Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Chapter 001 LP
Загружено:
jacaranda73Исходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chapter 001 LP
Загружено:
jacaranda73Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
1 Introduction to the Human Body
TEACHING FOCUS
In this chapter, students will have the opportunity to learn the terms anatomy and physiology. Students will be introduced to the levels of organization of the human body. They will describe the 11 major organ systems and will define homeostasis. Students will also describe anatomical position and list common terms used for relative positions of the body. They will describe the three major planes of the body, list the anatomical terms for regions of the body, and describe the major cavities of the body.
Lesson Plan
MATERIALS & RESOURCES
Blank index cards for the Line Em Up, Match Em Up, and Word Sort class activities (Lessons 1.1
and 1.2)
Modeling clay for the Shape It Up class activities (Lesson 1.2) Overhead transparency or photocopies of Review Your Knowledge: MatchingDirections of the
Body (p. 13) for the Pretest (Lesson 1.1) Poster board (one piece per group, cut in half) for the Demonstrate It class activity (Lesson 1.2)
LESSON CHECKLIST
Preparations for this lesson include: lecture method of student evaluation for entry-level knowledge to achieve competency print the descriptions for the Match Em Up class activity on note cards (Lesson 1.2)
Copyright 2007 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
The Human Body in Health and Illness, 3rd ed. Herlihy
Chapter 1Introduction to the Human Body
TERMS & DEFINITIONS
abdominal cavity (p. 10) abdominopelvic cavity (p. 10) anatomical position (p. 7) anatomy (p. 2) anterior (p. 7) cells (p. 3) central (p. 7) circulatory system (p. 3) cranial cavity (p. 9) deep (p. 7) digestive system (p. 4) distal (p. 7) dorsal (p. 7) dorsal cavity (p. 9) endocrine system (p. 3) frontal plane (p. 8) homeostasis (p. 4) homeostatic imbalance (p. 7) homeostatic mechanisms (p. 4) inferior (p. 7) integumentary system (p. 3) lateral (p. 7) lymphatic system (p. 4) medial (p. 7) mediastinum (p. 10) morphology (p. 2) muscular system (p. 3) nervous system (p. 3) organs (p. 3) organ systems (p. 3) pathophysiology (p. 2) pelvic cavity (p. 10) peripheral (p. 7) physiology (p. 2) pleural cavities (p. 10) posterior (p. 7) proximal (p. 7) quadrants (p. 11) reproductive system (p. 4) respiratory system (p. 4) sagittal plane (p. 8) skeletal system (p. 3) spinal (vertebral) cavity (p. 9) superficial (p. 7) superior (p. 7) thoracic cavity (p. 10) tissues (p. 3) transverse plane (p. 8) urinary system (p. 4) ventral (p. 7) ventral cavity (p. 10) viscera (p. 9)
ADDITIONAL RESOURCES
PowerPoint slides (IR, Evolve): 1-17 Transparency Masters (Evolve)
Legend
EILR EVOLVE Instructors Learning Resource
ESLM EVOLVE Self-Paced Learning Module
IR Instructors Resource CD-ROM
PPT PowerPoint Slides (EILR and IR)
SG Study Guide
TB Test Bank (EILR and IR)
TM Transparency Masters (EILR) Class Activities are indicated in italic.
Copyright 2007 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
The Human Body in Health and Illness, 3rd ed. Herlihy
Chapter 1Introduction to the Human Body
LESSON 1.1 PRETEST
Review Your Knowledge: MatchingDirections of the Body (p. 13)
BACKGROUND ASSESSMENT
Question: Name four of the major organ systems of the human body. Answer: The major organ systems of the human body are the: integumentary, skeletal, muscular, nervous, endocrine, circulatory, lymphatic, respiratory, digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems. Question: What are the divisions of each of the two major cavities of the body? Answer: The divisions of the dorsal cavity are the cranial cavity and the spinal (vertebral) cavity. The divisions of the ventral cavity are the thoracic cavity and the abdominopelvic cavity.
CRITICAL THINKING QUESTION
Why must complex systems, such as the human body, maintain homeostasis? Guidelines: Students may discuss the fact that if a system does not succeed in reestablishing its balance the system may stop functioning properly. Complex systems must have homeostasis to maintain stability and to survive. Many disorders may result from an imbalance of internal equilibrium that is unable to be adjusted by the bodys physiological processes. Some examples would be diabetes, heat stroke, dehydration, and hypothermia.
OBJECTIVES
CONTENT
TEACHING RESOURCES
Lecture Slides 2-3 Reading assignment: pp. 2-7 Figure 1-1 (p. 2) Structure and function are closely related. Do You Know . . . Why This Grave Is Being Robbed, and Why the Grave Robber Is in Big, Big Trouble? (p. 3) Do You Know . . . Why This Famous Anatomy Laboratory Was Built Over a Small River in Italy? (p. 3) Matching: General Terms (SG p. 2) Chapter 1 Review Questions 1-2
Class Activity: Clinical Situation Ask students
Define the terms Anatomy and physiology: What anatomy and they are (p. 2) physiology. Whats it mean? (p. 2) Why do I need to know this? (p. 2)
to observe their own bodies and provide an example similar to those in Figure 1-1, showing the relationship of structure and function. List the levels of The bodys levels of organization organization of (p. 3) the human Organ-to-organ system (p. 3) body. Slide 4 Figure 1-2 (p. 4) Levels of organization: from atom to human organism. Chapter 1 Review Question 3
Copyright 2007 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
The Human Body in Health and Illness, 3rd ed. Herlihy
Chapter 1Introduction to the Human Body
OBJECTIVES
CONTENT
TEACHING RESOURCES
Class Activity: Line Em Up Write the words in
Figure 1-2 on cards, shuffle, and ask the students to line `em up from simple to complex. Describe the 11 major organ systems. Major organ systems (p. 3) Slides 5-9 Figure 1-3 (pp. 5-6) Major organ systems of the body.
Class Activity: Clue Me In Divide the class into
small groups. Have each group sit in a circle for a game. One member gives a one- or two-word clue from the major organ system descriptions in the textbook. The member of the group opposite that player in the circle must name the correct system. Play continues to the left, giving each group member a turn to give a clue and answer a question. Define homeostasis. Homeostasis: Staying the same (p. 4) Slide 10 Chapter 1 Review Question 4
Class Activity: List It Have students work in
small groups to make a list of homeostatic mechanisms and any disorders they are aware of that are associated with the homeostatic imbalance of each mechanism.
1.1 Homework/Assignments:
Make A List Have each student make a list of at least three examples from the animal worldsuch as the
elephants trunk and the elevated placement of the crocodiles eyesthat illustrate the relationship between structure and function.
1.1 Instructors Notes/Student Feedback:
Copyright 2007 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
The Human Body in Health and Illness, 3rd ed. Herlihy
Chapter 1Introduction to the Human Body
LESSON 1.2 CRITICAL THINKING QUESTION
Why is it important to understand anatomical terms? Guidelines: Students might discuss the fact that understanding anatomical terms will help them as they chart information about patients that will need to be read and understood by other health professionals. Likewise, students must be able to interpret a patients chart and understand the location, position, and regions of body parts described.
OBJECTIVES
Describe the anatomical position.
CONTENT
Anatomical terms: Talking about the body (p. 7) Anatomical position (p. 7)
TEACHING RESOURCES
Slides 11-12 Reading assignment: pp. 7-13 Figure 1-4 (p. 7) Anatomical position. Chapter 1 Review Question 5
Class Activity: Shape It Up Divide the class
into four groups and give each group some clay. Have each group create a small figure in anatomical position (see Figure 1-4). Save these figures for a later class activity. List common terms used for relative positions of the body. Relative positions (p. 7) Slide 13 Sum It Up! (p. 7) Matching: Anatomical Terms (SG p. 3) Chapter 1 Review Question 6 Quiz 1Directional Terms (TM p. 1-2)
Class Activity: Act It Out Ask for volunteers to
come to the front of the class and act out one pair of relative positions while the other students name the positions. Describe the three major planes of the body. Planes and sections of the body (p. 7) Slide 14 Figure 1-5 (p. 8) Planes of the body. Chapter 1 Review Question 7 Class Activity: Shape It Up Divide the class into the same four groups used to create the clay anatomical figures. Have each group use the figure created to demonstrate one plane of the body. Have one group of students section their figure into a sagittal plane, another group into a transverse plane, the third group into a frontal plane, and the last group into a coronal plane. Display and discuss the sectioning, noting that the frontal and coronal planes are the same.
Copyright 2007 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
The Human Body in Health and Illness, 3rd ed. Herlihy
Chapter 1Introduction to the Human Body
OBJECTIVES
CONTENT
TEACHING RESOURCES
Class Activity: Demonstrate It Divide the class
into small groups and have group members demonstrate the planes of the body using two halves of a piece of poster board to indicate each plane on another group member. List anatomical terms for regions of the body. Regional terms (p. 8) Slide 15 Figure 1-6 (p. 9) Regional terms. Review Your Knowledge: MatchingRegional Terms (p. 13) Read the Diagram; Xs, Ys, Zs, and Circles; Matching: Regional Body Terms (SG pp. 4-6) Quizzes 2-3Regional Terms (A-B) (TM pp. 1-4 to 1-7)
Class Activity: Word Sort Have students write
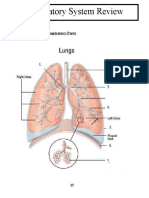
the words from Figures 1-4, 1-5, and 1-6 on index cards and sort the words into: 1. Two groups: words that refer to structures above the diaphragm and those that refer to structures below the diaphragm 2. Three groups: words that refer to the upper extremities, lower extremities, and all other words Cavities of the body (p. 9) Describe the major cavities of Dorsal cavity (p. 9) the body. Ventral cavity (p. 10) Thoracic cavity (p. 10) Abdominopelvic cavity (p. 10) Other cavities (p. 12) Summary outline (p. 12) Slides 16-17 Do You Know . . . What Your Post-Surgical Patient Has Done if He Eviscerated? (p. 12) Sum It Up! (p. 12) Figure 1-7 (p. 10) Major body cavities. Figure 1-8 (p. 11) Areas of the abdomen. Review Your Knowledge: Multiple Choice (p. 13) Matching: Cavities of the Body; Read the Diagram (SG pp. 7-8) Chapter 1 Review Questions 8-10 Quiz 4Cavities of the Body (TM p. 1-8)
Class Activity: Match Em Up Make a series of
cards with the following descriptions and any additional examples. Each team of students draws a card and identifies the correct quadrant and region. 1. The appendix is located in the right lower quadrant. 2. The patient complained of midepigastric
Copyright 2007 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
The Human Body in Health and Illness, 3rd ed. Herlihy
Chapter 1Introduction to the Human Body
OBJECTIVES
CONTENT
TEACHING RESOURCES
pain. 3. The umbilical region appeared reddened. 4. A mass was located in the right lower quadrant. 5. The spleen is located in the left upper quadrant. 6. The liver is located in the right upper quadrant.
Class Activity: Word Sort Have students write
the words from Figure 1-7 on index cards and sort the words into: 1. Two groups: words that pertain to the dorsal cavity and those that pertain to the ventral cavity 2. Three groups: words that are confined to the thoracic cavity and all other words
Performance Evaluation
Chapter 1 Practice Unit Exam: Matching (3 sets), Multiple Choice Chapter 1 Objective Unit Exam: Matching (2 sets), Multiple Choice (IR pp. 10-12) Part II: Putting It All Together, Part III: Challenge Yourself! (SG pp. 83-87) Chapter 1: Multiple Choice Supplemental QuizReview Your Knowledge (TM p. 1-10)
1.2 Homework/Assignments:
Tell-A-Story Have students write a story describing a common everyday event, such as walking to the
mailbox, starting a car, or chopping vegetables for a salad. The students should, however, use anatomical terms for each movement in their description.
1.2 Instructors Notes/Student Feedback:
Copyright 2007 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
The Human Body in Health and Illness, 3rd ed. Herlihy
Вам также может понравиться
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Cardiac Study GuideДокумент11 страницCardiac Study Guidesurviving nursing school100% (2)
- FINALMOP6 4 13WORDRADMay30 PDFДокумент256 страницFINALMOP6 4 13WORDRADMay30 PDFRyan Michael OducadoОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry of The Eye, 2ed. 2003Документ331 страницаBiochemistry of The Eye, 2ed. 2003Vuqar100% (3)
- Anabolic Priming Posture RestoreДокумент21 страницаAnabolic Priming Posture RestoreSamir KapetanovicОценок пока нет
- Structure and Function of A Skeletal SystemДокумент4 страницыStructure and Function of A Skeletal Systemapi-280073172Оценок пока нет
- 15 16 17 Respiratory Test ReviewДокумент3 страницы15 16 17 Respiratory Test ReviewRonaldo Manaoat0% (1)
- PALS Pre StudyДокумент28 страницPALS Pre Studynursesed100% (7)
- Management of Impacted TeethДокумент153 страницыManagement of Impacted TeethToma Irina100% (1)
- Cell Modification ModuleДокумент30 страницCell Modification ModuleDuane100% (1)
- MM TemperamentsДокумент27 страницMM TemperamentsKalpesh Jain100% (2)
- First Grading Exam BiotechnologyДокумент5 страницFirst Grading Exam BiotechnologyMel VilОценок пока нет
- Genetics and Plant Breeding Question BankДокумент4 страницыGenetics and Plant Breeding Question BankVivek Ponnusamy50% (2)
- OB Nursing-Q&AДокумент46 страницOB Nursing-Q&ABelle Moltio-BarcelonaОценок пока нет
- Femoral EmbolectomyДокумент13 страницFemoral EmbolectomyAndrea Aji SanayaОценок пока нет
- Anja Ainamo 1992 in His 18 Year Follow Up Study AfterДокумент215 страницAnja Ainamo 1992 in His 18 Year Follow Up Study AfterSuperna TiwariОценок пока нет
- EmotionsДокумент58 страницEmotionsthivyaashini SellaОценок пока нет
- Evaluation and Management of Elevated Intracranial Pressure in Adults - UpToDate PDFДокумент32 страницыEvaluation and Management of Elevated Intracranial Pressure in Adults - UpToDate PDFSebastianОценок пока нет
- HyperthyroidismДокумент54 страницыHyperthyroidismAsiah JelitaОценок пока нет
- PallorДокумент27 страницPallorAwatef AbushhiwaОценок пока нет
- Co-Ordination-Questions (Sec3)Документ2 страницыCo-Ordination-Questions (Sec3)Tiurma Simanjuntak MSiОценок пока нет
- My Journey With Mum & MDSДокумент54 страницыMy Journey With Mum & MDSIlene OngОценок пока нет
- Management of Osteoporosis in CKD: Pascale Khairallah and Thomas L. NickolasДокумент8 страницManagement of Osteoporosis in CKD: Pascale Khairallah and Thomas L. NickolasSlr RandiОценок пока нет
- Jurnal 5 CДокумент9 страницJurnal 5 CCintya RambuОценок пока нет
- Tumbuh Kembang 2013Документ42 страницыTumbuh Kembang 2013Siti Fadhilla Tsabitha100% (1)
- IS.5216 1982part2Документ27 страницIS.5216 1982part2Mahendra SuryavanshiОценок пока нет
- Stewart and Buffer Base.Документ69 страницStewart and Buffer Base.Yohanes George100% (1)
- Fluid and Electrolyte Therapy Hemant NewДокумент78 страницFluid and Electrolyte Therapy Hemant Newdrhemantparakh100% (1)
- 2011 - Mousavi Et Al - A General Overview On Manganese (MN) Importance For Crops ProductionДокумент5 страниц2011 - Mousavi Et Al - A General Overview On Manganese (MN) Importance For Crops ProductionHans Kristian AkarОценок пока нет
- Chynna Ashley Gonzales Pendon RNДокумент33 страницыChynna Ashley Gonzales Pendon RNChynna Ashley Gonzales PendonОценок пока нет
- LP. Nr.3 - Dr. IspasДокумент4 страницыLP. Nr.3 - Dr. Ispasinna3003Оценок пока нет