Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Ecr207 L7
Загружено:
Md Mahamudul Hasan HimelИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Ecr207 L7
Загружено:
Md Mahamudul Hasan HimelАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Electronics I
ECR 207_L7
Spring 2008
Lecture 7
Spring 2008
Instructor Dr. Abdur Razzak
IUB
Zener Diode &
Voltage Stabilizer
Dr. Abdur Razzak 1
Zener diode
ECR 207_L7
Spring 2008
When the reverse bias on a p-n diode is increased, a critical voltage, called breakdown voltage, is reached where the reverse current increases sharply to a high value. The breakdown region is the knee of the reverse characteristic as shown in figure. The satisfactory explanation of this breakdown of the junction was first given by the American scientist C. Zener. Therefore, the breakdown voltage is sometimes called, Zener voltage and the sudden increase in current is known as Zener current.
IUB Dr. Abdur Razzak
Reverse characteristic of a Zener diode
2
Zener diode (contd..)
ECR 207_L7
Spring 2008
The breakdown or zener voltage depends upon the amount of doping. If the diode is heavily doped, depletion layer will be thin and consequently the breakdown of the junction will occur at a lower reverse voltage. On the other hand, a lightly doped diode has a higher breakdown voltage. When an ordinary crystal diode is properly doped so that it has a sharp breakdown voltage, it is called a zener diode. A properly doped crystal diode which has a sharp breakdown voltage is known as a zener diode (after the name of American scientist C. Zener).
Zener diode symbol
IUB Dr. Abdur Razzak 3
Zener diode (contd..)
Zener diode has the following properties :
ECR 207_L7
Spring 2008
A zener diode is like an ordinary diode except that it is properly doped so as to have a sharp breakdown voltage. A zener diode is always reverse connected i.e. it is always reverse biased. A zener diode has sharp breakdown voltage, called zener voltage VZ. When forward biased, its characteristics are just those of ordinary diode. The zener diode is not immediately burnt just because it has entered the breakdown region. As long as the external circuit connected to the diode, it limits the diode current to less than burn out value, therefore the diode will not burn out.
IUB Dr. Abdur Razzak 4
Equivalent circuit of zener diode
"On" state :
ECR 207_L7
Spring 2008
When reverse voltage across a zener diode is equal to or more than break down voltage VZ, the current increases very sharply. In this region, the curve is almost vertical. It means that voltage across zener diode is constant at VZ even though the current through it changes. Therefore, in the breakdown region, an ideal zener diode can be represented by a battery of voltage Vz as shown in Fig. (ii). Under such conditions, the zener diode is said to be in the "ON" state.
IUB
Dr. Abdur Razzak
Equivalent circuit of zener diode (contd.)
"Off" state :
ECR 207_L7
Spring 2008
When the reverse voltage across the zener diode is less than VZ but greater than 0 V, the zener diode is in the "OFF" state. Under such conditions, the zener diode can be represented by an open-circuit as shown in Fig. (ii).
IUB
Dr. Abdur Razzak
Zener diode as a voltage stabilizer
ECR 207_L7
Spring 2008
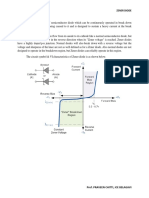
Zener diode can be used as a voltage regulator to provide a constant voltage from a source whose voltage may vary over sufficient range. The circuit arrangement is shown in Fig. (i). The zener voltage VZ is reverse connected across the load RL across which constant output is desired. The series resistance R absorbs the output voltage fluctuations so as to maintain constant voltage across the load. It may be noted that the zener diode will maintain a constant voltage VZ (= Eo) across the load so long as the input voltage does not fall below VZ.
IUB
Dr. Abdur Razzak
Zener diode as a voltage stabilizer (contd..)
ECR 207_L7
Spring 2008
When the circuit is properly designed, the load voltage Eo remains essentially constant (equal to VZ even though the input voltage Ei and load resistance RL may vary over a wide range. 1) Suppose the input voltage increases : Since the zener is in the breakdown region, the zener diode is equivalent to a battery VZ as shown in Fig. (ii). It is clear that output voltage remains constant at VZ (= Eo). The excess voltage is dropped across the series resistance R. This will cause an increase in the value of total current I. The zener will conduct the increase of current in I while the load current remains constant. Hence, output voltage E0 remains constant irrespective of the changes in the input voltage Ei.
IUB
Dr. Abdur Razzak
Zener diode as a voltage stabilizer (contd..)
ECR 207_L7
Spring 2008
1) . 2) Input voltage is constant but the load resistance RL decreases : This will cause an increase in load current. The extra current cannot come from the source because drop in R (and hence source current I) will not change as the zener is within its regulating range. The additional load current will come from a decrease in zener current Iz. Consequently, the output voltage stays- at constant value. 1) Voltage drop across R, VR = Ei - E0 2) Current through R, IR = Iz + IL
IUB
Dr. Abdur Razzak
Example 1
ECR 207_L7
Spring 2008
For the circuit shown in Fig., find: (i) the output voltage (ii) the voltage drop across series resistance (iii) the current through zener diode.
IUB
Dr. Abdur Razzak
10
Example 1 (contd..)
ECR 207_L7
Spring 2008
IUB
Dr. Abdur Razzak
11
Example 2
ECR 207_L7
Spring 2008
For the circuit shown in Fig. 9.49 (i), find the maximum and minimum values of zener diode current.
IUB
Dr. Abdur Razzak
12
Example 2 (contd..)
ECR 207_L7
Spring 2008
IUB
Dr. Abdur Razzak
13
Next lecture
ECR 207_L7
Spring 2008
Next lecture On
Special
Diodes
IUB Dr. Abdur Razzak 14
Вам также может понравиться
- BEEE UNIT IV - Lecture 6Документ31 страницаBEEE UNIT IV - Lecture 6Girish Shankar MishraОценок пока нет
- 6.zener Diode As A Voltage RegulatorДокумент3 страницы6.zener Diode As A Voltage Regulatorshakti sindhuОценок пока нет
- ECE 201: Electronics I Semiconductors, PN Junction and DiodesДокумент65 страницECE 201: Electronics I Semiconductors, PN Junction and DiodesSameh AtallahОценок пока нет
- The Zener DiodeДокумент8 страницThe Zener DiodemaanibrahimОценок пока нет
- Voltage Stabilisation: Output Voltage Changes With The Variations in The Input Voltage or LoadДокумент10 страницVoltage Stabilisation: Output Voltage Changes With The Variations in The Input Voltage or LoadLion kingОценок пока нет
- Some Important and Interesting Topics: Ac & DCДокумент3 страницыSome Important and Interesting Topics: Ac & DCsyed-md-shamsul-arifeen-459Оценок пока нет
- Electronics-Tutorials - Ws-The Zener DiodeДокумент10 страницElectronics-Tutorials - Ws-The Zener DiodeVenki EdeОценок пока нет
- Zener DiodeДокумент36 страницZener DiodeSurajguptarocks100% (1)
- A Zener Diode, Also Known As A Breakdown Diode, Is A Heavily Doped Semiconductor Device That Is Designed To Operate in The Reverse DirectionДокумент7 страницA Zener Diode, Also Known As A Breakdown Diode, Is A Heavily Doped Semiconductor Device That Is Designed To Operate in The Reverse DirectionJhan Ray Gomez BarrilОценок пока нет
- Zener DiodeДокумент6 страницZener DiodeKumar shantanu BasakОценок пока нет
- Zener Diode As A WaveshaperДокумент15 страницZener Diode As A WaveshaperpriyaОценок пока нет
- Zener Diode Tutorial: Understanding Voltage Regulation and Clipping CircuitsДокумент7 страницZener Diode Tutorial: Understanding Voltage Regulation and Clipping Circuitscelo81Оценок пока нет
- Lecture 4 (Analogue Electronics I)Документ8 страницLecture 4 (Analogue Electronics I)amash.emillyОценок пока нет
- Zener DiodeДокумент8 страницZener Diodekumar_9583Оценок пока нет
- Voltage Regulators:: Fig - Zener Voltage RegulatorДокумент7 страницVoltage Regulators:: Fig - Zener Voltage RegulatorRamesh SubramaniamОценок пока нет
- Zener DRДокумент4 страницыZener DRArchana SadanandanОценок пока нет
- U-1 (Boe 8-18)Документ11 страницU-1 (Boe 8-18)Tisha SetiaОценок пока нет
- Exp2 ZenerДокумент6 страницExp2 ZenerEdward Sevilla Dela CruzОценок пока нет
- Zenner DiodeДокумент23 страницыZenner DiodeKrishanu NaskarОценок пока нет
- Zener PracticalДокумент6 страницZener PracticalAzim KhanОценок пока нет
- Zener RegulatorДокумент3 страницыZener RegulatorBIBI MOHANANОценок пока нет
- Zener Diode and Diode ApplicationДокумент62 страницыZener Diode and Diode Applicationnibar dyllanОценок пока нет
- Experiment 7 Study of V - I Characteristics of Zener Diode and Determine Its Voltage Regulation.Документ7 страницExperiment 7 Study of V - I Characteristics of Zener Diode and Determine Its Voltage Regulation.Tushar SharmaОценок пока нет
- The Zener DiodeДокумент4 страницыThe Zener DiodeKeshav JhaОценок пока нет
- The Zener Diode: A Guide to Voltage Regulation and Clipping CircuitsДокумент11 страницThe Zener Diode: A Guide to Voltage Regulation and Clipping CircuitsGunda TejaОценок пока нет
- Lab 3Документ31 страницаLab 3張博翔Оценок пока нет
- Zener Diode & ApplicationsДокумент13 страницZener Diode & Applicationssrakhisharma41Оценок пока нет
- Zener 2Документ7 страницZener 2Mouaz MahmoudОценок пока нет
- Unit 1Документ81 страницаUnit 1Eswar suryaОценок пока нет
- This Study Resource Was: Lab Report#11Документ6 страницThis Study Resource Was: Lab Report#11malik jarrarОценок пока нет
- EC1001-L Zener DiodeДокумент28 страницEC1001-L Zener DiodeSouradeep GuptaОценок пока нет
- CH 03Документ11 страницCH 03Anb BajwaОценок пока нет
- Laboratory#3 Group-6Документ10 страницLaboratory#3 Group-6Ryan Ryan RyanОценок пока нет
- DC Power Supply: King Abdulaziz University Electronics IДокумент20 страницDC Power Supply: King Abdulaziz University Electronics IMohannad S. AlghamdiОценок пока нет
- Special Purpose Diode NOTESДокумент36 страницSpecial Purpose Diode NOTESMohamad Hanif100% (1)
- UNIT-1 Semiconductor Diodes and Applications P-N Junction Diode Characteristics and ParametersДокумент14 страницUNIT-1 Semiconductor Diodes and Applications P-N Junction Diode Characteristics and ParametersPRATHAP_CОценок пока нет
- Zener DiodeДокумент2 страницыZener DiodeRamanaButterflyОценок пока нет
- Zener DiodeДокумент16 страницZener Diodejamal ahmadОценок пока нет
- Zener Diode TheoryДокумент7 страницZener Diode TheoryCarlos IbaОценок пока нет
- Unit 1e PHY125Документ19 страницUnit 1e PHY1252023275863.rishiОценок пока нет
- Zener DiodeДокумент5 страницZener DiodePraveen ChittiОценок пока нет
- Module-2 Part-4Документ30 страницModule-2 Part-4MugelanОценок пока нет
- (L4) - (JLD 3.0) - Semiconductors - 30th DecДокумент66 страниц(L4) - (JLD 3.0) - Semiconductors - 30th DecAshfaq khanОценок пока нет
- 3 - Zener Diod VI Characteristic.Документ4 страницы3 - Zener Diod VI Characteristic.BBA UniversityОценок пока нет
- Zener Diode Guide: Construction, Working & ApplicationsДокумент29 страницZener Diode Guide: Construction, Working & ApplicationsVarsha PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- MEAEmod 02 Slide 04Документ17 страницMEAEmod 02 Slide 04D-2009 Saswat Pritam BaruahОценок пока нет
- Zener Diode Basic Operation and ApplicationsДокумент5 страницZener Diode Basic Operation and ApplicationsEvelyn P. GalanoОценок пока нет
- Special Purpose Diodes: S. Hashim BukhariДокумент23 страницыSpecial Purpose Diodes: S. Hashim BukharinasiruddinОценок пока нет
- Special-Purpose Diodes: Zener, Varactor and Optical DiodesДокумент45 страницSpecial-Purpose Diodes: Zener, Varactor and Optical DiodesAbdullahОценок пока нет
- BE UNIT-IIДокумент12 страницBE UNIT-IIhenryhorrid384Оценок пока нет
- Zener Diode Applications 1. Zener Diode As A VoltageДокумент3 страницыZener Diode Applications 1. Zener Diode As A VoltageSaravananОценок пока нет
- Zener Diode+regulationДокумент10 страницZener Diode+regulationammadm540Оценок пока нет
- Lab 3 - Zener Diode Voltage RegulationДокумент11 страницLab 3 - Zener Diode Voltage RegulationeyobОценок пока нет
- Electronics-I: SUBRATA BHOWMIK, Lecturer, Dept. of EEE, NSTUДокумент22 страницыElectronics-I: SUBRATA BHOWMIK, Lecturer, Dept. of EEE, NSTUIstihad EmonОценок пока нет
- ZenerДокумент14 страницZeneraravindh rhssОценок пока нет
- Zener Diode Characteristics and ApplicationsДокумент3 страницыZener Diode Characteristics and ApplicationsANIL KUMAR YARAMALAОценок пока нет
- Zener DiodeДокумент14 страницZener DiodeTanya SoodОценок пока нет
- +zener Voltage RegulationДокумент4 страницы+zener Voltage RegulationtrshaaaОценок пока нет
- Stochastic Models in ReliabilityДокумент280 страницStochastic Models in Reliabilitylalu100% (1)
- AN684 Microchip Elenota - PLДокумент16 страницAN684 Microchip Elenota - PLMd Mahamudul Hasan HimelОценок пока нет
- PIC12F675Документ136 страницPIC12F675Jovan KrickaОценок пока нет
- AVR Studio 4 TutorialДокумент9 страницAVR Studio 4 TutorialMd Mahamudul Hasan HimelОценок пока нет
- Carbon Monoxide Questions and Answers - CPSCДокумент4 страницыCarbon Monoxide Questions and Answers - CPSCMd Mahamudul Hasan HimelОценок пока нет
- AC Voltage Controller (AC-AC Converter)Документ9 страницAC Voltage Controller (AC-AC Converter)Nurindah Atika100% (4)
- Digital Image ProcessingДокумент6 страницDigital Image ProcessingMd Mahamudul Hasan HimelОценок пока нет
- Camera ModelДокумент7 страницCamera ModelMd Mahamudul Hasan HimelОценок пока нет
- Digital Image ProcessingДокумент6 страницDigital Image ProcessingMd Mahamudul Hasan HimelОценок пока нет
- AVR Studio 4 TutorialДокумент9 страницAVR Studio 4 TutorialMd Mahamudul Hasan HimelОценок пока нет
- Power Generation From CoalДокумент114 страницPower Generation From CoalOral KarahanОценок пока нет
- Fourier SeriesДокумент23 страницыFourier SeriesgavinilaaОценок пока нет
- Series RLC Circuit Alysis and Series ResonanceДокумент8 страницSeries RLC Circuit Alysis and Series ResonanceMd Mahamudul Hasan HimelОценок пока нет
- PIC Micro Controllers For Beginners BookДокумент205 страницPIC Micro Controllers For Beginners BookAmit kumar100% (12)
- AVR Studio 4 TutorialДокумент9 страницAVR Studio 4 TutorialMd Mahamudul Hasan HimelОценок пока нет
- FiltersДокумент6 страницFiltersMd Mahamudul Hasan HimelОценок пока нет
- EUCLID, The ElementsДокумент17 страницEUCLID, The ElementsMd Mahamudul Hasan HimelОценок пока нет
- Lecture 5Документ19 страницLecture 5Md Mahamudul Hasan HimelОценок пока нет
- Influence of Mystic Poet Lalon Shah on Bengali CultureДокумент5 страницInfluence of Mystic Poet Lalon Shah on Bengali CultureMd Mahamudul Hasan HimelОценок пока нет
- Electronics I: Lecture - 6Документ19 страницElectronics I: Lecture - 6Md Mahamudul Hasan HimelОценок пока нет
- A Manual MatlabДокумент32 страницыA Manual MatlabRohit Vishal Kumar100% (7)
- Lecture 06Документ17 страницLecture 06Md Mahamudul Hasan HimelОценок пока нет
- To 00-25-245Документ322 страницыTo 00-25-245Pedro SepulvedaОценок пока нет
- Tektronik 212 Scope Maintenance ManualДокумент83 страницыTektronik 212 Scope Maintenance ManualEduardo EscalanteОценок пока нет
- ISRO Rank-1 EC Interview Experience - QuoraДокумент3 страницыISRO Rank-1 EC Interview Experience - QuoraarajОценок пока нет
- P89C51RB2/P89C51RC2/P89C51RD2: 80C51 8-Bit Flash Microcontroller FamilyДокумент52 страницыP89C51RB2/P89C51RC2/P89C51RD2: 80C51 8-Bit Flash Microcontroller FamilylabbasatyamОценок пока нет
- Bhel Haridwar - Training Report - 800 MW Bar CIM Block 4 (EEE)Документ27 страницBhel Haridwar - Training Report - 800 MW Bar CIM Block 4 (EEE)Amit Kumar67% (6)
- Solid State Chemistry 13102066Документ43 страницыSolid State Chemistry 13102066Loveroop Singh62% (13)
- Quantum Qd110 SpecsheetДокумент2 страницыQuantum Qd110 SpecsheetElectromateОценок пока нет
- Crystalline Structure - PerfectionДокумент50 страницCrystalline Structure - PerfectionAbir RoyОценок пока нет
- TX3800 Service ManualДокумент36 страницTX3800 Service Manualp25digital2100% (2)
- Aust/Eee: Ahsanullah University of Science and TechnologyДокумент27 страницAust/Eee: Ahsanullah University of Science and Technologyruhul aminОценок пока нет
- DatasheetДокумент10 страницDatasheetCiacunОценок пока нет
- Handbook of Photovoltaic Science and Engineering: Instituto de Energ Ia Solar, Universidad Polit Ecnica de Madrid, SpainДокумент8 страницHandbook of Photovoltaic Science and Engineering: Instituto de Energ Ia Solar, Universidad Polit Ecnica de Madrid, SpainBijuОценок пока нет
- Current ElectricityДокумент85 страницCurrent Electricityanus3jan2007Оценок пока нет
- LTC3108 PresentationДокумент7 страницLTC3108 PresentationIonela CraciunОценок пока нет
- MMA 7260 3 Axis Accelerometer-User ManualДокумент6 страницMMA 7260 3 Axis Accelerometer-User ManualAnirudh ReddyОценок пока нет
- A Paul Kemble Web Page - Mission Cyrus 1 Integrated Amplifier2 PDFДокумент3 страницыA Paul Kemble Web Page - Mission Cyrus 1 Integrated Amplifier2 PDFZafer ÖzerОценок пока нет
- Jurnal JfetДокумент4 страницыJurnal JfetEdi Santoni NababanОценок пока нет
- Driver Pack WLAN Wnt5 x86-32Документ3 страницыDriver Pack WLAN Wnt5 x86-32Norang LalОценок пока нет
- Datasheet 325 330 335WДокумент2 страницыDatasheet 325 330 335WHichem ZouaouiОценок пока нет
- RF Voice TransmitterДокумент82 страницыRF Voice TransmittergumankhanОценок пока нет
- Close Exam 3Документ4 страницыClose Exam 3Joel Morada BalanОценок пока нет
- Research Task GraphДокумент1 страницаResearch Task Graphapi-419834532Оценок пока нет
- Antenna FundamentalsДокумент54 страницыAntenna FundamentalsMahmoudYasienMashhourОценок пока нет
- CO#1 Describe, Analyze, and Design of Basic BJT & NMOS Differential AmplifierДокумент6 страницCO#1 Describe, Analyze, and Design of Basic BJT & NMOS Differential AmplifierCJ CHОценок пока нет
- Valleylab Force EZ 8C高频电刀维修手册 (英文)Документ208 страницValleylab Force EZ 8C高频电刀维修手册 (英文)AlejandroVCMXОценок пока нет
- Module 4.5 Voltage Sources in SeriedДокумент11 страницModule 4.5 Voltage Sources in SeriedGeneva Mira AlvarezОценок пока нет
- Argus 7Документ4 страницыArgus 7prabhakaran_hdecОценок пока нет
- 7214Документ12 страниц7214Dan EsentherОценок пока нет
- BPSK Supressed Carrier NRZ Data Demodulation Using Costas Loop On Actel Microsemi FPGAДокумент33 страницыBPSK Supressed Carrier NRZ Data Demodulation Using Costas Loop On Actel Microsemi FPGAPrabhpreet Singh DuaОценок пока нет
- 32V-300A60kHz Edge Resonant Soft-Switching PWM DCDC Converter With DC Rail Series Switch-Parallel Capacitor Snubber Assisted by High-Frequency Transformer Parasitic Components PDFДокумент7 страниц32V-300A60kHz Edge Resonant Soft-Switching PWM DCDC Converter With DC Rail Series Switch-Parallel Capacitor Snubber Assisted by High-Frequency Transformer Parasitic Components PDFKapil AgrawalОценок пока нет