Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Microscopy and Cell Structure
Загружено:
Ahmed J AlhindaweИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Microscopy and Cell Structure
Загружено:
Ahmed J AlhindaweАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chapter 3: Microscopy and Cell Structure
Important Point:
Typical Bacterial Shapes
Also Pleomorphic Bacteria, which vary in their shape
(e.g., Corynebacterium).
Typical Bacterial Arrangements
streptococci
sarcina
staphylococci
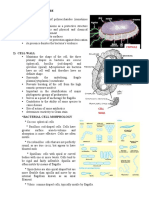
Prokaryotic Cell Structures
Typical Prokaryotic Cell
Cytoplasmic Membrane
Movement across membrane for many substances is controlled by membrane proteins. Escherichia coli has >200 membrane proteins. Many of these proteins are involved in transport across membranes.
Others of these proteins allow a bacterium to sense its surrounding environments (e.g., as in chemotaxis).
Movement is via:
Simple Diffusion (including osmosis)
Facilitated Diffusion (with concentration gradient & no energy expended) Active Transport (against concentration gradient & energy expended)
Simple Diffusion -- Osmosis
solute molecules/ions
Cytoplasmic Membrane
Protein-Mediated Transport
Active Transport
The Prokaryotic Cell Wall
The Prokaryotic Cell Wall
Determines cell shape.
In some cases recognized by host immune system.
Prevents osmotic lysis.
Target for antibiotics.
In Bacteria, composed of Peptidoglycan.
Part of cell envelope.
Gram-Pos vs. Gram-Neg.
Gram-Positive Cell Envelope
Gram-Negative Cell Envelope
cell wall endotoxin
Gram-Negative Cell Envelope
LPS: Protection from antibiotics such as penicillin plus against certain toxins.
Periplasm: Site of preliminary nutrient degradation.
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
Carbohydrate has negative charge and provides protection against some antibiotics & some toxins (e.g., detergents).
Lipid A = Endotoxin
Mycoplasma lack Cell Walls
Note: Pleomorphic
Mycoplasma pneumoniae causes Walking Pneumonia
Protection (e.g., Streptococcus pneumoniae from phagocytosis)
Glycocalyx
Attachment (e.g., Streptococcus mutans causing dental plaques)
Capsule Staining
Capsules are more regular and gelatinous.
Slime Layers are less regular and more diffuse.
Bacteria Flagella (plural)
Flagellar Arrangements
Polar Flagellum
e.g., E. coli
also atrichous
Also Phototaxis, etc.
Chemotaxis
Pili (sing. Pillus)
Fimbriae (a kind of pilli)
Tips are Adhesins, used to adhere, e.g., to animal tissues
Closed Circular Chromosome
Also Plasmids, which are smaller, circular pieces of DNA.
Plasmids usually encode expendable functions, e.g., antibiotic resistance.
Ribosomes: Sites of Translation
On order of 10,000 per cell!
Form inside of vegetative cells (hence endo).
Endospores
Characteristic of many soil bacteria, e.g., Bacillus spp. & Clostridium spp.
Highly resistant to heat, U.V., desiccation, etc.
Link to Next Presentation
Вам также может понравиться
- Bacterial MorphologyДокумент75 страницBacterial MorphologyJoan MelendresОценок пока нет
- BL42-Chi Nei Tsang III (ID-PDF) 12-17-15 PDFДокумент90 страницBL42-Chi Nei Tsang III (ID-PDF) 12-17-15 PDFJosé Tao75% (8)
- Swot Analysis MabДокумент4 страницыSwot Analysis MabparasmanishaОценок пока нет
- Bacterial Cell Structure and MorphologyДокумент45 страницBacterial Cell Structure and Morphologyauguz21acenaОценок пока нет
- 1.3 Bacterial MorphologyДокумент4 страницы1.3 Bacterial MorphologyJosh Miguel BorromeoОценок пока нет
- Procaryotic Cell ArchitectureДокумент18 страницProcaryotic Cell ArchitectureWindi Dawn SallevaОценок пока нет
- The Plasma (Cytoplasmic) MembraneДокумент6 страницThe Plasma (Cytoplasmic) Membraneprism1702Оценок пока нет
- Differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsДокумент122 страницыDifferences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsAdithya NanuvalaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Micropara (Outline)Документ5 страницChapter 3 Micropara (Outline)Jezrylle BalaongОценок пока нет
- CellДокумент16 страницCellanantchouhdary1709Оценок пока нет
- bacterial notes 2022Документ5 страницbacterial notes 2022Banji MaikaОценок пока нет
- Prokaryotic CellДокумент29 страницProkaryotic CellSeshime Thyrone DavidsonОценок пока нет
- Lecture 3 - Bacterial Anatomy and PhysiologyДокумент26 страницLecture 3 - Bacterial Anatomy and Physiologyapi-370335280% (5)
- Bacterial StructureДокумент31 страницаBacterial StructureSaid AbdelaОценок пока нет
- For Ntse CellДокумент73 страницыFor Ntse CellPrakhar RajОценок пока нет
- Fungi 4Документ64 страницыFungi 4aldin sakhaОценок пока нет
- Bacterial Cell Structure 1) Capsule: Spirillum (Spiral) - Mycoplasmas Are BacteriaДокумент4 страницыBacterial Cell Structure 1) Capsule: Spirillum (Spiral) - Mycoplasmas Are BacteriaTLCRОценок пока нет
- Bacterial Morphology Sci 111Документ7 страницBacterial Morphology Sci 111Orland HarryОценок пока нет
- MDR 1162 - 2 Cell Structure and FunctionДокумент67 страницMDR 1162 - 2 Cell Structure and Functionllenson0425Оценок пока нет
- Summary of ConceptsДокумент29 страницSummary of ConceptsEnzo GomesОценок пока нет
- Functions of Organelles in CellДокумент23 страницыFunctions of Organelles in CellZahid ShehzarОценок пока нет
- Microbial Taxonomy - System That Involves in The Organization, Classification, Naming orДокумент5 страницMicrobial Taxonomy - System That Involves in The Organization, Classification, Naming orRedelle Mae NiniОценок пока нет
- Cell Biology: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsДокумент10 страницCell Biology: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsPokemon GoОценок пока нет
- Prokaryote - WikipediaДокумент65 страницProkaryote - WikipediaBashiir NuurОценок пока нет
- Bacterial Morphology and Cell StructureДокумент14 страницBacterial Morphology and Cell StructureJe KirsteneОценок пока нет
- Cell WallДокумент1 страницаCell WallFrancine ValdezОценок пока нет
- Bacteria NotesДокумент8 страницBacteria NotesLloyd LozanoОценок пока нет
- Unit I Module 2: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsДокумент8 страницUnit I Module 2: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsMirunalini GobinathОценок пока нет
- The Bacterial Cell: Structures of Prokaryotes and Differences from EukaryotesДокумент3 страницыThe Bacterial Cell: Structures of Prokaryotes and Differences from EukaryotesanojanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 06Документ18 страницChapter 06Wajeeh Ahmed ZakaiОценок пока нет
- BDS Year 2 Lecture on Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell StructuresДокумент46 страницBDS Year 2 Lecture on Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell StructuresNarmathaa ThevarОценок пока нет
- Bacterial Morphology and StructureДокумент21 страницаBacterial Morphology and StructurevaidyamОценок пока нет
- Crizzel Ruth Padernal Castor GWAPAДокумент73 страницыCrizzel Ruth Padernal Castor GWAPACrizzel Ruth CastorОценок пока нет
- 1 - Introduction To Medical MicrobiologyДокумент63 страницы1 - Introduction To Medical MicrobiologyAhmed MohamedОценок пока нет
- 8 Cell NotesДокумент7 страниц8 Cell NotesAbhijeet AmetaОценок пока нет
- Bacterialmorphology 161031150548Документ42 страницыBacterialmorphology 161031150548Namo namoОценок пока нет
- Bacterial Cell StructureДокумент9 страницBacterial Cell StructureManWol JangОценок пока нет
- 5 Prokaryatic Structure and Function 5Документ31 страница5 Prokaryatic Structure and Function 5Sadam IrshadОценок пока нет
- Intro, Cell, TissueДокумент29 страницIntro, Cell, Tissueanisa930804Оценок пока нет
- Prokaryotic Cells DifferencesДокумент33 страницыProkaryotic Cells DifferencesYousef Wardat100% (1)
- Lecture 2 - Bacterial Cell Structure and FunctionДокумент90 страницLecture 2 - Bacterial Cell Structure and FunctionOdurОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1 Introduction PDFДокумент51 страницаLecture 1 Introduction PDFMomo KimОценок пока нет
- Bacterial Cell StructureДокумент6 страницBacterial Cell StructureCasey StuartОценок пока нет
- Prokaryotic Cells Are Also CalledДокумент25 страницProkaryotic Cells Are Also CalledArdo RamdhaniОценок пока нет
- Prokaryotic Cell Structure and Differences from Eukaryotic CellsДокумент3 страницыProkaryotic Cell Structure and Differences from Eukaryotic CellsHubdar Ali KolachiОценок пока нет
- Bacterial Cell ComponentsДокумент17 страницBacterial Cell ComponentsMahesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Prokaryotic Cell-1Документ26 страницProkaryotic Cell-1Sarah PavuОценок пока нет
- Module 1 Microorganisms in Food and SpoilageДокумент24 страницыModule 1 Microorganisms in Food and SpoilageSiddОценок пока нет
- Cell StructersДокумент13 страницCell StructersSumaiya JabinОценок пока нет
- Cell Biology Assignment Gr. 3Документ26 страницCell Biology Assignment Gr. 3Lamin N CeesayОценок пока нет
- La Celula EstresadaДокумент9 страницLa Celula EstresadaPedro CandelarioОценок пока нет
- Bacterial Structure, Growth, and Metabolism ExplainedДокумент77 страницBacterial Structure, Growth, and Metabolism ExplainedNelle ReneiОценок пока нет
- Cell The Unit of Life: 16 June 2022 03:52Документ19 страницCell The Unit of Life: 16 June 2022 03:52Dhanalakshmi LakshmiОценок пока нет
- IVMS Introduction To Cell Biology - AP High School Health Sciences Track Study GuideДокумент138 страницIVMS Introduction To Cell Biology - AP High School Health Sciences Track Study GuideMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.Оценок пока нет
- Cell Biology GuideДокумент37 страницCell Biology GuideManuelОценок пока нет
- Significance and Importance of Biochemistry in Nursing: UNIT-1Документ7 страницSignificance and Importance of Biochemistry in Nursing: UNIT-1Sunil PatelОценок пока нет
- Kingdom Fungi: Prof. Khaled Abu-ElteenДокумент70 страницKingdom Fungi: Prof. Khaled Abu-ElteenOdurОценок пока нет
- Cell Structure and Function of ProkaryotesДокумент37 страницCell Structure and Function of ProkaryotesShafira AnandaОценок пока нет
- 2 PARA 1 - Protozoa - FlagellatesДокумент13 страниц2 PARA 1 - Protozoa - FlagellatesTricia LlorinОценок пока нет
- BIO 001 Real Slide First SemesterДокумент44 страницыBIO 001 Real Slide First Semestermarkwelly367Оценок пока нет
- Julie Bui - Bacterial Structure FunctionДокумент2 страницыJulie Bui - Bacterial Structure Functionapi-522650514Оценок пока нет
- Mucosal Membrane Health: The Key to Preventing Inflammatory Conditions, Infections, Toxicity and DegenerationОт EverandMucosal Membrane Health: The Key to Preventing Inflammatory Conditions, Infections, Toxicity and DegenerationОценок пока нет
- Scanned by CamscannerДокумент10 страницScanned by CamscannerAhmed J AlhindaweОценок пока нет
- Scanned by CamscannerДокумент11 страницScanned by CamscannerAhmed J AlhindaweОценок пока нет
- Enterobacteriaceae Opportunistic PathogensДокумент45 страницEnterobacteriaceae Opportunistic PathogensAhmed J AlhindaweОценок пока нет
- 787Документ8 страниц787Ahmed J AlhindaweОценок пока нет
- Dissertation PDFДокумент115 страницDissertation PDFAhmed J AlhindaweОценок пока нет
- 55052Документ14 страниц55052Ahmed J AlhindaweОценок пока нет
- Identification of Enterobacter SPP by 16SrRNAgene Sequencing in Basrah Province IraqДокумент14 страницIdentification of Enterobacter SPP by 16SrRNAgene Sequencing in Basrah Province IraqAhmed J AlhindaweОценок пока нет
- By:Hend Eldeeb: Complete The Following SentencesДокумент6 страницBy:Hend Eldeeb: Complete The Following SentencesAhmed J AlhindaweОценок пока нет
- CamScanner Scans PDFs QuicklyДокумент4 страницыCamScanner Scans PDFs QuicklyAhmed J AlhindaweОценок пока нет
- GrammarДокумент118 страницGrammarAhmed J AlhindaweОценок пока нет
- (O, H, Vi) Free ImmunoprotectiveДокумент9 страниц(O, H, Vi) Free ImmunoprotectiveAhmed J AlhindaweОценок пока нет
- Escherichia ColiДокумент32 страницыEscherichia ColiAhmed J AlhindaweОценок пока нет
- 55439Документ13 страниц55439Ahmed J AlhindaweОценок пока нет
- Plasmid DNA Amplification of Bacteria Causing DiarrheaДокумент7 страницPlasmid DNA Amplification of Bacteria Causing DiarrheaAhmed J AlhindaweОценок пока нет
- Bilal 1Документ48 страницBilal 1Ahmed J AlhindaweОценок пока нет
- History of Animal Tissue Culture and Natural Surroundings For Animal CellДокумент16 страницHistory of Animal Tissue Culture and Natural Surroundings For Animal CellAhmed J AlhindaweОценок пока нет
- 32721Документ33 страницы32721prasadbheemОценок пока нет
- Seminar of Cell Culture TechniquesДокумент55 страницSeminar of Cell Culture TechniquesAhmed J AlhindaweОценок пока нет
- 48721Документ33 страницы48721Ahmed J AlhindaweОценок пока нет
- Polymerase Chain ReactionДокумент34 страницыPolymerase Chain Reactionmokshgoyal2597100% (3)
- Rapid IsolationДокумент2 страницыRapid IsolationAhmed J AlhindaweОценок пока нет
- Meat TestДокумент3 страницыMeat TestAhmed J AlhindaweОценок пока нет
- Innate ImmunityДокумент44 страницыInnate ImmunityAhmed J AlhindaweОценок пока нет
- DNA-based meat speciation techniquesДокумент4 страницыDNA-based meat speciation techniquesAhmed J AlhindaweОценок пока нет
- 032 Icetd2012 D10046Документ7 страниц032 Icetd2012 D10046Ahmed J AlhindaweОценок пока нет
- Windows 8 NoticeДокумент1 страницаWindows 8 NoticeAhmed J AlhindaweОценок пока нет
- PlasmidДокумент15 страницPlasmidndiugbegbeОценок пока нет
- DNA Structure and Central DogmaДокумент5 страницDNA Structure and Central DogmaAhmed J AlhindaweОценок пока нет
- Histone Variants: Are They Functionally Heterogeneous?: David T BrownДокумент6 страницHistone Variants: Are They Functionally Heterogeneous?: David T Brownnath211Оценок пока нет
- 1Документ2 страницы1Ahmed J AlhindaweОценок пока нет
- Laser: DR Uzair Ahmad Qureshi Consultant Dermatologist, STDS, Laser and Aesthetic SpecialistДокумент18 страницLaser: DR Uzair Ahmad Qureshi Consultant Dermatologist, STDS, Laser and Aesthetic SpecialistFakhra TehseenОценок пока нет
- BSДокумент6 страницBSBeda MalecdanОценок пока нет
- GRANDE ICU CASE SUMMARYДокумент3 страницыGRANDE ICU CASE SUMMARYanuzОценок пока нет
- Health Promotion and Disease Prevention in the ElderlyДокумент1 страницаHealth Promotion and Disease Prevention in the ElderlyBeverly PagcaliwaganОценок пока нет
- Book Eczema PsoriazisДокумент457 страницBook Eczema Psoriazisdaniel bОценок пока нет
- Progestin-Only Injectables: Characteristics and Health BenefitsДокумент11 страницProgestin-Only Injectables: Characteristics and Health BenefitsRazaria DailyneОценок пока нет
- Warehouse EssayДокумент8 страницWarehouse Essayafibojmbjifexj100% (2)
- The Politics of The Asia-Pacific Triumphs, Challenges, and Threats (Mark S. Williams (Editor)Документ381 страницаThe Politics of The Asia-Pacific Triumphs, Challenges, and Threats (Mark S. Williams (Editor)lelenaОценок пока нет
- MCQs blood & cell physiology blogДокумент8 страницMCQs blood & cell physiology bloglubna malikОценок пока нет
- بنك طب نفسيДокумент19 страницبنك طب نفسيمحمد نادر100% (1)
- Angina Pectoris: Dr. Naitik D Trivedi & Dr. Upama N. TrivediДокумент15 страницAngina Pectoris: Dr. Naitik D Trivedi & Dr. Upama N. TrivediNaveen KumarОценок пока нет
- Aapi Ebook June 19 2017Документ621 страницаAapi Ebook June 19 2017AAPIUSAОценок пока нет
- Chronic Medical IssuesДокумент9 страницChronic Medical IssuesomoshОценок пока нет
- Pre Miro Lab LesДокумент3 страницыPre Miro Lab Lesrain rainyОценок пока нет
- Cannabis Use and Disorder - Epidemiology, Comorbidity, Health Consequences, and Medico-Legal Status - UpToDateДокумент34 страницыCannabis Use and Disorder - Epidemiology, Comorbidity, Health Consequences, and Medico-Legal Status - UpToDateAnonymous kvI7zBNОценок пока нет
- Section 5 - Students WorksheetДокумент4 страницыSection 5 - Students WorksheetEsraa AhmedОценок пока нет
- Physiology of Sleep: Michael Schupp MD FRCA Christopher D Hanning MD FRCAДокумент6 страницPhysiology of Sleep: Michael Schupp MD FRCA Christopher D Hanning MD FRCArichie_ciandraОценок пока нет
- Parasitology study table overviewДокумент10 страницParasitology study table overviewBashaer GellehОценок пока нет
- Interstitial Cystitis (Painful Bladder Syndrome) - Causes & TreatmentДокумент12 страницInterstitial Cystitis (Painful Bladder Syndrome) - Causes & TreatmentJimmy GillОценок пока нет
- GugulipidДокумент7 страницGugulipidManish WadhwaniОценок пока нет
- Prestigi0us BiochemistryДокумент30 страницPrestigi0us Biochemistrybovey69015Оценок пока нет
- How Do We Use Philosophy To Figure Out What Is True?Документ5 страницHow Do We Use Philosophy To Figure Out What Is True?Pik NikОценок пока нет
- Addison On The Thing 1982Документ14 страницAddison On The Thing 1982Matheus TomazОценок пока нет
- Drugs Acting On Blood and Blood Forming OrgansДокумент42 страницыDrugs Acting On Blood and Blood Forming OrgansNazmul NabilОценок пока нет
- Wound Care InstructionsДокумент3 страницыWound Care InstructionsKat TaasinОценок пока нет
- Physical Paper +1ANNUALДокумент5 страницPhysical Paper +1ANNUALprabhnoorprimeОценок пока нет
- Dhatupaushtik ChurnaДокумент6 страницDhatupaushtik ChurnaShoeb MirzaОценок пока нет
- Emropub 2016 en 19266Документ45 страницEmropub 2016 en 19266jamshaidjiОценок пока нет