Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Analyzing Paper 1 - SL
Загружено:
Sushanta BaruaИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Analyzing Paper 1 - SL
Загружено:
Sushanta BaruaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
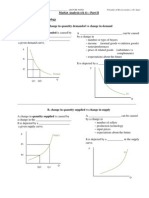
Analyzing Paper 1 (SL) May 2005 Explain how a buffer stock system might be used to stabilize agricultural prices.
Discuss the view that intervention in agricultural markets causes more problems than it solves. Describe the main causes of inflation. If inflation is a major problem faced by governments it must follow that the opposite, deflation, is desirable. To what extent do you agree with this statement? Describe three possible economic consequences of a persistent current account deficit for a country. Evaluate different methods of correcting a current account deficit. Explain the main characteristics of a market economy. Evaluate the proposition that economic development is best achieved through the market system.
November 2005 Explain the importance of price in allocating scarce resources. Evaluate the possible consequences of implementing maximum and minimum price controls. Explain the costs of inflation and the costs of deflation. Evaluate demand-side policies as a means of reducing inflation. Explain three factors which might cause the value of a currency to appreciate. Evaluate the possible effects of such an appreciation on an economy. Explain two significant barriers to economic growth in LDCs. Evaluate strategies that may be used to overcome the two barriers identified in (a).
Analyzing Paper 1 (SL) May 2006 The basic economic problem is one of scarcity of productive resources. Explain how resources are allocated between competing uses in a market economy. Discuss the view that there is strong justification for government intervention in the market for health care. Identify the components of aggregate demand and briefly explain two factors which might determine each of these components. Evaluate the likely impact on an economy of a substantial rise in the level of interest rates. Explain how changes in a countrys exchange rate may occur under a floating exchange rate system. Discuss the view that exchange rate changes are the most important factor in determining a countrys export sales. Explain how an increase in the quantity and quality of a nations factors of production can promote economic development. Evaluate the impact of globalization on the economic development of developing countries.
May 2007 Explain the signalling and incentive functions of price in market economy. Evaluate the proposition that government intervention in the market for tobacco is justified. Use AD/AS (aggregate demand/aggregate supply) diagrams to explain the causes of inflation Evaluate the view that governments should make the control of inflation their highest priority. Explain the likely consequences of a deterioration in the terms of trade for a countrys balance of payments on current account. Evaluate the view that a deterioration in the terms of trade is the most significant barrier to economic development that a developing country can face in the area of international trade. Explain the various types of aid which a developing country might receive. Aid is an ineffective means of promoting the development of poorer countries. Evaluate this statement.
Analyzing Paper 1 (SL) November 2007 Using supply and demand analysis, explain why the price of agricultural goods tends to fluctuate more than the price of manufactured goods. Evaluate the possible role of price controls in agricultural markets. Distinguish between cost push inflation & demand push inflation. Evaluate the view that the consequences of inflation are more harmful to an economy than the consequences of unemployment. Explain three types of protectionism that a government might adopt in the context of international trade. Evaluate the extent to which protectionism may be justified in international trade. Explain three institutional factors that contribute to potential economic growth in developing countries. Evaluate the view that economic growth will lead to economic development.
May 2008 The price elasticity of demand and the price elasticity of supply for many primary commodities tend to be low. Explain what is meant by this statement, and how this contributes to the problem of price instability for primary commodity producers. Evaluate the view that it is best to allow primary commodity prices to be determined purely through the free interaction of market forces. Explain how fiscal policy could be used to increase aggregate demand. In the long-run, a countrys economic performance can only be improved through the implementation of supply-side policies. Evaluate this statement. Identify three types of protectionism and explain how each may be used to correct a balance of payments deficit on current account. Evaluate the extent to which a deficit on a countrys current account might be considered an economic problem. Explain how development might be measured. Evaluate the view that the most effective way that a government could improve the welfare of its citizens is through the pursuit of faster economic growth.
Analyzing Paper 1 (SL) November 2008 With the aid of a diagram, explain the difference between actual economic growth and potential economic growth. Evaluate the extent to which economic growth may contribute to market failure. With the aid of diagrams, explain the causes of inflation. Evaluate the effectiveness of demand-side policies in reducing inflation. Explain the likely consequences of an increase in a countrys current account deficit. Evaluate the methods available to a government to correct a current account deficit. Explain three barriers to economic development for developing countries. Evaluate the view that trade is more effective than aid in achieving economic development.
May 2009 Using an appropriate diagram, explain how negative externalities are a type of market failure. Evaluate the measures that a government might adopt to correct market failure arising from negative externalities. There are various types of unemployment. Explain how any three types of unemployment may cause a rise in the unemployment rate of an economy. Evaluate the view that the unemployment rate can be most effectively reduced through the use of measures designed to increase aggregate demand in an economy. Explain three factors which may cause changes to occur in a countrys exchange rate under a floating exchange rate system. Evaluate the likely impact on a countrys economic performance of a substantial depreciation of its exchange rate. Institutional and political factors such as an ineffective taxation structure, political instability and an unequal distribution of income, as well as social and cultural factors such as gender issues and tradition, may all act as barriers to economic development. Explain how any three of these factors may act as barriers to economic development. Evaluate the view that, in terms of achieving economic development in less developed countries, interventionist strategies, with a role for the government, are preferable to market-led strategies.
Analyzing Paper 1 (SL) November 2009 Using at least one production possibility curve diagram, explain the concepts of scarcity, choice, opportunity cost and resource allocation. The process of resource allocation is most efficiently carried out through the free interaction of demand and supply. This means the provision of merit goods, such as health care and education, should always be left to market forces. Evaluate this statement. Explain two possible demand-side factors that may cause an increase in the level of unemployment. Evaluate the view that demand-side policies are more effective than supply-side policies in reducing the level of unemployment. Explain two factors that might negatively affect a countrys current account in its balance of payments. Evaluate the view that current account deficits are best corrected through the use of policies designed to reduce aggregate demand. Explain how buffer stock schemes/commodity price agreements may be used to reduce wide fluctuations in primary commodity prices. Evaluate the view that, to achieve greater growth and development, developing countries must lessen their dependence on the production of primary commodities.
Analyzing Paper 1 (SL) May 2010 With the aid of at least one diagram, explain the difference between a movement along an existing demand curve for a good and a shift of the demand curve for a good. Evaluate the view that the market forces of demand and supply will always lead to the best allocation of resources. Aggregate demand consists of consumption, investment, government spending and net exports (exports minus imports). Explain two factors that may influence consumption and two factors that may influence government spending. Evaluate the possible impact of an increase in consumption expenditure on the performance of an economy. Explain the possible consequences of an improvement in a countrys terms of trade for a country with a current account deficit. Evaluate the view that, in the long term, expenditure-switching policies (protectionism) are the most effective way to reduce a current account deficit. Explain the difference between economic growth and economic development, and how each of these may be measured. Evaluate the view that the best way that developed countries can help the growth and development process of very poor, highly indebted countries is through a general cancellation of debts.
November 2010 Explain how taxes and subsidies differ in their effect on the market price and quantity of a good. It is essential that a government supports its farmers by subsidizing agricultural output. Evaluate this view. Using appropriate diagrams, explain the difference between demand-side and supply-side economic policies. Evaluate the use of supply-side policies to improve the performance of an economy. Explain two factors which may cause an appreciation of a countrys exchange rate. Evaluate the extent to which an appreciating exchange rate may benefit or harm an economy. Explain why economic growth rates may differ between developing countries. Evaluate the role of foreign direct investment in assisting a developing country to achieve greater growth and development.
Analyzing Paper 1 (SL) May 2011 Explain the roles of market forces and government in allocating resources in a mixed economy. Evaluate the extent to which market forces should be used to lessen the problem of environmental pollution. Using appropriate diagrams, explain how a reduction in income tax could affect both aggregate demand and aggregate supply in an economy. The lower the level of both direct and indirect taxation, the better. Evaluate this view. Using a diagram, explain the factors which might cause a depreciation of a country's exchange rate. A depreciation of a countrys exchange rate will always have a beneficial effect on the performance of its economy." Evaluate this view. Explain the main features of market-led strategies used to achieve economic development in less-developed countries (LDCs). Evaluate the view that economic development in less-developed countries (LDCs) can best be achieved through market-led strategies rather than interventionist strategies.
November 2011 Explain the differences between price elasticity of demand (PED) and cross-elasticity of demand (XED) Discuss the usefulness of price elasticity of demand (PED) and cross-elasticity of demand (XED) to businesses trying to increase their sales revenue. Explain three factors that could cause an economy to go into a recession. Evaluate the effectiveness of governments using demand-side policies to take an economy out of a recession. Explain the benefits a country might experience from an increase in free trade. Evaluate the reasons why countries try to restrict free trade through protectionism. Explain the differences between foreign direct investment (FDI) and aid. Evaluate the view that aid is an effective means to achieve economic growth and development in less-developed countries (LDCs).
Analyzing Paper 1 (SL)
MICRO MACRO INTL DEVEP HyBRIDs
Вам также может понравиться
- Britain GDP Growth Exceeds Forecasts in 2013Документ4 страницыBritain GDP Growth Exceeds Forecasts in 2013Serge SedunovsОценок пока нет
- Business and Management HL P1Документ18 страницBusiness and Management HL P1FarrukhsgОценок пока нет
- Economics Practice IAДокумент6 страницEconomics Practice IAVanessaОценок пока нет
- Ib HL Economics Commentary 1 Microeconomics Alcohol PDFДокумент4 страницыIb HL Economics Commentary 1 Microeconomics Alcohol PDFMohd UvaisОценок пока нет
- 1.understand The Case Study IbGeniusДокумент13 страниц1.understand The Case Study IbGeniusVinodОценок пока нет
- Principles of MIcroeconomics - Notes - Markets/Supply/Demand - Part 2Документ4 страницыPrinciples of MIcroeconomics - Notes - Markets/Supply/Demand - Part 2Katherine SauerОценок пока нет
- How price elasticity affects tax incidenceДокумент2 страницыHow price elasticity affects tax incidencemohdportmanОценок пока нет
- Digital Table of Contents Ib EconomicsДокумент1 страницаDigital Table of Contents Ib Economicstesde lujoОценок пока нет
- Answering Paper 2 Questions: Economics For The IB DiplomaДокумент9 страницAnswering Paper 2 Questions: Economics For The IB Diploma정우창Оценок пока нет
- Economics and TOKДокумент7 страницEconomics and TOKJaffar Abbas AliОценок пока нет
- Elasticity Exam Paper Model AnswersДокумент5 страницElasticity Exam Paper Model AnswersNicole BostanОценок пока нет
- IB Econ Chap 16 Macro EQДокумент11 страницIB Econ Chap 16 Macro EQsweetlunaticОценок пока нет
- Macroeconomics Assignment 2Документ4 страницыMacroeconomics Assignment 2reddygaru1Оценок пока нет
- Resource Allocation and Price ControlsДокумент28 страницResource Allocation and Price ControlsAlexander Betz100% (1)
- IB Economics Notes - Macroeconomic Goals Low Unemployment (Part 1)Документ11 страницIB Economics Notes - Macroeconomic Goals Low Unemployment (Part 1)Pablo TorrecillaОценок пока нет
- 16NEconomics Paper 3 HLДокумент20 страниц16NEconomics Paper 3 HLMustafa Al-TaieОценок пока нет
- Business IaДокумент3 страницыBusiness IajjkjljОценок пока нет
- Economic Growth (Main Macro Objective) Essay (Edexcel)Документ3 страницыEconomic Growth (Main Macro Objective) Essay (Edexcel)Atom SonicОценок пока нет
- Consumer Surplus and Price Elasticity of DemandДокумент8 страницConsumer Surplus and Price Elasticity of Demandsweetice79Оценок пока нет
- IB Internal Assessment Economics SL: MacroeconomicsДокумент9 страницIB Internal Assessment Economics SL: MacroeconomicsAlvaro CarboneroОценок пока нет
- HL Pract 1Документ20 страницHL Pract 1snadim123Оценок пока нет
- Ib Economics Review Questions MicroeconomicsДокумент6 страницIb Economics Review Questions Microeconomicsapi-196719233100% (1)
- Group 3 Command TermsДокумент1 страницаGroup 3 Command Termsmgupta72Оценок пока нет
- MICROECONOMICS - Revison Notes 2013 S1 Ques Set 2Документ6 страницMICROECONOMICS - Revison Notes 2013 S1 Ques Set 2Imelda WongОценок пока нет
- IB Economics IA Coversheet PDFДокумент1 страницаIB Economics IA Coversheet PDFUkjun Jung0% (1)
- Cost Push InflationДокумент2 страницыCost Push InflationManoj KОценок пока нет
- EE EconomicsДокумент26 страницEE EconomicsChirag Hablani100% (1)
- Ib Economics Study Guide MicroДокумент48 страницIb Economics Study Guide Microapi-196719233Оценок пока нет
- Effects of pre-treatment and temperature on drying tomatoesДокумент14 страницEffects of pre-treatment and temperature on drying tomatoestibemОценок пока нет
- Paper 2 Irish Unemployment Case StudyДокумент2 страницыPaper 2 Irish Unemployment Case StudyLuvinga KahiseОценок пока нет
- IBDP Economics P3 - Revision WorksheetДокумент4 страницыIBDP Economics P3 - Revision WorksheetSahana Rao100% (1)
- ECB Bond Buying Boosts EurozoneДокумент3 страницыECB Bond Buying Boosts EurozoneUday SethiОценок пока нет
- IB Biology Command Terms: Objective 1Документ1 страницаIB Biology Command Terms: Objective 1loveis1020Оценок пока нет
- Demand Supply Equilibrium WorksheetДокумент2 страницыDemand Supply Equilibrium Worksheethuhu4545Оценок пока нет
- Importance of Demand Elasticity for Business DecisionsДокумент1 страницаImportance of Demand Elasticity for Business DecisionsGene CoatesОценок пока нет
- How To Structure Your Economics Essay PAPER I-2Документ3 страницыHow To Structure Your Economics Essay PAPER I-2Omar GobranОценок пока нет
- Economics Paper 2 HL M14Документ9 страницEconomics Paper 2 HL M14BL 11100% (1)
- 2017 Nyjc h3 EconsДокумент7 страниц2017 Nyjc h3 EconsMelissaОценок пока нет
- Economics IA: Formulations/articleshow/65424679.cmsДокумент2 страницыEconomics IA: Formulations/articleshow/65424679.cmsBhavye GuptaОценок пока нет
- Economics OLEVELSДокумент5 страницEconomics OLEVELSYu Yu Maw100% (1)
- Ib Econ External AssessmentДокумент4 страницыIb Econ External Assessmentapi-196719233Оценок пока нет
- IB Economics Internal AssessmentДокумент2 страницыIB Economics Internal AssessmentSandy Saddler0% (1)
- Economics Exam TechniquesДокумент13 страницEconomics Exam TechniquesMohammed Amine RAFIKОценок пока нет
- ElasticitypracticeДокумент3 страницыElasticitypracticeapi-2605125630% (1)
- Extended Essay: "To What Extent Has Tourism Impacted The Socio-Economic Status of Rural Communities in Rubavu?"Документ24 страницыExtended Essay: "To What Extent Has Tourism Impacted The Socio-Economic Status of Rural Communities in Rubavu?"ntwari kevinОценок пока нет
- IB Economics DefinitionsДокумент21 страницаIB Economics DefinitionsYokesh ProОценок пока нет
- IB ECONOMICS: IA RUBRICДокумент1 страницаIB ECONOMICS: IA RUBRICRITA CHANDRANОценок пока нет
- IB Workshop Summary For The New SyllabusДокумент54 страницыIB Workshop Summary For The New SyllabusousoulegrandОценок пока нет
- 1 ECONTWO IntroductionДокумент20 страниц1 ECONTWO IntroductionNang Kit SzeОценок пока нет
- Conflicts in Governments Objectives (Economics)Документ15 страницConflicts in Governments Objectives (Economics)MarcosОценок пока нет
- Economics Unit OutlineДокумент8 страницEconomics Unit OutlineHaris AОценок пока нет
- General Equilibrium, Growth, and Trade II: The Legacy of Lionel McKenzieОт EverandGeneral Equilibrium, Growth, and Trade II: The Legacy of Lionel McKenzieОценок пока нет
- How a sole proprietor counselor can effectively anticipate new insurance providersДокумент9 страницHow a sole proprietor counselor can effectively anticipate new insurance providersHannahOdellОценок пока нет
- IB Economics SL18 - Foreign Finance and DebtДокумент5 страницIB Economics SL18 - Foreign Finance and DebtTerran100% (1)
- Fresh Food Subsidised, Says StudyДокумент24 страницыFresh Food Subsidised, Says StudyOscar E. SánchezОценок пока нет
- Page 35 Answer Key Student Booklet - Classwork - 2: - Definitions of DemandДокумент4 страницыPage 35 Answer Key Student Booklet - Classwork - 2: - Definitions of DemandRumana AliОценок пока нет
- Business and Management - Course Companion - Lominé Muchena and Pierce - Oxford 2014Документ95 страницBusiness and Management - Course Companion - Lominé Muchena and Pierce - Oxford 2014Anthony Mafuta MayilameneОценок пока нет
- Checklist Calculation Ib EconomicsДокумент2 страницыChecklist Calculation Ib Economicstesde lujoОценок пока нет
- Mapúa Welding Shop PracticeДокумент7 страницMapúa Welding Shop PracticeJay EmОценок пока нет
- Assignment No. 8 (Culture 1) : Discuss The Significance of Montessori Cultural Exercises.? Hfodhfsfnsfsfsajk AnsДокумент10 страницAssignment No. 8 (Culture 1) : Discuss The Significance of Montessori Cultural Exercises.? Hfodhfsfnsfsfsajk Anseman zahraОценок пока нет
- Advisory Circular: Aircraft Maintenance Engineer Licence - Examination Subject 2 Aircraft Engineering KnowledgeДокумент44 страницыAdvisory Circular: Aircraft Maintenance Engineer Licence - Examination Subject 2 Aircraft Engineering KnowledgejashkahhОценок пока нет
- IT Technician CVДокумент3 страницыIT Technician CVRavi KumarОценок пока нет
- Endodontic Emergencies GuideДокумент27 страницEndodontic Emergencies GuideJitender Reddy100% (1)
- A. Rationale: Paulin Tomasuow, Cross Cultural Understanding, (Jakarta: Karunika, 1986), First Edition, p.1Документ12 страницA. Rationale: Paulin Tomasuow, Cross Cultural Understanding, (Jakarta: Karunika, 1986), First Edition, p.1Nur HaeniОценок пока нет
- UNDERSTANDING CULTURE SOCIETY & POLITICS12 - LAS - Week7Документ6 страницUNDERSTANDING CULTURE SOCIETY & POLITICS12 - LAS - Week7Bergonsolutions AingelОценок пока нет
- Radiant Tube BurnersДокумент18 страницRadiant Tube BurnersRajeshОценок пока нет
- Lecturer No 1 - Transformer BasicДокумент1 страницаLecturer No 1 - Transformer Basiclvb123Оценок пока нет
- Pure Quality Pure Natural: Calcium Carbonate Filler / MasterbatchДокумент27 страницPure Quality Pure Natural: Calcium Carbonate Filler / MasterbatchhelenОценок пока нет
- Iso 696 1975Документ8 страницIso 696 1975Ganciarov MihaelaОценок пока нет
- FrankensteinДокумент24 страницыFrankensteinLisa WardОценок пока нет
- No-Till For Micro Farms: The Deep-Mulch Method (Lean Micro Farm)Документ20 страницNo-Till For Micro Farms: The Deep-Mulch Method (Lean Micro Farm)Chelsea Green PublishingОценок пока нет
- Openstack Deployment Ops Guide PDFДокумент197 страницOpenstack Deployment Ops Guide PDFBinank PatelОценок пока нет
- Health Benefits of Kidney BeansДокумент17 страницHealth Benefits of Kidney BeansShyneAneeshОценок пока нет
- BH Tif03Документ21 страницаBH Tif03Andres R. OlguinОценок пока нет
- IELTS Writing Task 2/ IELTS EssayДокумент2 страницыIELTS Writing Task 2/ IELTS EssayOlya HerasiyОценок пока нет
- Equivalent Record Form: Department of Education MIMAROPA RegionДокумент1 страницаEquivalent Record Form: Department of Education MIMAROPA RegionEnerita AllegoОценок пока нет
- Transactionreceipt Ethereum: Transaction IdentifierДокумент1 страницаTransactionreceipt Ethereum: Transaction IdentifierVALR INVESTMENTОценок пока нет
- JNTUA Mechanical Engineering (R09) Syllabus BookДокумент147 страницJNTUA Mechanical Engineering (R09) Syllabus Bookslv_prasaad0% (1)
- Bimbo Marketing ResearchДокумент27 страницBimbo Marketing Researcheman.konsouhОценок пока нет
- ZO 503 Physiological Chemistry by Dr.S.S.KunjwalДокумент22 страницыZO 503 Physiological Chemistry by Dr.S.S.KunjwalAbhishek Singh ChandelОценок пока нет
- Bioav 3Документ264 страницыBioav 3Sabiruddin Mirza DipuОценок пока нет
- Master of Advanced Nursing Practice degreeДокумент2 страницыMaster of Advanced Nursing Practice degreeAgusfian Trima PutraОценок пока нет
- Sri Lanka, CBSLДокумент24 страницыSri Lanka, CBSLVyasIRMAОценок пока нет
- HDL Coder™ ReferenceДокумент487 страницHDL Coder™ ReferenceVictor Colpo NavarreteОценок пока нет
- Solution Proposal For SGF - BomДокумент2 страницыSolution Proposal For SGF - BomABHISHEK ADHIKARYОценок пока нет
- ScreenwritingДокумент432 страницыScreenwritingkunalt09100% (4)
- Session CommandsДокумент1 033 страницыSession Commandshan seongОценок пока нет
- More Med Surg Practice QuestionsДокумент14 страницMore Med Surg Practice QuestionsmisscoombsОценок пока нет