Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Ssas 2008 Tutorial
Загружено:
Chandrasekar GangadaranАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Ssas 2008 Tutorial
Загружено:
Chandrasekar GangadaranАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
SSAS Tutorial: SQL Server 2008 Analysis Services Tutorial
Page 1 of 19
1 877 849 1850
0808 234 2132
1 800 550 311
0 800 022 6730
020 795 420
+1 678 648 3113
SQL Server 2012 Training SSAS Training
SQL Server 2008 Training SSIS Training
SQL Server 2005 Training T-SQL Training
SQL Server 2000 Training
SSRS Training
Live Online Training Home About Contact Us
Introduction to SQL Server 2012 for Administrators Introduction to SQL Server 2012 Integration Services SQL Server 2008 Performance Tuning Introduction to SQL Server 2008 for Administrators SQL Server Training: Introduction to Microsoft SQL Server 2008 for Developers and Query Writers SQL Server 2008 MDX Training New Features for SQL Server 2008 R2 Developers SQL Server 2005: Advanced Topics SSRS Training: Introduction to SQL Server 2008 Reporting Services SSAS Training: Introduction to SQL Server 2008 Analysis Services SSIS Training: Introduction to SQL Server 2008 Integration Services Transact-SQL Training: Introduction to TSQL for SQL Server for Report Writing T-SQL Training: TSQL for SQL Server 2008 for Developers Live Online Training
SSAS Tutorial: SQL Server 2008 Analysis Services Tutorial
In-Depth SSAS Training For 3 days of in-depth SSAS training, please consider requesting Accelebrate's Introduction to SQL Server 2008 Analysis Services for you and your staff (SSAS 2008 course available upon request). Please contact us to request a formal quote.
Chapter 15: Analysis Services In this chapter: Understanding Analysis Services Introducing BIDS Creating a Data Cube Exploring a Data Cube
SSAS 2008 Downloads Exercise Sample DB from
Files needed: AdventureWorksCube1.zip AdventureWorksCube2.zip
So far in this course you've focused on getting data into a SQL Server database and th getting the same data out of the database. You've seen how to create tables, insert da use SQL statements, views, and stored procedures to retrieve the data. This activity, where individual actions deal with small pieces of the database, is sometimes online transaction processing, or OLTP.
But there's another use for databases, especially large databases. Suppose you run an book store and have sales records for 50 million book sales. Maybe books on introduct biology show a strong spike in sales every September. That's a fact that you could use advantage in ordering stock, if only you knew about it.
Searching for patterns like this and summarizing them is called online analytical proce or OLAP. Microsoft SQL Server 2008 includes a separate program called SQL Server An Services to perform OLAP analysis. In this chapter you'll learn the basics of using Analysis Services.
http://www.accelebrate.com/sql_training/ssas_2008_tutorial.htm
6/28/2012
SSAS Tutorial: SQL Server 2008 Analysis Services Tutorial
Page 2 of 19
SQL Server Training: Introduction to Microsoft SQL Server 2008 for Developers and Query Writers SQL Server 2005: Advanced Topics SSRS Training: Introduction to SQL Server 2008 Reporting Services SSAS Training: Introduction to SQL Server 2008 Analysis Services SSIS Training: Introduction to SQL Server 2008 Integration Services Transact-SQL Training: Introduction to TSQL for SQL Server for Report Writing T-SQL Training: TSQL for SQL Server 2008 for Developers T-SQL Training: TSQL for SQL Server 2005 for Developers Live Online Training
SSAS 2008 Tutorial: Understanding Analysis Services
The basic idea of OLAP is fairly simple. Let's think about that book ordering data for a moment. Suppose you want to know how many people ordered a particular book durin month of the year. You could write a fairly simple query to get the information catch is that it might take a long time for SQL Server to churn through that many rows data.
And what if the data was not all in a single SQL Server table, but scattered around in databases throughout your organization? The customer info, for example, might be in Oracle database, and supplier information in a legacy xBase database. SQL Server can distributed heterogeneous queries, but they're slower.
What if, after seeing the monthly numbers, you wanted to drill down to weekly or daily numbers? That would be even more time-consuming and require writing even more qu
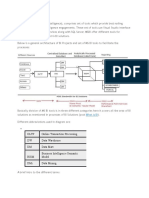
This is where OLAP comes in. The basic idea is to trade off increased storage space no speed of querying later. OLAP does this by precalculating and storing aggregates. Whe identify the data that you want to store in an OLAP database, Analysis Services analyz advance and figures out those daily, weekly, and monthly numbers and stores (and stores many other aggregations at the same time). This takes up plenty of disk s but it means that when you want to explore the data you can do so quickly. Later in the chapter, you'll see how you can use Analysis Services to extract information from your data. First, though, you need to familiarize yourself with a new vocabulary. The basic concepts of OLAP include: Cube Cube Dimension table Dimension Hierarchy Level Fact table Measure Schema
Please contact us for GSA pricing.
Contract # GS-35F-0307T
The basic unit of storage and analysis in Analysis Services is the cube. A cube is a colle data that's been aggregated to allow queries to return data quickly. For example, a cu order data might be aggregated by time period and by title, making the cube fast whe ask questions concerning orders by week or orders by title.
Recent Training Venues
Accelebrate has recently trained for clients in the following cities:
Huntsville, Alabama Montgomery / Birmingham, Alabama Anchorage, Alaska Edmonton & Calgary, Alberta Phoenix, Arizona Tucson, Arizona Fayetteville / Little Rock, Arkansas
Cubes are ordered into dimensions and measures. The data for a cube comes from a s staging tables, sometimes called a star-schema database. Dimensions in the dimension tables in the staging database, while measures come from fact tables database. Dimension table
A dimension table lives in the staging database and contains data that you'd like to us group the values you are summarizing. Dimension tables contain a primary key and an attributes that describe the entities stored in the table. Examples would be a that contains city, state and postal code information to be able to analyze sales geographically, or a Products table that contains categories and product lines to break sales figures.
http://www.accelebrate.com/sql_training/ssas_2008_tutorial.htm
6/28/2012
SSAS Tutorial: SQL Server 2008 Analysis Services Tutorial
Page 3 of 19
Amsterdam, The Netherlands / Brussels, Belgium Kamloops / Vancouver, British Columbia Oakland / San Jose / San Francisco, California Sacramento, California Oceanside / San Diego, California Pasadena / Orange County / Los Angeles, California San Bernardino / Riverside, California Boulder / Colorado Springs / Denver, Colorado Washington, DC Wilmington, Delaware Manchester / London, England Orlando, Florida Fort Lauderdale / Miami, Florida Gainesville / Jacksonville, Florida Saint Petersburg / Tampa, Florida Titusville & Melbourne, Florida Alpharetta & Atlanta, Georgia Augusta & Savannah, Georgia Macon & Columbus, Georgia Honolulu, Hawaii Boise, Idaho Bloomington, Illinois Chicago, Illinois Indianapolis, Indiana Cedar Rapids / Des Moines, Iowa Dublin, Ireland Wichita, Kansas Paducah / Lexington / Louisville, Kentucky Baton Rouge/New Orleans, Louisiana Portland, Maine Hagerstown & Frederick, Maryland Annapolis / Silver Spring / Baltimore, Maryland Boston / Cambridge, Massachusetts Hartford, Connecticut / Springfield, Massachusetts Ann Arbor / Farmington Hills / Detroit, Michigan Grand Rapids, Michigan Flint, Michigan Saint Paul / Minneapolis, Minnesota Jackson, Mississippi St. Louis, Missouri
Dimension
Each cube has one or more dimensions, each based on one or more dimension tables. dimension represents a category for analyzing business data: time or category in the examples above. Typically, a dimension has a natural hierarchy so that lower results c "rolled up" into higher results. For example, in a geographical level you might have cit aggregated into state totals, or state totals into country totals. Hierarchy
A hierarchy can be best visualized as a node tree. A company's organizational chart is example of a hierarchy. Each dimension can contain multiple hierarchies; some of natural hierarchies (the parent-child relationship between attribute values occur natura the data), others are navigational hierarchies (the parent-child relationship is developers.) Level
Each layer in a hierarchy is called a level. For example, you can speak of a week level month level in a fiscal time hierarchy, and a city level or a country level in a geograph hierarchy. Fact table
A fact table lives in the staging database and contains the basic information that you w summarize. This might be order detail information, payroll records, drug effectiveness information, or anything else that's amenable to summing and averaging. Any table you've used with a Sum or Avg function in a totals query is a good bet to be a fact tab fact tables contain fields for the individual facts as well as foreign key fields relating th to the dimension tables. Measure
Every cube will contain one or more measures, each based on a column in a fact table you';d like to analyze. In the cube of book order information, for example, the measur would be things such as unit sales and profit. Schema
Fact tables and dimension tables are related, which is hardly surprising, given that the dimension tables to group information from the fact table. The relations within a cu form a schema. There are two basic OLAP schemas: star and snowflake. In a every dimension table is related directly to the fact table. In a snowflake schema dimension tables are related indirectly to the fact table. For example, if your cube OrderDetails as a fact table, with Customers and Orders as dimension tables, and Cust is related to Orders, which in turn is related to OrderDetails, then you're dealing with a snowflake schema.
There are additional schema types besides the star and snowflake schemas supported by SQL Server 2008, including parent-child schemas and data-mining schemas. However, the star and snowflake schemas are the most common types in normal cubes.
http://www.accelebrate.com/sql_training/ssas_2008_tutorial.htm
6/28/2012
SSAS Tutorial: SQL Server 2008 Analysis Services Tutorial
Page 4 of 19
Whiteman Air Force Base / Kansas City, Missouri Lincoln / Omaha, Nebraska Reno and Las Vegas, Nevada Fredericton / Moncton / Saint John, New Brunswick Santa Fe / Albuquerque, New Mexico Princeton, New Jersey & Philadelphia, Pennsylvania Trenton, New Jersey Albany, New York Buffalo, New York White Plains / New York City, New York Charlotte, North Carolina Durham / Raleigh, North Carolina Bismarck & Fargo, North Dakota Halifax, Nova Scotia Bowling Green / Toledo, Ohio Canton / Akron, Ohio Cincinnati, Ohio Cleveland & Columbus, Ohio Dayton, Ohio Tulsa / Oklahoma City, Oklahoma Toronto, Ontario Portland, Oregon Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania Qubec City / Montreal, Qubec Providence, Rhode Island Saskatoon / Regina, Saskatchewan Edinburgh / Glasgow, Scotland Columbia & Charleston, South Carolina Spartanburg & Greenville, South Carolina Stockholm, Sweden Chattanooga / Knoxville, Tennessee Memphis / Jackson / Nashville, Tennessee College Station and Houston, Texas El Paso, Texas San Antonio / Austin, Texas Wichita Falls & Dallas, Texas Ogden / Salt Lake City, Utah Burlington, Vermont Fairfax / Dulles / McLean / Herndon / Reston, Virginia Richmond / Alexandria / Arlington, Virginia Virginia Beach / Norfolk, Virginia
SSAS 2008 Tutorial: Introducing Business Intelligence Developm Studio
Business Intelligence Development Studio (BIDS) is a new tool in SQL Server 2008 tha can use for analyzing SQL Server data in various ways. You can build three solutions with BIDS:
Analysis Services projects Integration Services projects (you'll learn about SQL Server Integration Services Chapter 16) Reporting Services projects (you'll learn about SQL Server Reporting Services in 17)
To launch Business Intelligence Development Studio, select Microsoft SQL Server 2008 Server Business Intelligence Development Studio from the Programs menu. BIDS shar Visual Studio shell, so if you have Visual Studio installed on your computer, this menu will launch Visual Studio complete with all of the Visual Studio project types (such as V Basic and C# projects).
SSAS 2008 Tutorial: Creating a Data Cube
To build a new data cube using BIDS, you need to perform these steps: Create a new Analysis Services project Define a data source Define a data source view Invoke the Cube Wizard
We'll look at each of these steps in turn.
You'll need to have the AdventureWorksDW2008 sample database installed to complete the examples in this chapter. This database is one of the samples that's available with SQL Server.
Creating a New Analysis Services Project To create a new Analysis Services project, you use the New Project dialog box in very similar to creating any other type of new project in Visual Studio. Try It! To create a new Analysis Services project, follow these steps:
1. Select Microsoft SQL Server 2008 > SQL Server Business Intelligence Developme Studio from the Programs menu to launch Business Intelligence Development St 2. Select File > New > Project. 3. In the New Project dialog box, select the Business Intelligence Projects project 4. Select the Analysis Services Project template. 5. Name the new project AdventureWorksCube1 and select a convenient location to it. 6. Click OK to create the new project.
Figure 15-1 shows the Solution Explorer window of the new project, ready to be popul with objects.
http://www.accelebrate.com/sql_training/ssas_2008_tutorial.htm
6/28/2012
SSAS Tutorial: SQL Server 2008 Analysis Services Tutorial
Page 5 of 19
Tacoma / Seattle, Washington Charleston, West Virginia Madison / Milwaukee, Wisconsin
Figure 15-1: New Analysis Services project
Defining a Data Source
A data source provides the cube's connection to the staging tables, which the cube use source data. To define a data source, you'll use the Data Source Wizard. You can launc wizard by right-clicking on the Data Sources folder in your new Analysis Services proje wizard will walk you through the process of defining a data source for your cube, inclu choosing a connection and specifying security credentials to be used to connect to the source. Try It! To define a data source for the new cube, follow these steps:
1. Right-click on the Data Sources folder in Solution Explorer and select New Data S 2. Read the first page of the Data Source Wizard and click Next. 3. You can base a data source on a new or an existing connection. Because any existing connections, click New. 4. In the Connection Manager dialog box, select the server containing your analysis services sample database from the Server Name combo box. 5. Fill in your authentication information. 6. Select the Native OLE DB\SQL Native Client provider (this is the default provider 7. Select the AdventureWorksDW2008 database. Figure 15-2 shows the filled Connection Manager dialog box.
http://www.accelebrate.com/sql_training/ssas_2008_tutorial.htm
6/28/2012
SSAS Tutorial: SQL Server 2008 Analysis Services Tutorial
Page 6 of 19
Figure 15-2: Setting up a connection
8. 9. 10. 11.
Click OK to dismiss the Connection Manager dialog box. Click Next. Select Use the Service Account impersonation information and click Next. Accept the default data source name and click Finish.
Defining a Data Source View
A data source view is a persistent set of tables from a data source that supply the data particular cube. It lets you combine tables from as many data sources as necessary to together the data your cube needs. BIDS also includes a wizard for creating data views, which you can invoke by right-clicking on the Data Source Views folder in Solut Explorer. Try It! To create a new data source view, follow these steps:
http://www.accelebrate.com/sql_training/ssas_2008_tutorial.htm
6/28/2012
SSAS Tutorial: SQL Server 2008 Analysis Services Tutorial
Page 7 of 19
1. Right-click on the Data Source Views folder in Solution Explorer and select New D Source View. 2. Read the first page of the Data Source View Wizard and click Next. 3. Select the Adventure Works DW data source and click Next. Note that you could launch the Data Source Wizard from here by clicking New Data Source. 4. Select the FactFinance(dbo) table in the Available Objects list and click the > bu move it to the Included Object list. This will be the fact table in the new cube. 5. Click the Add Related Tables button to automatically add all of the tables that ar directly related to the dbo.FactFinance table. These will be the dimension tables new cube. Figure 15-3 shows the wizard with all of the tables selected.
Figure 15-3: Selecting tables for the data source view
6. Click Next. 7. Name the new view Finance and click Finish. BIDS will automatically display the of the new data source view, as shown in Figure 15-4.
http://www.accelebrate.com/sql_training/ssas_2008_tutorial.htm
6/28/2012
SSAS Tutorial: SQL Server 2008 Analysis Services Tutorial
Page 8 of 19
Figure 15-4: The Finance data source view
Invoking the Cube Wizard As you can probably guess at this point, you invoke the Cube Wizard by right Cubes folder in Solution Explorer. The Cube Wizard interactively explores the data source view to identify the dimensions, levels, and measures in your cube. Try It! To create the new cube, follow these steps: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Right-click on the Cubes folder in Solution Explorer and select New Cube. Read the first page of the Cube Wizard and click Next. Select the option to Use Existing Tables. Click Next. The Finance data source view should be selected in the drop-down list at the top a checkmark next to the FactFinance table to designate it as a measure group ta click Next. 6. Remove the check mark for the field FinanceKey, indicating that it is not a meas wish to summarize, and click Next. 7. Leave all Dim tables selected as dimension tables, and click Next.
http://www.accelebrate.com/sql_training/ssas_2008_tutorial.htm
6/28/2012
SSAS Tutorial: SQL Server 2008 Analysis Services Tutorial
Page 9 of 19
8. Name the new cube FinanceCube and click Finish. Defining Dimensions
The cube wizard defines dimensions based upon your choices, but it doesn't dimensions with attributes. You will need to edit each dimension, adding any attributes your users will wish to use when querying your cube. Try It!
1. In BIDS, double click on DimDate in the Solution Explorer. 2. Using Table 15-1 below as a guide, drag the listed columns from the right (named Data Source View) and drop them in the left-hand panel (named Attribu include them in the dimension. DimDate
CalendarYear
CalendarQuarter
MonthNumberOfYear
DayNumberOfWeek
DayNumberOfMonth
DayNumberOfYear
WeekNumberOfYear
FiscalQuarter
FiscalYear
Table 15-1
3. Using Table 15-2, add the listed columns to the remaining four dimensions. DimDepartmentGroup
DepartmentGroupName
http://www.accelebrate.com/sql_training/ssas_2008_tutorial.htm
6/28/2012
SSAS Tutorial: SQL Server 2008 Analysis Services Tutorial
Page 10 of 19
DimAccount
AccountDescription
AccountType
DimScenario
ScenarioName
DimOrganization
OrganizationName
Table 15-2
Adding Dimensional Intelligence
One of the most common ways data gets summarized in a cube is by time. We want to sales per month for the last fiscal year. We want to see production values year compared to last year's production values year-to-date. Cubes know a lot about time.
In order for SQL Server Analysis Services to be best able to answer these questions fo needs to know which of your dimensions stores the time information, and which fields time dimension correspond to what units of time. The Business Intelligence Wizard hel specify this information in your cube. Try It!
1. With your FinanceCube open in BIDS, click on the Business Intelligence Wizard b on the toolbar. 2. Read the initial page of the wizard and click Next. 3. Choose to Define Dimension Intelligence and click Next. 4. Choose DimDate as the dimension you wish to modify and click Next. 5. Choose Time as the dimension type. In the bottom half of this screen are listed t of time for which cubes have knowledge. Using the Table 15-1 below, place a checkmark next to the listed units of time and then select which field in DimDate contains that type of data.
Time Property Name
Time Column
Year
CalendarYear
Quarter
CalendarQuarter
http://www.accelebrate.com/sql_training/ssas_2008_tutorial.htm
6/28/2012
SSAS Tutorial: SQL Server 2008 Analysis Services Tutorial
Page 11 of 19
Month
MonthNumberOfYear
Day of Week
DayNumberOfWeek
Day of Month
DayNumberOfMonth
Day of Year
DayNumberOfYear
Week of Year
WeekNumberOfYear
Fiscal Quarter
FiscalQuarter
Fiscal Year
FiscalYear
Table 15-1:Time columns for FinanceCube
6. Click Next. Hierarchies
You will also need to create hierarchies in your dimensions. Hierarchies are sequence of fields, and are often used to determine the rows or columns of a pivot tab querying a cube. Try It!
1. In BIDS, double-click on DimDate in the solution explorer. 2. Create a new hierarchy by dragging the CalendarYear field from the left (called Attributes) and drop it in the middle pane (called Hierarchies.) 3. Add a new level by dragging the CalendarQuarter field from the left-hand panel drop it on the <new level> spot in the new hierarchy in the middle-panel. 4. Add a third level by dragging the MonthNumberOfYear field to the <new level> s the hierarchy. 5. Right-click on the hierarchy and rename it to Calendar. 6. Adding Dimensional IntelligenceIn the same manner, create a hierarchy named F that contains the fields FiscalYear, FiscalQuarter and MonthNumberOfYear. Figur shows the hierarchy panel.
http://www.accelebrate.com/sql_training/ssas_2008_tutorial.htm
6/28/2012
SSAS Tutorial: SQL Server 2008 Analysis Services Tutorial
Page 12 of 19
Figure 15-5: DimDate hierarchies
Deploying and Processing a Cube
At this point, you've defined the structure of the new cube - but there's still more work done. You still need to deploy this structure to an Analysis Services server and the cube to create the aggregates that make querying fast and easy.
To deploy the cube you just created, select Build > Deploy AdventureWorksCube1. Thi deploy the cube to your local Analysis Server, and also process the cube, building the aggregates for you. BIDS will open the Deployment Progress window, as shown in Figu 5, to keep you informed during deployment and processing. Try It! To deploy and process your cube, follow these steps:
1. In BIDS, select Project > AdventureWorksCube1 from the menu system. 2. Choose the Deployment category of properties in the upper left-hand corner of t project properties dialog box. 3. Verify that the Server property lists your server name. If not, enter your server Click OK. Figure 15-6 shows the project properties window.
http://www.accelebrate.com/sql_training/ssas_2008_tutorial.htm
6/28/2012
SSAS Tutorial: SQL Server 2008 Analysis Services Tutorial
Page 13 of 19
Figure 15-6: Project Properties
4. From the menu, select Build > Deploy AdventureWorksCube1. Figure 15 Cube Deployment window after a successful deployment.
http://www.accelebrate.com/sql_training/ssas_2008_tutorial.htm
6/28/2012
SSAS Tutorial: SQL Server 2008 Analysis Services Tutorial
Page 14 of 19
Figure 15-7: Deploying a cube
One of the tradeoffs of cubes is that SQL Server does not attempt to keep your OLAP cube data synchronized with the OLTP data that as its source. As you add, remove, and update rows in the underlying OLTP database, the cube will get out of date. To update the cube, you can select Cube > Process in BIDS. You can also automate cube updates using SQL Server Integration Services, which you'll learn about in Chapter 16.
SSAS 2008 Tutorial: Exploring a Data Cube
At last you're ready to see what all the work was for. BIDS includes a builtthat lets you interactively explore the data in any cube that has been deployed and pro To open the Cube Browser, right-click on the cube in Solution Explorer and select Brow Figure 15-8 shows the default state of the Cube Browser after it's just been opened.
http://www.accelebrate.com/sql_training/ssas_2008_tutorial.htm
6/28/2012
SSAS Tutorial: SQL Server 2008 Analysis Services Tutorial
Page 15 of 19
Figure 15-8: The cube browser in BIDS
The Cube Browser is a drag-and-drop environment. If you've worked with pivot tables Microsoft Excel, you should have no trouble using the Cube browser. The pane to the includes all of the measures and dimensions in your cube, and the pane to the right gi drop targets for these measures and dimensions. Among other operations, you can:
Drop a measure in the Totals/Detail area to see the aggregated data for Drop a dimension hierarchy or attribute in the Row Fields area to summarize by value on rows. Drop a dimension hierarchy or attribute in the Column Fields area to summarize value on columns. Drop a dimension hierarchy or attribute in the Filter Fields area to enable filterin members of that hierarchy or attribute. Use the controls at the top of the report area to select additional filtering expres
In fact, if you've worked with pivot tables in Excel, you'll find that Cube Browser works exactly the same, because it uses the Microsoft Office PivotTable control as its basis.
Try It! To see the data in the cube you just created, follow these steps: 1. Right-click on the cube in Solution Explorer and select Browse.
http://www.accelebrate.com/sql_training/ssas_2008_tutorial.htm
6/28/2012
SSAS Tutorial: SQL Server 2008 Analysis Services Tutorial
Page 16 of 19
2. Expand the Measures node in the metadata panel (the area at the left of the use interface). 3. Expand the Fact Finance measure group. 4. Drag the Amount measure and drop it on the Totals/Detail area. 5. Expand the Dim Account node in the metadata panel. 6. Drag the Account Description attribute and drop it on the Row Fields area. 7. Expand the Dim Date node in the metadata panel. 8. Drag the Calendar hierarchy and drop it on the Column Fields area. 9. Click the + sign next to year 2001 and then the + sign next to quarter 3. 10. Expand the Dim Scenario node in the metadata panel. 11. Drag the Scenario Name attribute and drop it on the Filter Fields area. 12. Click the dropdown arrow next to scenario name. Uncheck all of the checkboxes for the one next to the Budget value.
Figure 15-9 shows the result. The Cube Browser displays month-by-month budgets by account for the third quarter of 2001. Although you could have written queries to extra information from the original source data, it's much easier to let Analysis Services do t heavy lifting for you.
Figure 15-9: Exploring cube data in the cube browser
SSAS 2008 Tutorial: Exercises
Although cubes are not typically created with such a single purpose in mind, your task create a data cube, based on the data in the AdventureWorksDW2008 sample databas answer the following question: what were the internet sales by country and product na married customers only?
http://www.accelebrate.com/sql_training/ssas_2008_tutorial.htm
6/28/2012
SSAS Tutorial: SQL Server 2008 Analysis Services Tutorial
Page 17 of 19
Solutions to Exercises To create the cube, follow these steps:
1. Select Microsoft SQL Server 2008 SQL Server Business Intelligence Developme Studio from the Programs menu to launch Business Intelligence Development 2. Select File > New > Project. 3. In the New Project dialog box, select the Business Intelligence Projects project ty 4. Select the Analysis Services Project template. 5. Name the new project AdventureWorksCube2 and select a convenient location to it. 6. Click OK to create the new project. 7. Right-click on the Data Sources folder in Solution Explorer and select New 8. Read the first page of the Data Source Wizard and click Next. 9. Select the existing connection to the AdventureWorksDW2008 database and click 10. Select Service Account and click Next. 11. Accept the default data source name and click Finish. 12. Right-click on the Data Source Views folder in Solution Explorer and select New D Source View. 13. Read the first page of the Data Source View Wizard and click Next. 14. Select the Adventure Works DW2008 data source and click Next. 15. Select the FactInternetSales(dbo) table in the Available Objects list and button to move it to the Included Object list. 16. Click the Add Related Tables button to automatically add all of the tables that ar directly related to the dbo.FactInternetSales table. Also add the DimGeography dimension. 17. Click Next. 18. Name the new view InternetSales and click Finish. 19. Right-click on the Cubes folder in Solution Explorer and select New Cube. 20. Read the first page of the Cube Wizard and click Next. 21. Select the option to Use Existing Tables. 22. Select FactInternetSales and FactInternetSalesReason tables as the Measure Gro Tables and click Next. 23. Leave all measures selected and click Next. 24. Leave all dimensions selected and click Next. 25. Name the new cube InternetSalesCube and click Finish. 26. In the Solution Explorer, double click the DimCustomer dimension. 27. Add the MaritalStaus field as an attribute, along with any other fields desired. 28. Similarly, edit the DimSalesTerritory dimension, adding the SalesTerritoryCountr along with any other desired fields. 29. Also edit the DimProduct dimension, adding the EnglishProductName field along any other desired fields. 30. Select Project > AdventureWorksCube2 Properties and verify that your server na correctly listed. Click OK. 31. Select Build > Deploy AdventureWorksCube2. 32. Right-click on the cube in Solution Explorer and select Browse. 33. Expand the Measures node in the metadata panel. 34. Drag the Order Quantity and Sales Amount measures and drop it on the Totals/D area. 35. Expand the Dim Sales Territory node in the metadata panel. 36. Drag the Sales Territory Country property and drop it on the Row Fields area. 37. Expand the Dim Product node in the metadata panel. 38. Drag the English Product Name property and drop it on the Column Fields area. 39. Expand the Dim Customer node in the metadata panel. 40. Drag the Marital Status property and drop it on the Filter Fields area.
http://www.accelebrate.com/sql_training/ssas_2008_tutorial.htm
6/28/2012
SSAS Tutorial: SQL Server 2008 Analysis Services Tutorial
Page 18 of 19
41. Click the dropdown arrow next to Marital Status. Uncheck the S checkbox. Figure 15-10 shows the finished cube.
Figure 15-10: The AdventureWorksCube2 cube
In-Depth SSAS Training For 3 days of in-depth SSAS training, please consider requesting Accelebrate's Introduction to SQL Server 2005 Analysis Services for you and your staff. Please contact us to request a formal quote.
More Tutorials: SSRS, SSIS
Java and all Java-based marks are registered trademarks of the Oracle Corporation in the U.S. and other
city links
VB.NET, C#, ASP, & ASP.NET Training SharePoint Training Adobe Training
Java Training
SQL Server Training Perl Training Sitemap
PHP Training
XML Training
http://www.accelebrate.com/sql_training/ssas_2008_tutorial.htm
6/28/2012
SSAS Tutorial: SQL Server 2008 Analysis Services Tutorial
Page 19 of 19
Accelebrate, Accelerated Learning Celebrated Results, and the Accelebrate logo are registered trademarks of Accelebrate, Inc. All other product names and trademarks are property of their respective owners. Course outline content may mirror or be derived from the book that each student receives with the course. Otherwise, all content is copyright 2003- 2012 by Accelebrate, Inc. of Atlanta, Georgia, USA. To contact us, please use the contact form, email info@accelebrate.com us, or call 1 877 849 1850 in the US and Canada, 0808 234 2132 in the UK, 1 800 550 311 in Ireland, or +1 678 648 3113 from all other locations. Recent client sites: Birmingham, AL | Phoenix, AZ | Los Angeles, CA | Sacramento, CA | San Diego, CA | San Francisco, CA | San Jose, CA | Denver, CO | Washington, DC | Jacksonville, FL | Miami, FL | Orlando, FL | Tampa, FL | Atlanta, GA | Chicago, IL | Indianapolis, IN | Boston, MA | Baltimore, MD | Detroit, MI | Minneapolis, MN | Kansas City, MO | Saint Louis, MO | Charlotte, NC | Raleigh, NC | Albuquerque, NM | Las Vegas, NV | Albany, NY | New York City, NY | Cincinnati, OH | Cleveland, OH | Columbus, OH | Dayton, OH | Oklahoma City, OK | Toronto, ON | Portland, OR | Philadelphia, PA | Pittsburgh, PA | Memphis, TN | Nashville, TN | Austin, TX | Dallas, TX | Houston, TX | San Antonio, TX | Salt Lake City, UT | Seattle, WA | Dublin, Ireland | London, UK
http://www.accelebrate.com/sql_training/ssas_2008_tutorial.htm
6/28/2012
Вам также может понравиться
- MSB I Cheat SheetДокумент11 страницMSB I Cheat Sheetarjun.ec633Оценок пока нет
- Aggregate FunctionsДокумент3 страницыAggregate FunctionsZhel Geron MercadoОценок пока нет
- Indian Bank Case StudyДокумент7 страницIndian Bank Case StudyKapil DevatwalОценок пока нет
- Msbi SQL QueriesДокумент88 страницMsbi SQL QueriesraamanОценок пока нет
- Database: NoteДокумент81 страницаDatabase: NoteShambadityaОценок пока нет
- Data Warehouse PracticesДокумент38 страницData Warehouse PracticesHafiyyan Faza SantosoОценок пока нет
- Q1. What Is Dax ?Документ6 страницQ1. What Is Dax ?Suresh GunduОценок пока нет
- Rami Reddy (Msbi) ResumeДокумент3 страницыRami Reddy (Msbi) ResumeHuur ShaikОценок пока нет
- DB QuestionsДокумент32 страницыDB QuestionsRoshan ahapaatraОценок пока нет
- Sahil SQL QueriesДокумент18 страницSahil SQL QueriesDaljitОценок пока нет
- How To Format Datetime & Date With Century?: DD 0 DD 0Документ18 страницHow To Format Datetime & Date With Century?: DD 0 DD 0Michelle LobendinoОценок пока нет
- Database Normalization 7Документ12 страницDatabase Normalization 7VinodKumarОценок пока нет
- CS322: Database Systems: PL/ SQLДокумент47 страницCS322: Database Systems: PL/ SQLAnonymous aQxekTRОценок пока нет
- MSBIДокумент5 страницMSBIPavan ChОценок пока нет
- Ssas 2016Документ49 страницSsas 2016Lilantha Lakmal GallabaОценок пока нет
- Outline: ETL Extraction Transformation LoadingДокумент38 страницOutline: ETL Extraction Transformation Loadinghiprabu123Оценок пока нет
- BSL SQL Training Part IДокумент127 страницBSL SQL Training Part IAnkita RoyОценок пока нет
- ETL ReviewДокумент10 страницETL Reviewapi-3831106100% (3)
- SSIS Best PracticesДокумент14 страницSSIS Best PracticesmailtopvvkОценок пока нет
- Windowing FunctionsДокумент54 страницыWindowing FunctionsSorin PopescuОценок пока нет
- Database CloningДокумент2 страницыDatabase CloningriteshhtyОценок пока нет
- Power BI Course Syllabus - by Murali P N, Besant TechnologiesДокумент6 страницPower BI Course Syllabus - by Murali P N, Besant TechnologiesPradeep Karthik PotnuruОценок пока нет
- SQL Notes by PunjabkiddaДокумент45 страницSQL Notes by Punjabkiddamanoj kumarОценок пока нет
- SSAS - Dwbi TutorialsДокумент81 страницаSSAS - Dwbi TutorialspjkarthikmcaОценок пока нет
- Msbi Developer: B.Sreedhara Reddy Email Id: Bsreedharreddy86 Mobile: +91-9590911350Документ4 страницыMsbi Developer: B.Sreedhara Reddy Email Id: Bsreedharreddy86 Mobile: +91-9590911350sureshОценок пока нет
- Unit-I PPT DWDMДокумент90 страницUnit-I PPT DWDMGiriDharanОценок пока нет
- Teradata SQLДокумент36 страницTeradata SQLrupeshvinОценок пока нет
- Sybase Isql Cheat-SheetДокумент20 страницSybase Isql Cheat-SheetBiswajit DasОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4: Advanced SQL: Database System Concepts, 5th EdДокумент58 страницChapter 4: Advanced SQL: Database System Concepts, 5th EdAmit BaghelОценок пока нет
- Dimensional Modeling TutorialДокумент9 страницDimensional Modeling Tutorialvektor1972Оценок пока нет
- Olap Case Study - VJДокумент16 страницOlap Case Study - VJVijay S. GachandeОценок пока нет
- SQL FaqsДокумент16 страницSQL Faqssriram kantipudiОценок пока нет
- SQL Refresher Complete Notes PDFДокумент352 страницыSQL Refresher Complete Notes PDFDeepasri PrasadОценок пока нет
- Basic DefinitionsДокумент5 страницBasic DefinitionsBujji BujjiОценок пока нет
- Window FunctionsДокумент15 страницWindow Functionschenna kesavaОценок пока нет
- 01-Introduction To BIДокумент41 страница01-Introduction To BIOssama AhmadОценок пока нет
- Datastage Transformer FunctionsДокумент71 страницаDatastage Transformer FunctionsAnonymousHPОценок пока нет
- Tips and Tricks For SQL-BI - Sequence Container in SSIS - Different Ways of Using Sequence ContainersДокумент3 страницыTips and Tricks For SQL-BI - Sequence Container in SSIS - Different Ways of Using Sequence ContainerswicvalОценок пока нет
- SQL Full Class NotesДокумент83 страницыSQL Full Class NotesRed ranger100% (1)
- SQL Query, For Trigger, Store Procedure, Functionand ViewДокумент6 страницSQL Query, For Trigger, Store Procedure, Functionand Viewcap.rohit550Оценок пока нет
- Getting Started With SSISДокумент60 страницGetting Started With SSIScpaz_navarroОценок пока нет
- What Are The Components of Physical Database Structure of Oracle DatabaseДокумент27 страницWhat Are The Components of Physical Database Structure of Oracle DatabaseAnusha Verghese100% (2)
- SSIS Tasks: Data Flow TaskДокумент3 страницыSSIS Tasks: Data Flow TaskmailtopvvkОценок пока нет
- DBMS - JS in Database Management Systems With Its Operations and Its FunctionalitiesДокумент71 страницаDBMS - JS in Database Management Systems With Its Operations and Its FunctionalitiesSuganya PeriasamyОценок пока нет
- Clover Intv QSTNДокумент10 страницClover Intv QSTNDevvrataОценок пока нет
- SQL FullДокумент75 страницSQL FullKranthi Kumar KhariduОценок пока нет
- 2 Structured Query LanguageДокумент28 страниц2 Structured Query LanguageAKASH PALОценок пока нет
- MDX QueryДокумент51 страницаMDX QuerySachitra KhatuaОценок пока нет
- Useful Netezza Queries and TipsДокумент6 страницUseful Netezza Queries and Tipssumit38494Оценок пока нет
- SSIS Design Pattern - Incremental Loads: Andy LeonardДокумент55 страницSSIS Design Pattern - Incremental Loads: Andy LeonardmirajvsenОценок пока нет
- Basics On Creating SSIS PackagesДокумент19 страницBasics On Creating SSIS PackagesSatish BeuraОценок пока нет
- Extending SSIS With Custom Tasks - Darren GreenДокумент27 страницExtending SSIS With Custom Tasks - Darren GreenSergio Bolaños CotoОценок пока нет
- SQL NotesДокумент18 страницSQL NotesBaljit KaurОценок пока нет
- Mohan ResumeДокумент4 страницыMohan ResumeRamesh NaiduОценок пока нет
- SSIS Interview Questions and Answers: DeploymentДокумент9 страницSSIS Interview Questions and Answers: Deploymentssingh_scribdОценок пока нет
- DBMS Lab # 9 Procedures PDFДокумент7 страницDBMS Lab # 9 Procedures PDFsaqib idreesОценок пока нет
- Advance SQLДокумент45 страницAdvance SQLDDОценок пока нет
- Unit TestingДокумент23 страницыUnit TestingUdayan DattaОценок пока нет
- Junit TutorialДокумент24 страницыJunit TutorialChandrasekar GangadaranОценок пока нет
- Junit TutorialДокумент24 страницыJunit TutorialChandrasekar GangadaranОценок пока нет
- JUnit TutorialДокумент32 страницыJUnit TutorialFadwa ZedОценок пока нет
- C# - Catch Vs Catch (Exception E) and Throw Vs Throw e - Stack OverflowДокумент3 страницыC# - Catch Vs Catch (Exception E) and Throw Vs Throw e - Stack OverflowChandrasekar GangadaranОценок пока нет
- Oop ConceptsДокумент11 страницOop ConceptsBrahmanand SinghОценок пока нет
- Smoke and Sanity TesingДокумент6 страницSmoke and Sanity TesingChandrasekar GangadaranОценок пока нет
- BusinessObjects and PowerBI ComparisonДокумент11 страницBusinessObjects and PowerBI ComparisonNyan FiveОценок пока нет
- How Azure Sentinel Works - Learn - Microsoft DocsДокумент5 страницHow Azure Sentinel Works - Learn - Microsoft DocsDavidОценок пока нет
- Chapter No.02Документ25 страницChapter No.02Muhammad FaisalОценок пока нет
- Common Data Management in AribaДокумент11 страницCommon Data Management in AribaRajat GОценок пока нет
- Business Communication Essentials 7th Edition Bovee Test BankДокумент47 страницBusiness Communication Essentials 7th Edition Bovee Test Bankboccacinnamyl.1zjf100% (23)
- Article EVA PDFДокумент180 страницArticle EVA PDFLika LanićОценок пока нет
- Comparative Study of Nosql Databases For Big Data Storage: International Journal of Engineering & TechnologyДокумент5 страницComparative Study of Nosql Databases For Big Data Storage: International Journal of Engineering & TechnologyJose Guillermo Andrade CariОценок пока нет
- DD s03 l03Документ10 страницDD s03 l03Sladjan UgrenovicОценок пока нет
- ORACLE Fundamental - SQL 1 أ آاروأ: Mohamed - SuezДокумент4 страницыORACLE Fundamental - SQL 1 أ آاروأ: Mohamed - SuezuserОценок пока нет
- PDF Scanned & Optical Character Recognition (OCR)Документ47 страницPDF Scanned & Optical Character Recognition (OCR)MegasquidОценок пока нет
- Design and Implementation For Recommender SystemДокумент112 страницDesign and Implementation For Recommender SystemAbdullah MarufОценок пока нет
- Oracle Data Pump (Expdp, Impdp) in Oracle Database 10g, 11g, 12c, 18cДокумент20 страницOracle Data Pump (Expdp, Impdp) in Oracle Database 10g, 11g, 12c, 18cmarcosperez81Оценок пока нет
- Retgen: A Joint Framework For Retrieval and Grounded Text Generation ModelingДокумент15 страницRetgen: A Joint Framework For Retrieval and Grounded Text Generation Modelingahmad raihanОценок пока нет
- Database Programming With SQL 2-2: Limit Rows Selected Practice ActivitiesДокумент3 страницыDatabase Programming With SQL 2-2: Limit Rows Selected Practice Activitieschristian tombilayukОценок пока нет
- Tamalika NewДокумент1 страницаTamalika NewAmitesh DebnathОценок пока нет
- CAD vs. GISДокумент13 страницCAD vs. GISelectrical_hackОценок пока нет
- Storage Devices and Their TypesДокумент3 страницыStorage Devices and Their TypessarjueОценок пока нет
- Lecture 3Документ12 страницLecture 3Saadia MobeenОценок пока нет
- Level 2 Coc ExamsДокумент7 страницLevel 2 Coc ExamsMk Fisiha25% (4)
- Cloudera Developer Training For Apache SparkДокумент3 страницыCloudera Developer Training For Apache SparkkeshОценок пока нет
- U.S. List of Exhibits Rafael Caro QuinteroДокумент42 страницыU.S. List of Exhibits Rafael Caro QuinteroChivis MartinezОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Transaction ProcessingДокумент20 страницIntroduction To Transaction ProcessingSatrio MangkunegoroОценок пока нет
- Managing The Linux File SystemДокумент100 страницManaging The Linux File SystemQuân Nguyễn Trần AnhОценок пока нет
- Challenges ProjectMissingMoneyMattersДокумент2 страницыChallenges ProjectMissingMoneyMattersntn.anh05Оценок пока нет
- Hospital ProposalДокумент27 страницHospital ProposalSiti Noor MashitahОценок пока нет
- Eaadhaar 442910215551 01082017075641 316979Документ1 страницаEaadhaar 442910215551 01082017075641 316979Narasimhulu dhanikelaОценок пока нет
- CO4752 Web Development Assignment (2020 A) : Learning Outcomes AssessedДокумент3 страницыCO4752 Web Development Assignment (2020 A) : Learning Outcomes AssessedStudy TipsОценок пока нет
- Assignment No: 3: Aim: Objective: Theory:-Inverted IndexДокумент2 страницыAssignment No: 3: Aim: Objective: Theory:-Inverted IndexPratik BОценок пока нет
- Chapter No.2 Database Design Using ER ModelДокумент50 страницChapter No.2 Database Design Using ER ModelMonkey dragon10Оценок пока нет
- CS3492-DBMS Questions and AnswersДокумент5 страницCS3492-DBMS Questions and AnswersShalini KОценок пока нет
- Business Intelligence Strategy and Big Data Analytics: A General Management PerspectiveОт EverandBusiness Intelligence Strategy and Big Data Analytics: A General Management PerspectiveРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- Grokking Algorithms: An illustrated guide for programmers and other curious peopleОт EverandGrokking Algorithms: An illustrated guide for programmers and other curious peopleРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (16)
- Optimizing DAX: Improving DAX performance in Microsoft Power BI and Analysis ServicesОт EverandOptimizing DAX: Improving DAX performance in Microsoft Power BI and Analysis ServicesОценок пока нет
- Blockchain Basics: A Non-Technical Introduction in 25 StepsОт EverandBlockchain Basics: A Non-Technical Introduction in 25 StepsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (24)
- Fusion Strategy: How Real-Time Data and AI Will Power the Industrial FutureОт EverandFusion Strategy: How Real-Time Data and AI Will Power the Industrial FutureОценок пока нет
- THE STEP BY STEP GUIDE FOR SUCCESSFUL IMPLEMENTATION OF DATA LAKE-LAKEHOUSE-DATA WAREHOUSE: "THE STEP BY STEP GUIDE FOR SUCCESSFUL IMPLEMENTATION OF DATA LAKE-LAKEHOUSE-DATA WAREHOUSE"От EverandTHE STEP BY STEP GUIDE FOR SUCCESSFUL IMPLEMENTATION OF DATA LAKE-LAKEHOUSE-DATA WAREHOUSE: "THE STEP BY STEP GUIDE FOR SUCCESSFUL IMPLEMENTATION OF DATA LAKE-LAKEHOUSE-DATA WAREHOUSE"Рейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)
- DB2 9 System Administration for z/OS: Certification Study Guide: Exam 737От EverandDB2 9 System Administration for z/OS: Certification Study Guide: Exam 737Рейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (2)
- SQL QuickStart Guide: The Simplified Beginner's Guide to Managing, Analyzing, and Manipulating Data With SQLОт EverandSQL QuickStart Guide: The Simplified Beginner's Guide to Managing, Analyzing, and Manipulating Data With SQLРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (46)
- Microsoft Access Guide to Success: From Fundamentals to Mastery in Crafting Databases, Optimizing Tasks, & Making Unparalleled Impressions [III EDITION]От EverandMicrosoft Access Guide to Success: From Fundamentals to Mastery in Crafting Databases, Optimizing Tasks, & Making Unparalleled Impressions [III EDITION]Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (8)
- Modelling Business Information: Entity relationship and class modelling for Business AnalystsОт EverandModelling Business Information: Entity relationship and class modelling for Business AnalystsОценок пока нет
- High-Performance Oracle: Proven Methods for Achieving Optimum Performance and AvailabilityОт EverandHigh-Performance Oracle: Proven Methods for Achieving Optimum Performance and AvailabilityОценок пока нет
- Joe Celko's SQL for Smarties: Advanced SQL ProgrammingОт EverandJoe Celko's SQL for Smarties: Advanced SQL ProgrammingРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)
- Data Architecture: A Primer for the Data Scientist: A Primer for the Data ScientistОт EverandData Architecture: A Primer for the Data Scientist: A Primer for the Data ScientistРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)














































































































![Microsoft Access Guide to Success: From Fundamentals to Mastery in Crafting Databases, Optimizing Tasks, & Making Unparalleled Impressions [III EDITION]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/610686937/149x198/9ccfa6158e/1714467780?v=1)










