Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Our Watery Planet: Arctic Ocean Pacifi C Ocean Atlantic Ocean Indian Ocean Southern Ocean
Загружено:
eibsourceИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Our Watery Planet: Arctic Ocean Pacifi C Ocean Atlantic Ocean Indian Ocean Southern Ocean
Загружено:
eibsourceАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
geog.
pages 118-119
7.1
Our watery planet
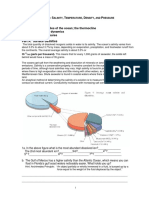
This is about the oceans that make up nearly three quarters of the planets surface.
Arctic Ocean Pacic Ocean
EUROPE ASIA
Atlantic Ocean
NORTH AMERICA
Indian Ocean Southern Ocean
AFRICA SOUTH AMERICA OCEANIA
1 Write the ocean names in the correct place on the map. You may use an atlas to help you. 2 Fill in the gaps in these paragraphs. Choose words from the box. Earth is sometimes called the blue planet because it looks blue from _________. Nearly ___________of the earths surface is ocean. The _____ covered by oceans is the same size as 1,470 United Kingdoms. In nearly half of the oceans the water is more than ______ deep, thats nearly 2 miles! The deepest part of the ocean is almost 11km deep, thats very nearly _______ miles. The water in the oceans is salty, if you drink it you become ______________ and you may die. 3 Design and draw a logo that shows what the oceans are like. Try to include some of the amazing facts.
area dehydrated 3 km space seven three-quarters
The ocean
59
geog.3
pages 120-121
geog.3
pages 122-123
7.2
The essential ocean
7.3
B 1. Little fish eat the phytoplankton 2. Big fish eat the little fish 3. Bacteria and worms feed on animal waste and dead things on the ocean floor 4. This releases CO2 and nutrients which are carried upwards by ocean currents 5. The CO2 and nutrients are then recycled by the phytoplankton
How we use the ocean
This is about the important role that oceans play in the life of our planet. A 1. Carbon dioxide (CO2) is absorbed by the ocean 2. Tiny plants called phytoplankton use the CO2 and water to make glucose 3. The glucose is made through photosynthesis, which needs sunlight to happen 4. Phytoplankton use glucose and nutrients from the water to help them grow 5. Photosynthesis produces oxygen, which goes into the atmosphere
This is about the ways in which we use the ocean.
a Dumping waste in the ocean is banned b 80 million tonnes of fish are fished every year c Oil and gas is taken from under the ocean d Wind farms are being built in the sea e Container ships carry goods around the world
1. The ocean provides us with oxygen but also controls the level of CO2 in the atmosphere. Choose either box A or box B and draw a series of pictures to show what happens.
f People surf, swim and sail on the ocean g Waves and tides are used to generate electricity h Ferries are used for shorter sea journeys. 1 Our use of the ocean affects marine life in many ways. Underline in red the things that are good for the whale, and in blue the things that you think are bad. 2 Choose one good effect and one bad effect. Explain the effects on the whale. Good effect: a b c d e f g h (circle your choice)
Bad effect:
a b c d e f g h (circle your choice)
2. Describe what might happen if the numbers of phytoplankton became less. How might this affect humans?
3 Imagine you are the whale. Do you mind us using your ocean? Explain your thoughts.
60
The ocean
The ocean
61
geog.3
pages 124-125
geog.3
pages 116-125
7.4
Now for the bad news
And to finish
This is about the ocean and how our actions may lead to climate change. Land ice is melting in the Arctic and Antarctic The amount of CO2 in the air is rising because of the burning of fossil fuels Low lying land may flood Increased levels of CO2 helps to cause global warming Sea levels are rising 1 Look at the statements above about global warming. Put numbers 15 in the boxes to put them in the correct order.
What have you learnt about this chapter? 1. Complete the following sentences. Choose from the terms in the box below . a The _______ __________ is where the land slopes gently down to the ocean. b A _________ __________ is built up of limestone secreted by animals called polyps. c The circulation of water from oceans by evaporation, to clouds, to rainfall and back to the oceans again is called the ________ ________. d An ________ __________ is the permanent movement in the oceans of unusually warm or cold surface water. e An _______ _______ is formed where one tectonic plate is being forced under another.
continental shelf coral reef water cycle ocean current ocean trench ocean ridges phytoplankton global conveyor
The ocean current that gives Europe its mild climate, called the North Atlantic Drift, may be under threat. Underwater currents form a system called the global conveyor. This starts in the Arctic where ocean water freezes to ice. Salt is left in the ocean and makes the sea water heavier so it sinks. It then ows away as a deep current. Warm water replaces the cold sinking current, and this starts the conveyor. If fresh water from land ice melting increases, there will be less salt, less sea water will sink and the global conveyor may stop. Global warming may lead to Europe cooling.
f ___________ _________ are long mountain ranges under the oceans. g _____________ are tiny plants that live in the sea. h The ________ __________ is a system of underwater currents.
warm shallow current cold deeper current
2 Write a brief account of how the following effects of human activity are harming the ocean ecosystem. A Global warming
B Overfishing
2 If the global conveyor stops it will affect the ocean ecosystem and our climate. Parts of the UK are on a latitude of between 51 and 58 degrees North of the equator, just like parts of Canada and Russia. Temperatures in the UK may become 5 degrees lower. How might this affect you if it happens? C Pollution
62
The ocean
The ocean
63
Вам также может понравиться
- Exercise SST 2Документ7 страницExercise SST 2Imran AiОценок пока нет
- Define The Following Terms:: I. 1. Biosphere: 2. Isthmus: 3. Strait: 4. Trench: IIДокумент3 страницыDefine The Following Terms:: I. 1. Biosphere: 2. Isthmus: 3. Strait: 4. Trench: IItomaransh94Оценок пока нет
- Global Issues 1 Test PDFДокумент20 страницGlobal Issues 1 Test PDFchandara rimОценок пока нет
- 10 1 Impacts of Climate Change On The Natural WorldДокумент6 страниц10 1 Impacts of Climate Change On The Natural Worldapi-212901753Оценок пока нет
- Geo-Studies chp-1 (Water)Документ9 страницGeo-Studies chp-1 (Water)habiba buttОценок пока нет
- Atmosphere Hydrosphere Notes Worksheet and KeyДокумент12 страницAtmosphere Hydrosphere Notes Worksheet and KeyAinu MuawidzahОценок пока нет
- Water PDFДокумент5 страницWater PDFSonia Sánchez BarrancoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 WaterДокумент2 страницыChapter 5 Waterravi_padur1330Оценок пока нет
- Chap.6 Geo SST 7thДокумент7 страницChap.6 Geo SST 7thsppsdjdjОценок пока нет
- Water Is Everywhere!: Title CardДокумент11 страницWater Is Everywhere!: Title CardJervin ManabatОценок пока нет
- 10.1 - Earth's Supply of WaterДокумент4 страницы10.1 - Earth's Supply of Waterapi-251806635100% (1)
- Earth's Water Resources ExplainedДокумент22 страницыEarth's Water Resources ExplainedMaria Salve50% (2)
- Ashleigh 1Документ23 страницыAshleigh 1api-253530068Оценок пока нет
- Nlenvirte 5163Документ5 страницNlenvirte 5163api-244168124Оценок пока нет
- UD 3 The Hydrosphere 1º ESO PDFДокумент7 страницUD 3 The Hydrosphere 1º ESO PDFPaulaОценок пока нет
- Text Book Phan 2Документ529 страницText Book Phan 2Van Phuong TranОценок пока нет
- Knowledge About EarthДокумент9 страницKnowledge About EarthAsif AliОценок пока нет
- Latihan Pas Bahasa InggrisДокумент18 страницLatihan Pas Bahasa InggrisFarris RasyadОценок пока нет
- Reading, Grammar, WritingДокумент4 страницыReading, Grammar, WritingAna Paula Mendes Marques DiasОценок пока нет
- Section 4: Questions 31-35 Choose The Correct Letter, A, B, or CДокумент16 страницSection 4: Questions 31-35 Choose The Correct Letter, A, B, or CĐức ThiênОценок пока нет
- KV Sector 47 Chandigargh Class 11 SUBJECT: Fundamental of Physical GeographyДокумент8 страницKV Sector 47 Chandigargh Class 11 SUBJECT: Fundamental of Physical GeographyRohiniОценок пока нет
- Surface Salinities Temperature Profiles of The Ocean The Thermocline Seawater Density Dynamics Deep Ocean PressuresДокумент11 страницSurface Salinities Temperature Profiles of The Ocean The Thermocline Seawater Density Dynamics Deep Ocean PressuresSyahdan DzulhajОценок пока нет
- Soal USBN English Conversation Kelas 12Документ9 страницSoal USBN English Conversation Kelas 12Elvira LolangionОценок пока нет
- High School Earth Science 14-26Документ529 страницHigh School Earth Science 14-26Andrei PopaОценок пока нет
- Make Your Own TerrariumДокумент6 страницMake Your Own TerrariumAlisha ChopraОценок пока нет
- Year 8 Oceans Extended Homework-Krishna.G-8pGe3Документ3 страницыYear 8 Oceans Extended Homework-Krishna.G-8pGe3Krishna GajendraОценок пока нет
- Adec Al Quaa School For Boys Grade 8: - Text 2Документ2 страницыAdec Al Quaa School For Boys Grade 8: - Text 2موفق جباعتةОценок пока нет
- Hydrosphere Class 7 NotesДокумент5 страницHydrosphere Class 7 NotesDEOHE BOTOKO GAMER100% (1)
- The Earth's Water Sphere: Oceans, Freshwater and the HydrosphereДокумент2 страницыThe Earth's Water Sphere: Oceans, Freshwater and the Hydrosphereanon_874156217Оценок пока нет
- Week Ten Study GuideДокумент3 страницыWeek Ten Study GuideJadyn BussingerОценок пока нет
- Water BodiesДокумент16 страницWater Bodieschowdarych247Оценок пока нет
- Minerals and Their PropertiesДокумент103 страницыMinerals and Their Propertiesnef blanceОценок пока нет
- Melting of The PolesДокумент9 страницMelting of The Polesdanny1377Оценок пока нет
- Hydro SphereДокумент10 страницHydro SphereJennifer LinthoiОценок пока нет
- English ALS Project-Melting GlaciersДокумент12 страницEnglish ALS Project-Melting GlaciersRadhikaa BehlОценок пока нет
- Hydrosphere 2Документ45 страницHydrosphere 2Rahul S KiniОценок пока нет
- Five OceansДокумент35 страницFive OceansRenny AmeliaОценок пока нет
- Module 3 Unit 1 Sharpening Your Thinking Skills: Eng100 English Enhancement CourseДокумент5 страницModule 3 Unit 1 Sharpening Your Thinking Skills: Eng100 English Enhancement CourseAMPONIN EUNICEОценок пока нет
- Prediction Test 4Документ18 страницPrediction Test 4ielts teamОценок пока нет
- Realms of The EarthДокумент5 страницRealms of The EarthSumantra MukherjeeОценок пока нет
- Water DiversionsДокумент4 страницыWater Diversionsapi-235669157100% (1)
- Back To NatureДокумент10 страницBack To NaturetattoОценок пока нет
- Task 1 Day 11 Describing A CycleДокумент6 страницTask 1 Day 11 Describing A CycleyaleghafirОценок пока нет
- 01 Introduction To Studying The EarthДокумент25 страниц01 Introduction To Studying The EarthjcasafrancaОценок пока нет
- © Ncert Not To Be Republished: Ater CeansДокумент9 страниц© Ncert Not To Be Republished: Ater Ceansurs4everrrОценок пока нет
- How Will Global Warming Affect My World?Документ28 страницHow Will Global Warming Affect My World?Shazad HassanОценок пока нет
- 9th Class-TS-EM-Social Studies-3 - HydrosphereДокумент9 страниц9th Class-TS-EM-Social Studies-3 - HydrosphereSiddhenki StephenОценок пока нет
- MELTING OF THE POLES: A THREAT TO OUR PLANETДокумент7 страницMELTING OF THE POLES: A THREAT TO OUR PLANETEMILIA POLANCO Y ARCINIEGASОценок пока нет
- Climate Change: Prepared By: John Edward CapellanДокумент32 страницыClimate Change: Prepared By: John Edward CapellanJaymar PastorОценок пока нет
- 8unit1ch1slideshow2011 1Документ42 страницы8unit1ch1slideshow2011 1api-238589602Оценок пока нет
- Victoriano, Vanessa F. Bs Psychology Earth Science: 1. A 2. C 3. C 4. A 5. D 6. C 7. D 8. B 9. C 10. BДокумент3 страницыVictoriano, Vanessa F. Bs Psychology Earth Science: 1. A 2. C 3. C 4. A 5. D 6. C 7. D 8. B 9. C 10. BDIANA DIZONОценок пока нет
- Antarctica Homework ProjectДокумент20 страницAntarctica Homework ProjecterbatesОценок пока нет
- ENVIRONMENTAL THREATSДокумент16 страницENVIRONMENTAL THREATSNastja VogrincОценок пока нет
- Water Cycle Webquest2Документ6 страницWater Cycle Webquest2api-330185541Оценок пока нет
- OceanarticleДокумент7 страницOceanarticleapi-265859321Оценок пока нет
- White Paper FinalДокумент6 страницWhite Paper Finalapi-470662827Оценок пока нет
- Week 1 Origin and Structures of The EarthДокумент2 страницыWeek 1 Origin and Structures of The EarthDesiree UrsulumОценок пока нет
- IB Source Catalog 2013-2014Документ112 страницIB Source Catalog 2013-2014eibsource0% (1)
- 9781904534242Документ5 страниц9781904534242eibsourceОценок пока нет
- CIE Source 2013 CatalogДокумент94 страницыCIE Source 2013 CatalogeibsourceОценок пока нет
- The Life Cycle of Plants: Grade 5Документ3 страницыThe Life Cycle of Plants: Grade 5eibsourceОценок пока нет
- 9789814321754Документ2 страницы9789814321754eibsourceОценок пока нет
- CIE Source 2013 CatalogДокумент94 страницыCIE Source 2013 CatalogeibsourceОценок пока нет
- Grade 1: Book CHP No Topics Objectives 1AДокумент2 страницыGrade 1: Book CHP No Topics Objectives 1AeibsourceОценок пока нет
- (Old CAMBRIDGE PRIMARY LO) Life Processes Common To Plants Include Growth, Nutrition andДокумент1 страница(Old CAMBRIDGE PRIMARY LO) Life Processes Common To Plants Include Growth, Nutrition andeibsourceОценок пока нет
- 9789814321457Документ2 страницы9789814321457eibsourceОценок пока нет
- 9789814321600Документ1 страница9789814321600eibsource0% (1)
- 9789814321693Документ2 страницы9789814321693eibsourceОценок пока нет
- 9789814321488Документ2 страницы9789814321488eibsourceОценок пока нет
- Book CHP No Topics ObjectivesДокумент2 страницыBook CHP No Topics ObjectiveseibsourceОценок пока нет
- Living Things and Their Environment: Grade 2Документ1 страницаLiving Things and Their Environment: Grade 2eibsourceОценок пока нет
- 9789814321549Документ1 страница9789814321549eibsourceОценок пока нет
- 9789814321303Документ2 страницы9789814321303eibsourceОценок пока нет
- 9789814321518Документ2 страницы9789814321518eibsourceОценок пока нет
- 9789814321426Документ2 страницы9789814321426eibsourceОценок пока нет
- I Am Learning About Rivers, Mountains and Deserts.: Atlantic OceanДокумент2 страницыI Am Learning About Rivers, Mountains and Deserts.: Atlantic OceaneibsourceОценок пока нет
- 9789814321396Документ2 страницы9789814321396eibsourceОценок пока нет
- 9789814321365Документ2 страницы9789814321365eibsourceОценок пока нет
- 9780199153480Документ4 страницы9780199153480eibsourceОценок пока нет
- 9780199135028Документ2 страницы9780199135028eibsourceОценок пока нет
- 9789814321334Документ2 страницы9789814321334eibsourceОценок пока нет
- 9789814321273Документ2 страницы9789814321273eibsourceОценок пока нет
- Grade 1: Book CHP No Topics Objectives 1AДокумент2 страницыGrade 1: Book CHP No Topics Objectives 1AeibsourceОценок пока нет
- People and Cities: FirstДокумент2 страницыPeople and Cities: FirsteibsourceОценок пока нет
- 9780199153459Документ6 страниц9780199153459eibsourceОценок пока нет
- Health, Fitness and Exercise: The Big PictureДокумент6 страницHealth, Fitness and Exercise: The Big PictureeibsourceОценок пока нет
- Problem 1.1AДокумент23 страницыProblem 1.1AJohnathan Ortega MenesesОценок пока нет
- Environmental Crisis and Sustainable Development SolutionsДокумент62 страницыEnvironmental Crisis and Sustainable Development SolutionsAnti Happy100% (1)
- India Second National Communication To UNFCCC FSDДокумент340 страницIndia Second National Communication To UNFCCC FSDRamu BattaОценок пока нет
- Mine Air Refrigeration MethodsДокумент14 страницMine Air Refrigeration MethodsDeepakKattimaniОценок пока нет
- Rapport PFE C.G Et F.MДокумент90 страницRapport PFE C.G Et F.MHaithem100% (1)
- 02 WholeДокумент344 страницы02 WholeedithgclemonsОценок пока нет
- Long Term Seed BucketДокумент8 страницLong Term Seed BucketseattlesevenОценок пока нет
- Paper 1 Answers KeyДокумент7 страницPaper 1 Answers KeyAnshul BhangaleОценок пока нет
- ExamДокумент39 страницExamJessica Nisperos EspenillaОценок пока нет
- Operator Training ManualДокумент55 страницOperator Training ManualDiego Corona100% (1)
- Nicu ReportДокумент18 страницNicu ReportKabita KarakОценок пока нет
- Biogas PlantДокумент37 страницBiogas PlantMahaManthra100% (1)
- Water Treatment HandbookДокумент46 страницWater Treatment HandbookraotalhaОценок пока нет
- CONFIDENTIAL - Property of Infinity SAV USA Incorporated Gary Tripp 1-206-383-2245Документ43 страницыCONFIDENTIAL - Property of Infinity SAV USA Incorporated Gary Tripp 1-206-383-2245folitasОценок пока нет
- F2 IS Exam 1 (10-11)Документ7 страницF2 IS Exam 1 (10-11)羅天佑Оценок пока нет
- Safety Notes (SABIC)Документ15 страницSafety Notes (SABIC)Tayyab Ali100% (1)
- Natural Abundance of The Stable Isotopes of C, O and HДокумент36 страницNatural Abundance of The Stable Isotopes of C, O and Hkishan kumarОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9 SolutionsДокумент45 страницChapter 9 Solutionsbrayan100% (1)
- PhotosynthesisДокумент6 страницPhotosynthesisAnonymous yEPScmhs2qОценок пока нет
- 5994-2138 Hydrogen Impurity Analysis Agilent 990 Micro GCДокумент4 страницы5994-2138 Hydrogen Impurity Analysis Agilent 990 Micro GCphoenix_lwpОценок пока нет
- 11 Vesda Eco Detector Tds A4 LoresДокумент2 страницы11 Vesda Eco Detector Tds A4 LoresEduardo ParrudoОценок пока нет
- Jacs 1c13368Документ10 страницJacs 1c13368Евгения ИконниковаОценок пока нет
- Bio GasДокумент24 страницыBio GasMohit PunaniОценок пока нет
- Environmental Studies: Submitted byДокумент37 страницEnvironmental Studies: Submitted byAvreen RandhawaОценок пока нет
- CEP Magazine 2023 1691466815Документ6 страницCEP Magazine 2023 1691466815SameerОценок пока нет
- CHEMISTRY PROJECT On Content of Cold Drinks Available in The MarketДокумент5 страницCHEMISTRY PROJECT On Content of Cold Drinks Available in The MarketKiran ShajiОценок пока нет
- Lake Nyos Case StudyДокумент4 страницыLake Nyos Case Studyu3537671Оценок пока нет
- 0800-45-MC Calibration Cylinder Accessories - enДокумент6 страниц0800-45-MC Calibration Cylinder Accessories - enSalim MuftahОценок пока нет
- Venkat Spongeironrotarykilnmodel IMPC2010Документ12 страницVenkat Spongeironrotarykilnmodel IMPC2010PRASSAN SHAHОценок пока нет
- Byk '110 MsdsДокумент12 страницByk '110 Msdsهیمن مОценок пока нет