System Models (AGC)
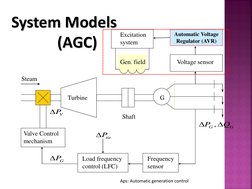
Steam Turbine
Excitation system
Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR)
Gen. field
Voltage sensor
G Shaft
P V
Valve Control mechanism
P , QG G
P tie
Load frequency control (LFC) Frequency sensor
PG
Aps: Automatic generation control
� For
efficient and reliable operation of Power Systems, the control of voltage should satisfy the following objective: Voltages at the terminals of all equipment in the system are within acceptable limits. Maintaining voltages within the required limits is complicated due to the fact that the power system supplies power to vast number of loads and fed from many generating units.
Aps: Automatic generation control
�Automatic Voltage Regulation
System voltage is closely related to the system reactive power which is a reactive loads such as inductors and capacitors dissipate zero power, yet the fact that they drop voltage and draw current gives the deceptive impression that they actually do dissipate power.
The proper selection and coordination of equipment for controlling the system voltage and the reactive power are among the major challenges in power system operation.
Aps: Automatic generation control
�Automatic Voltage Regulation
Reactive
Power (QV) is one of the two main elements in the power system must be controlled. voltage error in the system is sensed, measured, and transformed into reactive-power command signal. objective of the AVR is to keep the system terminal voltage at the desired value by means of feedback control
Aps: Automatic generation control
Any
The
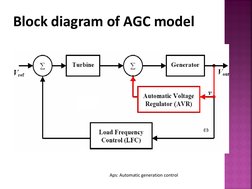
�Block diagram of AGC model
Aps: Automatic generation control
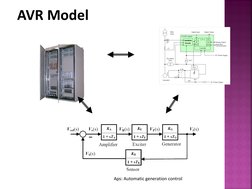
�AVR Model
Aps: Automatic generation control
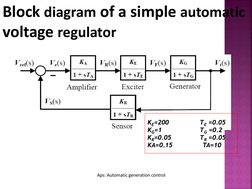
�Block diagram of a simple automatic voltage regulator
KE=200 KG=1 KR=0.05 KA=0.15
TE =0.05 TG =0.2 TR =0.05 TA=10
Aps: Automatic generation control
�Block diagram of a simple automatic voltage regulator (AVR)
Voltage error is improved by controlling the rotor fieldcurrent generator EMF.
The steady state voltage error can be eliminated using an integral controller. The AVR has a substantial effect on transient stability when varying the field voltage to maintain the terminal voltage constant.
Aps: Automatic generation control
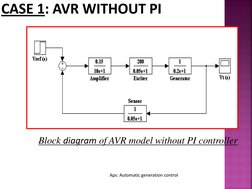
Case 1: AVR without PI (Proportional and Integral ) controller.
Case 2: AVR with PI controller. Case 3: AVR with optimal control.
Aps: Automatic generation control
�Block diagram of AVR model without PI controller
Aps: Automatic generation control
�The output response without controller voltage
Overshoot error V Steady State error
Overshoot
Steady state error
output voltage response when Ka of the amplifier is 0.15
The output voltage response when Ka of the amplifier was changed to 0.1
Aps: Automatic generation control
�model with Ki and Kp gainsock diagram of AVR
Aps: Automatic generation control
�The output voltage response with PI controller
Overshoot
Time (s)
�Aps: Automatic generation control
�Step1: state variables and output equations:
U ( s) x 4
x3
x3
x 2 20 x2 4000 x3
x2
x3 0.1x3 0.01 x4 0.01u (t )
x2
x1
x1 5 x1 5 x2
x4
x4 20 x4 20 x1
x1
Aps: Automatic generation control
�State
differential Equation:
x(t ) Ann x(t ) Bnmu (t )
Output
Equation:
y (t ) C pn x(t ) D pm u (t )
A=[-5 5 0 0; 0 -20 4000 0; 0 0 -0.1 -0.01;20 0 0 -20] B=[0;0;0.01;0] C=[1 0 0 0] D=[0]
Aps: Automatic generation control
�AGC system
Aps: Automatic generation control
� Our
goal in the end is to design a control system that serves the power network in the UAE for better performance and better power services in terms of consumption and supplement. our skills and understanding of Engineering project design and management. the best as an outcome of a successful group
Enhance
Achieve
work.
Aps: Automatic generation control