Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Operational Amplifier
Загружено:
Vasudha JoshiИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Operational Amplifier
Загружено:
Vasudha JoshiАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
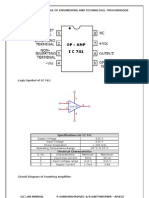
Basic Op-Amp
Operational amplifier or op-amp, is a very high gain differential
amplifier with a high input impedance (typically a few meg-Ohms)
and low output impedance (less than 100 O).
Note the op-amp has two inputs and one output.
1
Op-Amp Gain
Op-Amps have a very high gain. They can be connected open-loop or
closed-loop.
Open-loop refers to a configuration where there is no feedback
from output back to the input. In the open-loop configuration
the gain can exceed 10,000.
Closed-loop configuration reduces the gain. In order to control
the gain of an op-amp it must have feedback. This feedback is a
negative feedback. A negative feedback reduces the gain and
improves many characteristics of the op-amp.
2
Inverting Op-Amp
The signal input is applied to the inverting () input
The non-inverting input (+) is grounded
The resistor R
f
is the feedback resistor. It is connected from the output to
the negative (inverting) input. This is negative feedback.
3
Inverting Op-Amp Gain
Gain can be determined from
external resistors: R
f
and R
1
Unity gainvoltage gain is 1
The negative sign denotes a 180
phase shift between input and
output.
1
f
i
o
v
R
R
V
V
A = =
1
R
R
A
R R
1
f
v
1 f
=
=
=
Constant GainR
f
is a multiple of R
1
4
Virtual Ground
An understanding of the
concept of virtual ground
provides a better
understanding of how an op-
amp operates.
The non-inverting input pin is
at ground. The inverting input
pin is also at 0 V for an AC
signal.
The op-amp has such high input impedance
that even with a high gain there is no
current from inverting input pin, therefore
there is no voltage from inverting pin to
groundall of the current is through R
f
.
5
Practical Op-Amp Circuits
Inverting amplifier
Noninverting amplifier
Unity follower
Summing amplifier
Integrator
Differentiator
6
Inverting/Noninverting Op-Amps
1
1
f
o
V
R
R
V
=
Inverting Amplifier Noninverting Amplifier
1
1
f
o
V )
R
R
1 ( V + =
7
Unity Follower
1 o
V V =
8
Summing Amplifier
Because the op-amp has a
high input impedance, the
multiple inputs are
treated as separate inputs.
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ + =
3
3
f
2
2
f
1
1
f
o
V
R
R
V
R
R
V
R
R
V
9
Integrator
The output is the integral
of the input. Integration
is the operation of
summing the area under
a waveform or curve over
a period of time. This
circuit is useful in low-
pass filter circuits and
sensor conditioning
circuits.
}
= (t)dt v
RC
1
(t) v
1 o
10
Differentiator
The differentiator
takes the derivative of
the input. This circuit
is useful in high-pass
filter circuits.
dt
(t) dv
RC (t) v
1
o
=
11
Op-Amp SpecificationsDC Offset
Parameters
Input offset voltage
Input offset current
Input offset voltage and input offset current
Input bias current
Even when the input voltage is zero, there can be an
output offset. The following can cause this offset:
12
Input Offset Voltage (V
IO
)
The specification sheet for an op-amp indicate an
input offset voltage (V
IO
).
The effect of this input offset voltage on the output
can be calculated with
1
f 1
IO o(offset)
R
R R
V V
+
=
13
Output Offset Voltage Due to Input Offset
Current (I
IO
)
The input offset Current (I
IO
) is specified in the specifications
for the op-amp.
The effect on the output can be calculated using:
f IO ) I to due o(offset
R I V
IO
=
If there is a difference between the dc bias currents for the same
applied input, then this also causes an output offset voltage:
14
Total Offset Due to V
IO
and I
IO
Op-amps may have an output offset voltage due to both
factors V
IO
and I
IO
. The total output offset voltage will be
the sum of the effects of both:
) I to due (offset V ) V to due (offset V (offset) V
IO o IO o o
+ =
15
Input Bias Current (I
IB
)
A parameter that is related to input offset current (I
IO
) is called
input bias current (I
IB
)
The separate input bias currents are:
The total input bias current is the average:
2
I
I I
IO
IB IB
+ =
+
2
I
I I
IO
IB IB
=
2
I I
I
IB IB
IB
+
+
=
16
An op-amp is a wide-bandwidth amplifier. The following
affect the bandwidth of the op-amp:
Gain
Slew rate
Frequency Parameters
17
Gain and Bandwidth
The op-amps high frequency
response is limited by
internal circuitry. The plot
shown is for an open loop
gain (A
OL
or A
VD
). This means
that the op-amp is operating
at the highest possible gain
with no feedback resistor.
In the open loop, the op-amp
has a narrow bandwidth. The
bandwidth widens in closed-
loop operation, but then the
gain is lower.
18
Slew Rate (SR)
Slew rate (SR) is the
maximum rate at which an
op-amp can change output
without distortion.
The SR rating is given in
the specification sheets as
V/s rating.
s) V/ (in
t
V
SR
o
=
19
Maximum Signal Frequency
The slew rate determines the highest frequency of
the op-amp without distortion.
where V
P
is the peak voltage
p
V 2
SR
f s
20
General Op-Amp Specifications
Other ratings for op-amp found on specification sheets
are:
Absolute Ratings
Electrical Characteristics
Performance
21
Absolute Ratings
These are common
maximum ratings
for the op-amp.
22
Electrical Characteristics
Note: These ratings are for specific circuit conditions, and they often
include minimum, maximum and typical values.
23
CMRR
One rating that is unique to op-amps is CMRR or common-mode
rejection ratio.
Because the op-amp has two inputs that are opposite in phase
(inverting input and the non-inverting input) any signal that is common
to both inputs will be cancelled.
Op-amp CMRR is a measure of the ability to cancel out common-mode
signals.
24
Op-Amp Performance
The specification sheets will also
include graphs that indicate the
performance of the op-amp over
a wide range of conditions.
25
Вам также может понравиться
- EDC Lecture NotesДокумент187 страницEDC Lecture NotesKARTHIKAMANI RОценок пока нет
- Experiment - Feedback Amplifiers: 3.2.1 ObjectiveДокумент13 страницExperiment - Feedback Amplifiers: 3.2.1 ObjectiveskmrajkumarОценок пока нет
- Parallel Operation of Two Single Phase Transformers: Experiment No: 05Документ18 страницParallel Operation of Two Single Phase Transformers: Experiment No: 05Bhanoth MohanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 - Multistage Amplifier (Cascode)Документ26 страницChapter 3 - Multistage Amplifier (Cascode)GakushaОценок пока нет
- Multistage AmplifierДокумент22 страницыMultistage AmplifierVijay AnandhОценок пока нет
- CH 2 - Op-Amp ApplicationДокумент52 страницыCH 2 - Op-Amp Applicationknighthood4all100% (2)
- LIC+COM Lab Manual - 17ECL48Документ58 страницLIC+COM Lab Manual - 17ECL48Surendra K V100% (4)
- 01 RLC Circuit and ResonanceДокумент46 страниц01 RLC Circuit and ResonanceLatif Nurohman Bayu Nugroho60% (5)
- ColpittsДокумент8 страницColpittsRavi Teja100% (1)
- Digital To Analog Converter Using R 2R Ladder Network and 741 Op AmpДокумент3 страницыDigital To Analog Converter Using R 2R Ladder Network and 741 Op AmpPuneeth Siddappa100% (1)
- UNIT5 Fundamentals of Communication EngineeringДокумент20 страницUNIT5 Fundamentals of Communication EngineeringUpender Rao Sunkishala100% (4)
- Half Wave Rectification Experiment - 3: TheoryДокумент10 страницHalf Wave Rectification Experiment - 3: TheoryLakshayОценок пока нет
- Analysis of CE AmplifierДокумент8 страницAnalysis of CE Amplifierramjee26Оценок пока нет
- Electronics Workshop VivaДокумент14 страницElectronics Workshop VivaUsha ShanmugamОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Wave GuidesДокумент150 страницChapter 2 Wave GuidesMohdIhsanОценок пока нет
- LIC Lab ManualДокумент79 страницLIC Lab ManualSakthikumar Balasundaram67% (3)
- Unijunction Transistor: By: Smridhi ChawlaДокумент27 страницUnijunction Transistor: By: Smridhi Chawlasmridhi chawla100% (1)
- Circuit Analysis Using Fourier SeriesДокумент16 страницCircuit Analysis Using Fourier SeriesJidan FikriОценок пока нет
- Common Source Amplifier ExperimentДокумент3 страницыCommon Source Amplifier Experimentappuamreddy100% (3)
- Unit-3::Half Wave Rectifier, Ripple Factor, Full WaveДокумент12 страницUnit-3::Half Wave Rectifier, Ripple Factor, Full WaveHemant TulsaniОценок пока нет
- Unit-1 Semiconductor Diodes PDFДокумент103 страницыUnit-1 Semiconductor Diodes PDFRajarao MandaОценок пока нет
- IC 723 Voltage RegulatorsДокумент16 страницIC 723 Voltage RegulatorsAtheessh .B0% (1)
- Notes Opamp Sem 4Документ18 страницNotes Opamp Sem 4Narendra SinhaОценок пока нет
- Viva QuestionsДокумент7 страницViva QuestionsAshmika PОценок пока нет
- Lecture 5 Ohm MetersДокумент24 страницыLecture 5 Ohm MetersAbdur RahmanОценок пока нет
- Multiple Choice Questions With Answers On Power Electronics and DrivesДокумент3 страницыMultiple Choice Questions With Answers On Power Electronics and DrivesRaees AslamОценок пока нет
- Generation of WaveformsДокумент9 страницGeneration of WaveformsNivas Kumar SureshОценок пока нет
- Experiment No.3-Voltage Regulation of A 3-Phase Alternator by ZPF and ASA MethodДокумент6 страницExperiment No.3-Voltage Regulation of A 3-Phase Alternator by ZPF and ASA Method61EEPrabhat Pal100% (1)
- LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRUITS - 2 Marks Question Bank - IV Sem ECEДокумент19 страницLINEAR INTEGRATED CIRUITS - 2 Marks Question Bank - IV Sem ECEJOHN PETER100% (7)
- Analog Communication Basic Questions AnswerДокумент13 страницAnalog Communication Basic Questions AnswerSourav Ghosh100% (1)
- Analog Electronic Circuits Lab ManualДокумент86 страницAnalog Electronic Circuits Lab ManualsanjuОценок пока нет
- Eca Lab-Min PDFДокумент87 страницEca Lab-Min PDFAkashita SharmaОценок пока нет
- Power Electronics Lab ManualДокумент47 страницPower Electronics Lab Manualshaan_patil100% (1)
- Power Electronics Single-Phase Half-Wave Rectifier.Документ37 страницPower Electronics Single-Phase Half-Wave Rectifier.Hassan technologist0% (1)
- RLC CircuitДокумент7 страницRLC CircuitPriya JakoonОценок пока нет
- An Introduction To Two - Port Networks: The University of Tennessee Electrical and Computer Engineering Knoxville, TNДокумент34 страницыAn Introduction To Two - Port Networks: The University of Tennessee Electrical and Computer Engineering Knoxville, TNajaypal100% (3)
- Expt No. 03 - To Design and Test Op Amp Integrator For Given FrequenciesДокумент7 страницExpt No. 03 - To Design and Test Op Amp Integrator For Given FrequenciesPrakash Narkhede100% (1)
- Op PPT 12Документ16 страницOp PPT 12Jaymin PatelОценок пока нет
- Analog Integrated Circuits LAB ManualДокумент51 страницаAnalog Integrated Circuits LAB ManualVishurockОценок пока нет
- Alternating Current Fundamental NotesДокумент25 страницAlternating Current Fundamental NotesSiddharth Gupta100% (1)
- EXP17 Class A Power AmplifierДокумент3 страницыEXP17 Class A Power AmplifierMohammed Dyhia AliОценок пока нет
- Experiment: Title: DC Power Supply Unit: Transformer ObjectiveДокумент14 страницExperiment: Title: DC Power Supply Unit: Transformer ObjectiveLian Ai Chen100% (1)
- Lab Manual Full Wave RectifierДокумент5 страницLab Manual Full Wave RectifierVivek SuranaОценок пока нет
- Multiple Choice Questions and Answers On Op-Amp (Operational Amplifier) - Electronics PostДокумент6 страницMultiple Choice Questions and Answers On Op-Amp (Operational Amplifier) - Electronics PostDurga Devi100% (1)
- O.C.C. & Load Test On Separately Excited D.C. GeneratorДокумент18 страницO.C.C. & Load Test On Separately Excited D.C. GeneratorSuyash KothawadeОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 PDFДокумент32 страницыChapter 3 PDFEndalew kassahunОценок пока нет
- Experiment No:9: Op-Amp As A DifferentiatorДокумент2 страницыExperiment No:9: Op-Amp As A DifferentiatorBhadresh Renuka100% (1)
- 5.) Common Drain AmplifierДокумент5 страниц5.) Common Drain AmplifierJuay Mae Riano100% (1)
- Ece III Network Analysis (10es34) NotesДокумент111 страницEce III Network Analysis (10es34) NotesGautam Sharma80% (10)
- Eee 1217 Op AmpДокумент51 страницаEee 1217 Op AmpEbrahim SiddikОценок пока нет
- Op Amp and Its Applications2.0Документ27 страницOp Amp and Its Applications2.0Arpita Sharma100% (1)
- Op AmpДокумент24 страницыOp AmpMadeleine NavarreteОценок пока нет
- AE Unit - 5Документ7 страницAE Unit - 5aamirnasirОценок пока нет
- Sensors and ActuatorsДокумент43 страницыSensors and Actuatorshitesh reddyОценок пока нет
- Unit 4.1 Op-AmpДокумент20 страницUnit 4.1 Op-AmpKaneez AsmaОценок пока нет
- Chapter3 Op Amp (1) 80911Документ62 страницыChapter3 Op Amp (1) 80911Azman Mat HussinОценок пока нет
- CH 1 - Op-AmpДокумент65 страницCH 1 - Op-AmpMohana VivanaОценок пока нет
- Op AmpsДокумент17 страницOp AmpsshilpaОценок пока нет
- Signal Conditioning Op-AmpsДокумент41 страницаSignal Conditioning Op-AmpsSaleem Haddad100% (1)
- Fisa Tehnica Camera Supraveghere Exterior Dahua Starlight HAC-HFW1230T-A-0360BДокумент3 страницыFisa Tehnica Camera Supraveghere Exterior Dahua Starlight HAC-HFW1230T-A-0360BDanielTeglasОценок пока нет
- Tution ProposalДокумент9 страницTution ProposalUsman AliОценок пока нет
- Datasheet Avaya Phone-1608Документ29 страницDatasheet Avaya Phone-1608jetsoilderОценок пока нет
- Volvo Transport SolutionsДокумент16 страницVolvo Transport SolutionsForomaquinas100% (1)
- Lift Monitor Manual PDFДокумент10 страницLift Monitor Manual PDFReza KühnОценок пока нет
- Modula WMSДокумент8 страницModula WMSIbai Zabala BengoaОценок пока нет
- Sr. Devops Engineer Job SampleДокумент2 страницыSr. Devops Engineer Job SampleSannithiBalajiОценок пока нет
- NTT Data Ai Governance v04Документ23 страницыNTT Data Ai Governance v04radhikaseelam1Оценок пока нет
- 10-Inch Daylight Radar: 1932 MARK-2Документ2 страницы10-Inch Daylight Radar: 1932 MARK-2Thien NguyenОценок пока нет
- Data SheetДокумент24 страницыData Sheetbashok20Оценок пока нет
- Google Chrome Keyboard ShortcutsДокумент2 страницыGoogle Chrome Keyboard ShortcutsMaRkY A1r0E1s6Оценок пока нет
- Dnp3 Master Ethernet ManualДокумент143 страницыDnp3 Master Ethernet ManualunnikuttanОценок пока нет
- Roland Vs 640 Mechanical DrawingДокумент40 страницRoland Vs 640 Mechanical DrawingEdwardo RamirezОценок пока нет
- Big Data GuideДокумент58 страницBig Data GuideDhivyaaShanmugamОценок пока нет
- An Efficient Power Flow Algorithm For Distribution Systems With Polynomial LoadДокумент16 страницAn Efficient Power Flow Algorithm For Distribution Systems With Polynomial Loadishak789Оценок пока нет
- UPS 348-01-01 PowerWAVE 3000T PDFДокумент4 страницыUPS 348-01-01 PowerWAVE 3000T PDFShahin ShajahanОценок пока нет
- Ahoy Bookaneers! Ela Meagan Oakley: 2 Classes at Each Grade LevelДокумент8 страницAhoy Bookaneers! Ela Meagan Oakley: 2 Classes at Each Grade Levelmeaganlee86Оценок пока нет
- Customer Webinar Company Administrators FiS - September 09 2021Документ35 страницCustomer Webinar Company Administrators FiS - September 09 2021kudret aytasОценок пока нет
- Abacus Junior 30Документ4 страницыAbacus Junior 30郑伟健Оценок пока нет
- Group Chat Project ReportДокумент18 страницGroup Chat Project ReportSoham JainОценок пока нет
- Integrated CircuitДокумент13 страницIntegrated CircuitGilberto ManhattanОценок пока нет
- T4S Post Amendment 15.09.2020Документ130 страницT4S Post Amendment 15.09.2020kambanОценок пока нет
- Present Perfect PracticeДокумент25 страницPresent Perfect PracticeManuel Tutacha ™100% (1)
- Object Oriented Programming Methodology Using Java: Prof: Pradnya Sadigale (E&Tcdepartment)Документ39 страницObject Oriented Programming Methodology Using Java: Prof: Pradnya Sadigale (E&Tcdepartment)pradnya sadigaleОценок пока нет
- DEEP SEA - DSE8620-MKII - Installation InstructionsДокумент2 страницыDEEP SEA - DSE8620-MKII - Installation InstructionsGustavo DuarteОценок пока нет
- eWPT WriteupДокумент4 страницыeWPT WriteupBertrand Lorente YanezОценок пока нет
- Yaesu FT-1900R Service ManualДокумент0 страницYaesu FT-1900R Service ManualetchegarayfОценок пока нет
- Basic FPGA Tutorial Vivado VHDLДокумент273 страницыBasic FPGA Tutorial Vivado VHDLTito SaulОценок пока нет
- CV Eko Prasetyo Lengkap PDFДокумент4 страницыCV Eko Prasetyo Lengkap PDFEko PrasetyoОценок пока нет
- Prius Energy FlowДокумент1 страницаPrius Energy Flowmsfz751Оценок пока нет