Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Anatcrmy T - : I: - : It Yl.i"! I Fi" (" Thi !,R - R"ors:: I
Загружено:
eary05Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Anatcrmy T - : I: - : It Yl.i"! I Fi" (" Thi !,R - R"ors:: I
Загружено:
eary05Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Anatcrmy
Practicallr
_;" -"'.rso (vellus) hairs on the scalp are club hairs. Kligman estimates t--: I tir 3 per cent of all other hairJ are in this resting Jtage. About eaci :--: as. it grows, there forms a keratinized cytindric"al tule yl.i"! is i:r-,-i,:,.J by the inner root sheaths of Huxley and Henle. This fills the pctt:-i:=- space about the hair at the follicular orifice. Nails. i[i-= r,..ils are convex trans]ucent horny plates situated on the dorsal sur:":r:; i the distal phalanges of the fi"["* and toes. The large exposed pa- :: called the body; thi anterior exte-nsion from the body tf,e free edge; !,r rrortion extending under the skin the nail root. There is a whitish crs.irt near the base oT the nail (the lunula), which is due to a lessened trar-.lucerrc'of the pa^rt. The nail lies o, u or soft layer, a speciallr ::,,'ffied portion^or ur" corium, the nail-r"orswhtch beneath bted, the nail root :: i so.,rewhat anterior to it is known as the mairix. by corriffcation of the cer. multiplying in the root from the stratum lucidum the nail grows fon'ar . The n-ail is b-ounded posteriorry and raterary by fords of skin, the- naii +r,LJ,s. and from the latter,'a thin mlmbrane stretlhes crescentshaped for a stc,rt distance over the lunula. Blood \-essels. There are three systems of blood vessels in the skin: a deep coarse one in the subcutaneous iatty tissue, a second of intermediate size situated i, the corium immediately atove the subcutaneous tissue, and a fi1re mini11sl. ramifying one in the corium beneath the papi[ary i";; - Lymphatics. Relatively few lymphatic vessels with distinct errdothelial lining are fourrd in the normal rkirr,- b,rt there are numerous intercellular lym-ph spaces in the epithelial layer of the epidermis and i" tt corium. Nerves. Both niedullated and nonmeduilJted sensory nerve fibers are " found in the skin. \,{edullated ffbers from the subcutaneous tissue ramify upward into the corium in company with the blood vessels. In the papillary layer- they lose their medullarf sheaths, forming a network of fine fibrils which extend into the epidermis between the priJkle ,, t* as the stratum-lucidum, there forming the interepitheriar prexus. N.rrrr".o* medul""[, lated ffbers terminate in-the"pacinian boiies, the iactile and end bulbs, and also pass to the cdnnective tissue coats of the "o.prr"t", hair follicles. Here they lose their sheaths and subdivide, forming a plexus between the epidermal cells of the erternal root sheath. The no*nm6duilated ffbers probably supply the musculi arrectores pilorum, the sweat urrJ the blood
vessels.
"oitr,
Muscles. The muscles of the skin are all of the smooth, or nonstriated, involuntary kind except a few voruntary muscle fibers found in the face. The musculi arrectores- pilorum are made up of small b";Jl"; of smooth muscle ffbers which run fiom a neighboring iapilla obliq""ly to the hair follicle, to which they are attachei by el-asiiJ threads.'Thl contiguous sebaceous_ gland lies ln the angle between the follicle and the muscle b.ndles" on contracting theyq" hair, probabty pl"y ," i-portant part "r99i in regulating the -;d il expressing _action of the brood and il-rpt :he contents of the sebaceous glands. sucldei contraction-or-tt ""ti"rt, musculi pilorum produces cutis anserina (goose flesh) in certain regions. " :I""1?'"r -'mooth muscle fibers also surround the coir grands arril ,r" present in the ',.'alls of the blood vessels. Larger masses of smooth muscle frbers arranged in layers are found in -rrtain loca,tions, such as in the skin of the sciltum, ,/o,r"a tne areolae i the nipples, and in the eyelids. Pigment. The color of the skin is influenced by the amount of pigmen-
Вам также может понравиться
- Mephitinve, Spilogale, Conepatus, Me Phitis. Mephgtis Conetatus. Mefhlt S: M. Macrura, .M. 2utorlus, MethitlcaДокумент18 страницMephitinve, Spilogale, Conepatus, Me Phitis. Mephgtis Conetatus. Mefhlt S: M. Macrura, .M. 2utorlus, MethitlcaLouis CyferОценок пока нет
- 03 Human Anatomy 1st YearДокумент9 страниц03 Human Anatomy 1st Yearit's EimyОценок пока нет
- Histology Final Exam CoverageДокумент19 страницHistology Final Exam CoverageJAWAD, JAINA A.Оценок пока нет
- Journal of Entomology and Zoology Volume Eleven, Number Two, June 1919От EverandJournal of Entomology and Zoology Volume Eleven, Number Two, June 1919Оценок пока нет
- Anatomy Assigntment (Mamad)Документ4 страницыAnatomy Assigntment (Mamad)del AjjahОценок пока нет
- Lec 1-ScalpДокумент7 страницLec 1-ScalpالهاشميОценок пока нет
- L3 Integumentary System and Cardiovascular SystemДокумент55 страницL3 Integumentary System and Cardiovascular SystemmohammedОценок пока нет
- Material - Engleza - Medicina Anul 1, Sem 2Документ58 страницMaterial - Engleza - Medicina Anul 1, Sem 2Gabriella CoadaОценок пока нет
- The Adrenal GlandsДокумент34 страницыThe Adrenal Glandsashgee1Оценок пока нет
- Borders of The Muscular TriangleДокумент14 страницBorders of The Muscular TriangleJayОценок пока нет
- CRR Histology Lab 6: Lymphatic System CRR Week 8Документ2 страницыCRR Histology Lab 6: Lymphatic System CRR Week 8Hermenegildo GutierrezОценок пока нет
- Basic Anatomy NotesДокумент5 страницBasic Anatomy NotesFloyd Cedrick BalansagОценок пока нет
- Questions and Their Ideal AnswersДокумент17 страницQuestions and Their Ideal AnswersHamzaShabaka100% (2)
- Chapter 6.PDF THORAXДокумент94 страницыChapter 6.PDF THORAXharshkumaronn8Оценок пока нет
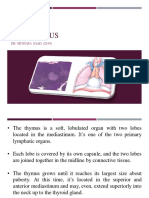
- Embryology and Anatomy of The Thymus Gland: Carla PalumboДокумент2 страницыEmbryology and Anatomy of The Thymus Gland: Carla PalumbokatyОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Anatomy: DR - Raja'a Al-Adhami (2) January 28, 2021 The SkinДокумент6 страницIntroduction To Anatomy: DR - Raja'a Al-Adhami (2) January 28, 2021 The Skinscort cherОценок пока нет
- VB Atlas2 Preview-1Документ11 страницVB Atlas2 Preview-1Dragan MitrovicОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology of Sweat GlandДокумент43 страницыAnatomy and Physiology of Sweat GlandUjjwala VermaОценок пока нет
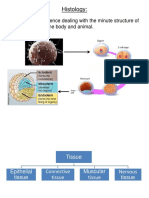
- Histology:: It Is A Branch of Science Dealing With The Minute Structure of Different Tissue of The Body and AnimalДокумент47 страницHistology:: It Is A Branch of Science Dealing With The Minute Structure of Different Tissue of The Body and Animalnourhan yousefОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1 ScalpДокумент5 страницLecture 1 Scalpnatheer ayedОценок пока нет
- Biomechanics of Peripheral and Spinal Nerve RootsДокумент86 страницBiomechanics of Peripheral and Spinal Nerve RootsJawad HassanОценок пока нет
- Atlas Do Corpo HumanoДокумент11 страницAtlas Do Corpo HumanoAlfredo Nunes da SilvaОценок пока нет
- Anatomy & Science DentistДокумент1 страницаAnatomy & Science DentistArif ShaikhОценок пока нет
- Circulatory System: Professor Meng YunlianДокумент64 страницыCirculatory System: Professor Meng Yunlianapi-19641337Оценок пока нет
- Histology LabДокумент207 страницHistology LabDandali100% (3)
- Tiomico - BSP 2A - Tissue RepairДокумент14 страницTiomico - BSP 2A - Tissue RepairpiescesОценок пока нет
- Matary Surgical Anatomy 2013Документ320 страницMatary Surgical Anatomy 2013Raouf Ra'fat Soliman96% (23)
- Lacrimal AppДокумент17 страницLacrimal Appdrsaavi87Оценок пока нет
- Comparative Neurology.: JournalДокумент18 страницComparative Neurology.: JournalAnis Rita PratiwiОценок пока нет
- Matary Surgical Anatomy 2013 AllTebFamily ComДокумент320 страницMatary Surgical Anatomy 2013 AllTebFamily Comrusu_alexandra_4Оценок пока нет
- BI 121 ch5 - STДокумент3 страницыBI 121 ch5 - SThughe2rjОценок пока нет
- Course 4Документ9 страницCourse 4bordinessrineОценок пока нет
- The Lymphatic System and Immunity by Navarro and Orjalo BS Psy 3 1Документ27 страницThe Lymphatic System and Immunity by Navarro and Orjalo BS Psy 3 1markОценок пока нет
- With The Aid of A DiagramДокумент2 страницыWith The Aid of A DiagramNini AvsajanishviliОценок пока нет
- The Autonomic Nervous SystemДокумент26 страницThe Autonomic Nervous SystemFerencОценок пока нет
- Thymus & Spleen Histology & AnatomyДокумент55 страницThymus & Spleen Histology & AnatomySarah100% (1)
- HistologyДокумент16 страницHistologyHohai ConcepcionОценок пока нет
- Penis: This Is The Male Organ Used in Sexual Intercourse. It Has Three PartsДокумент16 страницPenis: This Is The Male Organ Used in Sexual Intercourse. It Has Three PartsYeLah BauyonОценок пока нет
- Blood Brain BarrierДокумент11 страницBlood Brain Barrierdmutethia68Оценок пока нет
- Histology of MuscleДокумент49 страницHistology of MuscleTewachew Dessie100% (1)
- The Spinal Cord: Lec-11-Dr - Maysoon AlkazzazДокумент12 страницThe Spinal Cord: Lec-11-Dr - Maysoon AlkazzazRose ParisОценок пока нет
- VB AnatomyAtlas Preview 112513Документ11 страницVB AnatomyAtlas Preview 112513Ahmad FaramiОценок пока нет
- Saladin 21 Ext OutlineДокумент30 страницSaladin 21 Ext OutlineAlvin L. RozierОценок пока нет
- Maharastra Paper - 2011Документ140 страницMaharastra Paper - 2011Abhishek ChakravortyОценок пока нет
- TissuesДокумент60 страницTissuesTedi Hoxha100% (1)
- Exercise 14 Circulatory SystemДокумент9 страницExercise 14 Circulatory SystemJovelou MihangosОценок пока нет
- Lymphatic TissueДокумент50 страницLymphatic TissueRukshan RanatungaОценок пока нет
- Faculty of Medicine: Practical Work No. 9Документ3 страницыFaculty of Medicine: Practical Work No. 9Andrei TimofteОценок пока нет
- Blood Vessels, AnatomyДокумент20 страницBlood Vessels, AnatomyAbu BakarОценок пока нет
- Snell AbdomenДокумент43 страницыSnell AbdomenBenОценок пока нет
- Saccule and UtricleДокумент4 страницыSaccule and UtricleMalek ElgmatiОценок пока нет
- Exercise 15 Lymphoid OrganДокумент7 страницExercise 15 Lymphoid OrganJovelou MihangosОценок пока нет
- Figure 1: The Cochlea and Organ of CortiДокумент3 страницыFigure 1: The Cochlea and Organ of CortiLouie BelloОценок пока нет
- Autonomic Nervous System: Aqsa Khan (MPT Sem)Документ19 страницAutonomic Nervous System: Aqsa Khan (MPT Sem)furquan 810Оценок пока нет
- Lecture Two Anatomy1Документ7 страницLecture Two Anatomy1moh.ahm3040Оценок пока нет
- Characteristics of Histology SlidesДокумент4 страницыCharacteristics of Histology SlidesLaiq Khan100% (1)
- SCALP: (Keith L Moore)Документ5 страницSCALP: (Keith L Moore)rajtanniruОценок пока нет
- Perbedaan Papila Dan Folikel Pada MataДокумент2 страницыPerbedaan Papila Dan Folikel Pada MataMuhammad Agus Nashir100% (1)
- Baylissascaris LarvisДокумент136 страницBaylissascaris LarvisAlejoDubertiОценок пока нет
- Walt Disney: SpeechДокумент2 страницыWalt Disney: SpeechBuşuMihaiCătălinОценок пока нет
- (Tham Khảo) Tài Liệu Ngoại Ngữ Y2Документ55 страниц(Tham Khảo) Tài Liệu Ngoại Ngữ Y2Nam TruongОценок пока нет
- PNS - Bafs 267.2019 Code of Good Animal Husbandry Practice For SwineДокумент20 страницPNS - Bafs 267.2019 Code of Good Animal Husbandry Practice For Swinejoriz klenz sabeteОценок пока нет
- Polar Bear (Report Text)Документ14 страницPolar Bear (Report Text)Adeb Wahyu100% (1)
- Sense OrgansДокумент6 страницSense Organsannmarie100% (1)
- Gibberish WordsДокумент4 страницыGibberish WordsDaniel PopaОценок пока нет
- Savage Worlds Cheatsheets PowersДокумент15 страницSavage Worlds Cheatsheets Powersschwartz5350Оценок пока нет
- Prepared by D.sirag Al-Hamadi Tripoli University Dental FacultyДокумент59 страницPrepared by D.sirag Al-Hamadi Tripoli University Dental Facultypepe_074Оценок пока нет
- Case 1Документ6 страницCase 1Nico AguilaОценок пока нет
- Organs of Hearing and Tactile ResponsesДокумент4 страницыOrgans of Hearing and Tactile ResponsesNarasimha MurthyОценок пока нет
- Aarthi Minor AllДокумент52 страницыAarthi Minor AllVenkatesan Vidhya100% (1)
- Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2021Документ25 страницMark Scheme (Results) Summer 2021Gaia PhyllisОценок пока нет
- Kumri-In Goat :A Laboratory Epidemiological Outbreak Investigation in Banke District of Mid-Western Region of Nepal.Документ7 страницKumri-In Goat :A Laboratory Epidemiological Outbreak Investigation in Banke District of Mid-Western Region of Nepal.Karki KedarОценок пока нет
- Comparative Anatomy of The Horse, Ox, and Dog-The Brain and Associated VesselsДокумент11 страницComparative Anatomy of The Horse, Ox, and Dog-The Brain and Associated VesselsmichiparisОценок пока нет
- Modic Type 1 Vs Tuberculous SpondylitisДокумент5 страницModic Type 1 Vs Tuberculous SpondylitisAgnes JauwОценок пока нет
- Genetics Icar1Документ18 страницGenetics Icar1elanthamizhmaranОценок пока нет
- Formation of Faeces and DefecationДокумент11 страницFormation of Faeces and Defecationbiologi88Оценок пока нет
- The Vitamin C Treatment of Whooping CoughДокумент14 страницThe Vitamin C Treatment of Whooping CoughoneclickgroupОценок пока нет
- Diaphragmatic Breathing: The Foundation of Core StabilityДокумент7 страницDiaphragmatic Breathing: The Foundation of Core StabilityLevyОценок пока нет
- Animal BiotechnologyДокумент12 страницAnimal BiotechnologyMoises Von De GraciaОценок пока нет
- Production Objectives and Management Strategies of Livestock Keepers in South-East Kenya: Implications For A Breeding ProgrammeДокумент18 страницProduction Objectives and Management Strategies of Livestock Keepers in South-East Kenya: Implications For A Breeding Programmeabraha gebruОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 - Respiratory SystemДокумент43 страницыChapter 2 - Respiratory SystemSYAZWANIОценок пока нет
- Maurice Blanchot Thomas The Obscure 1Документ124 страницыMaurice Blanchot Thomas The Obscure 1backwardsduchamp100% (2)
- Physiology 8 Nervous SystemДокумент7 страницPhysiology 8 Nervous SystemFahim Khan100% (18)
- Guide:-Prof. Dr. V. P. Joglekar Dept. of Agadatantra, Tilak Ayu. Mahavidyalaya, Pune Author: - Dr. Nishant B. BarapatreДокумент24 страницыGuide:-Prof. Dr. V. P. Joglekar Dept. of Agadatantra, Tilak Ayu. Mahavidyalaya, Pune Author: - Dr. Nishant B. BarapatreDrNishant Barapatre100% (1)
- Background of The StudyДокумент4 страницыBackground of The StudyFerreze AnnОценок пока нет
- Thesis Statement For Animal ResearchДокумент5 страницThesis Statement For Animal Researchtit0feveh1h3100% (1)
- Medical Parasitology in The Philippines 3rd Ed PDFДокумент535 страницMedical Parasitology in The Philippines 3rd Ed PDFroland mamburam75% (16)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessОт Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (33)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityОт EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (6)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisОт EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceОт EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (18)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldОт EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (597)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomОт EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (216)
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseОт EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (52)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsОт EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (6)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceОт EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (517)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerОт EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (393)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainОт EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (111)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedОт EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (11)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesОт EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (397)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionОт EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (812)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainОт EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (65)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveОт EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (66)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemОт EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (116)
- Remnants of Ancient Life: The New Science of Old FossilsОт EverandRemnants of Ancient Life: The New Science of Old FossilsРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (3)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildОт EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (44)
- Darwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignОт EverandDarwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (19)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindОт EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (93)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueОт EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (38)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorОт EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorОценок пока нет