Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Med Surg II Unit 2 Exam Review
Загружено:
ashleymalloryИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Med Surg II Unit 2 Exam Review
Загружено:
ashleymalloryАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
PARTS
OF NERVOUS SYSTEM
CNS: Brain & Spinal Cord Peripheral: Crainial & Spinal nerves Autonomic: part of peripheral, Sympathetic & parasympathetic
NEUROTRANSMITTERS
Chemical substances that excite, inhibit, or modify response of another neuron. Neuron releases it.
COVERINGS
OF THE BRAIN
Grey matter(outer part of the brain) billions of neurons. Neurons basic cells of the nervous system .3 components: Cell body: controls the function of the neuron Axon: impulses away cell body Dendrites: impulses towards cell body
FORAMEN
MAGNUM
Spinal cord continuation of the brainstem Exits skull through the foramen magnum: opening at the base of the skull
CRANIAL
NERVES HOW MANY PAIR
12 pairs of cranial nerves. Originated from the brain or brainstem. Most from brainstem. Functions: Sensory Motor mixed
FUNCTION FIGHT
OF
ANS
Main function is to maintain homestasis
OR FLIGHT RESPONSE
Subdivision on the ANS: sympathetic & parasympathetic Sympathetic: activated by stress fight or flight Increased HR Increased BP Vasoconstriction Decreased Peristalsis Dilated pupils Increased secretions of epinephrine & sweat
Decreased secretions of digestive juices & saliva
GLASGOW
COMA SCALE
OBJECTIVE tool for assessing consciousness in clients (mainly head injuries) Eye opening Verbal response Motor response Total scores indicate coma severity 15: oriented 7: state coma 3:deep coma
PERRLA
Equal round and reactive to light & demonstrate accommodation ONLY when pupil is normal. Abnormal in one or both, finding written out for clarity.
ATAXIA
Inability to preform any of the following movements. Incoordination of voluntary muscle action.
ROMBERG
Test for BALANCE. Feet together arms in front eyes closed. slight sway normal. Always stand in front of client, anticipating a fall.
TERMS
ON PG.
1267
PLANTAR
REFLEX
Superficial reflex Fanning: positive BABInskis reflex. Plantar flexion , curling under of the toes should occur.
SKULL
FRACTURES
FRACTURES are usually caused by extreme force. CLOSED-dura mater is intact OPEN-Dura mater is torn Manifestation is pain.
LINEAR-nondisplaced cracks. COMMINUTED-fragments DEPRESSED-fragments pressing into intracrainial cavity. BASILAR- base of skull. Basilar particular concern because of the proximity of fragile sinus bones & adhesions of dura mater in this area. CSF could leak into EARS & NOSE Internal Carotid Artery & Cranial Nerves can easily be damaged.
TESTS
FOR NERVOUS SYSTEM DISORDERS
Lumbar puncture (LP) Electroencephalogram(EEG) Electromyogram(EMG) Cerebral angiography Brain scan Myelogram Imaging: CT PET SPECT MRI
TYPES
OF BRAIN INJURY
CAUSES: ACCELERATION-baseball bat (object moving). DECELERATION-car dashboard (head moving). ROTATIONAL-whiplash (twisting brainstem). PENETRATING MISSLE-bullet. Open: Closed: Hemorrhage: Increased Intracranial Pressure:
CEREBRAL
LACERATION
Tearing of the cortical tissue DAI(diffuse axonal injury) in conjunction with brainstem injuries. This widespread damage to nerve cells in white matter causes immediate coma, extension posturing, increased intracranial pressure
CONTUSION
Surface bruises Unconscious for a longer period of time than with concussion. Pulse bp resp all below norm. Cerebral edema with widespread injury.
INTRACRANIAL
HEMORRHAGE
COMMON COMPLICATION OF ANY HEAD INJURY.
Epidural hematoma: momentary unconscious followed by conscious state of few hrs or wk. Neurological status deteriorates. Headaches seizures, hemiparesis, decrebration(severing of spinal cord) dilated fixed pupils. Surgery: evacuate the hematoma, stop the bleeding, relieve pressure on the brain. Subdural hematoma:immediate. Acute(48 hrs) subacute(2-14 days) chronic(2wks-mths) Headaches drowsiness, slow mentation, confusion Small:reabsorbed Large: hematomas surgical removal Subarachnoid: intraventricular common inSEVERE Nuchial rigidity: stiffness or inability to bend neck + increases intracranial pressure. MORE
CONCUSSION
Transients neurological deficits caused by shaking of the brain CLOSED Blunt force COUP injuries- impact head against object. CONTRECOUP injuries-impact brain opposite side of skull.
PARALYSIS
LOWER EXTREMITIES HEMATOMAS
INTRACRANIAL CVA TIA RISK
FACTORS STROKE STAGES DISTURBANCE
SEIZURE
ELECTRICAL
HERNIATED SPINAL
DISK CAUSES
SHOCK MEDICATION
PARKINSONS MS
MEDICATION MEDICATION
ALZHEIMERS NEURALGIA
ENCEPHALITIS MIGRAINES EAR
WAX ON PG.
TERMS
1312
HEARING LOSS
SENSORINEURAL PROF TYPES
TIP PG.
1318
OF EAR INFECTION FORMS OF GLAUCOMA
PRIMARY
NEARSIGHTEDNESS DETACHED INCREASED
RETINA INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Pediatric NursingДокумент97 страницPediatric NursingFreeNursingNotes100% (1)
- Nursing Cheat SheetДокумент1 страницаNursing Cheat Sheetabardwell100% (85)
- Materials For The 21st Century PDFДокумент336 страницMaterials For The 21st Century PDFanon_68148822100% (1)
- Columbian Exchange Graphic OrganizerДокумент2 страницыColumbian Exchange Graphic Organizerapi-327452561100% (1)
- Conflict Stimulation and Conflict Management TechniquesДокумент32 страницыConflict Stimulation and Conflict Management TechniquesGaurav Kumar Singh100% (1)
- Neurological System Key Terms CHДокумент2 страницыNeurological System Key Terms CHashleymalloryОценок пока нет
- Pedia NotesДокумент7 страницPedia NotesFreeNursingNotes100% (1)
- Obstetrical NursingДокумент36 страницObstetrical NursingFreeNursingNotes100% (7)
- Obstetrical Nursing NotesДокумент25 страницObstetrical Nursing NotesFreeNursingNotes81% (16)
- Name: DateДокумент12 страницName: DateashleymalloryОценок пока нет
- Patient Worksheet MedSurg 3patientДокумент1 страницаPatient Worksheet MedSurg 3patientashleymalloryОценок пока нет
- 150 Years of PharmacovigilanceДокумент2 страницы150 Years of PharmacovigilanceCarlos José Lacava Fernández100% (1)
- Heparin - ClinicalKeyДокумент85 страницHeparin - ClinicalKeydayannaОценок пока нет
- Vijayalakshmi MenopauseДокумент7 страницVijayalakshmi MenopauseakankshaОценок пока нет
- Bladder IrrigationДокумент19 страницBladder IrrigationDwight Kristian CruzОценок пока нет
- Benign Paratesticlar Cyst - A Mysterical FindingДокумент2 страницыBenign Paratesticlar Cyst - A Mysterical FindingInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyОценок пока нет
- Cardiology UQU 2022Документ29 страницCardiology UQU 2022Elyas MehdarОценок пока нет
- Essay ModelДокумент4 страницыEssay ModelEmma MalekОценок пока нет
- ElectrocardiogramДокумент17 страницElectrocardiogramvinnu kalyanОценок пока нет
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Biol1318.001 05f Taught by Lee Bulla (Bulla)Документ1 страницаUT Dallas Syllabus For Biol1318.001 05f Taught by Lee Bulla (Bulla)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupОценок пока нет
- Molecules - 1 (Carbs & Lipids) V2Документ13 страницMolecules - 1 (Carbs & Lipids) V2ormattОценок пока нет
- Leaky Gut TreatmentДокумент5 страницLeaky Gut Treatmentfsilassie8012Оценок пока нет
- SterilizationДокумент6 страницSterilizationIndranath ChakrabortyОценок пока нет
- NHH TemplateДокумент6 страницNHH TemplateCaryl EteОценок пока нет
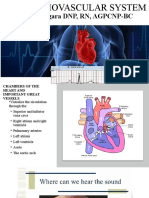
- The Cardiovascular System ReviewДокумент18 страницThe Cardiovascular System ReviewDanisha Reeves100% (1)
- English XIIДокумент12 страницEnglish XIIdanielОценок пока нет
- Ki Breathing TranslationДокумент52 страницыKi Breathing TranslationNataly Kur100% (1)
- Opalescence Boost Whitening PDFДокумент2 страницыOpalescence Boost Whitening PDFVikas AggarwalОценок пока нет
- Deenanath Mangeshkar HospitalДокумент11 страницDeenanath Mangeshkar HospitalIti GoyalОценок пока нет
- Complete DentureДокумент57 страницComplete Denturedr_ahmad_zuhdi100% (3)
- Spiritual Wrestling PDFДокумент542 страницыSpiritual Wrestling PDFJames CuasmayanОценок пока нет
- Trial Kedah 2014 SPM Biologi K2 SkemaДокумент14 страницTrial Kedah 2014 SPM Biologi K2 SkemaCikgu Faizal100% (1)
- Grand Case Pres FDARДокумент11 страницGrand Case Pres FDARMika SaldañaОценок пока нет
- English 1Документ4 страницыEnglish 1Rida SariОценок пока нет
- 10.1055s 0039 1688815 - CompressedДокумент15 страниц10.1055s 0039 1688815 - CompressedYolanda Gómez LópezОценок пока нет
- Esmee Sabina 19-5372 PDFДокумент3 страницыEsmee Sabina 19-5372 PDFEsme SabinaОценок пока нет
- Review Article Hijamah (Cupping Therapy) - A Comprehensive ReviewДокумент8 страницReview Article Hijamah (Cupping Therapy) - A Comprehensive ReviewMohamed ShiffaОценок пока нет
- Mag MicroДокумент67 страницMag MicroAneesh AyinippullyОценок пока нет