Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Surgery Study Guide
Загружено:
Amy WenigerИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Surgery Study Guide
Загружено:
Amy WenigerАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
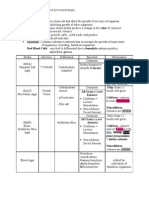
SUBCUTIULAR STICH ILEUS o No mechanical cause for impaired bowel motility o Causes= hypokalemia, intrabdominal infections, electrolyte abrnormalities,
opiods SBO o Common causes mechanical: adhesions, incarcerated hernias, IBD, caners o Functional= paralytic ileus LBO o Common mechanical causes= volvulus, diverticulitis/ischemic strictures, colorectal cancers o Functional= Ogilvies Syndrome (Colonic ileus) o Listen for high-pitched rushes or diminished bowel sounds BILIARY TRACT DISEASE o CHOLELITHIASIS o BILIARY COLIC/CHRONIC CHOLECYSTITIS Symptomatic cholelithiasis caused by stone blocking the neck of the cystic duct pain occurs as gallbladder contracts Post-prandial pain Similar episodes in the past o ACUTE CHOLECYSTITIS Stone impacted in the cystic duct leading to inflammation of the gall bladder gallbladder wall becomes thickened History of biliary colic/intermittent RUQ pain Look for potential fevers/chills Inflammation causes elevation of WBCs, Alk Phos (made in bile duct wall) may be elevated Ultrasound Findings= Gallbladder distended, stones present, wall thickening, pericholecystic fluid, sono murphys sign Pathology (help determine timing of disease process) Edema, mucosal changes, Inflammation o Choledocolithiasis stone in common bile duct which becomes impacted Look for jaundice (scleral icterus), acholic stools, urine LFTs elevated (esp bilirubin), Elevated Alk Phos (made in walls of common bile duct), WBCs Ultrasound dilated CBD indicates CBD stones Cholangiogram, Pre-operative ERCP o Cholangitis= choledocolithiasis with super infection of bile Superinfection of bile results in sepsis very high WBCs (20,000s), LFTs (total bili, LDH, AST, ALT elevations), Alk Phos; as patients become septic elevated BUN, creatinine and glucose results o Gall Stone Pancreatitis= choledocolithiasis with blockage of the pancreatic duct leading to inflammation of the pancreas Lab abnormalities of pancreatitis ( AST/ALT, amylase/lipase, WBCs) o Ultrasound Normal Gallbladder should be distended, smooth mucosa, no pericholecystic fluid o HIDA Scan Used when ultrasound is inconclusive
Look for non-filling of gall bladder Absence of duodenal filling indicates DBD stones ACUTE APPENDICITIS o Most common etiology of acute abdominal pain o Obstruction of the lumen of appendix by lymphoid hyperplasia or fecalith continued mucous production results in distension impaired venous return impaired arterial supplyischemiagangrene of appendix perforation peritonitis Plhegmon or abscess may occur instead of perforation Phlegmon = aggregation of inflammatory tissue o The pathophysiology of appendicitis is not uniform across ages. Thus, while appendicitis can occur (much less commonly) due to ischemic, infectious, or oncologic process, the overall prevailing mechanism is lumenal obstruction that causes proximal appendiceal inflammation and subsequent rupture. o + Obturator sign o + Psoas sign o Labs in appendicitis CBC elevated WBC (12-15), check Hgb/hematocrit ( seen in acute bleeding episode or cancer, hematocrit seen in dehydration), platelets (important preoperatively) BMP severe vomiting can cause abnormalities in Na, K, Cl, HCO3 BUN/creatinine ratio normal = 10/1 In dehydration BUN/Creatinine ratio= 20/1 Glucose= abnormally elevated in infections LFTs Should be normal acute appendicitis (LFTs should be elevated in acute hepatitis, choledocolithiasis, cholangitis, acute choleystitis) UA rules in or out kidney stones Look for RBCs in urine No tenderness on exam WBCs (look for pyelo, CVA tenderness on exam) b-hCg helps rule out ectopic pregnancy Amylase/Lipase help rule out pancreatitis o Imaging CT Scan-use IV & oral contrast Most appendixes come out of cecum between 2-6 oclock if you can find the cecum you can find the appendix Look for hyperemia in the wall, inflammation surrounding the appendix, fat stranding NOTE oral contrast does not enter the appendix b/c the appendix is OBSTRUCTED!! BARIATRIC SURGERY o BMI= weight (kg)/height (M)2 o Indications for surgery Patients qualify for bariatric surgery if BMI > 40 or BMI > 35 with comorbidities (diabetes, hypertension, sleep apnea) o Blodwork
o o
HbA1C, Thyroid function tests (to r/o hypothyroidism) lipids, LFTs, micronutrients (iron, B12, folate) Types of Surgeries Restrictive amount of food patient can eat (patient feels fuller faster, eats less) Gastric band Malabsorptive amt of calories/nutrients patient absorbs from foods Biliary pancreatic diversion Duodenal switch Combination Gastric Bypass more dramatic weight loss than seen with band Post Op Monitoring Monitor for leak o Look for tachycardia o Gastrgafin swallow can be used to look for leak/obstruction Clear liquids for 7-10 days Glucose control Monitor for PE tachycardia, hypoxia Monitor for dehydration
Вам также может понравиться
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Latin Eugenics in Comparative PerspectiveДокумент356 страницLatin Eugenics in Comparative PerspectivemafeОценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Stacey Waters CVДокумент5 страницStacey Waters CVapi-479651018Оценок пока нет
- PharmacyДокумент27 страницPharmacyJenilОценок пока нет
- Nebosh Exams Questions and Answers - Nebosh Question Paper 2021Документ4 страницыNebosh Exams Questions and Answers - Nebosh Question Paper 2021faceji67% (3)
- Reflection PaperДокумент7 страницReflection Paperapi-623973327Оценок пока нет
- 50 Maternal and Child NCLEX QuestionsДокумент14 страниц50 Maternal and Child NCLEX QuestionsShengxy Ferrer100% (2)
- Selective, Differential, & Enriched Media Lab ChartДокумент2 страницыSelective, Differential, & Enriched Media Lab ChartFrankiesgirl6yr100% (6)
- Using The Childrens Play Therapy Instrument CPTIДокумент12 страницUsing The Childrens Play Therapy Instrument CPTIFernando Hilario VillapecellínОценок пока нет
- KLP 5 - Nutrition Intake and MedicationДокумент4 страницыKLP 5 - Nutrition Intake and MedicationdzakyОценок пока нет
- Starlight ProgramsДокумент12 страницStarlight Programsllacara@nncogannett.comОценок пока нет
- Aquatics BrochureДокумент24 страницыAquatics BrochurethuronОценок пока нет
- 3f PDFДокумент4 страницы3f PDFYidne GeoОценок пока нет
- Owner's Manual: Ironman TRIAD TreadmillДокумент34 страницыOwner's Manual: Ironman TRIAD Treadmilljtaylor888Оценок пока нет
- Centrifugal ChillerДокумент24 страницыCentrifugal ChillerARUL SANKARANОценок пока нет
- BNMHGДокумент34 страницыBNMHGAnonymous lt2LFZHОценок пока нет
- PSC Question BankДокумент9 страницPSC Question BankFaisal qblp100% (29)
- 11th Bio Zoology EM Official Answer Keys For Public Exam Mhay 2022 PDF DownloadДокумент3 страницы11th Bio Zoology EM Official Answer Keys For Public Exam Mhay 2022 PDF DownloadS. TAMIZHANОценок пока нет
- Updated Nutrition Spreadsheet (With Workout Tracker)Документ54 страницыUpdated Nutrition Spreadsheet (With Workout Tracker)Kit LbjОценок пока нет
- Material Safety Data Sheet: AES-A-350-RBДокумент7 страницMaterial Safety Data Sheet: AES-A-350-RBSajidawan. OlineОценок пока нет
- Aeon 4000 SDSДокумент13 страницAeon 4000 SDSmarcos luqueОценок пока нет
- Health Information On The Internet: The Case of GreeceДокумент12 страницHealth Information On The Internet: The Case of GreecemaryОценок пока нет
- Internet Addiction Kids and The South Korean Govt Boot CampsДокумент5 страницInternet Addiction Kids and The South Korean Govt Boot Campslgheorma0Оценок пока нет
- Matter For PGDIPC Course PromotionДокумент1 страницаMatter For PGDIPC Course PromotionAnkur VasudevaОценок пока нет
- Arihant DRX Ascend Case Study PDFДокумент2 страницыArihant DRX Ascend Case Study PDFsaurav.martОценок пока нет
- Editable CULC Application FormДокумент4 страницыEditable CULC Application Formnniki9decОценок пока нет
- Form 1 AДокумент2 страницыForm 1 ARohit Jain100% (2)
- Know About Dengue FeverДокумент11 страницKnow About Dengue FeverKamlesh SanghaviОценок пока нет
- Secondary P.E. 10 Q3Документ9 страницSecondary P.E. 10 Q3Jayzi VicenteОценок пока нет
- Diet's CardДокумент8 страницDiet's CardJORGE ATRIANOОценок пока нет
- Pitbull StatementДокумент4 страницыPitbull StatementThe Citizen NewspaperОценок пока нет