Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
7 1
Загружено:
Muhammad Rizki Yofachri0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
23 просмотров2 страницыSolve each quadratic equation by using extraction of roots to obtain exact solutions. Approximate any irrational solutions to the nearest hundredth.
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
7.1
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документSolve each quadratic equation by using extraction of roots to obtain exact solutions. Approximate any irrational solutions to the nearest hundredth.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
23 просмотров2 страницы7 1
Загружено:
Muhammad Rizki YofachriSolve each quadratic equation by using extraction of roots to obtain exact solutions. Approximate any irrational solutions to the nearest hundredth.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
J'
v2 v2
5. a. z = 30rz -3; z "" :to.471
Vf7
b. x = 4 or x = 4 x "" :t 1.031
1. An equation that can be written in the standard form
ail + bx + c = 0 is called a equation.
2. The notation is read plus or minus.
3. By extraction of roots, the solutions of x
2
k are the
real numbers for k > o.
4. To use extraction of roots to solve a quadratic equation,
we first write the left side of the equation as a perfect
1. Evaluate V36 by inspection.
2. Use a calculator or a spreadsheet to approximate v'39
to the nearest thousandth.
3. Use a calculator or a spreadsheet to approximate V3 to
the nearest thousandth. 5
Objective 1 Solve Quadratic Equations by Extraction of
Roots
In Exercises 1-12, solve each quadratic equation by using
extraction of roots to obtain exact solutions. Then
approximate any irrational solutions to the nearest
hundredth.
2
tQ;)m
2
4 2. m = 25
3. x
2
= 2
11
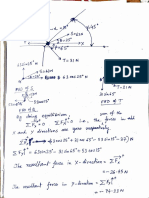
5.5i = 45 6. III 1,100
= 39 2v
2
= 38
9.2w
2
72 = 0 10. 1O.ic,2 - 90 0
11. lOz
2
50 = 0 12. 3z
2
- 21 0
8. "Lm"';forni'';'"
9. The annual interest rate is approximately 7.36%.
v';';3dt 1/;;';;".:2:2
5. If VX and vY are both real numbers, then the product
rule for square roots says v.xy = ____
6. If Vx and vY are both real numbers and y > 0, then
'x
the quotient rule for square roots says y=
7. The process of rewriting a radical expression so that
denominator does contain any radicals is called
____ the denominator.
35
4. Reduce 77 to lowest terms.
oX
5. Solve 1 + 2 = 9.
Objective 2 Use the Product Rule for Radicals to
Simplify Square Roots
In Exercises 13-18, simplify each expression using the
product rule for square roots.
@VI6-5
\v'20
@jV200 18. V75
In Exercises 19-24, solve each quadratic equation by using
extraction of roots to obtain exact solutions. Then
approximate any irrational solutions to the nearest
hundredth.
18
21.3i 81 22. 5i = 40
23. 7a
2
- 56 0 24. 3a
2
150 = 0
\IS
In Exercises 3
extraction of I
approximate a
hundredth.
33. 4v
2
= 81
35. 3&2 - 7
Objective 4 S
Rationalizing
In Exercises
rationalizing tfl
3
,V5
-- v'2
In Exercises 45
extraction of ro
approximate an
hundredth.
45. 20
47. IOw
2
- 14
Skill Developm
In Exercises 49
extraction of r,
49. (n 1)2 =
51. (2b + 3)2 =
53. Ox - 1)2
Comparison of
Equations
In Exercises 55
LinearEqu
55. a. 2x = 36
56. a. w 2
57. a. 2m 1
58. a. 2(y - 1)
Jduct
:hen
:hat the
he
'usmg
7.1
Objective 3 Use the Quotient Rule for Radicals to
Simplify Square Roots
In Exercises 25-32, simplify each expression using the
quotient rule for square roots.
(4 [E
27. f6
25. 'V"9 26. '-/ 16
'-/"49
l/ '-/64
.{;) \120 \Xij)V99
@VT8
GVW
.':/ \15 QVIT
V
V245
In Exercises 33-36, solve each quadratic equation by using
extraction of roots to obtain exact solutions. Then
approximate any irrational solutions to the nearest
hundredth.
33,4v
2
81 34. 25v
2
= 121
35.3&2 7 0 36. &lil 5 == 0
Objective 4 Simplify Expressions of the Form by
Rationalizing the Denominator b
In Exercises 37-44, simplify each expression by
rationalizing the denominator.
fi?:J 3 6 ..
40. 15
{jI'vs 38.
Vi V5
v'3
42. v'2
43.jt
44.f1t
In Exercises 45-48, solve each quadratic equation by using
extraction of roots to obtain exact solutions. Then
approximate any irrational solutions to the nearest
hundredth.
45. 8; 20 46. 15x
2
= 55
14 = 0 48. 70w
2
- 110 = 0
Skill Development
In Exercises 49-54, solve each quadratic equation by
e1'traction of roots.
49. (n \)2 = 36 50. (n + 2)2 64
51. (2b + 3)2 = 49 52. (2b 3)2 169
53. (3x - 1)2 + 7 = 32 54. (5x + 1)2 - 2 79
Comparison of Linear Equations and Quadratic.
Equations
In Exercises 55-58, solve eaeh equation.
Linear Equation Equation
2
h. x 36
56. R. w - 2 25 b. (w 2)2 = 25
57. R. 2m I 9 b. (2m - 1)2 = 9
58. a. 2(y - 1) - 3 == 1 b. (y - 1)2 3 = I
Extraction of Roots and Properties of Square Roots (7-11) 551
Review and Concept Development
59. Use the graph of y == (2x - 1)2 - 1 to:
a. Solve (2x - 1)2 1 = O.
b. Solve (2x - 1)2 1<0.
c. Solve (2x - 1)2 - 1 > O.
y
60. Use the graph of y (x - 2)2 3 to:
a. Solve (x 2)2 - 3 O.
b. Solve (x 2)2 - 3 < O.
c. Solve (x - 2)2 - 3 > O.
2
61. a. Determine the exact solutions of x - 6 O.
b. Determine the exact z,eros of x
2
6.
c. Determine the exact x-intercepts of the parabola
whose equation is y == il 6.
62. a. Determine the exact solutions of (2x 1)2 - 5 O.
b. Determine the exact zeros of (2x - 1)2 - 5.
c. Determine the exact x-intercepts of the parabola
whose equation is y (2x - 1)2 - 5.
63. Construct a quadratic equation in x that has the given
solutions.
a. -7 and 7 b. -0and 0
64. Construct a quadratic equation in x that has the given
solutions.
a. -11 and 11 b. -VIT and v'fI
Connecting Algebra to Geometry
In Exercises 65 and 66, use the
given lengths of legs a and band c .
. 2 b .
the equatlOn a- + - = c to
approximate the length of the .........-.,.....--------...
hypotenuse c to the nearest tenth
of a centimeter.
65. a 29.5 cm, b == 35.7 cm
66. a 43.6 cm, b = 57.3 em
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- DMS 48 NormesДокумент11 страницDMS 48 NormesSonia WittmannОценок пока нет
- Mitigating arc ash hazards design constraintsДокумент6 страницMitigating arc ash hazards design constraintswaqas_a_shaikh4348Оценок пока нет
- 6907 6 52 0040Документ35 страниц6907 6 52 0040amitkumar8946Оценок пока нет
- Manhattan Project SummaryДокумент5 страницManhattan Project Summaryapi-302406762Оценок пока нет
- Obeid Specialized Hospital - Riyadh: Inpatient DeptsДокумент4 страницыObeid Specialized Hospital - Riyadh: Inpatient DeptsLovelydePerioОценок пока нет
- Five Sheets For Technology PlanДокумент16 страницFive Sheets For Technology Planapi-200984070Оценок пока нет
- IIT BOMBAY RESUME by SathyamoorthyДокумент1 страницаIIT BOMBAY RESUME by SathyamoorthySathyamoorthy VenkateshОценок пока нет
- 102DNДокумент2 страницы102DNManuel ZavalaОценок пока нет
- Tes P 119 10 R0 PDFДокумент43 страницыTes P 119 10 R0 PDFAbin Meetu100% (4)
- Final Paper - PARTIALДокумент64 страницыFinal Paper - PARTIALDeanna GicaleОценок пока нет
- NCP 1014Документ24 страницыNCP 1014rodricaldasОценок пока нет
- Designing of 3 Phase Induction Motor Blackbook DoneДокумент30 страницDesigning of 3 Phase Induction Motor Blackbook Donetryd0% (1)
- Food Conformity BA 550-13Документ9 страницFood Conformity BA 550-13puipuiesperaОценок пока нет
- Project Planning HandbookДокумент21 страницаProject Planning HandbookPhilip JonesОценок пока нет
- Acer Veriton S480G Service ManualДокумент90 страницAcer Veriton S480G Service ManualAndreea Georgiana ChirilaОценок пока нет
- Flap System RiginДокумент12 страницFlap System RiginHarold Reyes100% (1)
- Motorship Oct 2023Документ56 страницMotorship Oct 2023Sahil PakhaliОценок пока нет
- LADY BroshureДокумент2 страницыLADY BroshureMcGabi GabrielОценок пока нет
- Introducing The Phenomenon To Be Discussed: Stating Your OpinionДокумент8 страницIntroducing The Phenomenon To Be Discussed: Stating Your OpinionRam RaghuwanshiОценок пока нет
- Marketing Assignment (Cool Air India)Документ10 страницMarketing Assignment (Cool Air India)Mandira PantОценок пока нет
- An Overview On Recognition of State in International LawДокумент17 страницAn Overview On Recognition of State in International LawRamanah VОценок пока нет
- HIBAH PKSM Sps 2021Документ9 страницHIBAH PKSM Sps 2021Gargazi Bin HamidОценок пока нет
- Kunduz Tutor Job Apply Question 1Документ2 страницыKunduz Tutor Job Apply Question 1anirbanОценок пока нет
- 8602 BookДокумент240 страниц8602 BookSohail100% (2)
- Eccsa Five Year (2014 15 - 2018 19) Strategic PlanДокумент95 страницEccsa Five Year (2014 15 - 2018 19) Strategic Planyayehyirad100% (1)
- CH - 1Документ4 страницыCH - 1Phantom GamingОценок пока нет
- Mobile Phone: Service ManualДокумент129 страницMobile Phone: Service ManualAlexОценок пока нет
- MD SHAFIUL ISLAM 沙菲 ID;20183290290Документ23 страницыMD SHAFIUL ISLAM 沙菲 ID;20183290290SHAFIUL SETUОценок пока нет
- Vehicle Tracker Offer SheetДокумент1 страницаVehicle Tracker Offer SheetBihun PandaОценок пока нет
- Fish HatcheryДокумент14 страницFish HatcheryYared Mesfin FikaduОценок пока нет