Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Wilson Current Sourc1
Загружено:
prinxesparrowИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Wilson Current Sourc1
Загружено:
prinxesparrowАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Wilson current source
A Wilson current mirror or Wilson current source is a circuit configuration designed to provide a constant current source or sink. The circuit is shown in the image. It is named after George Wilson, KL an integrated circuit design engineer working for Tektronix. Rumour has it that Wilson came up with this configuration after being challenged to come up with a useful new circuit that used three active devices.
Circuit Analysis:
1. All transistors have the same current gain . 2. Q1 and Q2 are matched, so their collector currents are equal. Therefore, IC1 = IC2 (= IC) and IB1 = IB2 (= IB) ... (1) From the above equation we can see that if And the output current (assuming the base-emitter voltage of all transistors to be 0.7 V) is calculated as
If VCC is not stable, the output current will not be stable. Thus the circuit Base current of Q3 is given by,...(2) and emitter current by,... (3) From the schematic, it is evident that IE3 = IC2 + IB1 + IB2 ... (4) substituting for IC2, IB1 and IB2 from (1) in (4), IE3 = IC + 2.IB ... (5) so, substituting for IE3 from (3), rearranging,... (7) Current through R1 is given by, IR1 = IC1 + IB3 ... (8) But, IC1 = IC2 = IC Substituting for IC from (7) in (8) and since we get,... (9) Therefore, ... (10) And finally,... (11) does not act as a constant current source. In order for it to work as a constant current source, R1 must be replaced with a constant current source.
Advantages over other configurations:
This circuit has the advantage of virtually eliminating the base current mis-match of the conventional current mirror thereby ensuring that the output current IC3 is almost equal to the reference or input current IR1. It also has a very high output impedance.
Improvement:
Adding a fourth transistor to the Wilson current mirror improves its linearity at higher current levels. It accomplishes this by equalizing the collector voltages of Q1 and Q2 at 1 Vbe.This leaves the finite beta and voltage differences of each of Q1 and Q2 as the remaining unbalancing influences in the mirror.
Widlar current source
A Widlar current source is a modification of the basic two-transistor current mirror that incorporates an emitter degeneration resistorfor only the output transistor, enabling the current source to generate low currents using only moderate resistor values. The Widlar circuit may be used with bipolar transistors, MOS transistors, and even vacuum tubes. An example application is the 741 operational amplifier, and Widlar used the circuit as a part in many designs.
Analysis:
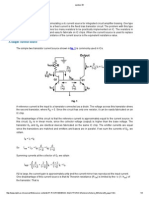
Widlar current source using bipolar transistors, where the emitter resistor R2 is connected to the output transistor Q2, and has the effect of reducing the current in Q2 relative to Q1. The key to this circuit is that the voltage drop across the resistor R2subtracts from the base-emitter voltage of transistor Q2, thereby turning this transistor off compared to transistor Q1. This observation is expressed by equating the base voltage expressions found on either side of the circuit in Figure where 2 is the beta-value of the output transistor, which is not the same as that of the input transistor, in part because the currents in the two transistors are very different.[8] The variable IB2 is the base current of the output transistor, VBE refers to base-emitter voltage. This equation implies (using the Shockley diode law)
where VT is the thermal voltage. This equation makes the approximation that the currents are both much larger than the scale currents IS1, IS2, an approximation valid except for current levels near cut off. In the following the distinction between the two scale currents is dropped,
although the difference can be important, for example, if the two transistors are chosen with different areas.
Design procedure with specified current:
To design the mirror, the output current must be related to the two resistor values R1 and R2. A basic observation is that the output transistor is in active mode only so long as its collector-base voltage is non-zero. Thus, the simplest bias condition for design of the mirror sets the applied voltage VA to equal the base voltage VB. This minimum useful value of VA is called the compliance voltage of the current source. With that bias condition, the Early effect plays no role in the design.
Output impedance:
An important property of a current source is its small signal incremental output impedance, which should ideally be infinite. The Widlar circuit introduces local current feedback for transistor. Any increase in the current in Q2 increases the voltage drop across R2, reducing the VBE for Q2, thereby countering the increase in current. This feedback means the output impedance of the circuit is increased, because the feedback involving R2 forces use of a larger voltage to drive a given current. Output resistance is found using a small-signal model for the circuit, shown in Figure. Transistor Q1 is replaced by its small-signal emitter resistance rE because it is diode connected. Transistor Q2 is replaced with its hybrid-pi model. A test current Ix is attached at the output.
Вам также может понравиться
- Power Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsОт EverandPower Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (2)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1От EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Рейтинг: 2.5 из 5 звезд2.5/5 (3)
- Common Emitter Amplifier: S.No Name of The Component/ Equipment Specifications QtyДокумент0 страницCommon Emitter Amplifier: S.No Name of The Component/ Equipment Specifications Qtyagama1188Оценок пока нет
- The Common Emitter Amplifier CircuitДокумент11 страницThe Common Emitter Amplifier CircuitJennifer Kennedy100% (1)
- Gainclone CompositeДокумент7 страницGainclone CompositeDragan LalkovicОценок пока нет
- High Speed Design Techniques PDFДокумент416 страницHigh Speed Design Techniques PDFbolermОценок пока нет
- XP 620Документ8 страницXP 620Far PilonОценок пока нет
- Constant Current BiasДокумент36 страницConstant Current BiasKRISHNAVINOD100% (6)
- Tripath TA2024 - Class T Digital Audio 2x15W Amplifier - Mod - Fenice 20Документ6 страницTripath TA2024 - Class T Digital Audio 2x15W Amplifier - Mod - Fenice 20igor_bruniОценок пока нет
- UPF Design and Power ManagementДокумент7 страницUPF Design and Power ManagementPrabhudatta MohantyОценок пока нет
- Capacitor Less LdoДокумент11 страницCapacitor Less LdoantharmukiОценок пока нет
- EC8453-Linear Integrated Circuits Department of ECE 2018-19Документ26 страницEC8453-Linear Integrated Circuits Department of ECE 2018-19senОценок пока нет
- ClassДокумент35 страницClassSrikkanth RamachandranОценок пока нет
- EEC-501 NOTES: INTEGRATED CIRCUITSДокумент160 страницEEC-501 NOTES: INTEGRATED CIRCUITSpcjoshi02Оценок пока нет
- Ec8453-Linear Integrated Circuits-1451692048-Lic Notes Ec8453Документ131 страницаEc8453-Linear Integrated Circuits-1451692048-Lic Notes Ec8453Dr.T.sivakami biherОценок пока нет
- Diffrential Amplifier 2Документ5 страницDiffrential Amplifier 2jaigodaraОценок пока нет
- Current Mirrors: Basic BJT Current MirrorДокумент8 страницCurrent Mirrors: Basic BJT Current MirrorjagruthimsОценок пока нет
- Lecture - 10:: Biploar TransistorДокумент21 страницаLecture - 10:: Biploar TransistorGEORGEОценок пока нет
- ANALOG ELECTRONICS: Amplifier Classifications and Biasing TechniquesДокумент15 страницANALOG ELECTRONICS: Amplifier Classifications and Biasing TechniquesRenuka SarmishtaОценок пока нет
- Bipolar Transistor Biasing PDFДокумент11 страницBipolar Transistor Biasing PDFAliza TariqОценок пока нет
- Module2a BEEДокумент16 страницModule2a BEEmd hasanОценок пока нет
- Analogue Electronic Design Module E EEE2039 / EEE2026 / EEE2042Документ36 страницAnalogue Electronic Design Module E EEE2039 / EEE2026 / EEE2042Arvish RamseebaluckОценок пока нет
- الفصل 2tДокумент23 страницыالفصل 2tmustafaasaad020Оценок пока нет
- Power Electronics محاضراتДокумент159 страницPower Electronics محاضراتHasan Al-asadiОценок пока нет
- EC6404 UwДокумент354 страницыEC6404 UwRamarao GudeОценок пока нет
- Bypassed Emitter Resistor CircuitДокумент6 страницBypassed Emitter Resistor CircuitSandesh AdhikaryОценок пока нет
- Ecd Lab 6Документ8 страницEcd Lab 6Muhammad HamzaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Msbte Asked QuestionsДокумент10 страницChapter 3 Msbte Asked Questionsrutu surve (Ru.)Оценок пока нет
- 1-4 Coen 309Документ20 страниц1-4 Coen 309mahmoud sadiqОценок пока нет
- LIC Lecture 3-Current Sources As Active Loads and Voltage Sources MaterialsДокумент4 страницыLIC Lecture 3-Current Sources As Active Loads and Voltage Sources MaterialsMadhavan SamОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2Документ74 страницыLecture 2anushreewankhade35Оценок пока нет
- Word Bipolar TransistorДокумент9 страницWord Bipolar TransistorAliza TariqОценок пока нет
- EE315 Lecture2 DiffMultAmp V 301Документ44 страницыEE315 Lecture2 DiffMultAmp V 301Abdulaziz Al-ShamanОценок пока нет
- Measuring Transistor CharacteristicsДокумент6 страницMeasuring Transistor CharacteristicsAhmed SalehОценок пока нет
- Common Emitter Amplifier Circuit BiasingДокумент10 страницCommon Emitter Amplifier Circuit Biasingjain_arvind20027119Оценок пока нет
- 20013122-034-EDC Lab Manual#10Документ7 страниц20013122-034-EDC Lab Manual#10Usama MughalОценок пока нет
- MCQ in DC Biasing - BJTsДокумент6 страницMCQ in DC Biasing - BJTsPaolo PerezОценок пока нет
- A Bipolar Junction TransistorДокумент29 страницA Bipolar Junction Transistor76697669Оценок пока нет
- ICL8038 Linear Sweep Function Generator CCTДокумент2 страницыICL8038 Linear Sweep Function Generator CCTian_new100% (1)
- Experiment 5Документ5 страницExperiment 5dummy008Оценок пока нет
- Power ElectronicДокумент10 страницPower Electronickalyan mondalОценок пока нет
- Common Emitter AmplifierДокумент11 страницCommon Emitter AmplifierZnevba Quintano100% (1)
- Iare - Ica - Lecture - Notes EeeДокумент128 страницIare - Ica - Lecture - Notes EeeAishwarya R100% (1)
- Current SourceДокумент6 страницCurrent SourceArangulavan ShanmugamОценок пока нет
- Current SourceДокумент3 страницыCurrent SourceNirmal Kumar PandeyОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 BJT AmplifiersДокумент13 страницChapter 6 BJT AmplifiersCamilleОценок пока нет
- Differential Amplifier CircuitДокумент19 страницDifferential Amplifier Circuitbbwx4114Оценок пока нет
- BJT ReportДокумент15 страницBJT Reportالزهور لخدمات الانترنيتОценок пока нет
- Q4: Differential AmplifierДокумент5 страницQ4: Differential Amplifiersrikanthpatel132Оценок пока нет
- BJT Circuits - Basic Electronics GuideДокумент55 страницBJT Circuits - Basic Electronics GuideNenad Stamenović100% (1)
- CE Amp Circuit GuideДокумент12 страницCE Amp Circuit GuideAffo AlexОценок пока нет
- Module 3Документ10 страницModule 3Joseph JohnОценок пока нет
- APP Elec II CH - 2Документ25 страницAPP Elec II CH - 2Bizuayehu MamuyeОценок пока нет
- EE 230 - Analog Lab - 2021-22/I (Autumn) Experiment 2: DC Power SupplyДокумент5 страницEE 230 - Analog Lab - 2021-22/I (Autumn) Experiment 2: DC Power SupplySruthiОценок пока нет
- Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTS) : Chapter No. 04Документ58 страницBipolar Junction Transistors (BJTS) : Chapter No. 04munazarОценок пока нет
- 8- Bipolar Junction TransistorДокумент38 страниц8- Bipolar Junction TransistorShahnail MemonОценок пока нет
- Common Emitter Curves:: BE 1 B CEДокумент4 страницыCommon Emitter Curves:: BE 1 B CEHarish KumarОценок пока нет
- Analog Fault DerivationДокумент89 страницAnalog Fault DerivationSachidananda SwarОценок пока нет
- Baki Ali Neft MəktəbiДокумент18 страницBaki Ali Neft MəktəbiFerid AslanliОценок пока нет
- BJT Written Report Group 8Документ11 страницBJT Written Report Group 8Jayvee GusenalemОценок пока нет
- A Buad Power SectionДокумент7 страницA Buad Power SectionSamОценок пока нет
- VTU Notes Basic ElectronicsДокумент22 страницыVTU Notes Basic ElectronicsCicira BОценок пока нет
- Electronic Semiconductor: Conductivity ModulationДокумент14 страницElectronic Semiconductor: Conductivity ModulationSachin PoriaОценок пока нет
- Transistor BiasingДокумент6 страницTransistor Biasingengineer.chiranjitОценок пока нет
- Study of Voltage Gain and Frequency Response of CC AmplifierДокумент4 страницыStudy of Voltage Gain and Frequency Response of CC AmplifierBinita SedhaiОценок пока нет
- SEPIC Converter Design Document: Ndsu, Ece 637Документ16 страницSEPIC Converter Design Document: Ndsu, Ece 637hismarcheОценок пока нет
- CTRL F GodДокумент13 страницCTRL F GodNichole BalagatОценок пока нет
- Icom Ic A110Документ38 страницIcom Ic A110radioclubcopiapoОценок пока нет
- Syllabus - DigitalElectronics and MicroprocessorДокумент2 страницыSyllabus - DigitalElectronics and Microprocessorrockin_ravi_vitОценок пока нет
- CPE/EE 427, CPE 527 VLSI Design I Sequential Circuits: - Combinational Logic - Sequential LogicДокумент25 страницCPE/EE 427, CPE 527 VLSI Design I Sequential Circuits: - Combinational Logic - Sequential LogicKamal Kumar Kalra0% (1)
- Courses in Electrical Engineering: Digital Electronics Chapter Six: Combinatory LogicДокумент29 страницCourses in Electrical Engineering: Digital Electronics Chapter Six: Combinatory LogicNGOUNEОценок пока нет
- Compre AДокумент3 страницыCompre Ak.b.aditya reddyОценок пока нет
- High-efficiency 3A step-down converter for 4.75-40V inputsДокумент1 страницаHigh-efficiency 3A step-down converter for 4.75-40V inputsMototolea CatalinОценок пока нет
- VLSI I - V CharacteristicsДокумент46 страницVLSI I - V CharacteristicsMALATHI .LОценок пока нет
- Low Noise Amplifier Basics: by V. M. García-ChocanoДокумент4 страницыLow Noise Amplifier Basics: by V. M. García-ChocanoPranjal Jalan100% (1)
- Ami Microproject FinalДокумент15 страницAmi Microproject Finalvivekspatil2005Оценок пока нет
- Sony EF29M31Документ8 страницSony EF29M31Rodolfo ArosemenaОценок пока нет
- LD Didactic OP-AMP Com3 ManualДокумент91 страницаLD Didactic OP-AMP Com3 ManualYohannes FekaduОценок пока нет
- Ece 32 Lab 4Документ24 страницыEce 32 Lab 4caryl gadianОценок пока нет
- Krell KAV Sterophile ReviewДокумент11 страницKrell KAV Sterophile ReviewDRF254Оценок пока нет
- NCP1050, NCP1051, NCP1052, NCP1053, NCP1054, NCP1055 Monolithic High Voltage Gated Oscillator Power Switching RegulatorДокумент25 страницNCP1050, NCP1051, NCP1052, NCP1053, NCP1054, NCP1055 Monolithic High Voltage Gated Oscillator Power Switching RegulatorArie DinataОценок пока нет
- Weekend VHF Uhf Power AmplifierДокумент5 страницWeekend VHF Uhf Power AmplifierEm GomezОценок пока нет
- Operational AmplifierДокумент10 страницOperational AmplifierSalman AliОценок пока нет
- April 2003 Ray Marston - Understanding and Using OTA Op-AmpsДокумент5 страницApril 2003 Ray Marston - Understanding and Using OTA Op-AmpsMeatheadMerlin100% (1)
- Constant Volume FET Amplifier CircuitДокумент5 страницConstant Volume FET Amplifier CircuitdmprescottgОценок пока нет
- 8086 Final ProjectДокумент30 страниц8086 Final ProjecttiggafputuhsОценок пока нет
- ECE351 April 11'Документ8 страницECE351 April 11'Mirza DanishОценок пока нет
- General block diagram of AK19Pro TV chassisДокумент40 страницGeneral block diagram of AK19Pro TV chassisAdam LiviuОценок пока нет
- A Compendium of Blog Posts On Op Amp Design Topics: by Bruce TrumpДокумент37 страницA Compendium of Blog Posts On Op Amp Design Topics: by Bruce TrumpJustine ManningОценок пока нет
- Digital CMOS IC DesignДокумент44 страницыDigital CMOS IC DesignAnkur PatelОценок пока нет