Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
John Deere Valve Adjustment
Загружено:
autobritaiИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
John Deere Valve Adjustment
Загружено:
autobritaiАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
- - ------------
Engine Repair
Cylinder Head, Valves and Camshaft
20-05-1
Group 05 CYLINDER HEAD, VALVES, AND CAMSHAFT
PRELIMINARY VALVE CHECKS
During disassembly, inspect the valve train for the following malfunctions and causes. Sticking Valves Carbon deposits on valve stem Worn valve guides Warped valve stems Cocked or broken valve springs Worn or distorted valve seats Insufficient lubrication
Camshaft Failures
Scored camshaft lobes due to inadequate lubrication Excessive end play due to thrust plate wear Broken or warped camshaft due to improper timing
Checking Valve Clearance
Four-Cylinder Engine
Warped, Worn, or Distorted Valve Guides
Lack of lubrication Cylinder head distortion Excessive heat Unevenly tightened cylinder head cap screws
Distorted Cylinder Head and Cylinder Head Gasket Leakage
Improperly tightened cylinder head cap screws Faulty gasket installation Incorrect gasket material Excessive oil pressure Improper cylinder liner height above cylinder block
Worn or Broken Valve Seats
Misaligned valves Distorted cylinder head Carbon deposits on seats due to incomplete combustion Valve spring tension too weak Excessive heat Improper valve clearance Improper valve timing
Fig. 1-Sening "TOC"
Burned, Pitted, Worn, or Broken Valves
Worn or distorted valve seats Worn valve guides Insufficient cooling Insufficient lubrication Cocked or broken valve springs Preignition Improper engine operation Improper valve train timing Faulty valve rotators Warped or distorted valve stems "Stretched" valves due to excessive spring tension Warped cylinder head Bent push rods Carbon build-up on valve seats Rocker arm failure
TM-1106 (Jan-79) Litho in U.S.A.
1. Rotate engine to position No. 1 piston at TDC of its compression stroke. 2. Turn flywheel until timing mark on flywheel lines up with mark on housing (Fig. 1).
Engines - 400 Series
20-05-2
Cylinder Head, Valves, and Camshaft
Engine Repair
Checking
Valve Clearance-Continued
Six Cylinder Engine
.......
Four Cylinder Engine
3
I
I E
2 E I
1
I E
T2284?N VALVE CLEARANCE SPECIFICATION
II
R 27478NJ
Intake and Exhaust Valves
0.018 In. (0.46 mm)
lj
Fig. 3-Setting "TOC"
Fig. 2-Four-Cylinder Valve Clearance Adjustment
3. Adjust valve clearance on No. 1 and 3 exhaust valves and No. 1 and 2 intake valves. 4. Rotate flywheel 360 degrees until No.4 piston is at TOC of its compression stroke.
5. Adjust valve clearance on No. 2 and 4 exhaust valves and No. 3 and 4 intake valves to the specification listed above.
1. Use JOE-81 Engine Rotation Tool Set (A, Fig. 3) to position No. 1 piston at TOC of its compression stroke. 2. Turn flywheel until timing pin engages timing hole in flywheel and both valves on No. 1 cylinder are in the up position (rocker arms loose).
OF ENGINE-
432
E I
lEE
I E
NO. I TDC COMPRESSION STROKE
EI
IE
EI
IE
EI
IE
R 11117
NO.6
TDC COMPRESSION STROKE
VALVE CLEARANCE SPECIFICATIONS
Intake Valves Exhaust Valves
0.018 in. (0.46 mm) 0.028 in. (0.71 mm)
Fig. 4-Six-Cylinder Valve Clearance Adjustment
TM-1106 (Jan-79) Litho in U.S.A.
Engines
- 400
Series
-------.
Engine Repair
Cylinder Head, Valves, and Camshaft
20-05-3
Checking
Valve Lift
Measuringvalve liftcan give an indicationof wear to cam lobes, cam followers, and push rods. 1. Set valve clearance to specifications as previously indicated.
Fig. 5-Checking Valve Clearance
3. Adjust valve clearance on No.1, 3, and 5 exhaust valves and No.1, 2, and 4 intake valves (Fig. 5). 4. Rotate flywheel 360 degrees until NO.6 piston is at "TOG" of its compression stroke, and tool timing pin engages flywheel hole.
Fig. 6-Checking Valve Lift (6-Cylinder shown)
5. Adjustvalve clearance on No.2, 4, and 6 exhaust valves and No.3, 5, and 6 intake valves to the specifications listed above.
2. Place dial indicator on rotator (Fig. 6). 3. Manually turn engine in running direction (counterclockwise) . 4. After rocker arm contacts valve stem, observe
dial indicator reading as valve is moved to full open.
VALVE LIFT NEW PART SPECIFICATIONS
4270 Intake Valves. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. 0.431 to 0.461 in. (10.95 to 11.71 mm) Exhaust Valves 0.427 to 0.457 in. (10.85 to 11.61 mm) 64040 and 64660 Intake Valves. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. 0.424 to 0.454 in. (10.77 to 11.53 mm) Exhaust Valves. . . . . . . . . . . . .. 0.414 to 0.444 in. (10.52 to 11.28 mm) 6404T and A; 6466T and A Intake Valves. .. . . . . . . . . . . . .. 0.412 to 0.442 in. (10.46 to 11.23 mm) Exhaust Valves. . . . . . . . . . .. .. 0.413 to 0.443 in. (10.49 to 11.25 mm)
TM-1106 (Jan-79) Litho in U.S.A.
Engines
400 Series
--
--------
-.
-- --- --- - ..-
20-05-4
Cylinder Head, Valves, and Camshaft
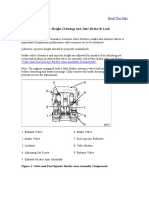
ROCKER Removal
Engine Repair ARM ASSEMBLY
CYLINDER HEAD AND VALVES Access
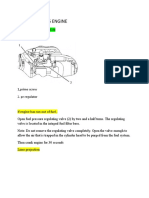
1. Disconnect battery ground cables and drain cooling system (not shown).
NOTE: 6466T (072864) and A (068223) engines use a one-piece rocker arm shaft clamp in place of the Nos. 1 and 2 and 5 and 6 clamps. 1. Remove rocker arm shaft clamp cap screws. NOTE: When removing rocker arm shaft components, identify for reassembly into original position.
Fig. 7-Left Side Removal Steps
(6466A Engine Shown)
A-End Plug..
B-Oil Holes
C-Adjusting
Screws
2. Remove air cleaner, mufflerand exhaust elbow. 3. Remove intercooler ("A" engines) with intake manifold. 4. Remove turbocharger ("T"and "A"engines) with exhaust manifold.
Fig. 9-Rocker Arm Shaft Components (6-Cylinder Shown)
2. Remove rocker arm shaft end plugs and slide components from shaft (Fig. 9).
Inspection and Repair
1. Inspect rocker arm shaft for scratches, scores, or excessive wear at points of rocker arm contact.
NOTE: Wear could indicate weak valve springs, bent push rods, or loose rocker arm shaft clamps.
2. Be sure that all oil holes are open and clean (B, Fig. 9). 3. Check rocker arm adjusting nut and screw for damage (C, Fig. 9). 4. Check for cups or concave wear on ends of rocker arms where they contact valve tips (A, Fig. 10).
Fig. 8-Right Side Removal Steps
(6466A Engine Shown)
5. Remove water manifold. 6. Remove fuel lines and leak-off line. Plug openings to prevent contamination. 7. Remove fuel injection nozzles. 8. Remove rocker arm cover.
TM-1106 (Jan-79) Litho in U.S.A.
Engines - 400 Series
Engine Repair
Cylinder Head, Valves, and Camshaft
20-05-5
VALVES, VALVE SPRINGS, VALVE ROTATORS, AND WEAR CAPS Removal
1. Remove rocker arm assembly as previously described. 2. Remove head. NOTE: When removing valves, valve springs, and valve rotators, identify for reassembly into original positions.
R 26131N A-Worn Area
Fig. 10-Rocker Arm Wear
3. Use a valve spring compressor to remove valves from head.
Inspection Valve Springs
And Repair
5. Examine spacer springs on shaft between rocker arms, and be sure they are strong enough to exert a positive pressure on arms. NOTE: If the rocker arm has been damaged by a valve failure, replace it and the push rod when replacing valves.
1. Inspectvalve springsfor alignment,wear, and damage. 2. Placespringson a flat surfaceto see that they are squareand parallel. 3. Checkvalve spring tension on a spring tester.
VALVESPRINGNEWPARTSPECIFICATIONS
Assembly and Installation
1. Assemble parts on rocker arm shaft in reverse of sequence removed. 2. Make sure rocker arm shaft end plugs are firmly seated in end of shaft.
Compression Height 54 to 62 Ibs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.81 in. (240.2 to 275.8 N) (45.9 mm) 133 to 153 Ibs.. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.36 in. (591.6 to 680.5 N) (34.5 mm)
Valves, Rotators and Wear Caps 1. Insure that valve rotators will turn freely in one direction. If defective, replace with new. 2. Replace valve wear caps if pitted or worn. 3. Visually check valve face and stem for wear or damage. 4. Perform the following cleaning procedure before measuring or repairing valves. Cleaning Valves
A /~
R 26136NI
__
- --B-Locatlng Hole
__I
1. Hold each valve firmly against a wire wheel on a bench grinder. 2. Make sure all carbon is removed from the valve head, face and stem. IMPORTANT: Any carbon left on the stem will affect alignment in valve refacer if valves need to be refaced. 3. Polish the valve stems with steel wool or fine emery cloth to remove any scratch marks left by the wire brush. Engines - 400 Series
A-Spring Pin
Fig. 11-Rocker Arm Shaft Locating Holes
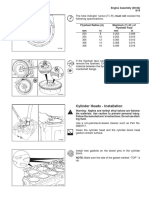
3. Position rocker arm shaft on head, insuring that spring pin (A, Fig. 11) and locating hole (B) in rocker arm shaft line up. 4. Tighten rocker arm shaft clamp cap screws to 55 ft-Ibs (75 Nm) (7.5 kgm). TM-1106 (Jan-79) Litho in U.S.A.
20-05-6
Cylinder Head, Valves, and Camshaft
Valve Guides
Engine Repair
Inspection and Repair-Continued
1. Use a valve guide cleaning brush to clean valve guides before inspection or repair.
NOTE: A few drops of light oil or kerosene will help to fully clean the guide.
RG1l77 A-44-1/2 (42700,64040) 29.1/2 (6404T, A and 6466)
~.3715 to 0.3725 In. (9.43 to 9.46 mm)
Fig. 12-Valve Specifications
4. Compare valve stem 0.0. (B, Fig. 12) with valve guide 1.0. to determine stem-to-guide clearance.
A-Valve Guide
B-Telescope
Fig. 14-Checking Valve Guide
Gauge
2. Measure valve guides for wear (Fig. 14).
VALVE GUIDE NEW PART SPECIFICATIONS
,.
/"A
/'
'?
1.0. of guide in a new head ... 0.3745 to 0.3755 in. (9.512 to 9.537 mm) New guide-to-valve stem clearance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.0020 to 0.0040 in. (0.051 to 0.102 mm)
\
1 ;J
R 26139N Fig. 13-lnspecting Valves
NOTE: Worn guides can allow a clearance of 0.006 in. (0.15 mm) and still be acceptable. Worn guides may be knurled to return them to specified clearance if valve-to-guide clearance is 0.010 in. (0.25 mm) or less. If clearance exceeds 0.010 in. (0.25 mm), install oversize valves.
5. Use D-05058ST Valve In.spectionCenter (Fig. 13) to determine if valves are out of round, bent or warped.
TM-1106 (Jan-79) Litho in U.S.A.
Engines - 400 Series
Engine Repair
Cylinder Head, Valves, and Camshaft
20-05-7
R26126N
A-Valve Seat Insert B-Valve Seat Angle (4270D, 6404D) .450 (6404T, A and 6466). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .300 C--Valve Seat Width. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.083 to 0.093 In. (2.11 to 2.36 mm) D-Valve Seat Runout (Maximum). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. 0.002 In. . (0.05 mm)
Fig. 17-Valve Seat Specifications
A-Knurler B-Reamer
C--Speed Reducer D-Lubricant
Fig. 15-Knurling Valve Guides
Grinding
Valve Seats
3. Use No. D-20002WI Knurling Tool Set to knurl valve guides (Fig. 15). NOTE: Use tool set exactly as directed by the manufacturer. Valve Seats
Fig. 18-Grinding Valve Seats
III>
'R26142N Fig. 16-Cleaning Valve Seats
1. Do not grind too long. Only a few seconds are required to recondition the average valve seat. Avoid the natural tendency to grind off too much. 2. Do not use too much pressure. While grinding, support the weight of the driver to avoid excess pressure on the stone. 3. Keep the work area clean. 4. Check the seat width and contact pattern between the seat and valve with blueing.
1. Use an electric hand drill with wire cleaning brush (Fig. 16) and remove all carbon. 2. Check seats for cracks, pits, or excessive wear. 3. Recondition valve seat by grinding.
TM-1106 (Jan-79) Litho in U.S.A.
Engines - 400 Series
20-05-8
Cylinder Head, Valves, and Camshaft
Engine Repair
Inspection
and Repair-Continued
Replacing Valve Seat Inserts
Checking Valve Height 1. After grinding,installvalve.
Fig. 20-Removing
Valve Seats
1. Remove valve seats with JOE-41296 Valve Seat Puller (Fig. 20).
Fig. 19-Checking Valve Height
2. Use a dial indicator to check valve height (Fig. 19).
Valve Height Specification (In relation to cylinder head surface)
42700, 64040, 64660 Intake Valve. . . . . . . . . .. 0.038 to 0.050 in. below (0.96 to 1.27 mm below) Exhaust Valve . . . . . . . .. 0.054 to 0.068 in. below (1.37 to 1.72 mm below) 6404T and A, 6466T and A 0.038 in. above to 0.006 in. below (0.96 mm above to 0.15 below)
NOTE: If valve face protrudes, check valve face angle and valve seat angle. If valve is recessed, install either new valves, valve seats, or both, to obtain proper valve height.
A-Insert B-Replacement
C-JDE.7 Driver Ring
Fig. 21-lnstalling Valve Seat Inserts
2. Select the proper Replacement Ring from the following table:
Valve Seat
Ring
42700, 64040 and T, 64660
Intake. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . JOE-67 Exhaust . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . JOE-66 6404A, 6466T and A. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . JOE-79 3. Chill both new insert (A, Fig. 21) and Ring (8) to -20F (-29C) in dry ice. 4. Use JOE-7 Oriver (C) and proper Ring to drive inserts into place. 5. Grind valve seats.
TM-1106 (Jan-79) Litho in U.S.A.
Engines - 400 Series
- ---
--
--
Engine Repair
Cylinder Head, Valves, and Camshaft
20-05-9
Installing Oversize Inserts In some cases, the outside diameter of the valve seat bore may become damaged and require machining. In this case, oversize inserts are available in 0.010 in. (0.25 mm) oversize only. 1. Remove valve seats withJDE-41296 ValveSeat Puller. 2. Machine seat diameter to 1.7585 to 1.7595 in. (44.67 to 44.69 mm). 3. Replace inserts as previously indicated.
\
NOTE: Valves must move freely and seat properly. 3. Install valve springs making certain that cylinder head end of spring is located correctly in machined counter bore of the head. 4. Install rotators. 5. Compress valve springs with valve spring compressor. 6. Install retainer locks on valves.
Cylinder Head 1. Thoroughly clean the cylinder head.
7. Strike the end of each valve three or four times with a soft mallet to insure proper positioning of the retainer locks.
Installation
NOTE: See page 20-10-10 before installing cylinder head gasket on 64040 and 64660 engines. 1. Install cylinder head gasket dry. 2. Place cylinder head in correct position on block. 3. Dip cap screws and washers in clean engine oil.
R 26146N
Fig. 22-Checking Cylinder Head
2. Use a straight edge to check the head for level (Fig. 22). 3. Warpage should not exceed 0.001 in. (0.02 mm) for every 5 in. (127 mm) of head length. Assembly 1. Apply AR44402 Lubricant to valve stems and guides. NOTE: New exhaust and intake valves are color
R 26147N Fig. 23-Cylinder Head Cap Screw Tightening Sequence (Start at No.1)
coded green and yellow respectively on 6404T and A.
Valves are
coded black and red respectively on 64040
and 42700.
2. Install valves in guides from which they were removed.
TM-1106 (Jan-79) Litho in U.S.A.
Engines - 400 Series
20-05-10
Cylinder Head, Valves, and Camshaft
Engine Repair
Installation-Continued
4. Install cap screws and tighten to the following specifications using the sequence shown in Fig. 23.
CYLINDER HEAD CAP SCREW TORQUES
8. Tighten rocker arm shaft clamp cap screws to 55 ft-Ibs (75 Nm) (7.5 kgm). 9. Reverse access steps. 10. Run engine at 2100 RPM for 1/2 hour.
.Initial
42700
ft-Ibs
Nm
kgm
.....................
115
64040 ..................... 105 6404T and A ............... 80 64660, T and A. . . . . . . . . . . . . 105 Second 42700 .....................130 64040 ..................... 6404T and A ...............115 64660, T and A (plain head) .............. 64660, T, and A ("12.9" head)............
156 142 108 142 180 180 156 156 180
15.6 14.2 10.8 14.2 18.0 18.0 15.6 15.6 18.0
11. Retighten cylinder head cap screws to the following specifications using the sequence shown in Fig. 23.
CYLINDER HEAD CAP SCREW TORQUES
130
115 .130
ft-Ibs Final 42700 and 64040. . . . . . . . . . . 150 6404T and A ............... 130 64660, T and A (plain head) .............. 130 64660, T and A ("12.9" head) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Nm 204 180 180 204
kgm 20.4 18.0 18.0 20.4
CAMSHAFT Checking Camshaft End Play
1. Remove rocker arm cover. 2. Remove rocker arm assembly. 3. Remove push rods. Identify for reassembly. 4. Remove damper and pulley (6 cylinder engines). 5. Remove timfhg gear cover.
NOTE: Early model6466enginesmayhavea plain headed cap screw. Late models may have screws marked "12.9" on the head. 5. Install push rods in holes from which they were removed. 6. Install wear caps on valves making certain caps rotate freely.
A-Spring Pin
B-Locating Hole
Fig. 24-Rocker Arm Shaft Locating Hole
7. Position rocker arm shaft on head, insuring that spring pin (A, Fig. 24) and locating hole (8) in rocker arm shaft line up.
Fig. 25-Checking Camshaft End Play
TM-1106 (Jan-79) Litho in U.S.A.
Engines - 400 Series
---
Engine Repair
Cylinder Head, Valves, and Camshaft Inspection and Repair
20-05-11
1. Place a dial indicator on camshaft (Fig. 25). 2. Check camshaft end play.
CAMSHAFT END PLAY SPECIFICATIONS
Camshaft Gear 1. Inspect camshaft drive gear for worn or broken teeth and replace as necessary.
New engine end play . . . . . . . . . 0.0025 to 0.0085 in. (0.06 to 0.22 mm) Allowable end play 0.0150 in. (0.38 mm)
NOTE: If end play exceeds wear specification check thrust washer thickness during disassembly.
Removal
Fig. 27-6-Cylinder Camshaft Drive Gear
2. On 6-cylinder engines, inspect camshaft drive gear for slippage between the two parts of the gear. NOTE: An indexing mark has been placed across the parting line of the two parts of the gear (A, Fig. 27). If the mark has separated, the gear should be replaced. 3. Examine crankshaft gear and injection pump drive gear for worn or broken teeth or damage. NOTE: If either gear has failed, both gears must be replaced as a matched set. Removing Camshaft Gear 1. Remove cap screw and special washer.
Fig. 26-lnstalling Magnetic Holding Tool Set
1. Remove oil pan and oil pump. 2. Use D-15001NU Magnetic Holding Tool Set to hold cam followers away from camshaft (Fig. 26). 3. Remove four cap screws from thrust plate.
4. Carefully remove camshaft from cylinder block so that camshaft lobes do not drag in bores.
Fig. 28-Removing Camshaft Gear
TM-1106 (Jan-79) Litho in U.S.A.
Engines
400 Series
20-05-12
Cylinder Head, Valves, and Camshaft Lobes
Engine Repair
Inspection and Repair-Continued
2. Support camshaft gear in a press (Fig. 28). IMPORTANT: Prevent camshaft from striking floor when pressing camshaft from gear. 3. Press camshaft from gear.
1. Checkcamshaftlobesfor wear or damage.
2. Check camshaft oil pump drive gear for wear or damage.
NOTE: If camshaft is replaced due to a damaged oil pump drive gear, check gear and shaft on oil pump for damage and replace if necessary. If camshaft is replaced, cam fol/owers must also be replaced.
Thrust Plate
After removal of camshaft gear, check thrust plate for proper thickness. THRUSTPLATESPECIFICATIONS New Part Thickness 0.1860 to 0.1890 in. (4.72 to 4.80 mm) Acceptable wear thickness 0.1820 in. (4.62 mm)
Assembly
Bushings and Journals Checkcamshaftbushingsandjournalsfor wear or damage.
BUSHINGAND JOURNALSPECIFICATIONS New Journal O.D. 2.3745 to 2.3755 in. (60.31 to 60.34 mm) New Bushing I.D.. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.3775 to 2.3795 (60.39 to 60.44 mm) Clearance Allowable. . . . . . . .. 0.0060 in. (0.15 mm)
A-Thrust Plate B-Spacer A-Tool Locking Key B- Tool Mandrel C-Camshaft Bushing D-Engine Block
C-Woodruff Key D-Keyway
Fig. 30-Supporting Camshaft in Press
Fig. 29-lnstal/ing Camshaft Bushings
1. Support camshaft under first journal in a hydraulic press. (Fig. 30).
2. Install thrust plate (A) and spacer (B).
1. Use JDE-6 Camshaft Bushing Replacement Set to remove and install camshaft bushings. NOTE: The first two bushings can be reached from the front of the engine. The PTO assembly and flywheel must be removed to service the rear bushings. When new bushings are instal/ed, be sure that the elongated oil holes are to the top and are aligned with the oil holes in the cylinder block.
3. Install Woodruff key (C). 4. Align Woodruff key (C) and keyway (D) and place gear on camshaft with timing mark facing away from camshaft. 5. Press gear on until tight against camshaft shoulder.
TM-1106 (Jan-79) Litho in U.S.A.
Engines - 400 Series
Engine Repair
Cylinder Head, Valves, and Camshaft
20-05-13
Installation
If cam followers have been removed. reinstall using the D-15001NU (ND425) Magnetic Holding Tool Set to hold cam followers away from camshaft bore until camshaft is installed. 1. Coat camshaft with JDT405 High Temperature Grease, or equivalent.
2. Carefully install camshaft in cylinder block so that camshaft lobes do not drag in bores.
3. With No. 1 piston on TDC of its compression stroke, align timing marks (C, Fig. 31) on camshaft and crankshaft gears. 4. Turn camshaft gear to align thrust plate holes with cylinder block holes. 5. Tighten thrust plate-to-block cap screws to 20 ft-Ibs (27 Nm) (2.7 kgm). 6. Install special washer on camshaft. 7. Tighten camshaft gear-to-camshaft cap screw to 85 ft-Ibs (115 Nm) (11.5 kgm). 8. Check camshaft for 0.0025 to 0.0085 in. (0.06 to 0.22 mm) end play.
A-Location Mark B- Thrust Plate Cap Screw
C- Timing Mark
Fig. 31-Gear Timing
TM-1106 (Jan-79) Litho in U.S.A.
Engines - 400 Series
Вам также может понравиться
- Detroit s60 Valve AdjustmentДокумент12 страницDetroit s60 Valve AdjustmentÑengo Flow Full Record50% (2)
- Detroit s60 Valve Adjustment PDFДокумент12 страницDetroit s60 Valve Adjustment PDFDiego Monroy50% (2)
- C12 Adjust InjectorДокумент11 страницC12 Adjust Injectorzhenguo DongОценок пока нет
- Caterpillar 3406B Connecting RodsДокумент6 страницCaterpillar 3406B Connecting Rodsducatiss900100% (3)
- Peterbilt Rear Air Suspensions AdjustmentДокумент42 страницыPeterbilt Rear Air Suspensions AdjustmentCellblocX83% (6)
- CTC12Документ2 страницыCTC12Joffre Lautaro Benavides SeminarioОценок пока нет
- 3208 Pump Install Timing InstructionsДокумент4 страницы3208 Pump Install Timing InstructionsUliAlejandroRodriguezCorianga100% (1)
- Jacobs Brake Application Guide CaterpillarДокумент8 страницJacobs Brake Application Guide Caterpillarviemey1952100% (2)
- Cat C15 SDP Testing and Adjusting Manual 2 PDFДокумент138 страницCat C15 SDP Testing and Adjusting Manual 2 PDFDragan Krsmanovic100% (1)
- ENGINE C15 (Torque de Bielas)Документ4 страницыENGINE C15 (Torque de Bielas)Maquinaria Pesada ServisОценок пока нет
- Valve LashДокумент1 страницаValve LashJose Luis Poma MОценок пока нет
- CAT Compression Brake Lash - AdjustДокумент2 страницыCAT Compression Brake Lash - Adjustbenge henrique100% (2)
- Automatic Timing Advance 7FB1-Up, 4MG1-4MG3599Документ10 страницAutomatic Timing Advance 7FB1-Up, 4MG1-4MG3599EdivaldoVeronese100% (1)
- 3406e and 3456 EngineДокумент20 страниц3406e and 3456 EnginebejoythomasОценок пока нет
- Calibracion Valvulas Motor c12 CaterpillarДокумент5 страницCalibracion Valvulas Motor c12 CaterpillarOmar Diaz Segura100% (1)
- Inyector n3 TorquesДокумент2 страницыInyector n3 TorquesDiego MonroyОценок пока нет
- ENGINES & GENERATOR SETS - C13, C15, and C18 Generator Set Engines - Gear Group (Front) - TimeДокумент8 страницENGINES & GENERATOR SETS - C13, C15, and C18 Generator Set Engines - Gear Group (Front) - TimeJose Montoya100% (6)
- C13 TDC InstallДокумент4 страницыC13 TDC InstallEwgeny100% (1)
- 3054 Engine Valve Lash - InspectAdjustДокумент5 страниц3054 Engine Valve Lash - InspectAdjusthenry lavieraОценок пока нет
- In-Frame Overhaul Procedure: 3406E & C-15 Diesel Truck Engines Engine DesignДокумент2 страницыIn-Frame Overhaul Procedure: 3406E & C-15 Diesel Truck Engines Engine Design李文琪100% (1)
- Cummins L10 Series Workshop ManualДокумент558 страницCummins L10 Series Workshop ManualMarielis Contreras0% (1)
- Manual Compresor Holset Qe296 PDF Repair GuideДокумент5 страницManual Compresor Holset Qe296 PDF Repair GuideGuillermo Gerardo Sanchez Ponce25% (8)
- 3304B/3306B and 3406B/3406C: DipacoДокумент34 страницы3304B/3306B and 3406B/3406C: DipacoErick Alarcon67% (3)
- Fault Code 254Документ11 страницFault Code 254adrian maulana100% (3)
- n14 Cylinder Head InstallationДокумент3 страницыn14 Cylinder Head InstallationOumarba KamandaОценок пока нет
- Meritor Rockwell ZF 9 Speed RMX9 145BДокумент203 страницыMeritor Rockwell ZF 9 Speed RMX9 145BCarlos Chavez100% (2)
- Cummims Manuales de Servicio y Reparacion NT 855 PDFДокумент693 страницыCummims Manuales de Servicio y Reparacion NT 855 PDFJames Scott Valderrama100% (7)
- Testing and Adjusting: Pantalla AnteriorДокумент145 страницTesting and Adjusting: Pantalla AnteriorDEYNER100% (4)
- Install fuel injection pump on engineДокумент14 страницInstall fuel injection pump on enginemaxtal100% (2)
- 3406B (PEEC) Electronic TroubleshootingДокумент15 страниц3406B (PEEC) Electronic TroubleshootingRichard ChuaОценок пока нет
- SPN 931 FMI 3 - EFP Short To PWRДокумент3 страницыSPN 931 FMI 3 - EFP Short To PWRNestorAdanMerazОценок пока нет
- Celect Injector Adjustment 01-05Документ3 страницыCelect Injector Adjustment 01-055476492% (13)
- Torques 3406 Caterpillar PDFДокумент3 страницыTorques 3406 Caterpillar PDFjoseОценок пока нет
- Detroit Diesel - Low Power Bulletin - MBE4000-07Документ40 страницDetroit Diesel - Low Power Bulletin - MBE4000-07Juan Pablo Montaño Rivas100% (1)
- Cat 3176 Engine Manual: Table of ContentДокумент2 страницыCat 3176 Engine Manual: Table of Contententreprise.tgctp2015100% (1)
- Valv CAT 3116Документ8 страницValv CAT 3116Tatiano Brollo100% (1)
- Cylinder Head: Cerrar SIS Pantalla AnteriorДокумент2 страницыCylinder Head: Cerrar SIS Pantalla Anteriorallmachinessas machinesОценок пока нет
- Adjust The Valves and N3 Fuel Injector Settings As Follows:: Series 60 Service ManualДокумент4 страницыAdjust The Valves and N3 Fuel Injector Settings As Follows:: Series 60 Service ManualJavier Leyva Yuco100% (1)
- Cat 3406 Eddc IIДокумент85 страницCat 3406 Eddc IIKarim Ahmed Khodja100% (1)
- 379 Peterbuilt Heater-AcДокумент2 страницы379 Peterbuilt Heater-AcKeith Vest100% (2)
- Valve Lash For Cummins Engine K38Документ9 страницValve Lash For Cummins Engine K38Youssef Ali100% (1)
- CAT c10 and c12 Specification PDFДокумент182 страницыCAT c10 and c12 Specification PDFCristina100% (4)
- The Other Side Is TheДокумент2 страницыThe Other Side Is Themoomaed aliОценок пока нет
- Injection Pump Cat 3406Документ115 страницInjection Pump Cat 3406Vicente Ortiz Delgado94% (33)
- Series 60 - Section 1.11 Gear Case Cover Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) ModelДокумент14 страницSeries 60 - Section 1.11 Gear Case Cover Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) ModelJuan RiveraОценок пока нет
- ACT 32&uq 3656 - 34 - 275&ut John Deere Powertech 8.1l Diesel Engine Repair Manual PDF ctm86Документ6 страницACT 32&uq 3656 - 34 - 275&ut John Deere Powertech 8.1l Diesel Engine Repair Manual PDF ctm86иван Троянов100% (1)
- Eaton D170 ServiceДокумент90 страницEaton D170 ServiceJesús AraizaОценок пока нет
- GM Engines v-6, V-8Документ23 страницыGM Engines v-6, V-8jads301179Оценок пока нет
- Valve Lash AdjustmentsДокумент13 страницValve Lash AdjustmentsEnriqueОценок пока нет
- Calibración Serie 50Документ10 страницCalibración Serie 50Jesús AraizaОценок пока нет
- Valve Adjustment E7Документ16 страницValve Adjustment E7malcolm stewartОценок пока нет
- Adjust Caterpillar Engine Valve LashДокумент5 страницAdjust Caterpillar Engine Valve Lashjosel204Оценок пока нет
- Qdoc - Tips - Gy6 Engine Service ManualДокумент39 страницQdoc - Tips - Gy6 Engine Service ManualAislan ScaravattoОценок пока нет
- Valve Lash Check: Table 1Документ4 страницыValve Lash Check: Table 1Виталий ОрловОценок пока нет
- Husqvarna 611238238782 - 61Документ6 страницHusqvarna 611238238782 - 61Mauro OliveiraОценок пока нет
- Calibracion Inyector n3 Ddec VДокумент6 страницCalibracion Inyector n3 Ddec VJosue Juaniquina LucanaОценок пока нет
- Ajuste de Valvulas PDFДокумент8 страницAjuste de Valvulas PDFRoberto Rincon RoblesОценок пока нет
- Llave Hidraulica RodДокумент29 страницLlave Hidraulica RodCarlos TorradoОценок пока нет
- Volkswagen Engines - 4-CylinderДокумент12 страницVolkswagen Engines - 4-Cylinderjorge almarazОценок пока нет
- PerkinsДокумент12 страницPerkinsDalibor Sopina Duc100% (2)
- Gehl SL 4640 4840 5640 6640 Parts Manual PDFДокумент352 страницыGehl SL 4640 4840 5640 6640 Parts Manual PDFautobritai100% (5)
- Gehl SL 4640 4840 5640 6640 Parts ManualДокумент2 страницыGehl SL 4640 4840 5640 6640 Parts ManualautobritaiОценок пока нет
- Spare Parts Catalog Case 595 Sle 595 SLPДокумент550 страницSpare Parts Catalog Case 595 Sle 595 SLPautobritai100% (1)
- Carraro 711-19 Axle Workshop ManualДокумент34 страницыCarraro 711-19 Axle Workshop ManualautobritaiОценок пока нет
- EW160 AlarmsДокумент12 страницEW160 AlarmsIgor MaricОценок пока нет
- Carraro 711-19 Axle Workshop ManualДокумент0 страницCarraro 711-19 Axle Workshop ManualSelmirije2100% (1)
- Main Frame and Component PartsSerial N°Qty.2Документ309 страницMain Frame and Component PartsSerial N°Qty.2Andreea Boacara83% (12)
- Manual HP 43 2-2017 - ENДокумент43 страницыManual HP 43 2-2017 - ENautobritaiОценок пока нет
- Kubota V3300-1 PDFДокумент140 страницKubota V3300-1 PDFautobritai100% (1)
- Bobcat Loader CodesДокумент11 страницBobcat Loader CodesJose Pacheco Corrales100% (1)
- Deutz ManualДокумент76 страницDeutz Manualdim4erema50% (4)
- SB40Документ3 страницыSB40autobritaiОценок пока нет
- Manitou Tower ServiceДокумент35 страницManitou Tower ServiceKélio Wolfrane Santos MachadoОценок пока нет
- Mla628 12002 07Документ878 страницMla628 12002 07autobritai100% (1)
- Hakki Pilke Easy 38 Operators Manual SchematicsДокумент37 страницHakki Pilke Easy 38 Operators Manual SchematicsautobritaiОценок пока нет
- 940 (PriortoSN5476803) SkidSteerLoaderPartManual 000-34884 Ren09-08Документ174 страницы940 (PriortoSN5476803) SkidSteerLoaderPartManual 000-34884 Ren09-08Jaime Eduardo Madrid Hidalgo100% (3)
- BF4M2012 00010274800 PDFДокумент128 страницBF4M2012 00010274800 PDFAbbas AhmedОценок пока нет
- Hakki Pilke BigX50 ManualДокумент38 страницHakki Pilke BigX50 Manualautobritai100% (1)
- 2000 MTD Service ManualДокумент160 страниц2000 MTD Service Manualautobritai100% (1)
- SL4635 & SL4835 Parts ManualДокумент142 страницыSL4635 & SL4835 Parts ManualWilliam Arledge100% (2)
- Volvo Penta Aquamatic80 HandbookДокумент49 страницVolvo Penta Aquamatic80 HandbookautobritaiОценок пока нет
- Faults CodesДокумент10 страницFaults Codesautobritai100% (1)
- Hydraulics troubleshooting guideДокумент13 страницHydraulics troubleshooting guideautobritai100% (2)
- HR02 TerexДокумент112 страницHR02 Terexautobritai75% (4)
- MustangДокумент165 страницMustangautobritai100% (1)
- 940 (PriortoSN5476803) SkidSteerLoaderPartManual 000-34884 Ren09-08Документ174 страницы940 (PriortoSN5476803) SkidSteerLoaderPartManual 000-34884 Ren09-08Jaime Eduardo Madrid Hidalgo100% (3)
- Hakki Pilke 38 ManualДокумент36 страницHakki Pilke 38 ManualautobritaiОценок пока нет
- Torque Specifications Chart for Acura, Alfa Romeo, and Allis Chalmers EnginesДокумент124 страницыTorque Specifications Chart for Acura, Alfa Romeo, and Allis Chalmers EnginesZack Leon85% (13)
- Piston Pump FailureДокумент9 страницPiston Pump FailureautobritaiОценок пока нет
- Hakki Pilke 1X42 Hyrdo ManualДокумент93 страницыHakki Pilke 1X42 Hyrdo ManualautobritaiОценок пока нет
- Kohler KDI 1903 and 2504 Engine Service PartsДокумент204 страницыKohler KDI 1903 and 2504 Engine Service PartsKaddachiSayedОценок пока нет
- Cummins QuickServe OnlineДокумент2 страницыCummins QuickServe OnlinejengandxbОценок пока нет
- 6cta MedicoДокумент81 страница6cta MedicoCrespo JorgeОценок пока нет
- Makalah DASAR-DASAR Mesin: Untuk Memenuhi Salah Satu Tugas Mata Pelajaran Teknik Dasar OtomotifДокумент14 страницMakalah DASAR-DASAR Mesin: Untuk Memenuhi Salah Satu Tugas Mata Pelajaran Teknik Dasar OtomotifAevunx CthmОценок пока нет
- Reed valve removal and checkingДокумент1 страницаReed valve removal and checkingPHUONG NGUYENОценок пока нет
- Engine DisassemblyДокумент30 страницEngine Disassemblybertoy100% (1)
- LawnmowerДокумент2 страницыLawnmowerlili aboudОценок пока нет
- Ariel Corporation: JGR/JGJДокумент2 страницыAriel Corporation: JGR/JGJAhmed IbrahimОценок пока нет
- BMW Normal TISДокумент4 страницыBMW Normal TISjoeolaabidakunОценок пока нет
- Culata JD 6466Документ4 страницыCulata JD 6466TECNOTRAC AldanaОценок пока нет
- Weichai Marine Engine - WD12 SeriesДокумент3 страницыWeichai Marine Engine - WD12 SeriesAT Solution TechnologyОценок пока нет
- Shibaura Diesel Engine S773L - Tier4 XXДокумент28 страницShibaura Diesel Engine S773L - Tier4 XXMihai PopaОценок пока нет
- Case 595 P100 GBДокумент5 страницCase 595 P100 GBLAZARO GARCIAОценок пока нет
- Motoare VWДокумент5 страницMotoare VWSSSwОценок пока нет
- Motion of Vehicles & Engines ExplainedДокумент9 страницMotion of Vehicles & Engines ExplainedPusat Tuisyen Celik JayaОценок пока нет
- Cylinder Block 26227236Документ3 страницыCylinder Block 26227236dharmawan100% (1)
- EPL English AllДокумент18 страницEPL English AlliglesiasljОценок пока нет
- Airplane Engine e 00 Angl GoogДокумент442 страницыAirplane Engine e 00 Angl GoogviorelcroitoruОценок пока нет
- Operation and Maintenance ManualДокумент4 страницыOperation and Maintenance ManualVictor NunezОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of A Valve FailureДокумент1 страницаAnatomy of A Valve FailureJesseОценок пока нет
- IOP Hydraulic Power UnitsДокумент5 страницIOP Hydraulic Power Unitsswapneel_kulkarni100% (1)
- Driving the Aftermarket with Diesel Component ExpertiseДокумент2 страницыDriving the Aftermarket with Diesel Component ExpertiseTablet AlgoОценок пока нет
- Differences in crosshead lubrication arrangements between Sulzer and MAN B&W enginesДокумент1 страницаDifferences in crosshead lubrication arrangements between Sulzer and MAN B&W enginesVijay A100% (3)
- Yanmar DieselДокумент5 страницYanmar DieselSalwan Shubham100% (1)
- Mangalam Polytechnic College Presentation on Valvetronic Engine TechnologyДокумент11 страницMangalam Polytechnic College Presentation on Valvetronic Engine TechnologyAkshay AppuОценок пока нет
- UEC 37LA Main Engine Parts InventoryДокумент5 страницUEC 37LA Main Engine Parts InventoryjoreyvilОценок пока нет
- Chevy SB Cylinder Head ID GuideДокумент2 страницыChevy SB Cylinder Head ID Guideborreg1282% (11)
- Timing Chain Sprockets - Installation (Timing Chain) - ALLDATA RepairДокумент10 страницTiming Chain Sprockets - Installation (Timing Chain) - ALLDATA RepairRafael RafaelОценок пока нет
- ZASTAVAДокумент11 страницZASTAVAMarko ZivanovicОценок пока нет
- Ficha Tecnioca de Chevolet CMV y CMPДокумент44 страницыFicha Tecnioca de Chevolet CMV y CMPLenin Barahona Lazo100% (1)