Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Understanding Consumer Motivation Through Needs, Goals & Defense Mechanisms
Загружено:
Vaibhav SharmaИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Understanding Consumer Motivation Through Needs, Goals & Defense Mechanisms
Загружено:
Vaibhav SharmaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Understanding Motivation Understanding Goals & needs
Generic goals & specific goals Innate needs & acquired needs
Consumer Motivation
Needs and goals interdependency
Needs are never fully satisfied, New needs emerge as old needs are satisfied, People who achieve their goals set new & higher goals for them
Failure to achieve goals
Fight Flight: Aggression, Regression, Rationalization, Projection, Identification, Autism, Withdrawal, Repression
Understanding motive arousal
Physiological arousal Emotional arousal Cognitive arousal Environmental arousal
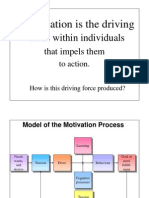
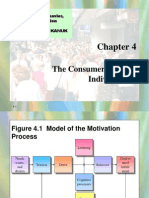
Figure 4.1 Model of the Motivation Process
Learning Needs wants, and demands Goal or need fulfillment
Tension
Drive
Behavior
Cognitive processes
Tension reduction
Types of Needs
Innate Needs
Physiological (or biogenic) needs that are considered primary needs or motives
Acquired needs
Generally psychological (or psychogenic) needs that are considered secondary needs or motives
Goals
Generic Goals
the general categories of goals that consumers see as a way to fulfill their needs e.g., I want to get a graduate degree. the specifically branded products or services that consumers select as their goals e.g., I want to get an MBA in Marketing from Kellogg School of
Product-Specific Goals
The Selection of Goals
The goals selected by an individual depend on their:
Personal experiences Physical capacity Prevailing cultural norms and values Goals accessibility in the physical and social environment
Motivations and Goals
Positive Motivation A driving force toward some object or condition Approach Goal
Negative Motivation A driving force away from some object or condition Avoidance Goal
A positive goal toward which behavior is directed
A negative goal from which behavior is directed away
Rational Versus Emotional Motives
Rationality implies that consumers select goals based on totally objective criteria such as size, weight, price, or miles per gallon Emotional motives imply the selection of goals according to personal or subjective criteria
The Dynamic Nature of Motivation
Needs are never fully satisfied New needs emerge as old needs are satisfied People who achieve their goals set new and higher goals for themselves
Frustration
Failure to achieve a goal may result in frustration. Some adapt; others adapt defense mechanisms to protect their ego.
Defense Mechanism
Methods by which people mentally redefine frustrating situations to protect their self-images and their self-esteem.
Table 4.2 Defense Mechanisms
Aggression Rationalization Regression Withdrawal Projection Autism Identification Repression
Arousal of Motives
Physiological arousal Emotional arousal Cognitive arousal Environmental arousal
Philosophies Concerned With Arousal of Motives
Behaviorist School
Behavior is response to stimulus Elements of conscious thoughts are to be ignored Consumer does not act, but reacts
Behavior is directed at goal achievement Need to consider needs, attitudes, beliefs, etc. in understanding consumer behavior
Cognitive School
Figure 4.9 Maslows Hierarchy of Needs
Self-Actualization (Self-fulfillment)
Ego Needs (Prestige, status, self esteem)
Social Needs (affection, friendship, belonging)
Safety and Security Needs (Protection, order, stability) Physiological Needs (Food, water, air, shelter, sex)
Table 4.3 Murrays List of Psychogenic Needs
Needs Associated with Inanimate Objects: Acquisition, Conservancy, Order, Retention, Construction
Needs Reflecting Ambition, Power, Accomplishment, and Prestige: Superiority, Achievement, Recognition, Exhibition, Infavoidance Needs Connected with Human Power: Dominance, Deferrence, Similance, Autonomy, Contrariance
Table 4.3 Murrays List of Psychogenic Needs
Sado-Masochistic Needs : Aggression, Abasement
Needs Concerned with Affection between People: Affiliation, Rejection, Nurturance, Succorance, Play
Needs Concerned with Social Intercourse: Cognizance, Exposition
Figure 4.10 Appeal to Egoistic Needs
Figure 4.11 Appeal to SelfActualization
A Trio of Needs
Power
individuals desire to control environment
need for friendship, acceptance, and belonging need for personal accomplishment closely related to egoistic and selfactualization needs
Affiliation
Achievement
Motivational Research
Qualitative research designed to uncover consumers subconscious or hidden motivations. Consumers are not always aware of, or may not wish to recognize, the basic reasons underlying their actions.
Вам также может понравиться
- Consumer Behaviour MotivationДокумент25 страницConsumer Behaviour MotivationmansinancyОценок пока нет
- Motivation As A Psychological ForceДокумент42 страницыMotivation As A Psychological ForceTia MejiaОценок пока нет
- Consumer Motivation: Understanding Needs, Goals and DriversДокумент28 страницConsumer Motivation: Understanding Needs, Goals and DriversRohit KumarОценок пока нет
- Consumer Motivation: by Balachandar K Reference Book: Consumer Behavior, Schiffman & KanukДокумент14 страницConsumer Motivation: by Balachandar K Reference Book: Consumer Behavior, Schiffman & KanukarashpreetОценок пока нет
- Consumer Motivation & NeedsДокумент6 страницConsumer Motivation & NeedsChaitanya YskОценок пока нет
- Need, Motivation and EmotionsДокумент37 страницNeed, Motivation and EmotionsAvani PatilОценок пока нет
- Motivation Is The Driving: Force Within IndividualsДокумент17 страницMotivation Is The Driving: Force Within Individualsrishu31789Оценок пока нет
- Types of Motivation & Models ExplainedДокумент25 страницTypes of Motivation & Models ExplainedaaryanОценок пока нет
- The Consumer As An Individual: Consumer Behavior, Eighth Edition Schiffman & KanukДокумент28 страницThe Consumer As An Individual: Consumer Behavior, Eighth Edition Schiffman & KanukfruitfulluftОценок пока нет
- Ch 3 Consumer Motivation & PersonalityДокумент4 страницыCh 3 Consumer Motivation & PersonalityZuhair RiazОценок пока нет
- The Consumer as an Individual: Understanding Motivation and Goal SettingДокумент31 страницаThe Consumer as an Individual: Understanding Motivation and Goal SettingSumedh BodadeОценок пока нет
- Chapter Outline: - Model of The Motivation Process - Goals - Motives - Needs - Motivational ResearchДокумент70 страницChapter Outline: - Model of The Motivation Process - Goals - Motives - Needs - Motivational ResearchpradeepОценок пока нет
- As A Psychological ForceДокумент3 страницыAs A Psychological ForceKristine Angela RanotОценок пока нет
- Module-3 INdividual Influences On Consumer BehaviourДокумент132 страницыModule-3 INdividual Influences On Consumer BehaviourAnonymous YweU6CОценок пока нет
- Consumer MotivationДокумент22 страницыConsumer MotivationKaran KhuranaОценок пока нет
- CB 4000Документ20 страницCB 4000Bhavin MandaliyaОценок пока нет
- Unit 3 Notes Consumer BehaviourДокумент10 страницUnit 3 Notes Consumer BehaviourSidra KhanОценок пока нет
- Consumer Motivation Summary NotesДокумент21 страницаConsumer Motivation Summary NotesAmber LiaqatОценок пока нет
- Motivation Resources and ActivitiesДокумент18 страницMotivation Resources and ActivitiesMaria Felisadae Lorenzo-RomanОценок пока нет
- Consumer Behavior - Module 3Документ16 страницConsumer Behavior - Module 3Dr VIRUPAKSHA GOUD GОценок пока нет
- Lesson-1 Understanding Consumer MotivationДокумент2 страницыLesson-1 Understanding Consumer MotivationKristine Angela RanotОценок пока нет
- Motivation 104Документ78 страницMotivation 104Rakesh Mohan SaxenaОценок пока нет
- Consumer Motivation and Personality: Understanding Drivers Like Needs, Goals and TraitsДокумент22 страницыConsumer Motivation and Personality: Understanding Drivers Like Needs, Goals and TraitsshahbazОценок пока нет
- Lecture Three: Consumer MotivationДокумент25 страницLecture Three: Consumer MotivationH. U. KonainОценок пока нет
- MotivationДокумент39 страницMotivationnavin_tiwari_king100% (1)
- Consumer MotivationДокумент18 страницConsumer MotivationChintan MehtaОценок пока нет
- Consumer Motivation and PersonalityДокумент5 страницConsumer Motivation and PersonalityParth DhingraОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3: Consumer Motivation and Personality: Learning ObjectivesДокумент8 страницChapter 3: Consumer Motivation and Personality: Learning ObjectivesMariyam NaeemОценок пока нет
- Consumer Motivation: Major-MFM IIДокумент37 страницConsumer Motivation: Major-MFM IIAbhigna DeshpandeОценок пока нет
- Motivation and PersonalityДокумент6 страницMotivation and PersonalityAsmath ShaikОценок пока нет
- Consumer Motivation & Personality: An Assignment OnДокумент8 страницConsumer Motivation & Personality: An Assignment OnFarhad HossainОценок пока нет
- MotivationДокумент15 страницMotivationTaimoor JanОценок пока нет
- MotivationДокумент5 страницMotivationBilal MalikОценок пока нет
- Week 6 - Perception: Learning ObjectivesДокумент31 страницаWeek 6 - Perception: Learning ObjectivestaniaОценок пока нет
- Consumer MotivationДокумент32 страницыConsumer MotivationVipulОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент13 страницUntitledIme RaaphorstОценок пока нет
- Consumer Behaviour PPT Most FinalДокумент38 страницConsumer Behaviour PPT Most FinalAbdullah Sheikh100% (1)
- N 41 A Basic Needs and Comfort MeasuresДокумент78 страницN 41 A Basic Needs and Comfort MeasuresheliОценок пока нет
- Consumer Needs and MotivationДокумент37 страницConsumer Needs and MotivationPreeti KumariОценок пока нет
- Motivation Theories ExplainedДокумент22 страницыMotivation Theories ExplainedaswathyОценок пока нет
- Consumer Motivation DoneДокумент29 страницConsumer Motivation DoneummatulОценок пока нет
- 3 Lec CBДокумент62 страницы3 Lec CBUsama ALiОценок пока нет
- Consumer Motivation and PersonalityДокумент15 страницConsumer Motivation and Personalityyashvi.kumarОценок пока нет
- Bahir Dar University Marketing AssignmentДокумент9 страницBahir Dar University Marketing AssignmentYeshambel EwunetuОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 Consumer As An IndividualДокумент17 страницUnit 2 Consumer As An IndividualRuhit SKОценок пока нет
- cbppt01 05Документ65 страницcbppt01 05Nishant RajОценок пока нет
- MOTIVATION THEORIES AND APPLICATIONSДокумент10 страницMOTIVATION THEORIES AND APPLICATIONSSvein SibealОценок пока нет
- Chapter04 MotivationДокумент40 страницChapter04 Motivationmihir_sikkaОценок пока нет
- Assessment in The Affective DomainДокумент8 страницAssessment in The Affective DomainFlordelis Ejercito50% (2)
- Introduction to Psychology(4) Motivation: Types, Theories and ApplicationsДокумент19 страницIntroduction to Psychology(4) Motivation: Types, Theories and Applicationsoscar3spurgeonОценок пока нет
- 3 Consumer MotivationДокумент23 страницы3 Consumer MotivationSaini JasОценок пока нет
- Assessment in The Affective DomainДокумент36 страницAssessment in The Affective DomainIson Ocampo100% (1)
- Notes On Consumer MotivationДокумент13 страницNotes On Consumer MotivationPalak AgarwalОценок пока нет
- What Is Social Class?: Income Refers To Earnings From Work or Investments, While Wealth Refers To All of Those Assets AnДокумент14 страницWhat Is Social Class?: Income Refers To Earnings From Work or Investments, While Wealth Refers To All of Those Assets Anmst_momena_akhterОценок пока нет
- Consumer Needs & MotivationДокумент7 страницConsumer Needs & MotivationaduggalОценок пока нет
- Schiffman CB10 PPT 04 1Документ18 страницSchiffman CB10 PPT 04 1Tabby TanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 Individual Influences On Consumer Behavior (PU DS) 565963786Документ80 страницChapter 5 Individual Influences On Consumer Behavior (PU DS) 565963786Vivek Lal KarnaОценок пока нет
- Cultivating Self-Discipline: A Path to Personal and Universal SuccessОт EverandCultivating Self-Discipline: A Path to Personal and Universal SuccessОценок пока нет
- AdvertisingДокумент10 страницAdvertisingVaibhav SharmaОценок пока нет
- BMДокумент181 страницаBMVaibhav SharmaОценок пока нет
- Co-Operative Marketing: A Project Report ONДокумент18 страницCo-Operative Marketing: A Project Report ONrajkumar568779Оценок пока нет
- Co-Operative Marketing: A Project Report ONДокумент18 страницCo-Operative Marketing: A Project Report ONrajkumar568779Оценок пока нет
- Principal Upanishads According To Sri RangaRamanuja-Muni Vol 1-3 DR N S Anantha Rangacharya (VAISHNAVA-edition)Документ1 306 страницPrincipal Upanishads According To Sri RangaRamanuja-Muni Vol 1-3 DR N S Anantha Rangacharya (VAISHNAVA-edition)Dhiraj Hegde100% (1)
- Correlationism and the Transition from Transcendental Idealism to RealismДокумент15 страницCorrelationism and the Transition from Transcendental Idealism to RealismIvan MrkvcОценок пока нет
- Discourse perspective in ESP course designДокумент10 страницDiscourse perspective in ESP course designÃßdØüLégềndàrioÇristÃlОценок пока нет
- IIUM educator profile and publicationsДокумент4 страницыIIUM educator profile and publicationskumar6125Оценок пока нет
- From Learning Organisation To Knowledge EntrepreneurДокумент9 страницFrom Learning Organisation To Knowledge EntrepreneurWessam HashemОценок пока нет
- Module 1 Buss. ReserachДокумент3 страницыModule 1 Buss. ReserachMÿćcä CañeteОценок пока нет
- PSY 406 Handouts 1-45 (Final)Документ86 страницPSY 406 Handouts 1-45 (Final)Aman AlviОценок пока нет
- Ibn Qayyim Al-Jawziyya and Divine AtributesДокумент331 страницаIbn Qayyim Al-Jawziyya and Divine AtributesblponezeОценок пока нет
- CreativityДокумент21 страницаCreativityBabasab Patil (Karrisatte)90% (10)
- Nature and Ethics of ResearchДокумент9 страницNature and Ethics of ResearchEya Delos Santos TañecaОценок пока нет
- Gamma Healing IntroductionДокумент17 страницGamma Healing IntroductionPeter Mican100% (2)
- A Synergistic Model of Organizational Career Development Kerry BernesДокумент118 страницA Synergistic Model of Organizational Career Development Kerry BernesAlex RichieОценок пока нет
- 7411684516be7 A Synopsis of Lecture Series by RdsirДокумент137 страниц7411684516be7 A Synopsis of Lecture Series by RdsirdeshawОценок пока нет
- Theosophy On SuicideДокумент18 страницTheosophy On SuicideMark R. JaquaОценок пока нет
- Aim of MaxismДокумент6 страницAim of MaxismBushra MumtazОценок пока нет
- Notes On Sartre's Critique of Dialectical Reason: Facebook Post Dated 19 January, 2018Документ5 страницNotes On Sartre's Critique of Dialectical Reason: Facebook Post Dated 19 January, 2018sabsvyasОценок пока нет
- Session-3 Motivation and Involvement, Attitudes and PersonalityДокумент23 страницыSession-3 Motivation and Involvement, Attitudes and PersonalityVipul VyasОценок пока нет
- Thself ModuleДокумент103 страницыThself ModuleAshera MonasterioОценок пока нет
- Christian Approach to Philosophy of TimeДокумент19 страницChristian Approach to Philosophy of TimeFrJohn SomersОценок пока нет
- Rowe's Decision Style InventoryДокумент3 страницыRowe's Decision Style InventorySubhan AnsariОценок пока нет
- American Lectures on Clairvoyance and Psychic DevelopmentДокумент39 страницAmerican Lectures on Clairvoyance and Psychic DevelopmentSatyanarayana Rao BaragadaОценок пока нет
- Interior Design Criticism - Between Excess and AusterityДокумент11 страницInterior Design Criticism - Between Excess and AusterityLekhaUmeshaОценок пока нет
- Lesson 7: Context and Basic Concepts Goals and Scope Principles Core ValuesДокумент17 страницLesson 7: Context and Basic Concepts Goals and Scope Principles Core ValuesNadia Caoile IgnacioОценок пока нет
- Feeling A Sense of Belonging in The Early Childhood Centre - An Ex PDFДокумент84 страницыFeeling A Sense of Belonging in The Early Childhood Centre - An Ex PDFManpreet KaurОценок пока нет
- Critical Thinking 4Документ12 страницCritical Thinking 4syofwanОценок пока нет
- Padmasiri de Silva - The Psychology of Emotions and Humour in Buddhism-Springer International Publishing - Palgrave Pivot (2018)Документ96 страницPadmasiri de Silva - The Psychology of Emotions and Humour in Buddhism-Springer International Publishing - Palgrave Pivot (2018)jotijatoОценок пока нет
- Koerner, Islamic Theology, Past and Present. A Comparative PerspectiveДокумент16 страницKoerner, Islamic Theology, Past and Present. A Comparative PerspectiveRezart BekaОценок пока нет
- What Is Secularism For Pre Seminar ReadingДокумент42 страницыWhat Is Secularism For Pre Seminar ReadingKumar GauravОценок пока нет
- Human Freedom and the Power of ChoiceДокумент5 страницHuman Freedom and the Power of ChoiceJerico LapurgaОценок пока нет
- Models of Decision MakingДокумент21 страницаModels of Decision MakingFarhinОценок пока нет