Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Lateral Earth Pressure Theories and Calculations
Загружено:
Jefferson Nobleza0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
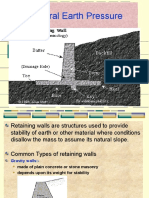
29 просмотров6 страницLateral Earth pressure is a function of vertical pressure p h = K P v. There are three type of lateral pressure as shown in Figure 4.
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Theory
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документLateral Earth pressure is a function of vertical pressure p h = K P v. There are three type of lateral pressure as shown in Figure 4.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
29 просмотров6 страницLateral Earth Pressure Theories and Calculations
Загружено:
Jefferson NoblezaLateral Earth pressure is a function of vertical pressure p h = K P v. There are three type of lateral pressure as shown in Figure 4.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 6
Theory
The lateral earth pressure is a function of vertical pressure
P
h
= K P
v
Where
p
h
lateral earth pressure,
p
v
is vertical pressure,
K is lateral earth pressure coefficient.
There are three type of lateral earth pressure as shown in Figure 4.1
1. Active pressure: when retaining wall is moving away from earth, K=Ka.
2. Passive pressure: when retaining wall is moving against soil, K=Kp
3. At rest pressure: when earth is at rest connection such as earth pressure against basement
walls, K=Ko
Determine resultant force of lateral earth pressure
Lateral earth pressure due to weight of soil for cohesionless soil
Total force of active earth pressure:
P
a
= H
2
K
a
/2
Total force of passive earth pressure:
P
p
= H
2
K
p
/2
Total force of at rest earth pressure:
P
o
= H
2
K
o
/2
Where:
P
a
: total active earth pressure.
P
p
: total passive earth pressure.
P
o
: total at rest earth pressure.
: unit weight (density) of soil
H: height of retaining wall
K
a
: active earth pressure coefficient.
K
p
: passive earth pressure coefficient.
K
o
: at rest earth pressure coefficient.
Lateral earth pressure due to weight of soil for cohesive soil
Total force of active earth pressure:
P
a
= H
2
K
a
/22C\K
a
where C is soil cohesion.
Lateral earth pressure due to surcharge:
Retaining wall is often subjected to surcharge such as addition depth of soil, weight of parking
vehicle or traffic, etc. Lateral earth pressure due to surcharge is normally assumed distributed
uniformly along the depth. Lateral earth pressure due to surcharge are calculated as follows:
Total force of active earth pressure from surcharge:
P'
a
= qHK
a
Total force of passive earth pressure:
P'
p
= qHK
p
Total force of at rest earth pressure:
P'
o
= qHK
o
Where q is the weight of surcharge
Lateral Earth pressure coefficients
There are two commonly uses lateral earth pressure theories: Coulomb (1776) and Rankine
(1857)
Rankine earth pressure coefficient
Retaining wall with horizontal backfill
Rankines Active earth pressure coefficient
K
a
= tan
2
(45-|/2)
2
Rankines Passive earth pressure coefficient
K
p
= tan
2
(45+|/2)
2
Where | is internal friction angle (degree) of soil.
Retaining wall with slope backfill
Rankines active earth pressure coefficient
Rankines passive earth pressure coefficient
Where | is the slope of the backfill from horizontal surface.
Assumptions for Rankines theory:
1. Soil is isotropic and homogeneous and is cohesionless.
2. Soil rapture in a plane and earth pressure applies to the wall is from movement of soil
wedge
3. Back of retaining wall is a vertical plane with no friction between soil and wall.
4. The retaining wall is long and soil is in plain strain condition.
Example 4.1: Rankine's lateral earth pressure with horizontal backfill
Given:
Height of earth at heel, H = 12 ft
Height of earth at toe , h = 2 ft
Friction angle of soil: | = 30 degree
Horizontal backfill,
Unit weight of backfill soil: = 115 lb/ft
3
Requirement:
Using Rankine's lateral earth pressure
1. determine Rankine total active force, P
a
, at heel per foot width of wall
2. determine Rankine's total passive force, P
p
at toe per foot width of wall
Solution:
Active earth pressure coefficient:
K
a
= tan
2
(45-|/2)
2
= 0.333
Total active force:
P
a
= H
2
K
a
/2 = 2760 lb/ft (per one ft width of wall)
Passive earth pressure coefficient:
K
p
= tan
2
(45+|/2)
2
= 3
Total passive force:
P
p
= H
2
K
p
/2 = 690 lb/ft (per one ft width of wall)
Example 4.2: Rankine's earth pressure with slope backfill
Given:
Height from top of earth to bottom of footing, H = 12 ft
Height from top of backfill to bottom of toe, h = 2 ft
Friction angle of soil: 30 degree
Slope of backfill soil at heel: 20 deg
Slope of backfill soil at toe: -20 deg
Unit weight of backfill soil: = 115 lb/ft
3
Requirement:
Using Rankine's lateral earth pressure theory
1. Determine total force, P
a
, at heel per foot width of wall
2. Determine total passive force, P
p
at toe per foot width of wall
Solution:
| = 20 deg
Active earth pressure coefficient:
Total active force:
P
a
= H
2
K
a
/2 = 3430 lb/ft (per one ft width of wall)
Passive earth pressure coefficient:
Total passive force:
P
p
= H
2
K
p
/2 = 490 lb/ft (per one ft width of wall)
Coulomb earth pressure coefficients
Coulomb active earth pressure coefficient:
Coulomb passive earth pressure coefficient:
Where
| is internal friction angle of the soil,
| is the slope of the backfill
o is the angle of the back of retaining wall
o is friction angle between soil and back of retaining wall
Assumptions for Coulombs theory:
1. Soil is isotropic, homogeneous, and cohesionless.
2. Soil rapture in a plane and earth pressure applies to the wall is from movement of soil
wedge
3. Back of retaining wall is a plane with friction between soil and wall distributes uniformly
4. The retaining wall is long and soil is in plain strain condition.
Example 4.3: Coulomb's lateral earth pressure with horizontal backfill on
smooth vertical back face
Given:
Height of earth at heel, H = 12 ft
Height of earth at toe, h = 2 ft
Friction angle of soil: 30 degree
Horizontal backfill
Unit weight of backfill soil: = 115 lb/ft
3
Angle of back of retaining wall: o = 90 deg
Friction angle between soil and back of retaining wall: o = 0 deg
Requirement:
Using Coulomb's lateral earth pressure theory
1. determine total active force, P
a
, at heel per foot width of wall
2. determine total passive force, P
p
at toe per foot width of wall
Solution:
| = 20 deg
Active earth pressure coefficient:
Total active force:
P
a
= H
2
K
a
/2 = 2313 lb/ft (per one ft width of wall)
Passive earth pressure coefficient:
Total passive force:
P
p
= H
2
K
p
/2 = 356 lb/ft (per one ft width of wall)
Example 4.4: Coulomb's earth pressure with slope backfill on smooth
vertical back face
Given:
Height from top of earth to bottom of footing, H = 12 ft
Height from top of backfill to bottom of toe, h = 2 ft
Friction angle of soil: 30 degree
Slope of backfill soil at heel: 20 deg
Slope of backfill soil at toe: -20 deg
Unit weight of backfill soil: = 115 lb/ft
3
Angle of back of retaining wall: o = 90 deg
Friction angle between soil and back of retaining wall: o = 0 deg
Requirement:
Using coulomb's lateral earth pressure theory
1. Determine total force, P
a
, at heel per foot width of wall
2. Determine total passive force, P
p
at toe per foot width of wall
Solution:
| = 20 deg
Active earth pressure coefficient:
Total active force:
P
a
= H
2
K
a
/2 = 3652 lb/ft (per one ft width of wall)
Passive earth pressure coefficient:
Total passive force:
P
p
= H
2
K
p
/2 = 356 lb/ft (per one ft width of wall)
Example 4.5: Coulomb's earth pressure with slope backfill on rough
slope back face
Given:
Height from top of earth to bottom of footing, H = 12 ft
Height from top of backfill to bottom of toe, h = 2 ft
Friction angle of soil: 30 degree
Slope of backfill soil at heel: 20 deg
Slope of backfill soil at toe: -20 deg
Unit weight of backfill soil: = 115 lb/ft
3
Angle of back of retaining wall: o = 80 deg
Friction angle between soil and back of retaining wall: o = 2 0 deg
Requirement:
Using coulomb's lateral earth pressure theory
1. Determine total force, Pa, at heel per foot width of wall
2. Determine total passive force, Pp at toe per foot width of wall
Solution:
| = 20 deg
Active earth pressure coefficient:
Total active force:
P
a
= H
2
K
a
/2 = 4474 lb/ft (per one ft width of wall)
Passive earth pressure coefficient:
Total passive force:
P
p
= H
2
K
p
/2 = 386 lb/ft (per one ft width of wall)
Вам также может понравиться
- Lateral Earth PressureДокумент2 страницыLateral Earth PressureLaura HernandezОценок пока нет
- Loka-The Buddha's Formulation of The Universe Rick CrutcherДокумент12 страницLoka-The Buddha's Formulation of The Universe Rick CrutcherjonrcrowleyОценок пока нет
- Retaining WallДокумент46 страницRetaining WallTushar SaxenaОценок пока нет
- Geotechnical Engineering - Ii (Foundation Engineering) : Prepared By: Mc-Lloyd G. SarateДокумент39 страницGeotechnical Engineering - Ii (Foundation Engineering) : Prepared By: Mc-Lloyd G. SaratePascasio Pascasio100% (2)
- Rilling Ngineering Course (2 Ed.)Документ43 страницыRilling Ngineering Course (2 Ed.)MarcoОценок пока нет
- Pressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksОт EverandPressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksОценок пока нет
- Ce 132 - Geotechnical Engineering 2: Mindanao State University Fatima, General Santos City PhilippinesДокумент28 страницCe 132 - Geotechnical Engineering 2: Mindanao State University Fatima, General Santos City PhilippinesAngelica Curambao100% (1)
- Design of Concrete Cantilever Retaining WallДокумент18 страницDesign of Concrete Cantilever Retaining Wallhendra_571% (7)
- Retaining Wall DesignДокумент55 страницRetaining Wall DesignMohit Kohli100% (1)
- Foundation-Ch 7 PDFДокумент19 страницFoundation-Ch 7 PDFAlbanОценок пока нет
- Low Voltage - Two Tube Regen ReceiverДокумент8 страницLow Voltage - Two Tube Regen Receiverest_nuОценок пока нет
- Foundation Analysis and Design 1 PDFДокумент48 страницFoundation Analysis and Design 1 PDFagpsimoes100% (1)
- Class Notes - Design of Cantilever Retaing WallДокумент49 страницClass Notes - Design of Cantilever Retaing WallPrince A Jayswal100% (1)
- SPE 63041 Design and Installation of Sand Separation and Handling SystemДокумент10 страницSPE 63041 Design and Installation of Sand Separation and Handling Systemalexalek2000Оценок пока нет
- Optical Fiber LecturesДокумент161 страницаOptical Fiber LecturesZakareya FathallaОценок пока нет
- Lateral Earth Pressure Due To Weight of Soil For Cohesive SoilДокумент9 страницLateral Earth Pressure Due To Weight of Soil For Cohesive Soilmido medoОценок пока нет
- Coulomb Theory For Retaining WallДокумент11 страницCoulomb Theory For Retaining WallTahir Ur RahmanОценок пока нет
- Tugas Mekanika Tanah IIДокумент10 страницTugas Mekanika Tanah IIAriОценок пока нет
- Lateral Earth PressureДокумент7 страницLateral Earth PressureShafiullah KhanОценок пока нет
- Comprehensive Step by Step Calculations For Retaining Wall Analysis Are Provided BelowДокумент15 страницComprehensive Step by Step Calculations For Retaining Wall Analysis Are Provided BelowLakshmiWijayasiriОценок пока нет
- Earth Pressure CalculationsДокумент35 страницEarth Pressure Calculationskeddy lamarОценок пока нет
- 2 BAA3513 Lateral Earth Pressure (Part 2)Документ42 страницы2 BAA3513 Lateral Earth Pressure (Part 2)احمد يوسفОценок пока нет
- Coulomb's Lateral Earth PressureДокумент9 страницCoulomb's Lateral Earth PressureL N MALVIYA INFRA PROJECTSОценок пока нет
- Foundation Ch.7Документ19 страницFoundation Ch.7Anonymous 8f2veZf100% (1)
- Topic 6.2 - Retaining Walls (Lateral Earth Pressure)Документ34 страницыTopic 6.2 - Retaining Walls (Lateral Earth Pressure)ZxeroОценок пока нет
- Soil Mechanics Earth PressureДокумент32 страницыSoil Mechanics Earth PressureManish VankudreОценок пока нет
- Coulomb's Theory ExamplesДокумент4 страницыCoulomb's Theory ExamplesLevis MithamoОценок пока нет
- Basement Wall - 2003Документ4 страницыBasement Wall - 2003mostafiz18jun2007Оценок пока нет
- Unit 1Документ30 страницUnit 1imamadnan69Оценок пока нет
- Rankine's Theory of Active Earth PressureДокумент14 страницRankine's Theory of Active Earth PressureZeeshanОценок пока нет
- Retaining Wall DesignДокумент15 страницRetaining Wall DesignFarhan IqbalОценок пока нет
- Chapter 11Документ61 страницаChapter 11Haziq RoslanОценок пока нет
- Unit 3 - Lateral Earth PressureДокумент12 страницUnit 3 - Lateral Earth PressurePrince AJОценок пока нет
- ENCE 461 Lateral Earth Pressure TheoryДокумент11 страницENCE 461 Lateral Earth Pressure TheorySushil DhunganaОценок пока нет
- LEP3Документ34 страницыLEP3renadОценок пока нет
- Unit 9: Earth Pressure TheoryДокумент15 страницUnit 9: Earth Pressure Theoryajai chyОценок пока нет
- Rankine Passive PRINTДокумент2 страницыRankine Passive PRINTHari KurniawanОценок пока нет
- Shallow Foundation Analysis and DesignДокумент74 страницыShallow Foundation Analysis and Designofadol830Оценок пока нет
- Lateral Earth Pressure ExplainedДокумент20 страницLateral Earth Pressure Explainedanon_917763370Оценок пока нет
- Lateral Earth PressureДокумент3 страницыLateral Earth PressureDupio German IIОценок пока нет
- Ch11 Sol 1of2Документ27 страницCh11 Sol 1of2Akın ÖzçelikОценок пока нет
- LATERAL EARTH PRESSURE CALCULATIONSДокумент55 страницLATERAL EARTH PRESSURE CALCULATIONSRakesh SheteОценок пока нет
- 2 BAA3513 Lateral Earth Pressure (Part 3)Документ38 страниц2 BAA3513 Lateral Earth Pressure (Part 3)احمد يوسفОценок пока нет
- SWCE232 Soilmechaincs PPT6Документ18 страницSWCE232 Soilmechaincs PPT6Mr.KRISHNAMOORTHY NОценок пока нет
- Earth Pressure at Rest Rankine's Theory of Earth PressureДокумент27 страницEarth Pressure at Rest Rankine's Theory of Earth PressureDrSuman ManandharОценок пока нет
- 7-Lateral Earth PressureДокумент31 страница7-Lateral Earth PressureshorooqОценок пока нет
- Course: Soil Mechanics: Retaining Walls Lateral Earth Pressure TheoryДокумент44 страницыCourse: Soil Mechanics: Retaining Walls Lateral Earth Pressure TheoryPabloОценок пока нет
- Geo BДокумент34 страницыGeo BMohamed HelmyОценок пока нет
- Earth PressuretheoriesДокумент27 страницEarth PressuretheoriessrjmbmОценок пока нет
- Structure IV: Bachelor of Architecture Cosmos College of Management and TechnologyДокумент18 страницStructure IV: Bachelor of Architecture Cosmos College of Management and Technologysujan pokhrelОценок пока нет
- LATERAL PRESSURE CALCULATIONS FOR RETAINING WALLSДокумент4 страницыLATERAL PRESSURE CALCULATIONS FOR RETAINING WALLSTing Wee KietОценок пока нет
- Design and Detailing of Retaining Walls: SIL211 MEKANIKA TANAH, 3 (2-3)Документ55 страницDesign and Detailing of Retaining Walls: SIL211 MEKANIKA TANAH, 3 (2-3)BitbitterОценок пока нет
- Lateral Earth PresuureДокумент81 страницаLateral Earth PresuureesprindiaОценок пока нет
- Earthquake Resistant Design of Retaining StructuresДокумент25 страницEarthquake Resistant Design of Retaining StructuresDipinder Grewal100% (3)
- C2 Lateral Earth PressureДокумент45 страницC2 Lateral Earth PressureSara LaiОценок пока нет
- What Is A Retaining Wall?Документ18 страницWhat Is A Retaining Wall?dwerfОценок пока нет
- Retaining Walls - WebsiteДокумент20 страницRetaining Walls - Websiteag_007Оценок пока нет
- Based On Darcy's LowДокумент22 страницыBased On Darcy's LowAhmedMahirОценок пока нет
- تربة المحاظرة 6 PDFДокумент22 страницыتربة المحاظرة 6 PDFنور عليОценок пока нет
- Pressure, Resistance, and Stability of Earth American Society of Civil Engineers: Transactions, Paper No. 1174, Volume LXX, December 1910От EverandPressure, Resistance, and Stability of Earth American Society of Civil Engineers: Transactions, Paper No. 1174, Volume LXX, December 1910Оценок пока нет
- FALLSEM2018-19 - MEE1004 - ETH - MB309 - VL2018191003741 - Reference Material I - Fluid Mechanics-3 PDFДокумент69 страницFALLSEM2018-19 - MEE1004 - ETH - MB309 - VL2018191003741 - Reference Material I - Fluid Mechanics-3 PDFSivaram PeramОценок пока нет
- Mass Transfer CoefficientsДокумент3 страницыMass Transfer CoefficientsjuandiegoCOОценок пока нет
- Hydrogen Spectral LinesДокумент17 страницHydrogen Spectral LinesarnoldОценок пока нет
- CH 6Документ157 страницCH 6qusayОценок пока нет
- Adiabatic Flow in a Duct with FrictionДокумент7 страницAdiabatic Flow in a Duct with FrictioncroprobosОценок пока нет
- BIIOДокумент4 страницыBIIOTimothy RandallОценок пока нет
- Physics Paper IДокумент13 страницPhysics Paper IJalaja RajОценок пока нет
- MDRU PIMS Update 2014 PDFДокумент2 страницыMDRU PIMS Update 2014 PDFVictor ValdiviaОценок пока нет
- E Ax Ay: Sin Ɵ Cos Ø, (A) Find The Electric Flux DensityДокумент2 страницыE Ax Ay: Sin Ɵ Cos Ø, (A) Find The Electric Flux DensitySabareshwar SankaranarayananОценок пока нет
- Tensor Algebra: 2.1 Linear Forms and Dual Vector SpaceДокумент13 страницTensor Algebra: 2.1 Linear Forms and Dual Vector SpaceashuОценок пока нет
- Continuum Mechanics HW On Index NotationДокумент4 страницыContinuum Mechanics HW On Index NotationIlbey KarakurtОценок пока нет
- Rock Stress Measurement MethodsДокумент50 страницRock Stress Measurement MethodschouszeszeОценок пока нет
- Unveiling The Secrets of String TheoryДокумент2 страницыUnveiling The Secrets of String Theorybic1973Оценок пока нет
- Electric ChargeДокумент14 страницElectric Chargefrancis solivenОценок пока нет
- Laser PhysicsДокумент41 страницаLaser PhysicsdarthpatxОценок пока нет
- ICSE 2017 Chemistry Science Sample Paper 2 PDFДокумент7 страницICSE 2017 Chemistry Science Sample Paper 2 PDFPrabhat BhatОценок пока нет
- MANU PPT - PPTX 2Документ13 страницMANU PPT - PPTX 2Karan JoshiОценок пока нет
- Essential Soil Tests for Building FoundationsДокумент6 страницEssential Soil Tests for Building FoundationsJustin MusopoleОценок пока нет
- Thermal properties of ammonium nitrateДокумент4 страницыThermal properties of ammonium nitratesj_scribdОценок пока нет
- Filled Polyamide 12 Using The Multi Jet Fusion Printing ProcessДокумент21 страницаFilled Polyamide 12 Using The Multi Jet Fusion Printing Processpat151Оценок пока нет
- 1 Tutorial - Mechanical SeparationДокумент2 страницы1 Tutorial - Mechanical SeparationSENG LEE LIMОценок пока нет
- Part II - Lecture 5: Expansion Waves (Prandtl-Meyer Flow)Документ8 страницPart II - Lecture 5: Expansion Waves (Prandtl-Meyer Flow)Watcharakorn Viva la VidaОценок пока нет
- 6 Carboxylic AcidsДокумент7 страниц6 Carboxylic AcidsThinaya JayarathneОценок пока нет
- 1.chemical KineticsДокумент24 страницы1.chemical KineticsVinod AgrawalОценок пока нет
- Exp 2. AbstractДокумент5 страницExp 2. AbstractBrev Candare50% (2)