Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Invpresentationv1 1267187349133 Phpapp01
Загружено:
Abhishek RaveendranИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Invpresentationv1 1267187349133 Phpapp01
Загружено:
Abhishek RaveendranАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Investment Banking
A Report by Raymund Sanchez
Agenda
Definitions Functions of an Investment Banker Distribution Methods Events in a Negotiated Sale Private Placements References
Definitions
Investment Banker:
A financial specialist involved as an intermediary in the merchandising of securities. Acts as a middleman by facilitating the flow of savings from those economic units that want to invest to those units that want to raise funds.
Functions of an Investment Banker
Functions of an Investment Banker
Core Business
Middle Office
Underwriting Distributing Advising Others
Operations Technology
Back Office
Risk Management Corporate Treasury Financial Control Corporate Strategy Compliance
Functions of an Investment Banker
Core Business > Underwriting
assuming the risk of selling a security issue at a satisfactory price term borrowed from insurance
Functions of an Investment Banker
Core Business > Distributing
selling function of investment banking the primary function of an investment bank is buying and selling products.
Functions of an Investment Banker
Core Business > Advising
providing advise in the issuance & marketing of securities research is the division which reviews companies and writes reports about their prospects, often with "buy" or "sell" ratings.
Functions of an Investment Banker
Core Business > Others
Global transaction banking Investment management Merchant banking
Functions of an Investment Banker
Middle Office > Risk Management
involves analyzing the market and credit risk that traders are taking onto the balance sheet in conducting their daily trades setting limits on the amount of capital that they are able to trade in order to prevent 'bad' trades having a detrimental effect to a desk overall
Functions of an Investment Banker
Middle Office > Corporate Treasury
responsible for an investment bank's funding, capital structure management, and liquidity risk monitoring.
Functions of an Investment Banker
Middle Office > Financial Control
tracks and analyzes the capital flows of the firm adviser on essential areas such as controlling the firm's global risk exposure and the profitability and structure of the firm's various businesses
Functions of an Investment Banker
Middle Office > Compliance
responsible for an investment bank's daily operations' compliance with government regulations and internal regulations
Functions of an Investment Banker
Back Office > Operations & Technology
data-checking trades that have been conducted, ensuring that they are not erroneous, and transacting the required transfers
Distribution Models
Distribution Models
Negotiated Purchase Competitive Bid Price Commission / Best Efforts Basis Privileged Subscription Direct Sale
Distribution Models
Negotiated Purchase
the underwriting firm that needs funds makes contact with an investment banker & deliberations concerning the new issue begin. most prevalent method of distributing securities in the private sector most profitable technique as far as investment bankers are concerned
Distribution Models
Competitive Bid Price
several underwriting groups bid for the right to purchase the new issue from the corporation that is raising funds. undue influence of the investment banker over the firm is mitigated & the price received by the firm for each security should be higher as far as fund raising is concerned, the benefits gained from the advisory function of the investment banker is lost
Distribution Models
Commission / Best Efforts Basis
investment banker acts as an agent rather than as a principal in the distribution process. typically used for more speculative issues
Distribution Models
Privileged Subscription
new issue is marketed to a definite & select group of investors 3 target markets involved (1) current stock holders (2) employees (3) customers
Distribution Models
Direct Sale
the issuing firm sells directly to the public without going through an investment banker in the process relatively rare
Events in a Negotiated Sale
Events in a Negotiated Sale
Selection of an investment banker Pre-underwriting conferences Formation of the underwriting syndicate Registering of the securities Formation of the selling group Due diligence meeting Price pegging Syndicate termination
Events in a Negotiated Sale
Selection of an investment banker Pre-underwriting conferences
Key Items to be discussed: Amount of capital to be raised Whether capital markets seem to be receptive at the time & the type of financing instrument Whether the proposed use of funds appears reasonable Tentative underwriting agreement Approximate price the investment banker will pay for the securities Upset price (escape mechanism for the benefit of the issuing firm)
Events in a Negotiated Sale
Formation of the underwriting syndicate
syndicate: temporary association of investment bankers formed to purchase a security issue from a corporation for subsequent resale, for a profit to the underwriters. purpose of syndicates:
The original investment banker could not finance the entire underwriting himself Lowers the risk of loss for a single underwriter Widens the eventual distribution effort
Events in a Negotiated Sale
Registering of the securities
Registration statement
Historical facts about the firm Financial facts about the firm Administrative facts about the firm
Events in a Negotiated Sale
Formation of the selling group Due diligence meeting: a last chance gathering to get
everything in order before taking the offering public
Price pegging: placing orders to buy at the agreed upon public
offering price to mitigate downward price movements in the secondary markets
Syndicate termination: dissolution of the syndicate at the end
of the contractual agreement
Private Placements
Private Placements
Public offerings :security issuer does not meet the ultimate investors in the financial instruments Private placements :securities are sold directly to a limited number of institutional investors
Private Placements
Advantages
Speed Reduced floatation costs Financing capability
Interest costs Restrictive covenants Possibility of future SEC registration
Disadvantages
References
Stanley Block & Geoffrey Hirt, Foundations of Financial Management, 1994, P430 John Martin, William Petty, Arthur Keown, David Scott, Basic Financial Management, 1979, p512
-END-
Вам также может понравиться
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- MCDДокумент65 страницMCDFrancisco Javier CazaresОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Layers of Earth's Atmosphere: Presented by Abhishek RaveendranДокумент10 страницIntroduction To Layers of Earth's Atmosphere: Presented by Abhishek RaveendranAbhishek RaveendranОценок пока нет
- Investment Banking OverviewДокумент8 страницInvestment Banking OverviewAbhishek RaveendranОценок пока нет
- The Management Environment: LIS 580: Spring 2006 Instructor-Michael CrandallДокумент22 страницыThe Management Environment: LIS 580: Spring 2006 Instructor-Michael CrandallAbhishek RaveendranОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Discounting and Unwinding: Answer 2-No, Deferred Consideration Is Not A Contingent Consideration Because It Does NotДокумент5 страницDiscounting and Unwinding: Answer 2-No, Deferred Consideration Is Not A Contingent Consideration Because It Does NotM Azeem IqbalОценок пока нет
- BRS Practice QuestionsДокумент2 страницыBRS Practice Questionssyed ali raza kazmiОценок пока нет
- Pas 40 Investment PropertyДокумент4 страницыPas 40 Investment PropertykristineОценок пока нет
- Investment Banks: Financial InstitutionsДокумент3 страницыInvestment Banks: Financial Institutionsruthmae bumanglagОценок пока нет
- Banking VocabularyДокумент3 страницыBanking Vocabularytahar benattiaОценок пока нет
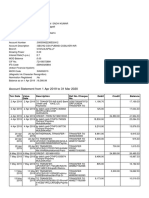
- Account Statement From 1 Apr 2019 To 31 Mar 2020: TXN Date Value Date Description Ref No./Cheque No. Debit Credit BalanceДокумент7 страницAccount Statement From 1 Apr 2019 To 31 Mar 2020: TXN Date Value Date Description Ref No./Cheque No. Debit Credit BalanceSadhi KumarОценок пока нет
- G12 Fabm2 Week 8Документ11 страницG12 Fabm2 Week 8Whyljyne GlasanayОценок пока нет
- RBI Format ROI PC PDFДокумент9 страницRBI Format ROI PC PDFmohana sundaram pОценок пока нет
- Receivable-Financing-Quizbowl DONE For CpaДокумент30 страницReceivable-Financing-Quizbowl DONE For CpaKae Abegail GarciaОценок пока нет
- CFP Risk Analysis and Insurance Planning Practice Book SampleДокумент34 страницыCFP Risk Analysis and Insurance Planning Practice Book SampleMeenakshi100% (7)
- ADV ACC TBch03Документ18 страницADV ACC TBch03hassan nassereddineОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6: Accounting For Plant Assets and Depreciation. ContentsДокумент46 страницChapter 6: Accounting For Plant Assets and Depreciation. ContentsSimon MollaОценок пока нет
- Sbaa7001 Banking and Insurance Management II MBA - BATCH (2019-2021) Semester Iii - August 2020 School of Management StudiesДокумент38 страницSbaa7001 Banking and Insurance Management II MBA - BATCH (2019-2021) Semester Iii - August 2020 School of Management StudiesGracyОценок пока нет
- Verotel Merchant Services B.V. v. Rizal Commercial Bank 2021Документ90 страницVerotel Merchant Services B.V. v. Rizal Commercial Bank 2021hyenadogОценок пока нет
- Coding and Decoding QuestionsДокумент28 страницCoding and Decoding QuestionsAbdulawwal IntisorОценок пока нет
- Question 2: Ias 19 Employee Benefits: Page 1 of 2Документ2 страницыQuestion 2: Ias 19 Employee Benefits: Page 1 of 2paul sagudaОценок пока нет
- Completing The Accounting Cycle: Service Concern: Subject-Descriptive Title Subject - CodeДокумент12 страницCompleting The Accounting Cycle: Service Concern: Subject-Descriptive Title Subject - CodeRose LaureanoОценок пока нет
- Zenith Bank Statement Ronald Morris For Dec 20TH To 22ND 2023Документ2 страницыZenith Bank Statement Ronald Morris For Dec 20TH To 22ND 2023Emeka AmaliriОценок пока нет
- A Mba Lo SurrenderДокумент6 страницA Mba Lo SurrenderGabe AmbaloОценок пока нет
- Pulse TNC Booklet CombinedffdДокумент62 страницыPulse TNC Booklet CombinedffdRrdОценок пока нет
- A Comparative Analysis of Financial Products in Banking Industry With Special Reference To ICICI Bank and State Bank of IndiaДокумент98 страницA Comparative Analysis of Financial Products in Banking Industry With Special Reference To ICICI Bank and State Bank of IndiaWhatsapp stutsОценок пока нет
- Chapter 13 - Financial Asset at Fair ValueДокумент10 страницChapter 13 - Financial Asset at Fair ValueMark LopezОценок пока нет
- Assignment, Managerial AccountingДокумент8 страницAssignment, Managerial Accountingmariamreda7754Оценок пока нет
- 25885110Документ21 страница25885110Llyana paula SuyuОценок пока нет
- 1) Introduction To Management Accounting-2Документ34 страницы1) Introduction To Management Accounting-2fpasanfiverОценок пока нет
- Ba Smart Jul-AprДокумент68 страницBa Smart Jul-AprShubham KashyapОценок пока нет
- PF PFi Terms and ConditionsДокумент20 страницPF PFi Terms and ConditionsAzeizulОценок пока нет
- Income Statement - ExДокумент14 страницIncome Statement - ExQuân Uông Đình MinhОценок пока нет
- Star PREMIUM CHART 18%Документ5 страницStar PREMIUM CHART 18%Rajat GuptaОценок пока нет
- Chap 009Документ30 страницChap 009Ngọc Lan Anh TrầnОценок пока нет