Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Gases
Загружено:
vennicesumoИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Gases
Загружено:
vennicesumoАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
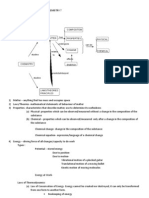
PROPERTIES OF GASES 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Gases may be compressed Gases expand when less pressure is applied.
Gases can be mixed Gases exert a constant pressure on its container walls. Gases have low densities.
KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF GASES 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Gases always move in straight lines and in constant motion Gases are widely spaced Gases collide with each other and with their container walls without loss of kinetic energy Gases behave as individual particles, attraction between them is negligible The actual volumes of gases are insignificant compared to the space they previously occupy
PARAMETERS OF GASES 1. Pressure- chaotic movement of gases make pressure measurement important 1 atm. = 760 mmHg = 760 torr 2. Temperature = gases expand when heated, contract when cooled K = 0C + 273 3. Volume = mL, liter 1 liter = 1000 mL 4. Quantity= grams and or moles GAS LAWS Mathematical statements of the properties and behaviour of gases 1. Boyles Law= At constant temperature, the volume of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure VP = K 2. Charles Law= At constant pressure the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature V/T = K 3. Gay Lussacs Law = At constant volume the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature P/T = K 4. Combined Gas Law = For a given amount of the gas, any change in the condition of one of the variables will also cause a change in the other two variables in accordance to Boyles Law and Charles law. For this reason we can combine the 2 gas laws into one mathematical equation called combined gas law. VP/T = K 5. Ideal Gas Law PV = nRT Where P=pressure in atm. n = moles of gas derived from P V = K Boyles law P/T = K Charles law P/n = K Combining the 3 laws PV/nT = K PV = nKT PV = nRT
V= volume in liter T = absolute temperature 0 R = 0.082 l-atm/mole K (universal gas constant)
1 mole = 22.4 liters o o 0 C = 273 K 1 atm. molar gas volume
standard conditions of temperature and pressure
6. Avogadros Law = Equal volumes of gases under same conditions of temperature and pressure contain equal number of molecules Means Mole Ratio = Volume Ratio
Example :
CH4
+ 2
O2 >>>>> CO2
2H2O
mole ratio
1 mole CH4 2 moles O2
at STP
volume ratio
1 mole CH4 x 22.4 liter s 2 moles O2 x 22.4 liters
1 2
7. Grahams law of Diffusion= The rate of diffusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of the molecular mass of the gas MW increaseas rate decreases ( slow) MW decreases rate increases (fast)
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- MathsДокумент38 страницMathsjyoti jha0% (1)
- Afar Answer by NoemeДокумент22 страницыAfar Answer by NoemeNoeme Lansang100% (5)
- Maths X Assertion Reasoning Chapter 06Документ16 страницMaths X Assertion Reasoning Chapter 06puneet mangla50% (6)
- SolutionsДокумент5 страницSolutionsvennicesumoОценок пока нет
- Dipole Induced Dipole: CH C O CHДокумент4 страницыDipole Induced Dipole: CH C O CHvennicesumoОценок пока нет
- Chemical BondsДокумент6 страницChemical BondsvennicesumoОценок пока нет
- Composition Has Undergoes Relates Can BeДокумент3 страницыComposition Has Undergoes Relates Can BevennicesumoОценок пока нет
- 101 CompositionДокумент3 страницы101 CompositionvennicesumoОценок пока нет
- 3DPLM Placement Papers PDF Download PDFДокумент15 страниц3DPLM Placement Papers PDF Download PDFMahesh SalotagiОценок пока нет
- B7 Term 2 Maths All WeeksДокумент51 страницаB7 Term 2 Maths All WeeksMaverick BryteОценок пока нет
- Degah, The Triple Chariot of God-Symbolism in ArchitectureДокумент8 страницDegah, The Triple Chariot of God-Symbolism in ArchitectureBina AdhikariОценок пока нет
- Table of Specification Second Periodical Test (Mathematics V) No. of Ite Ms Item Placeme NTДокумент7 страницTable of Specification Second Periodical Test (Mathematics V) No. of Ite Ms Item Placeme NTRenalyn Sural Malaca100% (1)
- Current Trends in Mathematics and Future Trends in Mathematics Education (Peter J Hilton)Документ18 страницCurrent Trends in Mathematics and Future Trends in Mathematics Education (Peter J Hilton)Mary Jane AnarnaОценок пока нет
- A Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in RatioДокумент3 страницыA Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in RatioNorsiya MontilaОценок пока нет
- ContinueДокумент5 страницContinueRamesh BurhadeОценок пока нет
- Seventh Grade - 2004 Pg. 17Документ18 страницSeventh Grade - 2004 Pg. 17Aira Joyce Nepomuceno CuaternoОценок пока нет
- Practice Test #1 Data Sufficiency (218 Questions)Документ414 страницPractice Test #1 Data Sufficiency (218 Questions)Karan PatniОценок пока нет
- IBPS PO Previous Year Question Paper 2018: Quantitative Aptitude (Questions & Solutions)Документ15 страницIBPS PO Previous Year Question Paper 2018: Quantitative Aptitude (Questions & Solutions)Raksha JagatapОценок пока нет
- Concrete Mix Ratio PDFДокумент7 страницConcrete Mix Ratio PDFEng Abdikarim WalhadОценок пока нет
- Bilal PDF DissertationДокумент115 страницBilal PDF DissertationkamilbismaОценок пока нет
- SUMMATIVE TEST IN BUSSINESS MATH - Quarter 1Документ8 страницSUMMATIVE TEST IN BUSSINESS MATH - Quarter 1Nancy AtentarОценок пока нет
- MMC 2007 Gr5 DivДокумент2 страницыMMC 2007 Gr5 DivApril Joy Pahilagao PoblacionОценок пока нет
- 11127maths - Ratio, Age, PartnershipcrwillДокумент12 страниц11127maths - Ratio, Age, PartnershipcrwillPrabhat Kumar TiwariОценок пока нет
- RPH M12Документ17 страницRPH M12MITCHELL WONG MoeОценок пока нет
- Table of Specification Mathematics Vi Second Periodical TestДокумент5 страницTable of Specification Mathematics Vi Second Periodical Testjamel mayorОценок пока нет
- Epidemiologic MeasurementsДокумент34 страницыEpidemiologic MeasurementsalaineaОценок пока нет
- Septiya Agestin Cahyaningrum - Resume of Disease Frequency MeasurementДокумент17 страницSeptiya Agestin Cahyaningrum - Resume of Disease Frequency MeasurementSepty KawaiОценок пока нет
- Math 7 Ratios & ProportionsДокумент29 страницMath 7 Ratios & Proportionsceci100% (1)
- Calculating Physical Properties of Slurries - Cheresources PDFДокумент3 страницыCalculating Physical Properties of Slurries - Cheresources PDFTamaОценок пока нет
- UNIT V Ratio ProportionДокумент32 страницыUNIT V Ratio ProportionJagriti RanawatОценок пока нет
- Gold and Silver Ratio - Jan 2011Документ8 страницGold and Silver Ratio - Jan 2011Shiv AgarwalОценок пока нет
- Fish Culture CLMДокумент43 страницыFish Culture CLMGideonCavidaОценок пока нет
- Short Trick To Conquer Quantitative Aptitude..Документ54 страницыShort Trick To Conquer Quantitative Aptitude..Chiranjeevi Kanike0% (1)
- Geodesic Dome Dims - 2V DOME: Estimated DimensionДокумент12 страницGeodesic Dome Dims - 2V DOME: Estimated DimensionmarinerОценок пока нет
- Edited - Ramosa, Kiana 1BSN6 Module Ans. GEДокумент22 страницыEdited - Ramosa, Kiana 1BSN6 Module Ans. GEKiana RamosaОценок пока нет