Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Make Up
Загружено:
kanilkadianИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Make Up
Загружено:
kanilkadianАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Birla Institute of Technology & Science, Pilani, Rajasthan 333031 COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION II Semester, 2011-2012 Course Title: Chemistry
Laboratory Course Number: CHEM F110 Date: 11.05.2012 Make up (CLOSED BOOK) Time: 60 minutes Max. Marks: 60
Note:
Q.1 Conductance of three liquids I,J and K (each occupying volume of 50 ml) was measured as cI, cJ and cK respectively, using same conductivity cell. Chemical analysis proved that I was triply distilled water, J was 0.1 N hydrochloric acid and K was 0.1 N acetic acid. 1 ml of 0.1 N NaOH was added to each of these and the conductance was measured again. What can you comment about the conductometric observations of these liquids? (A) |cI-cJ| increases and |cJ-cK| decreases on addition of the base. (B) |cI-cJ| decreases and |cJ-cK| increases on addition of the base. (C) |cI-cJ| as well as |cJ-cK| decrease on addition of the base. (D) |cI-cJ| as well as |cJ-cK| increase on addition of the base. Q. 2 In a conductometric titration of acetic acid against potassium hydroxide, the rate of increase in conductance before the endpoint is less than the one after the endpoint. The dominant factor responsible for this is.... (A) K+ ions are bulkier than H+ ions (B) CH3COO- ions are bulkier than OH- ions (C) Water molecules are created before endpoint thereby reducing the (D) Conductivity of OH- ions is always greater than that of H+ ions Q.3 In a conductivity cell, the two metal plates of dimensions I x J cm2 are held parallel to each other at a distance K cm. Which of the following alterations will keep the conductivity measurements using the cell unaltered? (A) I is doubled, J is halved and K is increased to 1.5 times the original (B) I is halved, J is doubled and K is halved (C) I is doubled, K is doubled and J kept unaltered (D) I, J and K are all doubled Q. 4 CH3COOH (aq) + C2H5OH (aq) = CH3COOC2H5 (aq) + H2O (l), for this reaction, y ml z (N) NaOH is required for the neutralization of the mixture containing 4 ml 4(N) HCl, pure ethanol and 1 ml glacial acetic acid. x ml z (N) NaOH is required for the neutralization of 4 ml 4(N) HCl. If density of glacial acetic acid is b gml-1, then the amount of ethanol is consumed in the esterification is as follows (MW of glacial acetic acid is 60): (A) z(y x)/1000 mol (B) z(x-y)/1000 mol (C) [b/60 z(y-x)/1000] mol (D) [b/60 z(x-y)/1000] mol Q. 5 Which is the rate determining step in the following mechanism of esterification: (A)
There are three pages with 30 questions on the first two pages, and the third page is the answer sheet. Match the Code A or B on all pages of your question paper with the code on your answer sheet. Indicate the most appropriate answer by entering A, B, C or D in the box provided in the answer sheet. Do not overwrite. Do not do rough work on the answer sheet. Do not use pencil. Each correct answer will be awarded two marks. One mark will be deducted for every two wrong answers. Useful data (At. Wt.: Na = 23, K = 39, Ca = 40, Cu = 63)
(B)
(C) 1
(D)
Q. 6 The activation energy for esterification of propionic acid with ethanol and 1-butanol are 52.6 and 47.3 kJmol-1, respectively. For the same increment of temperature in esterification of propionic acid with ethanol and 1-butanol, separately, the relative change of rate of forward reaction (A) will be faster with ethanol than that of propanol (B) will be slower with ethanol than that of propanol (C) will be initially faster with ethanol but at a certain temperature the rate will be slower than that of propanol (D) rate of the reactions in both cases will remain unaffected with temperature. Q.7 Total calcium and magnesium ions content in water is at least 0.05 mmol/L. What volume of the EDTA solution with a concentration of 10 mmol/L should be added when 50 mL of a water sample is titrated? (A) 2.50 mL (B) 0.25 mL (C) 0.025 mL (D) 25 mL Q. 8 At the end point in the complexometric titration of a standard solution of EDTA, the blue colour is due to (A) EDTA (B) Eriochrome Black T (C) Calcium ions (D) Magnesium ions Q. 9 In determination of total hardness of water with EDTA, the reaction at end point is (wherein H 2Y2- is disodium salt of EDTA) (A) Mg+2 + HIn2- MgIn- + H+ (B) MgIn- + H+ Mg+2 + HIn2+2 + 2(C ) Mg + H + MgY MgIn + H2Y2 (D) Ca+2 + H2Y2- CaY2-+ 2H+ Q.10 During the acid-base titration of acetic acid using NaOH, which statement is true regarding oxalic acid? (A) Oxalic acid helps to identify the end point during the acetic acid- NaOH titration (B) Oxalic acid is a primary standard (C) Oxalic acid takes part in the titration reaction of acetic acid with NaoH (D) Oxalic acid gives pink color with phenolphthalein so it is used during the titration where phenolphthalein is used as an indicator. Q. 11 The pH at the equivalence point is more than 7 for the titration of (A) Strong acid-Weak Base (B) Strong Acid- Strong Base (C) Weak Acid-Strong Base (D) Weak Acid-Weak Base Q. 12 Calculate the pH of the buffer solution made from 0.20M HC 2H3O2 and 0.50M C2H3O2- that has acid dissociation constant for HC2H3O2 of 1.8 X 10-5. (A) 5.1 (B) 4.3 (C) 2.7 (D) 4.7 Q. 13 A first order reaction is half-completed in 45 minutes. How long does it take for 99.9% of the reaction to be completed? (a) 300 mins (b) 576 mins (c) 460mins (d) 448 mins Q. 14 For a first order reaction which equation is correct? (X = conc of the reactant at time t, X0 = initial conc of the reactant; k = rate constant of the reaction) (A) ln[X] = ln[X0] + kt (B) ln[X0] = ln[X] kt (C) ln[X] = ln[X0] kt (D) ln[X] = ln[X0] k/t 2
Q. 15. An increase of temperature from 500 K to 510 K increases the number of bimolecular collision by about. (A) 10% (B) 1% (C) 50% (D) 100% Q. 16 Given the following compounds: A) succinic acid B) citric acid C) tartaric acid D) glucose. Which of the following statements is incorrect: (A) A is a dicarboxylic acid which condenses with acidified resorcinol followed by NaOH addition to give green fluorescence (B) B is a dicarboxylic acid which gives white ppt with cold CaCl2 solution (C) C is a dicarboxylic acid which gives silver mirror with Tollen's reagent (D) D is a sugar which gives a solid osazone product with 2,4-DNP Q. 17 Given two statements: 1. Fructose contains aldehydic functional group 2. Fructose gives +ve tollen's test. Choose the correct statement: (A) 1 is true, 2 is true (B) ) 1 is true, 2 is false (C) ) 1 is false, 2 is false (D) ) 1 is false, 2 is true Q. 18 Statement 1: Aldehydes give negative Tollen's test. Statement 2: Ketones give negative test with 2,4-DNP. Choose the correct option for the two statements: (A) 1 is correct, 2 is incorrect (B) 1 is correct, 2 is correct (C) 1 is incorrect, 2 is incorrrect (D) 1 is incorrect, 2 is correct Q. 19 The equivalent weight of sodium thiosulfate pentahydrate is (A) 124.08 (B) 157.91 (C) 248.17 (D) 78.95 Q. 20 25 mL of household bleach [Ca(OCl)Cl] solution was mixed with 30 mL of 0.50 M KI and 10 mL of 4N acetic acid. In the titration of the liberated iodine, 48 mL of 0.25 N Na2S2O3 was used to reach the end point. The molarity of the household bleach solution is (A) 0.48 M (B) 0.96 M (C) 0.24 M (D) 0.024 M Q. 21 Which of the following statement in incorrect? (A) In iodometric titration analyte is reducing species (B) Iodometric titration is an indirect titration (C) In iodometry there are two reactions (D) In iodometric titration, KI is added to the reaction mixture to increase the solubility of iodine Q. 22 [Cu(C2O4)2]2- exist in (A) Monomeric (B) dimeric (C) Polymeric (D) amorphous form
Q. 23 FTIR of K2[Cu(C2O4)2].2H2O might give idea about (A) C-O bond strength (B) d-d transition energy of Cu(II) (C) Copper to oxalate charge transfer energy (D) oxalate to copper charge transfer energy Q. 24 One mmole of CuSO4.5H2O reacted completely with potassium oxalate to result in 0.283 gm of recrystallized K2[Cu(C2O4)2].2H2O. Under this reaction condition, the % yield of product will be (A) 100 (B) 80 (C) 60 (D) 50 Q. 25 Synthesis of dibenzolactone is an example of ................................... reaction! (A) Friedel-craft (B) Claisen-Schmidt condensation (C) Michael addtion (D) Bechmann rearrangement Q. 26 The rate of self aldol condensation of acetone is ..................w.r.t the rate of aldol condensation reaction with benzaldehdye. (A) faster (B) slower (C) equal in rate (D) initially slower then faster Q. 27 Among the carbonyls given, which will form dibenzalacetone type product faster with acetone? (A) p-OMe-Benzaldehyde (B) benzaldehyde (C) p-NO2-Benzaldehyde (D) o-Me-Benzaldehyde
Q. 28 Activation of a TLC plate is:
(A) removing of water/moisture (B) removing of adsorbed substance (C) removing of moisture and adsorbed impurity (D) to stabilize the silica gel Q. 29 An example of stationary phase in normal phase chromatography: (A) calcium phosphate (B) cellulose powder (C) long chain aliphatic acid (D) aluminium sulphate
Q. 30 To run a normal TLC plate, a chemist:
(A) places it in a jar with solvent among iodine crystals (B) places it in an oven to dry it (C) places it under a UV lamp (D) places it
4. (d)
=448 mins 5.(C) ln[X] = ln[X0] kt 6. (b) Here, we know frequency A of a bimolecular reaction
A=
RT S R e Nh
A1 T1 500 = = 0.99 A2 T2 510 Increase in the number of collision = 1 0.99 = 0.01 = 1%
So, AT and we can write
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
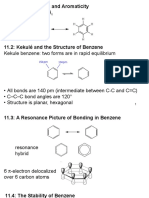
- Chapter 11Документ30 страницChapter 11kanilkadianОценок пока нет
- CHM 332 Fourth Examination NotesДокумент7 страницCHM 332 Fourth Examination NoteskanilkadianОценок пока нет
- 4 - Nucleophilic Aromatic SubstitutionДокумент11 страниц4 - Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitutionc1traОценок пока нет
- IJSO MultipleChoiceQuestion SolutionДокумент11 страницIJSO MultipleChoiceQuestion SolutionkanilkadianОценок пока нет
- AromaticityДокумент14 страницAromaticityeashelОценок пока нет
- Trigonometric Formula Sheet: Definition of The Trig FunctionsДокумент10 страницTrigonometric Formula Sheet: Definition of The Trig Functionsmonelmetal100% (1)
- Kinetic Vs Thermodynamic ControlДокумент15 страницKinetic Vs Thermodynamic ControlkanilkadianОценок пока нет
- AromaticityДокумент14 страницAromaticityeashelОценок пока нет
- Reactions of Alkyl Halides-1Документ8 страницReactions of Alkyl Halides-1kanilkadianОценок пока нет
- Answer Key 10thДокумент1 страницаAnswer Key 10thSanjay GuptaОценок пока нет
- Syllabus of The International Junior Science Olympiad - IJSOДокумент7 страницSyllabus of The International Junior Science Olympiad - IJSOrunnymeadowОценок пока нет
- MAT PaperДокумент9 страницMAT PaperkanilkadianОценок пока нет
- Geometric ReasoningДокумент38 страницGeometric ReasoningkanilkadianОценок пока нет
- Answers Test1 with CommentaryДокумент1 страницаAnswers Test1 with CommentarykanilkadianОценок пока нет
- Sample Paper - 2010 Class - IX Subject - English: Downloaded FromДокумент3 страницыSample Paper - 2010 Class - IX Subject - English: Downloaded FromAli Suhail JafriОценок пока нет
- NTSE 2012 West Bengal MAT PaperДокумент12 страницNTSE 2012 West Bengal MAT PaperkanilkadianОценок пока нет
- Reference 06 08 2012 125652Документ48 страницReference 06 08 2012 125652kanilkadianОценок пока нет
- Answers TEST4Документ1 страницаAnswers TEST4kanilkadianОценок пока нет
- Word ProblemsДокумент2 страницыWord ProblemskanilkadianОценок пока нет
- TL 2005 2599Документ4 страницыTL 2005 2599kanilkadianОценок пока нет
- Figure For Graphical AbstractДокумент1 страницаFigure For Graphical AbstractkanilkadianОценок пока нет
- Ed 045 P 94Документ4 страницыEd 045 P 94kanilkadianОценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Paper 2 GRE QuestionsДокумент67 страницPaper 2 GRE QuestionsA. Rebel100% (1)
- Detection of Pork in Processed Meat Experimenta PDFДокумент19 страницDetection of Pork in Processed Meat Experimenta PDFMet RizalОценок пока нет
- Module 1 - Chemical SafetyДокумент21 страницаModule 1 - Chemical SafetyJason ErecillaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Organic Agriculture LectureДокумент72 страницыIntroduction To Organic Agriculture LectureEduard Bruvi Valenzuela Añabieza100% (6)
- DownloadДокумент8 страницDownloadDado MottaОценок пока нет
- IJISRT23JUN864Документ6 страницIJISRT23JUN864International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyОценок пока нет
- Silicone SoftenersДокумент15 страницSilicone SoftenersAkash Sarker100% (2)
- Ariola Bschem4a Foodchempc MidtermДокумент3 страницыAriola Bschem4a Foodchempc Midtermjohn buenafeОценок пока нет
- Nutrition DietaryДокумент35 страницNutrition DietaryAbdul Quyyum100% (2)
- Flocculation Properties of Pectin in Various SuspensionsДокумент4 страницыFlocculation Properties of Pectin in Various SuspensionsLiliTorresОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Important-Questions-For CBSE - Class XIIДокумент40 страницChemistry Important-Questions-For CBSE - Class XIIkharemixОценок пока нет
- Pharma AssignДокумент8 страницPharma AssignTHIS PAHADIОценок пока нет
- If T Food ExperimentsДокумент63 страницыIf T Food ExperimentsMuhammad Sohail AkramОценок пока нет
- Edamame Extract Formulated into Skin Whitening CreamДокумент5 страницEdamame Extract Formulated into Skin Whitening CreamAldila Dina HairunnisyaОценок пока нет
- Hummel PG GlandsДокумент7 страницHummel PG GlandsBob JohnsonОценок пока нет
- DOWSIL™ General Purpose Silicone Sealant: Features & BenefitsДокумент4 страницыDOWSIL™ General Purpose Silicone Sealant: Features & BenefitsPranshu JainОценок пока нет
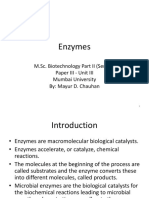
- Enzymes: M.Sc. Biotechnology Part II (Sem III) Paper III - Unit III Mumbai University By: Mayur D. ChauhanДокумент61 страницаEnzymes: M.Sc. Biotechnology Part II (Sem III) Paper III - Unit III Mumbai University By: Mayur D. ChauhanAkshitaОценок пока нет
- Importance of Sequestering Agent in Textile Proc 1Документ7 страницImportance of Sequestering Agent in Textile Proc 1guven44Оценок пока нет
- Saboor Khalid Et Al. 2021. JAEFSECДокумент41 страницаSaboor Khalid Et Al. 2021. JAEFSECSaboor OfficialОценок пока нет
- How to make glycerin soap in 5 minutesДокумент3 страницыHow to make glycerin soap in 5 minutesEunkimakimoto 89Оценок пока нет
- Carbon Black Feed StockДокумент2 страницыCarbon Black Feed StockdivyaОценок пока нет
- Quiz Questions With Answers Cognitive ChemistryДокумент18 страницQuiz Questions With Answers Cognitive ChemistryKarthika KarthiОценок пока нет
- Raven Biology of Plants: Eighth EditionДокумент43 страницыRaven Biology of Plants: Eighth EditionMoath EnnabОценок пока нет
- EDTA - A Molecule with Complex UsesДокумент6 страницEDTA - A Molecule with Complex UsescountdankОценок пока нет
- Malaysia's Leading Palm Oil Exporter & ManufacturerДокумент7 страницMalaysia's Leading Palm Oil Exporter & Manufacturerverlencia khosasihОценок пока нет
- MC2 Biochemistry Lecture Notes For BSN First Semester, 2019-2020 Prepared By: SALINA OSIAL - ALFADДокумент5 страницMC2 Biochemistry Lecture Notes For BSN First Semester, 2019-2020 Prepared By: SALINA OSIAL - ALFADAl-waleed JulkanainОценок пока нет
- Urine Screening For Metabolic DisordersДокумент9 страницUrine Screening For Metabolic DisordersXyleene Jency Bien IIОценок пока нет
- Vollhardt 6e Lecture PowerPoints - Chapter 12Документ74 страницыVollhardt 6e Lecture PowerPoints - Chapter 12superfr3shmОценок пока нет
- Manuali PDF 735Документ1 страницаManuali PDF 735Rakib Hossain 3A-159Оценок пока нет