Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Experiment No 11
Загружено:
Shreeraj PandeyИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Experiment No 11
Загружено:
Shreeraj PandeyАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
EXPERIMENT No.
11
Objective
To measure the radiation pattern and the gain of a wave- guide horn Antenna.
Equipment
Gunn power supply, Gunn oscillator, PIN modulator or Klystron mount with Klystron tube, Klystron Power Supply, Frequency meter, Isolator, Variable attenuator, Detector mount, Two-horn antenna, Turn table, VSWR meter, and accessories.
Theory
If a transmission line propagating energy is left open at one end, there will be radiation from this end. In case of a rectangular wave-guide this antenna presents a mismatch of about 2:1 and it radiates in many directions. The match will improve if the open wave-guide is a horn shape. The Radiation pattern of an antenna is a diagram of field strength or more often the power Intensity as a function of the aspect angle at a constant distance from the radiating antenna. An Antenna pattern is of course three-dimensional but for practical reasons it is normally presented as a two dimensional pattern in one or several planes. An antenna pattern consists of several lobes, the main lobe, side lobes and the back lobe. The major power is concentrated in the main lobe and it is required to keep the power in the side lobes and back lobe as low as possible. The power intensity at the maximum of the main lobe compared to the power intensity achieved from an imaginary omni-directional antenna ( radiating equally in all directions ) with the same power fed to the antenna is defined as gain of the antenna. 3dB Beam Width This is the angle between the two points on a main lobe where the power intensity is half the maximum power intensity. When measuring an antenna pattern, it is normally most interesting to plot the pattern far from the antenna.
The antenna Far field pattern is achieved at a minimum distance of
2D2
(For rectangle Horn antenna)
0
Where D is the size, of the broad wall of horn aperture and 0 is free space wave length. It is also very important to avoid disturbing reflection. Antenna measurement is normally made at outdoor ranges or in so called anechoic chambers made of absorbing materials. Antenna measurements are mostly made with unknown antenna as receiver. There are several methods to measure the gain of antenna. One method is to compare the unknown antenna with a standard gain antenna with known gain. Another method is to use tow identical antennas, as transmitter and other as receiver. From following formula the gain can be calculated.
Pt0G1G2 Pr = ( 4 S )2
Where Pt is transmitted power, Pr is received Power, G1, G2 are gain of transmitting and receiving Antenna respectively, S is the radial distance between two antennas and 0 is free space wave length. If both transmitting and receiving antenna are identical having gain G then above equation becomes.
Pt0G2 Pr = (4 S) 2
In the above equation Pt, Pr S and 0 can be measured and gain can be computed. As is evident from the above equation, it is not necessary to know the absolute value of Pt and Pr, only ratio is required which can be measured by VSWR meter.
Procedure
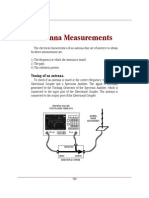
Gunn Power Supply
Gunn Oscillator
Isolator
PIN Modulator
Variable Attenuator
Frequency Meter
Detector Mount
VSWR Meter Fig1. Setup for the Antenna Gain & Pattern Measurement
Antenna Radiation Pattern Plotting
1. Set up the equipments as shown in the figure1, keeping the axis of both antennas in same axis line. 2. Energize the Microwave source for maximum output at desired frequency with square wave modulation by tuning square wave amplitude and frequency of modulating signal of Gunn Power Supply and by tuning the detector. 3. 4. Also tune the S-S Tuner in the line for maximum output (If S.S. Tuner is in the set up) Obtain full scale deflection (0dB) on normal dB scale (0- 10 dB) at any convenient range switch position of the VSWR meter by gain control knob of VSWR meter or by variable attenuator.
5.
Turn the receiving horn to the left in 2 0 or 5 0 steps up to 400 - 500
and note the
corresponding VSWR dB reading in normal dB range. When necessary change the range switches to next higher range and add 10 dB to the observed value. 6. Repeat the above step but this time turns the receiving horn to the right and note down the readings. 7. 8. Draw a relative power pattern i.e. output V/ S angle. From diagram determine 3dB-width (beam width) of the horn antenna .
Gain Measurement
1. 2. Set up the equipments as shown in fig. Both horns should be in line. Keep the range dB switch of VSWR meter at 50 dB position with gain control full. the Gunn Oscillator for maximum output at desired frequency with
3. Energize
modulating amplitude and frequency of Gunn Power Supply and by tuning of detector. 4. 5. Obtain full scale deflection in VSWR meter with variable attenuator. The transmitting horn by detector mount and change the appropriate range dB position to get the deflection ON Scale (do not touch the gain control knob) Note and record the range dB position and deflection of VSWR Meter. 6. Calculate the difference in dB between the power measured in step 4 and 5.
Observations for Radiation pattern measurement
S.No. Angle to the left in turn table VSWR Reading Output Voltage
S.No.
Angle to the right in turn table
VSWR Reading
Output Voltage
Observation for gain measurement
Result
Precautions
1. 2. 3. 4. All the instruments should be operated carefully. Cooling fan should be on while operating Klystron power supply. Take all the observations carefully. After the measurement, put all the instruments in off state.
Questions
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. What do you mean by radiation pattern? What is Antenna? What is Gain of an antenna? What is horn antenna? What is E-plane horn? What is H-plane horn? What is pyramidal horn antenna? What is conical horn antenna? What is open ended waveguide antenna? 10. What is far field pattern?
Вам также может понравиться
- Antenna Radiation Pattern MeasurementДокумент5 страницAntenna Radiation Pattern MeasurementHenri DassОценок пока нет
- Experiment-7: Measurement of The Gain and Polar Pattern of Horn Antenna ObjectivesДокумент5 страницExperiment-7: Measurement of The Gain and Polar Pattern of Horn Antenna ObjectivesSai KaneОценок пока нет
- Laboratorio Microondas 5Документ14 страницLaboratorio Microondas 5Daniel CamiloОценок пока нет
- Antenna Measurements: Experiment-3Документ6 страницAntenna Measurements: Experiment-3nad_chadi8816Оценок пока нет
- Microwave Engineering Labs ManualДокумент23 страницыMicrowave Engineering Labs ManualAbrash Khan SikandriОценок пока нет
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorОт Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Microwave Engineering Practical FileДокумент13 страницMicrowave Engineering Practical FileMohit Dutta100% (1)
- Audio IC Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesОт EverandAudio IC Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Radharaman Institutes of Research & Technology Bhopal Department of Electronics and CommunicationДокумент2 страницыRadharaman Institutes of Research & Technology Bhopal Department of Electronics and Communicationcrazy about readingОценок пока нет
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2От EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Оценок пока нет
- Lab Manual: Subject:ARWPДокумент19 страницLab Manual: Subject:ARWPbhavnaОценок пока нет
- Faculty of Engineering Electrical and Electronic Engineering Department EE521Документ16 страницFaculty of Engineering Electrical and Electronic Engineering Department EE521adamОценок пока нет
- Guide Wavelength Frequency of A Signal in A Rectangular WaveguideДокумент5 страницGuide Wavelength Frequency of A Signal in A Rectangular Waveguideaamreen81867% (3)
- Microwaves in WaveguideДокумент12 страницMicrowaves in Waveguideamit261287Оценок пока нет
- Experiment4 AntennaДокумент4 страницыExperiment4 AntennaRishikant KashyapОценок пока нет
- Experiment 7. Wave PropagationДокумент9 страницExperiment 7. Wave PropagationAlex TrinhОценок пока нет
- Ece481-Microwave and Optical Communication Laboratory ManualДокумент44 страницыEce481-Microwave and Optical Communication Laboratory Manualeceklu100% (1)
- Microwave Manual 2017Документ72 страницыMicrowave Manual 2017manjuri karОценок пока нет
- Antenna MeasurementsДокумент10 страницAntenna MeasurementsTariq SaboeraliОценок пока нет
- RFMW ManualДокумент30 страницRFMW ManualSRI HARSHA ACHIОценок пока нет
- Microwave Lab-Manual (B.tech 2014)Документ54 страницыMicrowave Lab-Manual (B.tech 2014)Ashish MangalОценок пока нет
- Experiment No 8: Aim: To Determine The Frequency & Wavelength in A Rectangular Waveguide Working inДокумент5 страницExperiment No 8: Aim: To Determine The Frequency & Wavelength in A Rectangular Waveguide Working inSanab KumarОценок пока нет
- Margin 6602b0a0a6eef 6602b07a39550Документ4 страницыMargin 6602b0a0a6eef 6602b07a39550Niveditha NisanamОценок пока нет
- Experiment 6Документ7 страницExperiment 6swamyОценок пока нет
- AntennaДокумент1 страницаAntennaAjus RaceОценок пока нет
- Experiment 1 Measurement of Frequency and WavelengthДокумент3 страницыExperiment 1 Measurement of Frequency and WavelengthengrkskОценок пока нет
- AWP Unit 4 Antenna MrasurementДокумент45 страницAWP Unit 4 Antenna Mrasurementjenath1Оценок пока нет
- Microwave Practile Bharati Vidyapeeth BE and MEДокумент43 страницыMicrowave Practile Bharati Vidyapeeth BE and MESantosh PotdarОценок пока нет
- Microwave Lab ManualДокумент64 страницыMicrowave Lab ManualPrannoy ChakravarthiОценок пока нет
- AntennaДокумент10 страницAntennaDeepika SinghОценок пока нет
- Experiment 3Документ3 страницыExperiment 3crazy about readingОценок пока нет
- Radiation Pattern Horn AntennaДокумент3 страницыRadiation Pattern Horn AntennaKalyani NagetiОценок пока нет
- Plane Wave Propagation: 4.1 Important NotesДокумент15 страницPlane Wave Propagation: 4.1 Important NotesboxinessОценок пока нет
- Experiment-4: Low, Medium and High VSWR MeasurementsДокумент5 страницExperiment-4: Low, Medium and High VSWR MeasurementsSai KaneОценок пока нет
- RF Lab Experiment Lab ManualДокумент9 страницRF Lab Experiment Lab ManualAMIT SHARMAОценок пока нет
- ECOM 4101 Antenna Lab Experiment 01Документ17 страницECOM 4101 Antenna Lab Experiment 01SRОценок пока нет
- Antenna Measurements TechniquesДокумент16 страницAntenna Measurements TechniquesM AОценок пока нет
- Compact Ranges: Microwave Antennas Need - U.P.W For Illumination - Far Field Distances in The SetupДокумент49 страницCompact Ranges: Microwave Antennas Need - U.P.W For Illumination - Far Field Distances in The SetupSyed MuzzuОценок пока нет
- Transmission Media Lab ManualДокумент21 страницаTransmission Media Lab ManualMohamed EidОценок пока нет
- Ec2405 - Optical and Microwave Laboratory (Manual)Документ32 страницыEc2405 - Optical and Microwave Laboratory (Manual)Jonathan SheltonОценок пока нет
- Open Ended Wave Guide)Документ5 страницOpen Ended Wave Guide)Tushar DaveОценок пока нет
- New Microwave Lab ManualДокумент35 страницNew Microwave Lab ManualRadhikaОценок пока нет
- 1 130322152456 PDFДокумент60 страниц1 130322152456 PDFAnonymous 7fP7O8ZОценок пока нет
- Microwave Engineering Experiments RGPVДокумент28 страницMicrowave Engineering Experiments RGPVYash JainОценок пока нет
- Frequency and Wavelength Measurement: Experiment-1Документ3 страницыFrequency and Wavelength Measurement: Experiment-1dhawanrishОценок пока нет
- Antenna and Microwave Lab ManualДокумент28 страницAntenna and Microwave Lab Manualडाँ सूर्यदेव चौधरीОценок пока нет
- Exp 5Документ5 страницExp 5Dilan TuderОценок пока нет
- Microwave Lab ManualДокумент52 страницыMicrowave Lab ManualDhanish VijayanОценок пока нет
- Mwe Expt3Документ5 страницMwe Expt3krОценок пока нет
- Antenna LabmanualДокумент10 страницAntenna LabmanualMoon Sun0% (1)
- Experiment 2 Low, Medium and High VSWR Measurements: E E E E E E SДокумент4 страницыExperiment 2 Low, Medium and High VSWR Measurements: E E E E E E SanandvmahadikОценок пока нет
- Electron Spin Resonance: ApplicationsДокумент5 страницElectron Spin Resonance: ApplicationsrameshamruthaluriОценок пока нет
- Laboratorio Microondas 3Документ10 страницLaboratorio Microondas 3Daniel CamiloОценок пока нет
- ECC309 Microwave Engineering LabДокумент56 страницECC309 Microwave Engineering Labdebu526mahanusОценок пока нет
- MDC Lab ManualДокумент74 страницыMDC Lab Manualmani kumarОценок пока нет
- Calle Zorro - Penis Size ParanoiaДокумент0 страницCalle Zorro - Penis Size ParanoiaAquarius Sharp BladeОценок пока нет
- Analysis of Rainfall and Temperature Variability To Guide Sorghum (Sorghum Bicolar) Production in Maitsebri District, Northwestern Tigray, EthiopiaДокумент6 страницAnalysis of Rainfall and Temperature Variability To Guide Sorghum (Sorghum Bicolar) Production in Maitsebri District, Northwestern Tigray, EthiopiafffОценок пока нет
- Logistic RegДокумент87 страницLogistic RegSiddhant SanjeevОценок пока нет
- 112-1 中英筆譯Документ15 страниц112-1 中英筆譯beenbenny825Оценок пока нет
- Match Headings Questions 1-5Документ2 страницыMatch Headings Questions 1-5Aparichit GumnaamОценок пока нет
- Compare and Contrast: Costa Rica and PanamaДокумент1 страницаCompare and Contrast: Costa Rica and PanamaHong NguyenОценок пока нет
- 2006 Consensus Agreement On The Design and Conduct of Clinical Studies With Low-Level Laser Therapy and Light Therapy For Musculoskeletal Pain and DisordersДокумент2 страницы2006 Consensus Agreement On The Design and Conduct of Clinical Studies With Low-Level Laser Therapy and Light Therapy For Musculoskeletal Pain and DisordersDetian WangОценок пока нет
- Telephone Triage For Oncology Nurses Print Replica Ebook PDFДокумент57 страницTelephone Triage For Oncology Nurses Print Replica Ebook PDFdaniel.salazar678100% (37)
- How Emotionally Intelligent Are You Wong and Law Emotional Intelligence Scale WLEISДокумент2 страницыHow Emotionally Intelligent Are You Wong and Law Emotional Intelligence Scale WLEISIsabela Bică100% (2)
- Answers For TimesetДокумент11 страницAnswers For TimesetMuntazirОценок пока нет
- Self Incompatibility: Dr. L.K.GangwarДокумент38 страницSelf Incompatibility: Dr. L.K.GangwarSiddhant Singh100% (1)
- Social Media Has Improve Human Communication (FOR AND DEBATE)Документ2 страницыSocial Media Has Improve Human Communication (FOR AND DEBATE)Abdul Raheman89% (9)
- Ethical Hacking and Penetration Testing Guide - Baloch, RafayДокумент2 страницыEthical Hacking and Penetration Testing Guide - Baloch, RafayAyush PoptaniОценок пока нет
- An Automated Machine Vision Based System For Fruit Sorting and GradingДокумент6 страницAn Automated Machine Vision Based System For Fruit Sorting and GradingMekaTronОценок пока нет
- Wedding Salmo Ii PDFДокумент2 страницыWedding Salmo Ii PDFJoel PotencianoОценок пока нет
- True Blood S2 Ep 3 English SubtitlesДокумент70 страницTrue Blood S2 Ep 3 English SubtitlesTrue Blood in Dallas100% (2)
- Project SelectingДокумент29 страницProject SelectingayyazmОценок пока нет
- Zambian Open University: School of Social Science and HumanitiesДокумент9 страницZambian Open University: School of Social Science and HumanitiesEvangelist Kabaso SydneyОценок пока нет
- Junto, Brian Cesar S.Документ1 страницаJunto, Brian Cesar S.Brian Cesar JuntoОценок пока нет
- Jurnal Teori Pertukaran SosialДокумент11 страницJurnal Teori Pertukaran SosialRhama PutraОценок пока нет
- Minimalism of InformationДокумент125 страницMinimalism of InformationRastko VukovicОценок пока нет
- Civil Law - Persons FamilyДокумент59 страницCivil Law - Persons FamilyCharmaine MejiaОценок пока нет
- Facebook MotionДокумент24 страницыFacebook MotionDealBookОценок пока нет
- Readable Elaine Kirn - Pamela Hartmenn, - 2009 - Interactions 1 - EnG 106 - 2020S - TEXTДокумент256 страницReadable Elaine Kirn - Pamela Hartmenn, - 2009 - Interactions 1 - EnG 106 - 2020S - TEXTle huy100% (1)
- Behind The Scrubs: Monica Velarde Saint Mary's College December 09, 2008Документ21 страницаBehind The Scrubs: Monica Velarde Saint Mary's College December 09, 2008EthanОценок пока нет
- Hands On With Google Data Studio: A Data Citizen's Survival Guide - Lee HurstДокумент5 страницHands On With Google Data Studio: A Data Citizen's Survival Guide - Lee HurstdowycyfoОценок пока нет
- John Zink - Flare - Upstream - ProductionДокумент20 страницJohn Zink - Flare - Upstream - ProductionJose Bijoy100% (2)
- Anthropometry in DesignДокумент45 страницAnthropometry in DesignShalini YadavОценок пока нет
- Ansari Ibnarabdoctrine 1999Документ45 страницAnsari Ibnarabdoctrine 1999JYOTI PALОценок пока нет
- Information Analyzer Data Quality Rules Implementations Standard Practices - 01052012Документ94 страницыInformation Analyzer Data Quality Rules Implementations Standard Practices - 01052012abreddy2003Оценок пока нет
- Conquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeОт EverandConquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (10)
- INCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesОт EverandINCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Electrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tОт EverandElectrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (27)
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionОт EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (543)
- Digital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosОт EverandDigital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Hacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsОт EverandHacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2)
- Practical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialОт EverandPractical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (3)
- Retro Gaming with Raspberry Pi: Nearly 200 Pages of Video Game ProjectsОт EverandRetro Gaming with Raspberry Pi: Nearly 200 Pages of Video Game ProjectsОценок пока нет
- Programming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonОт EverandProgramming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- 2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersОт Everand2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Analog Design and Simulation Using OrCAD Capture and PSpiceОт EverandAnalog Design and Simulation Using OrCAD Capture and PSpiceОценок пока нет
- A Mind at Play: How Claude Shannon Invented the Information AgeОт EverandA Mind at Play: How Claude Shannon Invented the Information AgeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (53)
- Heat Transfer Engineering: Fundamentals and TechniquesОт EverandHeat Transfer Engineering: Fundamentals and TechniquesРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Teach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionОт EverandTeach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (15)