент27 страницChemistry: The Study of Changejojo290125Оценок пока нет
- Physics Reviewer (First Quarter)Документ4 страницыPhysics Reviewer (First Quarter)Jaimarae SumalnapОценок пока нет
- Chemistry: The Study of ChangeДокумент28 страницChemistry: The Study of ChangeSoul Relaxation LabОценок пока нет
- Stoichiometry (Chemical)Документ71 страницаStoichiometry (Chemical)Ridhwan WokeyzОценок пока нет
- Physical QuantitiesДокумент16 страницPhysical QuantitiesLuis AndersonОценок пока нет
- AP Chemistry Notes - Chapter 1 Chemistry Notes - Chapter 1, 2, 3, & 4Документ31 страницаAP Chemistry Notes - Chapter 1 Chemistry Notes - Chapter 1, 2, 3, & 4Qises QiskaОценок пока нет
- 02 Atoms and The Atomic TheoryДокумент29 страниц02 Atoms and The Atomic TheoryBela JannahtiОценок пока нет
- 1 - Chemical CalculationsДокумент40 страниц1 - Chemical CalculationsHoney Nhassie Marie GonzagaОценок пока нет
- Chemistry OverviewДокумент33 страницыChemistry OverviewKarim HakimОценок пока нет
- AS 3600-2018 RC-PN Example 001Документ4 страницыAS 3600-2018 RC-PN Example 001Aashu chaudharyОценок пока нет
- Gann Time Price SquareДокумент5 страницGann Time Price Squareanudora0% (1)
- Free-Falling Object ExperimentДокумент9 страницFree-Falling Object ExperimentUgur ASİT100% (4)
- Linear and Nonlinear Propagation Characteristics of Multi-Gaussian Laser BeamsДокумент11 страницLinear and Nonlinear Propagation Characteristics of Multi-Gaussian Laser Beamsba mooОценок пока нет
- Physic Ss2 2019Документ4 страницыPhysic Ss2 2019sulayajannyОценок пока нет
- Rotor Flux Estimation Using Voltage Model of Induction MotorДокумент5 страницRotor Flux Estimation Using Voltage Model of Induction MotorBobby RinaldiОценок пока нет
- JFo - 3 - 4 ConvertДокумент32 страницыJFo - 3 - 4 ConvertKaltuma OmarОценок пока нет
- Self-Practice Coding QuestionsДокумент2 страницыSelf-Practice Coding QuestionsNguyen HoangОценок пока нет
- 9 - 28 - 0 - 0 - 40 - 5th Electrical DE&MPДокумент165 страниц9 - 28 - 0 - 0 - 40 - 5th Electrical DE&MPvijay kumar GuptaОценок пока нет
- C Sample Two Mark Question and Answer: 1) Who Invented C Language?Документ13 страницC Sample Two Mark Question and Answer: 1) Who Invented C Language?rajapst91% (11)
- Analog To DigitalДокумент46 страницAnalog To DigitalSaleem HaddadОценок пока нет
- Math 6 DLP 1 - Giving Meaning of Exponent and Base Giving The Value of Numbers Involving Exponent PDFДокумент9 страницMath 6 DLP 1 - Giving Meaning of Exponent and Base Giving The Value of Numbers Involving Exponent PDFZyreen Joy ServanesОценок пока нет
- Problem Set 3 (Solution)Документ5 страницProblem Set 3 (Solution)Mark AstigОценок пока нет
- GATE 2020 Online Test Series:: Civil EngineeringДокумент6 страницGATE 2020 Online Test Series:: Civil EngineeringAvinash JhaОценок пока нет
- Optimal Agricultural Land Use: An Efficient Neutrosophic Linear Programming MethodДокумент7 страницOptimal Agricultural Land Use: An Efficient Neutrosophic Linear Programming MethodScience DirectОценок пока нет
- Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Department of Mathematics MA11003 - Advanced Calculus Assignment - 1 Autumn 2020Документ1 страницаIndian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Department of Mathematics MA11003 - Advanced Calculus Assignment - 1 Autumn 2020Harsh GuptaОценок пока нет
- Deterministic Phase Retrieval: A Green's Function SolutionДокумент8 страницDeterministic Phase Retrieval: A Green's Function Solutionlednakashim100% (1)
- Syllabus Jan09 MAT183Документ2 страницыSyllabus Jan09 MAT183Mike ZakwanОценок пока нет
- Dosage Calculation: Key TermsДокумент30 страницDosage Calculation: Key TermsVijaОценок пока нет
- Summer Vacation Task HSD-2020-21 Viii & XДокумент5 страницSummer Vacation Task HSD-2020-21 Viii & XHimansu dasОценок пока нет
- GATE ECE Solved Paper - 2005Документ24 страницыGATE ECE Solved Paper - 2005Shashi KanthОценок пока нет
- Sek - Men.Keb. Tinggi Melaka (Malacca High School. Estd.1826)Документ19 страницSek - Men.Keb. Tinggi Melaka (Malacca High School. Estd.1826)Lee Shi HockОценок пока нет
- Prototyping Approach To Neuro-Fuzzy Speed Control of Trapezoidal Brushless DC MotorДокумент6 страницPrototyping Approach To Neuro-Fuzzy Speed Control of Trapezoidal Brushless DC MotorJournal of ComputingОценок пока нет
- Influence of Organizational Culture and Compensation On Employee Performance With Motivation Work As A Mediation Variable at Pt. Jasaraharja Branch RiauДокумент8 страницInfluence of Organizational Culture and Compensation On Employee Performance With Motivation Work As A Mediation Variable at Pt. Jasaraharja Branch RiauInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyОценок пока нет
- Standard Test Methods For Fire Tests of Building Construction and Materials E 119 - 07Документ22 страницыStandard Test Methods For Fire Tests of Building Construction and Materials E 119 - 07Frenzy BritoОценок пока нет
- Niterói, Volgograd and Trans-Tokyo Bay Steel Bridge Decks Abraham - Sanchez - Corriols - 2de2Документ135 страницNiterói, Volgograd and Trans-Tokyo Bay Steel Bridge Decks Abraham - Sanchez - Corriols - 2de2Miguel PerezОценок пока нет
- Hydrocyclones For Particle Size SeparationДокумент7 страницHydrocyclones For Particle Size SeparationJean DejardinОценок пока нет
- Jaime Sandoval Real EstateДокумент3 страницыJaime Sandoval Real EstateJaime R. SandovalОценок пока нет
- Full Download Ebook Ebook PDF Longitudinal Data Analysis by Donald Hedeker PDFДокумент41 страницаFull Download Ebook Ebook PDF Longitudinal Data Analysis by Donald Hedeker PDFsarah.steir690100% (42)