Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Chart
Загружено:
Tushar KumarИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chart
Загружено:
Tushar KumarАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Route of administration Author Dose (n) Oral Sublingual Rectal Vaginal
* Estimated from published graph. ** 10 non-pregnant women only. Time to peak concentration (minutes) Zieman et al.3 Danielsson et al. Tang et al.5 Abdel-Aleem et al.6 Khan and El-Refaey
7 4
400 g (20) 400 g (12) 400 g (40) 600 g (20) 600 g (20)
34 (17) 30 28 (15) 20 18 (8.8) 41 (16) 26 (12)
80 (27) 60120 longer
Peak concentration (pg/mL) Zieman et al.3 Danielsson et al. Tang et al.5 Abdel-Aleem et al.
6 4
400 g (20) 400 g (12) 400 g (40) 600 g (20) 600 g (20) 400 g (10)
227 (124) 280
*
165 (86) 65* 575 (251) 125 (54)
288 (144) 345 (269) 328 (103) 381
Khan and El-Refaey7 Andolina et al.
8
184 (65)
Area under curve to 4 hours (pg/hours/mL) Zieman et al.3 Khan and El-Refaey7 400 g (20) 600 g (20) 273 (110) 190 (125) 503 (297) 311 (141)
Area under curve to 6 hours (pg/hours/mL) Zieman et al.3 Tang et al.5 400 g (20) 400 g (40) 300 (103)** 403 (152) 744 (291) 957 (542)** 434 (183)
able 1. Serum misoprostol values and time course expressed as mean (standard deviation) following misoprostol administration by various routes.
The data tabulated in Table 2 suggest a more rapid time to peak concentration with oral and sublingual than vaginal or rectal administration, highest peak concentrations with sublingual, and greatest area under the time curve with sublingual and vaginal administration. Route Oral Pharmacokinetic studies Onset Peak Duration Total bioavailability Rapid High Short Low Slower Lower Long 23 oral Slower Lower Long 1.5 oral Rapid Highest Long Highest Vaginal Rectal Sublingual Intrauterine
Clinical studies for induction of labour Efficacy Moderate Better than oral Similar to vaginal Better than oral
Intrauterine pressure studies First trimester Rapid onset. Rapid time to peak Rapid onset (6 minutes). Duration 75 minutes. Slower onset and time to peak. More prolonged activity Rapid onset. Prolonged activity.
After delivery
Route Oral Vaginal Rectal Sublingual Intrauterine
Clinical studies prophylactically after delivery Efficacy Pyrexia and shivering Less than syntocinon Common No studies Insufficient data Less than oral
Theoretical considerations: use for treatment of PPH Administration Likely efficacy Advantages Easy Fast onset, limited duration Convenient, rapid onset of action Prominent Unknown Not feasible Slow onset Easy even if not conscious Slow onset Relatively convenient Apparently less than oral Relatively easy if conscious Good Best pharmacokinetic profile Unknown Invasive Unknown Possible local effect Likely to be low relative to effec
Side effects
Table 2. Qualitative comparisons of various routes of administration of misoprostol.
Вам также может понравиться
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- All Frequencies - OdtДокумент298 страницAll Frequencies - OdtJiggaWhaa100% (8)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Pediatric Drug Dosage - All in One PDFДокумент15 страницPediatric Drug Dosage - All in One PDFHuang Hasjim33% (9)
- ECG Lead PlacementДокумент3 страницыECG Lead PlacementLord Pozak MillerОценок пока нет
- Hospital Grades January 2014: 18 Southey Road P O. Box 2026 Harare El/fax: +236 4 778896/778798/778724Документ7 страницHospital Grades January 2014: 18 Southey Road P O. Box 2026 Harare El/fax: +236 4 778896/778798/778724Tony Peterz Kurewa100% (1)
- DVT and PeДокумент25 страницDVT and PeOmar AbdillahiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 - Hannah Wilder - ChorioamnionitisДокумент7 страницChapter 7 - Hannah Wilder - ChorioamnionitisEunice CortésОценок пока нет
- Haemodynamic Monitoring Learning Package: Hornsby Ku-Ring-Gai Hospital Intensive Care UnitДокумент41 страницаHaemodynamic Monitoring Learning Package: Hornsby Ku-Ring-Gai Hospital Intensive Care UnitPoldo ReinaldoОценок пока нет
- Atlas of Glaucoma 3E PDFДокумент353 страницыAtlas of Glaucoma 3E PDFSUSANA AGUILAR GARCIA100% (1)
- Energy Pen: MeridianДокумент11 страницEnergy Pen: Meridianjose luis lamadrid armasОценок пока нет
- Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Karnataka, BangaloreДокумент27 страницRajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Karnataka, BangaloreJyotiОценок пока нет
- Hipertensi KrisisДокумент30 страницHipertensi KrisisLuthfan HakimОценок пока нет
- Common Emergency DrugsДокумент61 страницаCommon Emergency DrugsFebee Gee100% (1)
- Oral Exam NotesДокумент3 страницыOral Exam NotesDrumz StaffОценок пока нет
- Lab 7 NewДокумент3 страницыLab 7 New202010187Оценок пока нет
- Dermoscopic Features of Pigmentary Disorders in Indian Skin: A Prospective Observational StudyДокумент10 страницDermoscopic Features of Pigmentary Disorders in Indian Skin: A Prospective Observational StudyIJAR JOURNALОценок пока нет
- Prediction of Pulmonary Embolism in The Emergency DepartmentДокумент10 страницPrediction of Pulmonary Embolism in The Emergency DepartmenttechiemedicОценок пока нет
- Xavier BrochureДокумент20 страницXavier BrochureJohn PareraОценок пока нет
- Paired Facial Treatment With 755nm Picosecond Laser With Diffractive Lens Array and 1060nm Laser Lipolysis of The Submentum - An Open-Label Prospective TriaДокумент7 страницPaired Facial Treatment With 755nm Picosecond Laser With Diffractive Lens Array and 1060nm Laser Lipolysis of The Submentum - An Open-Label Prospective TriaErik BrooksОценок пока нет
- Vanessa Hoos ResumeДокумент3 страницыVanessa Hoos Resumeapi-533753716Оценок пока нет
- Etiology, Classification and Clinical Approach: EndophthalmitisДокумент42 страницыEtiology, Classification and Clinical Approach: EndophthalmitisHieLdaJanuariaОценок пока нет
- Category Class Merit Round2 MBBS-BDSДокумент102 страницыCategory Class Merit Round2 MBBS-BDSSUSHIL LAKRAОценок пока нет
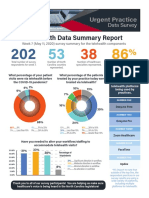
- UPDS Telehealth Data ReportДокумент3 страницыUPDS Telehealth Data ReportCorey LarkinsОценок пока нет
- PeritonitisДокумент21 страницаPeritonitischrisyenОценок пока нет
- Disabilities Act 1995Документ4 страницыDisabilities Act 1995directdeoОценок пока нет
- Summative Test No 4 in MapehДокумент2 страницыSummative Test No 4 in MapehDianaRoseAcupeadoОценок пока нет
- Workplace Health Longterm Sickness Absence and Capability To Work PDFДокумент38 страницWorkplace Health Longterm Sickness Absence and Capability To Work PDFFuzail AyazОценок пока нет
- (PDF) Diabetes Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentsДокумент1 страница(PDF) Diabetes Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentsBakaro ShafiОценок пока нет
- MEDISEP Hospital ListДокумент3 страницыMEDISEP Hospital ListQ8123Оценок пока нет
- Baxter (Flo-Gard 6201) Volumetric Infusion Pump Flow Rate Accuracy - Test Design and Performance VerificationДокумент21 страницаBaxter (Flo-Gard 6201) Volumetric Infusion Pump Flow Rate Accuracy - Test Design and Performance VerificationKousha TalebianОценок пока нет
- Online Training LINK Total Knee LCK - v1Документ16 страницOnline Training LINK Total Knee LCK - v1Daniela Carvallo BarriosОценок пока нет