Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
Загружено:
Vignesh KumarИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
Загружено:
Vignesh KumarАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
Infrastructure Sketch Solid Features Surfaces Assembly Design 2D Drawing
Design Table & Equation
A- 1
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
User Interface
File Name
Menu bar (all commands) Feature Manager (to switch the layout of toolbars) Folder for surfaces (3 hidden inside) Folder for solids (one visible inside) Lights on model
General
Geometry area/ Working area
Toolbars (commonly-used commands only)
Dimmed features (hidden)
Specification Tree (all features stored in historical order)
Version 1- May07
Global coordinate (never be changed)
A- 2
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
General
Type of Documents
The common documents are: A) A part document (. sldprt) , which contains information how the model is built
B) An assembly document (.sldasm), which contains the relative positions of components
C) A drawing document (.slddrw), which can be a part drawing or an assembly drawing
A
C B
A- 3
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Display Settings
To improve the 3D surface accuracy: Select Tools->Options... on the menu bar, then open the tab page Document Properties Then Select Image Quality Increase the value for HLR/HLV resolution
General
To change the background color of the geometry area:
Select Tools->Options... on the menu bar, then open the tab page System Options Then Select Colors Change the colors of Viewpoint Background , Top
Gradient Color & Bottom Gradient Color
A- 4
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
General
Change the view with the mouse
A. Rotating enables you to rotate the model around a point. Click and hold the middle mouse button, then drag the mouse. Panning enables you to move the model on a plane parallel to the screen. Press and hold Ctrl key, then click and hold the middle mouse button, then drag the mouse. Zooming enables you to increase or decrease the size of the model. Press and hold Shift key, then click and hold the middle button, then drag the mouse up or down.
Middle button
B.
C.
A- 5
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Sketch
Create a Sketch
Build a Sketch:1. Click Sketch Icon
2.
Select a plane or a planar face
3.
Draw a profile (with lines, curves and/or centerlines)
4.
Add geometrical constraints (relations)
5.
Add dimensional constraints & modify the values
Click Exit Sketch icon
6.
A- 6
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Sketch
Toolbars in sketch
Project external curves/sketches/edges onto the active sketch
Get the intersection curve between external curves/ sketches/edges/faces and the active sketch plane
A- 7
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Sketch
Construction Geometry
Construction geometry is created within a sketch to aid in profile creation. Only standard geometry will be used for creating solids or surfaces (Fig.1) Construction geometry is shown in dashed format. To convert an element into a construction element, select it and activate the option for construction. You can also toggle any construction elements from construction to standard by deselecting the option.
Construction geometry
Fig.1
A- 8
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Sketch
Constraining the sketch
Dimensional Constraints (click the icon, then select the element(s)) Geometrical Constraints (multi-select the two elements by pressing CTRL key and click the icon)
Length Distance
Perpendicularity Horizontal/Vertical Concidence Tangency Symmetry (multi-select the elements on the both side and then select the centerline)
Angle
Radius/Diameter Remark: To discontinue the command, click the icon again. You can also create constraints with other sketches and 3D elements out of the sketch
To show or hide all geometrical constraints on the screen, select View / Sketch Relations A- 9
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Sketch
Color and Diagnostic
1. 2. 3. Blue: Under-constrained Black: Fixed/Fully constrained Red: Over-constrained Case1
Case2
Only case 1 & 2 are allowable. For case 3, you must fix the error before quitting the sketch mode, otherwise a warning message will pop-out and you cannot continue until the error is fixed.
Size dimensions and location dimensions have been fully defined
Case3
One dimension is redundant
A- 10
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Sketch
View Orientation
By default, the screen is parallel to the sketch support. To making constraints between the sketch geometry and the 3D element, you may need to rotate the model into a 3D view. To return the default orientation, press space key on the keyboard to activate the menu of orientation, and then select Normal to (the viewpoint normal to the sketch plane)
We can create a distance constraint between the circle centre and the solid edge
A- 11
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Solids
Solid Modeling
Feature-Based Solid Modeling
Sketch
Extrude
Hole Fillet
Parent and Children Relation
If deleting Hole, we get:
If deleting Fillet, we get:
If deleting Extrude, we get:
A- 12
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Solids
Limit Type
Types of limit are :
A
A B C D E F G H
B E E
surface
A plane
surface Solid (body)
F
A- 13
Version 1- May07
G
Extrude in both directions
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Solids
Extrude
A. B. Extruded Boss/Base (material added by extruding a sketch) Extruded Cut (material removed by extruding a sketch)
A
By default, extrusion start from the sketch; but it can also start from the offset direction from the sketch Define the depth by different modes, e.g. dimension, up to next, through all, up to surface You can define the extrusion direction by selecting a datum plane, a line, a planar surface, and a straight solid edge.
Extrude in opposite direction Define wall thickness (optional) Define the region for Crossed profile
Written by Dickson Sham
A- 14
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Solids
Revolve
A. B. Revolved Boss/Base (material added by rotating a sketch) Revolved Cut (material removed by rotating a sketch)
A
Centerline
LINE
You can change the mode to Two-Direction or Midplane
You need to draw another straight line along the centerline so that the profile is closed A- 15
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Solids
Sweep
A. B. Swept Boss/Base (material added by sweeping a profile along a path) Cut-Sweep (material removed by sweeping a profile along a path)
A
Profile Control
- Follow Path keeping the angle value between the sketch plane used for the profile and the tangent of the path
- Keep Normal Constant
Sweeping the profile while the profiles normal is unchanged Path Profile
A- 16
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Solids
Loft
A. Lofted Boss/ Base (material added by sweeping one or more planar section curves along one or more guide curves Cut- Loft (material removed in the same way)
B.
A
Section 1
Make the loft tangent to the connecting faces on start/ finish ends
B
You can drag to change the closing point (blue point)
Section 2
- You can use an additional guide curve to control sweeping path
If sections do not have the same number of vertices, ratio coupling will be used by default
Section 3
A- 17
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Hole
A. B. Simple Hole (circular material removed from the existing solid); Hole Wizard Several types of holes are available: Simple, Tapered, Counterbored, Countersinked, Pipetap)
Solids
Click here to define the position of the hole
Recall the dimensions for standard screws
Define the depth of the hole
A- 18
Version 1- May07
You can add Dimensional relations between the hole center and the solid edges
Written by Dickson Sham
Not for commercial use
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Solids
Fillets
Fillet (creating a curved face of a constant or variable radius
that is tangent to, and that joins, two faces.)
Click to select the edge
Constant Radius
Variable Radius
Face to face
All round
Tangent Propagation: a fillet is applied to the selected edge and all edges tangent to the selected edge
The tangent edges are also highlighted by the system, according to Tangent Propagation
Without Setback
With Setback
A- 19
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Chamfer
Chamfer (removing & adding a flat section from a selected edge to create a beveled surface between the two original faces common to that edge.)
Solids
Length1
Two Dimensioning Modes for Edges
Angle
For Vertex
Length2 Length1
A- 20
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Solids
Draft
Draft (adding or removing material depending on the draft angle and the pulling direction)
Remark: Neutral plane always keeps unchanged after a draft is created Top face as neutral plane
Neutral Plane
Pulling direction
Case 1
Case 2
Side faces to draft
Bottom face as neutral plane
Version 1- May07
A- 21
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Solids
Other Features
Shell (empty a solid while keeping a given thickness on its sides)
Face to remove Wall thickness
Rib (create a wall by extending an open profile up to limiting faces)
Accepted
Accepted
Version 1- May07
A line with two ends, which are not touching solid faces
A- 22
The rib always touches the solid faces, not matter how the faces are changed / moved.
Written by Dickson Sham
Not for commercial use
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Reference Geometry
Reference Geometry
Select insert / Reference Geometry, then select
Reference
Select a line and a point Offset the reference plane up to a point Offset by value / Rotate by value Select a curve and a point Select a surface and a point
A- 23
Version 1- May07
Obtain the axis of a cylindrical surface
Written by Dickson Sham
Not for commercial use
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
3D Sketch
3D Sketch (Draw a sketch in 3D space; you dont need to create a plane before creating a 3D sketch)
Curves
Build a 3D Sketch:Click 3D Sketch Icon Draw a profile (with lines, curves and/or axis) (Remark: if you switch the viewpoint to Front View, the sketch plane will be Front Plane; similar for other viewpoints) (Remark: 3D sketch can be a non-planar curve) Add geometrical constraints (relations) Add dimensional constraints & modify the values Click 3D Sketch icon again to exit
This is a 3D sketch
A- 24
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Curves
Projected Curve
Sketch onto Face(s) (project a sketch onto a face. The projection can only be along the normal of the sketch)
Along the normal of the sketch
Limitations:
(1) Only planar sketches can be projected (2) You cannot select other projection direction than the normal of the sketch
You can project it onto a face of a surface or a solid
Sketch onto Sketch (create a curve resulting from the intersection of the extrusion of two curves. )
A 3D resultant Curve
The two extruded surfaces will not be created after this command
A- 25
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Curves
Helix Curve
Insert / Curve / Helix/Spiral
Pitch 3 ways to define a helix: 1) Pitch and revolution
2) Height and revolution Draw a circle on a sketch 3) Pitch and Height
Height
With Taper (optional)
Spiral Curve
Define Pitch and Revolution
Draw a circle on a sketch
A- 26
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Curves
Composite Curve
Insert / Curve / Composite Simply select the broken curves /edges and click ok to join them as one.
(A composite curve is then created, representing this group of curves/edges)
Curve through reference points
Cannot define the direction of tangency Control point Control point Control point
Create a 3D Spline by defining the control points
Limitation: Cannot define the direction of tangency at a control point.
Control point
If you need to control the direction, use 3D sketch
A- 27
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Surfaces
Extrude
Extrude (create a surface by extruding a profile along a given direction)
If the profile is planar, the direction will be its normal by default. But you can change it to other direction.
Revolve
Revolve (create a surface by revolving a planar profile about an axis)
Remark: The axis must be a straight line
A- 28
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Surfaces
Sweep
Sweep (create a surface by sweeping out a profile along a path)
Profile
Options Profile Orientation Additional Guide Curves Start /End Tangency
Path
Loft
Loft (create a surface by sweeping two or more section curves along an automatically computed or user-defined spine. The surface can be made to respect one or more guide curves. ) Options Additional Guide Curves Start /End Tangency Centerline A- 29
Version 1- May07 Written by Dickson Sham
Not for commercial use
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Surfaces
Offset
Offset (create a surface, or a set of surfaces, by offsetting an existing surface, or a set of surfaces)
Remark: if Offset value = 0, you can duplicate the selected surface
Fill
Fill (create a surface to fill the opening among a number of boundary segments) We can specify the desired continuity type between any selected support surfaces and the fill surface (Point or Tangent continuous)
The four points must be tangent-continuous
A- 30
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Surfaces
Trim Surface
Standard Trim (split a surface by means of a trim tool. The trim tool can be a surface or a sketch)
Trim Tool ( always keeps unchanged)
Result by Standard Trim Original
Mutual Trim (trim two or more surfaces)
Piece to keep
Trim by a sketch Result by Trim
Pieces to keep
A- 31
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Untrim - Surface
UNtrim (patch surface holes and external edges by extending an existing surface along its natural boundaries)
Surface untrim, select both left edges and the inner edge. Under Options, select Connect endpoints.
Surfaces
Surface untrim, select the face. Under Options, select All edges. All edges are extended to their natural boundaries.
OR
Knit - Surface
Knit (join surfaces as one element)
Version 1- May07
The two original surfaces A- 32 are hidden; a Knit surface is created Not for commercial use
REMARK: If the resultant surface hasnt any open ends, the enclosed volume can be transformed into a solid
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Surfaces
Surface- Fillets
Fillet (creating a curved face of a constant or variable radius
that is tangent to, and that joins, two surfaces.) Constant Radius Variable Radius Face to face All round
Same as Solid
Tangent Propagation: a fillet is applied to the selected edge and all edges tangent to the selected edge Without Setback A- 33
Version 1- May07
With Setback
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Surfaces
Extend (Surface only)
Extend the whole Surface / the surface from an edge
Click the face
The extrapolated surface is joined with the original surface as one Click the edge
Extend by Curvature Trend
Extend Surface along the tangential direction
A- 34
Version 1- May07
This will be a straight edge
Written by Dickson Sham
Not for commercial use
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Surfaces
Draft Analysis
Draft Analysis (analyze the draft angle on a surface/ a group of surfaces) STEPS: 1. Select Tools / Draft Analysis on the menu bar 2. Select a Direction as Direction of Pull 3. Enter a value as A (Angle), e.g 3 deg 4. Click Calculate icon If the big surface has no undercut, it should either all Green or all Red. Green: draft > 3deg Yellow: -3deg< draft <3deg Red: draft < -3 deg
Positive draft Negative draft Direction of Pull
Parting surface/plane
A- 35
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Solids + Surfaces
Cut Solid (with Surface)
Cut with Surface (split a solid with a plane or surface )
Thicken Surface
Thick Surface (add material to a surface in two opposite directions or in one direction)
A- 36
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Pattern /Mirror
Transformation (Solid/ Surface)
Features to Pattern - Select Hole1 & Fillet1 on the tree Bodies to Pattern - Select the solid body
Faces to Pattern - Select all faces of the hole
Instance to skip - Select the bad instance to skip A- 37
Version 1- May07
3 instances skipped
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Transformation (Solid/ Surface)
Translate, Rotate, Mirror, Scale
Select Insert/Features/ Move/Copy, then select Translate or Rotate
These commands are also valid for surfaces
Translate Rotate
Select Insert/Features/ Pattern/Mirror, then select Mirror
Select Insert/Features/ Scale
Mirror
Uniform Scale
A- 38
Version 1- May07
X-Y-Z Individual Scale
Written by Dickson Sham
Not for commercial use
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Face - Replace
Face - Replace (a Boolean operation combining a surface with a body. This capability adds or removes material by modifying the surface of the solid.)
Add a surface on top
Solids + Surfaces
Original Solid
The solid face is replaced; Material is added inside the cover surface
Face - Move
Face Move (offset, translate, and rotate faces and features directly on solid or surface models. )
Original Boss
Offset The radius of the curved face increases
A- 39
Version 1- May07
Translate The radius of the curved face remains the same.
Rotate
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Assembly
Assembly Design
An assembly stores a collection of components (parts or sub assemblies). The file extension is .sldasm.
Main Assembly
Part
Sub-assembly
Parts belonging to Sub-assembly
Constraints among the parts of sub-assembly Constraints between the part (base) and the sub-assembly
A- 40
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Assembly
Create a New Assembly
Create a New Assembly by: - Select File /New / Assembly
Insert existing components
Click Insert Component icon Select the file of the component Then press Enter key to complete (the component will be fixed at the assembly origin) Or Click on an empty space in the geometry area (the component will be placed at that location but it is still free-to-move) A- 41
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Move components
Upper Assembly is activated
Component being moved
Assembly
Remark: (1)You can only move the components of the active assembly The base is deactivated (2) To activate an assembly, right-click on it and then select Edit Assembly
Instant Simulation
Their axes are coincided
Drag the bucket by mouse
The base is fixed A- 42
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Assembly
Constraints between components
Click the icon Mate to define the constraints between two components
To align the axis onto another axis, select the corresponding circular faces and then use concentric mate A- 43
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Assembly
Interference check
Click Interference Detection icon Click Calculate icon Check the result on the list Press Esc key on the keyboard to exit
Interference result
The overlapped portion is highlighted A- 44
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
2D Drawing
Part /Assembly Drawings
We can create a 2D drawing from a part or an assembly. They have the parentand-child relationship; 3D model is the parent and the drawing is his child. If the 3D model is changed, the drawing will be changed automatically. The file extension of Solidworks drawings is *.slddrw, no matter it is a part drawing or an assembly drawing. Same as the assembly file, the drawing file cannot be opened properly if the system cannot locate the part/assembly file. Wherever when we open the drawing file, the system will try to locate the parent part/assembly file to update all the views. A- 45
Version 1- May07
It is unidirectional arrow; 3D can change 2D, but not vice versa
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
2D Drawing
Create Views
To create a 2D drawing:Select File/New on the menu Click Drawing and then OK Select a template, e.g. A-4 Landscape Click Browse, the select a part /assembly file Then Select Single View or Multiple Views (Single view create views one by one and we can see the preview; Multiple Views create many views at one time by highlighting the view icons below) If you want to scale down the view to fit it onto the paper, you can use Custom size. But generally, we prefer using a bigger paper to making the model views smaller.
To change the properties of the 2D drawing:Right-click on the paper and then select Properties We can now change the paper size and also change the projection method. (By default, First Angle projection is used. First Angle projection is commonly used in China, but Third angle projection is used in United states and Taiwan.) (Remark: After the projection method is changed, all existing views will be updated correspondingly) A- 46
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
2D Drawing
Create Views
To remove all tangent edges on a view:
-Right-Click on the view -Select Tangent Edge/ Tangent Edges Removed
To add or remove curves on a view:
(For dependent curves, projected from 3D) -We can only hide the curve that we dont want to see. We cannot delete it. -To hide the curve, right-click on the view and then select Hide edge then select the curve
(For independent curves, created on the view) - Simply select and delete it.
To show hidden edges on a view:
Single Click on the view Select Hidden Lines Visible on the pop-up window on the left
To create a section view:
-Double-click the parent view -Select insert/ Drawing View / Section on the menu bar -Pick two points to define the mirror line
A- 47
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
2D Drawing
Dimensioning
To Create Dimensions on a view:Click Smart Dimension icon Select an entity / entities to dimension Remark: Type of dimension (distance, length, angle, diameter) is automatically selected To add a tolerance, select the dimension and then change the type of tolerance, e.g. LIMIT or Symmetric
LIMIT
Symmetric
To add a text before or after the dimension, type in the text before or after <DIM>
To change the dimension properties of the sheet:Select Tools /Options on the menu bar Select Document Properties Select Detailing / Dimensions Change the arrow style to closed filled Select Precision to increase/decrease the number of decimal places Select Detailing /Arrows to change the arrow size
Select Detailing / Annotation Fonts/ Dimension to change the dimension
font size
Version 1- May07
A- 48
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
2D Drawing
Editing Title Block
To edit Title Block:-Double-click Sheet Format 1 on the tree (All the views will become invisible, and you can now select, add or delete any lines on the title block) -After editing, double-click Sheet Format1 again to exit
To add a text onto Title Block:Double-click Sheet Format 1 on the tree to activate Click Note icon Type in the text (You can change the text properties by the toolbar Formatting) Click ok to complete Drag the text to the desired position Double-click Sheet Format 1 on the tree again to exit
A- 49
Version 1- May07
Not for commercial use
Written by Dickson Sham
Solidworks 2006 Fundamentals
www.dicksonsham.com
Parameters
Equations and Design Tables
To Define an Equation to control parameter(s):(Use a simple box as an example) Height (30) = Length(80) - Width (50) Define Length and Width as the driving parameters, Height as the driven parameter. Select Tools /Equations on the menu bar Click Add.. Double-click the feature to show all related parameters Select the driven parameter Type = Select a driving parameter, then type - Select the other driving parameter, then click ok (The equation is added. Now the parameter Height is driven by Length and Width
To Create a Design Table to control parameter(s): Select Insert/ Design Table on the menu bar Select Blank as source; Select Block model edits that would update the design table; Deselect the below three options Click ok to create Double-Click on the feature Extrude1 to show all related parameters Double-Click the parameters to add them into the design table Add anther rows of values for these parameters Click on empty space to complete Select a configuration under Configuration Manager
A- 50
Version 1- May07
- ENDWritten by Dickson Sham
Not for commercial use
Вам также может понравиться
- NX 9 for Beginners - Part 2 (Extrude and Revolve Features, Placed Features, and Patterned Geometry)От EverandNX 9 for Beginners - Part 2 (Extrude and Revolve Features, Placed Features, and Patterned Geometry)Оценок пока нет
- Solid Works 2006 FundamentalsДокумент50 страницSolid Works 2006 FundamentalsDennis Li100% (2)
- WindshieldДокумент4 страницыWindshieldapi-269424168Оценок пока нет
- Certified Solidworks Professional Advanced Weldments Exam PreparationОт EverandCertified Solidworks Professional Advanced Weldments Exam PreparationРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Solidworks 2009 Design With Analysis: (Tutorial 3 - Deep Fry Basket)Документ118 страницSolidworks 2009 Design With Analysis: (Tutorial 3 - Deep Fry Basket)Javier Arredondo Ipiña100% (1)
- Catia V5 FundamentalsДокумент53 страницыCatia V5 FundamentalsMihai Miulescu100% (3)
- Autodesk Inventor - Projecting Geometry in Sheet Metal PartsДокумент4 страницыAutodesk Inventor - Projecting Geometry in Sheet Metal PartsNdianabasi UdonkangОценок пока нет
- SolidWorks 2015 Learn by doing-Part 2 (Surface Design, Mold Tools, and Weldments)От EverandSolidWorks 2015 Learn by doing-Part 2 (Surface Design, Mold Tools, and Weldments)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (5)
- Catia V5 FundamentalsДокумент53 страницыCatia V5 Fundamentalsmecheneg100% (2)
- NX 9 for Beginners - Part 3 (Additional Features and Multibody Parts, Modifying Parts)От EverandNX 9 for Beginners - Part 3 (Additional Features and Multibody Parts, Modifying Parts)Оценок пока нет
- CATIAv5 Tips PDFДокумент4 страницыCATIAv5 Tips PDFKelvin SudaniОценок пока нет
- Lab 11Документ20 страницLab 11IMTIAZ AHMADОценок пока нет
- SolidWorks 2018 Learn by doing - Part 2: Surface Design, Mold Tools, WeldmentsОт EverandSolidWorks 2018 Learn by doing - Part 2: Surface Design, Mold Tools, WeldmentsРейтинг: 2 из 5 звезд2/5 (1)
- Catia TutorialДокумент129 страницCatia TutorialSujay Umarani100% (3)
- Mouldexercises Parting Slider CATIAДокумент5 страницMouldexercises Parting Slider CATIASri Navin100% (1)
- Mold DesignДокумент40 страницMold Designre gardeniaОценок пока нет
- CATIA V5-6R2015 Basics - Part II: Part ModelingОт EverandCATIA V5-6R2015 Basics - Part II: Part ModelingРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- AutoCAD ppt-5 AutoCAD Three-Dimensional DrawingДокумент21 страницаAutoCAD ppt-5 AutoCAD Three-Dimensional DrawingBereket ArayaОценок пока нет
- 3D Modeling Auto CAD 2007Документ29 страниц3D Modeling Auto CAD 2007Siryo SoОценок пока нет
- Autodesk Inventor 2019 For Beginners - Part 1 (Part Modeling)От EverandAutodesk Inventor 2019 For Beginners - Part 1 (Part Modeling)Оценок пока нет
- Autocad 2007 Tutorial: Second Level: 3D ModelingДокумент29 страницAutocad 2007 Tutorial: Second Level: 3D ModelingAlbert DimayugaОценок пока нет
- SketchUp for Site Design: A Guide to Modeling Site Plans, Terrain, and ArchitectureОт EverandSketchUp for Site Design: A Guide to Modeling Site Plans, Terrain, and ArchitectureОценок пока нет
- Edu Cat en GSD As v5r20 CATIA V5Документ43 страницыEdu Cat en GSD As v5r20 CATIA V5spsharmagnОценок пока нет
- SolidWorks 2016 Learn by doing 2016 - Part 3От EverandSolidWorks 2016 Learn by doing 2016 - Part 3Рейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (3)
- Wildfire Sheet Metal DesignДокумент34 страницыWildfire Sheet Metal DesignhlschilleОценок пока нет
- Modeling and Visualizing Substrata Data With CIVIL 3DДокумент21 страницаModeling and Visualizing Substrata Data With CIVIL 3Dg5680Оценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Solid Modelling Using: Inventor 7Документ32 страницыFundamentals of Solid Modelling Using: Inventor 7George SmyrnakisОценок пока нет
- Wireframe and Surface Design: CATIA TrainingДокумент208 страницWireframe and Surface Design: CATIA Trainingkishore99939Оценок пока нет
- QuickStartTutorial Civil3DiДокумент34 страницыQuickStartTutorial Civil3DiDanny NguyenОценок пока нет
- Solidworks 2006 FundamentalsДокумент50 страницSolidworks 2006 FundamentalsmcreadmailОценок пока нет
- Autocad 2007 PDFДокумент29 страницAutocad 2007 PDFAryxan YBОценок пока нет
- 978 1 58503 656 1 3Документ65 страниц978 1 58503 656 1 3Milorad1583% (6)
- Autodesk Fusion 360 Black Book (V 2.0.6508) Part 1: Autodesk Fusion 360 Black Book (V 2.0.6508)От EverandAutodesk Fusion 360 Black Book (V 2.0.6508) Part 1: Autodesk Fusion 360 Black Book (V 2.0.6508)Оценок пока нет
- Learn Flat Slab-Flat Slab Analysis Design and Drawing SoftwareДокумент137 страницLearn Flat Slab-Flat Slab Analysis Design and Drawing SoftwareWanda BeasleyОценок пока нет
- Edu Cat e GSD FF V5R8Документ195 страницEdu Cat e GSD FF V5R8Arvind97Оценок пока нет
- Die Face StageДокумент14 страницDie Face StageRavindra KurisettiОценок пока нет
- CATIA V5-6R2015 Basics - Part I : Getting Started and Sketcher WorkbenchОт EverandCATIA V5-6R2015 Basics - Part I : Getting Started and Sketcher WorkbenchРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (10)
- Visual EnvironmentДокумент34 страницыVisual EnvironmentAli VarmazyarОценок пока нет
- Cad Cam Practical Record BookДокумент125 страницCad Cam Practical Record BookAKASHОценок пока нет
- CATIA Fry BasketДокумент135 страницCATIA Fry BasketSimona SimoneОценок пока нет
- CATIA Fry BasketДокумент135 страницCATIA Fry BasketPuix Ozil TherPanzerОценок пока нет
- Sheet Metal Best PracticesДокумент11 страницSheet Metal Best PracticesAng Tiong WeeОценок пока нет
- CatiaДокумент70 страницCatiaScarman21100% (5)
- Tut06 e GlaДокумент70 страницTut06 e GlaNavneet Sidhu ThandiОценок пока нет
- Compatibility Eqs RevДокумент7 страницCompatibility Eqs RevSooraj SivanОценок пока нет
- Mailam Engineering College Mailam, Villupuram (DT), Pin: 604304 Department of Mechanical EngineeringДокумент1 страницаMailam Engineering College Mailam, Villupuram (DT), Pin: 604304 Department of Mechanical EngineeringVignesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Ahp VigneshДокумент3 страницыAhp VigneshVignesh KumarОценок пока нет
- PDF FileДокумент7 страницPDF FileVignesh KumarОценок пока нет
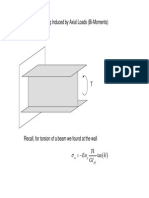
- Twisting by Axial LoadsДокумент15 страницTwisting by Axial LoadsVignesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Mailam Engineering College Mailam, Villupuram (DT), Pin: 604304Документ1 страницаMailam Engineering College Mailam, Villupuram (DT), Pin: 604304Vignesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Class Comittee Meeting III BminДокумент1 страницаClass Comittee Meeting III BminVignesh KumarОценок пока нет
- தமிழ் நாடு அரசு GOVERNMENT OF TAMIL NADUДокумент3 страницыதமிழ் நாடு அரசு GOVERNMENT OF TAMIL NADUVignesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Mailam Engineering College, MailamДокумент2 страницыMailam Engineering College, MailamVignesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Mailam Engineering College, MailamДокумент2 страницыMailam Engineering College, MailamVignesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Deviam RДокумент1 страницаDeviam RVignesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Non ConsumableДокумент8 страницNon ConsumableVignesh KumarОценок пока нет
- R.S Square Marketing PVT LTD: Distributor NameДокумент1 страницаR.S Square Marketing PVT LTD: Distributor NameVignesh KumarОценок пока нет
- It-Ii AhpДокумент1 страницаIt-Ii AhpVignesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Anna University Internal Test Time TableДокумент1 страницаAnna University Internal Test Time TableVignesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Kongu Engineering College: 11me507 Cad/Cam LaboratoryДокумент46 страницKongu Engineering College: 11me507 Cad/Cam LaboratoryVignesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Mailam Engineering College, Mailam-604 304: Department of Mechanical EngineeringДокумент1 страницаMailam Engineering College, Mailam-604 304: Department of Mechanical EngineeringVignesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Vigneshkumar.G: ObjectiveДокумент3 страницыVigneshkumar.G: ObjectiveVignesh KumarОценок пока нет
- M.Vivekanandhan.: Department Year Institute Board/University PercentageДокумент4 страницыM.Vivekanandhan.: Department Year Institute Board/University PercentageVignesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Answer All The Questions Total Marks-50: Sri Rangapoopathi College of EngineeringДокумент2 страницыAnswer All The Questions Total Marks-50: Sri Rangapoopathi College of EngineeringVignesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Anna University Internal Test Time TableДокумент1 страницаAnna University Internal Test Time TableVignesh KumarОценок пока нет
- ME2304 EMM SyllabusДокумент1 страницаME2304 EMM SyllabusVignesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Emm 2009Документ2 страницыEmm 2009Vignesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Optimizing Windmill Blade EfficiencyДокумент13 страницOptimizing Windmill Blade EfficiencyVinay MohanОценок пока нет
- The Features of Scientific Management? Henry Fayol?: Sri Rangapoopathi College of EngineeringДокумент1 страницаThe Features of Scientific Management? Henry Fayol?: Sri Rangapoopathi College of EngineeringVignesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Missing and BreakageДокумент1 страницаMissing and BreakageVignesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Name of Specimen No of QTY Issued Person Issued Date Recived Person & Date Return Person & Date Incharge Hod PrincipalДокумент1 страницаName of Specimen No of QTY Issued Person Issued Date Recived Person & Date Return Person & Date Incharge Hod PrincipalVignesh KumarОценок пока нет
- EG ModelДокумент1 страницаEG ModelVignesh KumarОценок пока нет
- CNC Lathe Circular ROD 2-Feet 15.nos 15.nos Nil 15.nosДокумент1 страницаCNC Lathe Circular ROD 2-Feet 15.nos 15.nos Nil 15.nosVignesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Guidelines For ME MTech MArch 2009 2010Документ21 страницаGuidelines For ME MTech MArch 2009 2010Vignesh KumarОценок пока нет
- ANG DELAVEGA FinalPositionPaperДокумент6 страницANG DELAVEGA FinalPositionPaperZane IbalaОценок пока нет
- ASME Pressue Vessel ExampleДокумент271 страницаASME Pressue Vessel ExamplesavanchandranОценок пока нет
- Recruitment and Selection in Canada 7Th by Catano Wiesner Full ChapterДокумент22 страницыRecruitment and Selection in Canada 7Th by Catano Wiesner Full Chaptermary.jauregui841100% (51)
- Reynold A. Nicholson - The Mystics of IslamДокумент65 страницReynold A. Nicholson - The Mystics of IslamLuminon SamanОценок пока нет
- Asaali - Project Estimation - Ce155p-2 - A73Документ7 страницAsaali - Project Estimation - Ce155p-2 - A73Kandhalvi AsaaliОценок пока нет
- End of Summer Course Test August 2021Документ16 страницEnd of Summer Course Test August 2021Thanh Nguyen vanОценок пока нет
- Manual of Sensorless Brushless Motor Speed Controller: Pentium SeriesДокумент4 страницыManual of Sensorless Brushless Motor Speed Controller: Pentium Seriesfosavo5839Оценок пока нет
- Hashimoto's Thyroiditis: Veena RedkarДокумент10 страницHashimoto's Thyroiditis: Veena RedkarSan RedkarОценок пока нет
- T.A.T.U. - Waste Management - Digital BookletДокумент14 страницT.A.T.U. - Waste Management - Digital BookletMarieBLОценок пока нет
- Test 2 Sku3023 A201 QuestionДокумент8 страницTest 2 Sku3023 A201 QuestionHafiz HafizanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 Dopant Diffusion - IДокумент32 страницыChapter 7 Dopant Diffusion - I강준호Оценок пока нет
- Orbitol Motor TMTHWДокумент20 страницOrbitol Motor TMTHWRodolfo ErenoОценок пока нет
- Maritime Management SystemsДокумент105 страницMaritime Management SystemsAndika AntakaОценок пока нет
- Isulat Lamang Ang Titik NG Tamang Sagot Sa Inyong Papel. (Ilagay Ang Pangalan, Section atДокумент1 страницаIsulat Lamang Ang Titik NG Tamang Sagot Sa Inyong Papel. (Ilagay Ang Pangalan, Section atMysterious StudentОценок пока нет
- Designing and Building A Computer TableДокумент9 страницDesigning and Building A Computer Tablemaster_codersОценок пока нет
- TM 10-3930-669-34 Forklift Truck 6K Drexel MDL R60SL-DC Part 1Документ294 страницыTM 10-3930-669-34 Forklift Truck 6K Drexel MDL R60SL-DC Part 1AdvocateОценок пока нет
- Cold Regions Science and TechnologyДокумент8 страницCold Regions Science and TechnologyAbraham SilesОценок пока нет
- Influence of Aesthetics Attributes of Brand Web Pages On Customer Brand EngagementДокумент22 страницыInfluence of Aesthetics Attributes of Brand Web Pages On Customer Brand EngagementNOOR AKMA AIDAОценок пока нет
- Course Code:TEX3021 Course Title: Wet Processing Technology-IIДокумент20 страницCourse Code:TEX3021 Course Title: Wet Processing Technology-IINakib Ibna BasharОценок пока нет
- Multi Pressure Refrigeration CyclesДокумент41 страницаMulti Pressure Refrigeration CyclesSyed Wajih Ul Hassan80% (10)
- G10Mapeh Exam First QuaterДокумент8 страницG10Mapeh Exam First QuaterJonas LamcisОценок пока нет
- Usp Description and SolubilityДокумент1 страницаUsp Description and SolubilityvafaashkОценок пока нет
- Addtional List Dissertation 040117Документ6 страницAddtional List Dissertation 040117Sagar Kansara100% (2)
- Hypothesis Testing - IДокумент36 страницHypothesis Testing - Isai revanthОценок пока нет
- 1F-Korean-Nami Mun - Miles From NowhereДокумент4 страницы1F-Korean-Nami Mun - Miles From NowhereNeil PatelОценок пока нет
- Patel 2013Документ116 страницPatel 2013hnphuocОценок пока нет
- The Working of KarmaДокумент74 страницыThe Working of KarmaSuhas KulhalliОценок пока нет
- Contoh CV / Daftar Riwayat HidupДокумент2 страницыContoh CV / Daftar Riwayat HiduprusmansyahОценок пока нет
- Essential Calculus Skills Practice Workbook With Full SolutionsДокумент528 страницEssential Calculus Skills Practice Workbook With Full SolutionsGerardo Navarro Sánchez94% (65)
- 5 Contracting Activity and Technical Staff RequirementsДокумент2 страницы5 Contracting Activity and Technical Staff RequirementsDaniyar KussainovОценок пока нет