Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Ir Spectos
Загружено:
umesh123patilОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Ir Spectos
Загружено:
umesh123patilАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Fluorescence Correlation
Spectroscopy
/
I
20050818
sunchul@sogang.ac.kr
Contents
1.What is FCS?
2.Setup
3.Base Theories
4.Whats FCS used for?
5.Example Experiment - Diffusion
6.Another Example
7.Summary
1. What is FCS ?
FCS is
Fluorescence/Fluctuation Correlation Spectroscopy
FCS is
Suggested 1972, and Renaissance 1990s
FCS is
Calculate correlation function from time
dependant intensity fluctuation of dye molecule by
confocal microscopy in single molecule level.
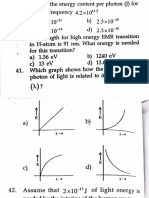
2. Setup
3. Based Theories Gaussian Beam
Sample
Dichroic
Mirror
Lens
laser :
1
By Uncertainty Principle
Focal Volume
3. Based Theories Fluorescence
Fluorescence
light :
2
Molecules are
Fluorescent
1
3. Based Theories Confocal Microscopy
O.M Resolution limit ~ 200nm
But we want to see single
molecule!
-> Confocal Microscopy
3. Based Theories Correlation Function
Time lag ()
4. Whats FCS used for ?
From Correlation Function, seeing
Chemical Dynamics,
Intra-molecular /
Inter-molecular
Dynamics,
Diffusion,
E T C
This Expt.
Study Region
5. Example Experiment - Diffusion
Why does the diffusion create?
-> Brownian Motion !
5. Example Experiment - Diffusion
Changing concentration
-> Changed Correlation Function
> < C
G
1
~ ) (t
Be used only Concentration ~ few nM
5. Example Experiment - Diffusion
0 2 4 6 8 10
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
1
/
G
(
0
)
Concentration (nM)
inverted g(0)
1E-5 1E-4 1E-3 0.01 0.1
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
N
o
r
m
a
l
i
z
e
d
A
u
t
o
c
o
r
r
e
l
a
t
i
o
n
f
u
n
t
i
o
n
.
Lag time ( )
200pM (norm)
500pM (norm)
1nM (norm)
2nM (norm)
5nM (norm)
10nM (norm)
1E-5 1E-4 1E-3 0.01 0.1
1.0
1.1
1.2
1.3
1.4
1.5
1.6
1.7
1.8
1.9
2.0
A
u
t
o
c
o
r
r
e
l
a
t
i
o
n
f
u
n
c
t
i
o
n
.
Lag time ( )
TMR (200pM)
TMR (500pM)
TMR (1nM)
TMR (2nM)
TMR (5nM)
TMR (10nM)
6. Another Example - Chemical Reaction
7. Summary
We know theory of FCS
: Uncertainty Principle Gaussian Beam
: Quantum Mechanics Fluorescence
: Geometric Optics Confocal Microscopy
: Statistical Mechanics Correlation function
We use FCS
Study Brownian Motion Diffusion
Reference
P.Schwile and E.Haustein, Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy
S.H.Kim, Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy
Y.H.Hwang Spectroscopy : Characterization of Material Properties
C.Gell, et al. Handbook of Single Molecule Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy
S.Weiss, Fluorescence Spectroscopy of Single Biomolecules
F.Reif, Fundamentals of Statistical and Thermal physics 4
th
edition
Saleh&Hahaa, Fundamentals of Photonics 4
th
edition
PerkinElmer, Avalanche Photodiode A User Guide
Hamamatsu, Photomultiplier tubes Basic and Applicaitions
RP Photonics www.rp-photonics.com
Nikon Microscopy www.microscopyu.com
Mek&Tosj www.mekentosh.com
Brownian Motion java animation
Supplement Brownian Motion Formula
Molecule Fluctuation Equation of motion : Langevin Equation
) (
int
t F v F
dt
dv
m
ext
+ = o )] 1 ( [
2
1 2 t
e t
kT
x
o
>= <
Use it -> Given Stokes-Einstein relation
R
kT
D
tq 6
=
Diffusion coefficient
q I n
dV t r C q r S r I t F
ex
=
=
}
o k
o o k o
0 0
)) , ( ( ) ( ) ( ) (
Intensity
Supplement Correlation function formula
2
A
( ) ( ) t A A 0
2
A
A
t
t
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) t t + =
}
t A t dtA
T
A A
T
T 0
1
lim 0
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ' '
1
lim 0
0
r r A r drA
R
r A A
R
R
+ =
}
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) t t + =
}
t B t dtA
T
B A
T
T 0
1
lim 0
Auto correlation function
Cross correlation function
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ' '
1
lim 0
0
r r B r drA
R
r B A
R
R
+ =
}
D
D w
r
C
B G
t
t
t
t
t
2
0
0
eff
) ( 1
1
) 1 (
1
V
1
) (
+
+
> <
+ =
D
r
w r V
D
eff
4
2
0
0
2
0
2
3
=
=
t
t
We use Autocorrelation Function (bottom)
Supplement Photon Counter
Counting A Few Photon
PMT
Photomultiplier tube
APD
Avalanche Photodiode
Supplement FRET
: Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer
Supplement Students DATA
Вам также может понравиться
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- ContraceptiveДокумент3 страницыContraceptiveumesh123patilОценок пока нет
- Bohlmann-Rahtz Reaction: Student Name:fawzeya KhundaqgyДокумент12 страницBohlmann-Rahtz Reaction: Student Name:fawzeya Khundaqgyumesh123patilОценок пока нет
- Programme Overview: Monday 21 October 2013Документ2 страницыProgramme Overview: Monday 21 October 2013umesh123patilОценок пока нет
- Journal of Fluorescence: Design and Synthesis of A Pyridine Based Noncyclic Receptor As Pb2+ Ion Selective ProbeДокумент26 страницJournal of Fluorescence: Design and Synthesis of A Pyridine Based Noncyclic Receptor As Pb2+ Ion Selective Probeumesh123patilОценок пока нет
- Lab Essentials Price List 2013 2014Документ372 страницыLab Essentials Price List 2013 2014umesh123patil50% (2)
- Antipyretic: Drugs FeverДокумент3 страницыAntipyretic: Drugs Feverumesh123patilОценок пока нет
- CMAR 35175 The Orphan G Protein Receptor Gpr55 As An Emerging Target in 062813Документ9 страницCMAR 35175 The Orphan G Protein Receptor Gpr55 As An Emerging Target in 062813umesh123patilОценок пока нет
- RJ Science Communicator AwardДокумент6 страницRJ Science Communicator Awardumesh123patilОценок пока нет
- 11 Unique Points..Документ3 страницы11 Unique Points..umesh123patilОценок пока нет
- MMC 1Документ6 страницMMC 1umesh123patilОценок пока нет
- Rls LetterДокумент1 страницаRls Letterumesh123patilОценок пока нет
- AntacidДокумент42 страницыAntacidumesh123patilОценок пока нет
- Science Reference: AnalgesicДокумент2 страницыScience Reference: Analgesicumesh123patilОценок пока нет
- Evaluative Report of The SchoolДокумент22 страницыEvaluative Report of The Schoolumesh123patilОценок пока нет
- Synthesis of 2, 6-Diaryl-4-5-Secondary Aminonicotinonitriles As Potent Antimicrobial AgentsДокумент5 страницSynthesis of 2, 6-Diaryl-4-5-Secondary Aminonicotinonitriles As Potent Antimicrobial Agentsumesh123patilОценок пока нет
- Review Article On Vilsmeier-Haack ReactionДокумент19 страницReview Article On Vilsmeier-Haack Reactionumesh123patil100% (1)
- Antacid: Topics Documents Terms AboutДокумент3 страницыAntacid: Topics Documents Terms Aboutumesh123patilОценок пока нет
- Anti-Diabetic Medication - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaДокумент12 страницAnti-Diabetic Medication - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaumesh123patilОценок пока нет
- Modified Vilsmeier-Haack Reactions of A-Methylene Ketones: Chapter ThreeДокумент48 страницModified Vilsmeier-Haack Reactions of A-Methylene Ketones: Chapter Threeumesh123patilОценок пока нет
- Information Broucher eДокумент17 страницInformation Broucher eumesh123patilОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- LASERДокумент30 страницLASERGagandeep SinghОценок пока нет
- Project Camelot David Wilcock LA Awake and Aware Conference TranscriptДокумент55 страницProject Camelot David Wilcock LA Awake and Aware Conference TranscriptChristian UFO IlluminatiОценок пока нет
- Science Islam and CosmologyДокумент69 страницScience Islam and CosmologyArafat FaniОценок пока нет
- Quiz 1Документ3 страницыQuiz 1Uyen V. Nguyen100% (1)
- Foundations and History of Statistical MechanicsДокумент6 страницFoundations and History of Statistical MechanicsbibbiblosОценок пока нет
- Molecular Energy Levels NotesДокумент5 страницMolecular Energy Levels Notesskrim2Оценок пока нет
- Fluorescence and PhosphorescenceДокумент15 страницFluorescence and PhosphorescencePalupi DarmantiОценок пока нет
- AguerДокумент23 страницыAguerHuruk BrosnanОценок пока нет
- CHEM1048A 2023 SC LG4 StudentДокумент40 страницCHEM1048A 2023 SC LG4 StudentRayyan RaufОценок пока нет
- DFT and TD-DFT Study On The Optical and Electronic Properties of Derivatives of 1,4-Bis (2-Substituted-1,3,4-Oxadiazole) BenzeneДокумент6 страницDFT and TD-DFT Study On The Optical and Electronic Properties of Derivatives of 1,4-Bis (2-Substituted-1,3,4-Oxadiazole) BenzeneJags BuddyОценок пока нет
- Collective Energy GapДокумент5 страницCollective Energy GapleОценок пока нет
- Dual Nature of Matter & Uncertainity PrincipleДокумент2 страницыDual Nature of Matter & Uncertainity PrincipleParthОценок пока нет
- Mössbauer Spectroscopy:: History, Principles and Potential Analysis of MaterialsДокумент22 страницыMössbauer Spectroscopy:: History, Principles and Potential Analysis of MaterialshaffizОценок пока нет
- 2009 Good A New Quantum Edge Detection Algorithm For Medical Images 16438527Документ7 страниц2009 Good A New Quantum Edge Detection Algorithm For Medical Images 16438527Isram RasalОценок пока нет
- NCERT Class 11 Physics Part 1Документ234 страницыNCERT Class 11 Physics Part 1Sumant Kumar Giri100% (2)
- Chan Paton Generalized Veneziano Model With Isospin PDFДокумент5 страницChan Paton Generalized Veneziano Model With Isospin PDFitt shОценок пока нет
- Electricity Class-1 NotesДокумент14 страницElectricity Class-1 Notesindrina guptaОценок пока нет
- The Origin of Planck ConstantДокумент2 страницыThe Origin of Planck ConstantDezso SarkadiОценок пока нет
- MCQ Questions For Class 7 Geography Chapter 1 Environment With AnswersДокумент1 страницаMCQ Questions For Class 7 Geography Chapter 1 Environment With AnswersSwapna vaniОценок пока нет
- UV-Vis: Theory, Concepts, and ApplicationsДокумент41 страницаUV-Vis: Theory, Concepts, and ApplicationsReese VespertineОценок пока нет
- 9302097v1 PDFДокумент94 страницы9302097v1 PDFarmhein64Оценок пока нет
- Distinguishing Jordan and Einstein FramesДокумент10 страницDistinguishing Jordan and Einstein FramesManuel RodriguesОценок пока нет
- Why Beliefs MatterДокумент25 страницWhy Beliefs Mattermelamin1980janОценок пока нет
- 2 3 Exit TicketДокумент1 страница2 3 Exit Ticketapi-259040408Оценок пока нет
- (Walls D.F., G.j.milburn.) Quantum OpticsДокумент370 страниц(Walls D.F., G.j.milburn.) Quantum OpticsFranklin RiosОценок пока нет
- Chapter2 Introduction To Quantum MechanicsДокумент32 страницыChapter2 Introduction To Quantum MechanicsTahsin MorshedОценок пока нет
- QC AbstractДокумент5 страницQC Abstract429by3Оценок пока нет
- J Cosrev 2018 11 002Документ21 страницаJ Cosrev 2018 11 002vedddaaaahОценок пока нет
- Pieces of Eight by Gordon White PDFДокумент146 страницPieces of Eight by Gordon White PDFvee100% (4)
- Qs Based On Photoelectric EffectДокумент5 страницQs Based On Photoelectric EffectsdrgrОценок пока нет