Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
CONVERTERS
Загружено:
Michael CampbellОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CONVERTERS
Загружено:
Michael CampbellАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
ECE 442 Power Electronics 1
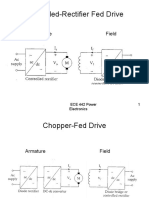
Controlled-Rectifier Fed Drive
Armature Field
ECE 442 Power Electronics 2
Chopper-Fed Drive
Armature Field
ECE 442 Power Electronics 3
Equivalent Circuit of a Separately-Excited
DC Motor
ECE 442 Power Electronics 4
f
f f f f
a
a a a a g
g v f
d t f a
d L
di
v R i L
dt
di
v R i L e
dt
e K i
T K i i
d
T J B T
dt
e
e
e
= +
= + +
=
=
= + +
ECE 442 Power Electronics 5
0
f f f
g v f
a a a g
a a a v f
d t f a
d L
d d
Steady state
d
dt
V R I
E K I
V R I E
V R I K I
T K I I
T B T
P T
e
e
e
e
=
=
=
= +
= +
=
= +
=
ECE 442 Power Electronics 6
a a a v f
a a a a a a
v f
f
v
f
V R I K I
V I R V I R
K I
V
K
R
e
e
= +
= =
| |
|
|
\ .
Solve for the motor speed
ECE 442 Power Electronics 7
Control of the motor speed
Control armature
voltage, V
a
Voltage control
Control the field
current, I
f
Current control
Control the armature
current, I
a
a a a
f
v
f
V I R
V
K
R
e
=
| |
|
|
\ .
ECE 442 Power Electronics 8
Magnetization Characteristic
ECE 442 Power Electronics 9
Characteristics of Separately-Excited Motors
Rated
speed
Use field-current control
Use armature
voltage control
ECE 442 Power Electronics 10
Equivalent circuit of a DC Series Motor
ECE 442 Power Electronics 11
( )
( )
( )
g v a
a a f a g
a a f a v f
d t a f
d L
a a f a
v f
E K I
V R R I E
V R R I K I
T K I I
T B T
V R R I
K I
e
e
e
e
=
= + +
= + +
=
= +
+
=
ECE 442 Power Electronics 12
Controlling the Motor Speed
Control the armature
voltage, V
a
Control the armature
current, I
a
( )
( )
( )
g v a
a a f a g
a a f a v f
d t a f
d L
a a f a
v f
E K I
V R R I E
V R R I K I
T K I I
T B T
V R R I
K I
e
e
e
e
=
= + +
= + +
=
= +
+
=
ECE 442 Power Electronics 13
Characteristics of DC Series motors
ECE 442 Power Electronics 14
Operating Modes
In variable-speed applications, a dc motor
may be operating in one or more of the
following Modes
Motoring
Regenerative braking
Dynamic braking
Plugging
ECE 442 Power Electronics 15
Motoring Mode
Back emf, E
g
is < supply voltage V
a
Both I
a
and I
f
are positive
Developed torque meets load demand
ECE 442 Power Electronics 16
Regenerative Braking Mode
Motor acts as a Generator
E
g
becomes > supply Voltage V
a
I
a
becomes negative
Kinetic energy of the motor is returned to the supply
ECE 442 Power Electronics 17
Dynamic Braking
Replace the supply voltage with a resistor
Power dissipated in the resistor rather than given back
to the source
ECE 442 Power Electronics 18
Plugging
Reverse the armature terminals while running
V
a
and E
g
act in the same direction
I
a
is reversed, producing braking torque
ECE 442 Power Electronics 19
Four-Quadrant Operation
ECE 442 Power Electronics 20
Single-Phase DC Drive
Change V
a
by changing firing angle o
Inductor L
m
is a smoothing Inductor to prevent
discontinuous current
ECE 442 Power Electronics 21
Armature Reversal
ECE 442 Power Electronics 22
Field Reversal
ECE 442 Power Electronics 23
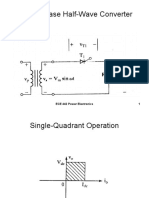
Single-Phase Half-Wave Converter Drive
(1 cos )
2
0
(1 cos )
0
m
a a
a
m
f f
f
V
V
V
V
o
t
o t
o
t
o t
= +
s s
= +
s s
ECE 442 Power Electronics 24
Quadrant of Operation
ECE 442 Power Electronics 25
Waveform Summary
ECE 442 Power Electronics 26
Single-Phase Semiconverter Drives
(1 cos )
0
(1 cos )
0
m
a a
a
m
f f
f
V
V
V
V
o
t
o t
o
t
o t
= +
s s
= +
s s
ECE 442 Power Electronics 27
Quadrant(s) of Operation
Semiconverter one quadrant converter
One polarity of output voltage and current
ECE 442 Power Electronics 28
Waveform Summary
ECE 442 Power Electronics 29
Single-Phase Full-Converter Drives
ECE 442 Power Electronics 30
Quadrant(s) of Operation
Full converter two quadrant converter
Output voltage polarity can be positive or negative
Output current has one polarity
ECE 442 Power Electronics 31
Waveform Summary
ECE 442 Power Electronics 32
Single-Phase Dual-Converter Drives
Dual converter can operate in all four quadrants
Output voltage and current can be positive or negative
Вам также может понравиться
- DC Motor Speed Control Using Chopper CircuitsДокумент32 страницыDC Motor Speed Control Using Chopper CircuitsChetan KotwalОценок пока нет
- Series Resonant Inverter With Bidirectional Switch: ECE 442 Power Electronics 1Документ27 страницSeries Resonant Inverter With Bidirectional Switch: ECE 442 Power Electronics 1mrboyedОценок пока нет
- Controlled-Rectifier Fed Drive: Armature FieldДокумент17 страницControlled-Rectifier Fed Drive: Armature FieldMaverick NaiduОценок пока нет
- ELEC 344 - Module 2 Lecture NotesДокумент45 страницELEC 344 - Module 2 Lecture NotesMax HornerОценок пока нет
- AC To DC ConvertersДокумент18 страницAC To DC ConvertersXen Operation DPHОценок пока нет
- Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis: Chapter ObjectivesДокумент20 страницSinusoidal Steady State Analysis: Chapter ObjectivesPartha MishraОценок пока нет
- Lectures Synchronous MachinesДокумент47 страницLectures Synchronous MachinesSaddy CoolОценок пока нет
- Jabalpur Engineering College, Jabalpur Electrical Engineering Department AC/DC Drives Lab. List of ExperimentДокумент63 страницыJabalpur Engineering College, Jabalpur Electrical Engineering Department AC/DC Drives Lab. List of ExperimentSajalОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1.2 DC MotorДокумент69 страницChapter 1.2 DC MotorMohammed M. ShobakiОценок пока нет
- Speed Control of Universal Motor Using 1 Phase SemiconverterДокумент2 страницыSpeed Control of Universal Motor Using 1 Phase SemiconverterscribsunilОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2-EE042-3-2-IES-DC MotorДокумент55 страницChapter 2-EE042-3-2-IES-DC Motortanaya.s.gadkariОценок пока нет
- Synchronous Machines GuideДокумент48 страницSynchronous Machines GuideMehtab AhmedОценок пока нет
- Synchronous Motors SlidesДокумент55 страницSynchronous Motors SlidesKaye Freyssinet Nermal Abanggan100% (1)
- VaTech-Lai 4-19Документ72 страницыVaTech-Lai 4-19panchalaiОценок пока нет
- Industrial ElectronicsДокумент74 страницыIndustrial ElectronicsAdriano Mercedes Jr. CanoОценок пока нет
- ECE 442 Power Electronics: - TextДокумент22 страницыECE 442 Power Electronics: - TextaylateОценок пока нет
- MODULE-4Документ22 страницыMODULE-4Mohammed ShoaibОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 DC Drives Part2Документ75 страницChapter 1 DC Drives Part2Mohammad MunzirОценок пока нет
- ELE-351 Electrical Energy Conversion Electrical Energy ConversionДокумент16 страницELE-351 Electrical Energy Conversion Electrical Energy Conversionhitesh89Оценок пока нет
- Electronic Logic and Auto Flight InstrumentsДокумент178 страницElectronic Logic and Auto Flight InstrumentsCleber SouzaОценок пока нет
- Basics of A Electric Motor: Dcmotor 1Документ47 страницBasics of A Electric Motor: Dcmotor 1selraj0708Оценок пока нет
- Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis: Chapter ObjectivesДокумент20 страницSinusoidal Steady State Analysis: Chapter ObjectivesWESTLY JUCOОценок пока нет
- PSD Course File 2011-12Документ40 страницPSD Course File 2011-12Sethupathi CmОценок пока нет
- DC Motor DrivesДокумент35 страницDC Motor DrivesMahua ChandaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5-Controlled RectifiersДокумент37 страницChapter 5-Controlled RectifiersBadr Al-SabriОценок пока нет
- Direct - Current Motor Characteristics and ApplicationsДокумент58 страницDirect - Current Motor Characteristics and ApplicationsMaman SomantriОценок пока нет
- Electrical Systems-2Документ38 страницElectrical Systems-2Pegah JanbakhshОценок пока нет
- Module 4 (A) : Controlled RectifiersДокумент22 страницыModule 4 (A) : Controlled RectifiersAishwarya PKamatagiОценок пока нет
- MmuДокумент113 страницMmuSunny SanОценок пока нет
- The Synchronous Generator: 2.1. Synchronizing A Generator To An AC SystemДокумент10 страницThe Synchronous Generator: 2.1. Synchronizing A Generator To An AC SystemsantoshkumarОценок пока нет
- Control System Lab EE-324-FДокумент45 страницControl System Lab EE-324-FDheeraj KumarОценок пока нет
- Dynamic Models: Part C: Electric CircuitsДокумент61 страницаDynamic Models: Part C: Electric CircuitsMuhammadОценок пока нет
- LEC - (DCG P-Operation)Документ22 страницыLEC - (DCG P-Operation)The Youtube TrainОценок пока нет
- PE Chapter 01 Fall 2019Документ51 страницаPE Chapter 01 Fall 2019سید کاظمیОценок пока нет
- Lecture 5: DC Motors: Instructor: Dr. Gleb V. Tcheslavski Contact: Office HoursДокумент105 страницLecture 5: DC Motors: Instructor: Dr. Gleb V. Tcheslavski Contact: Office HoursAnonymous m8oCtJBОценок пока нет
- DC Motor DrivesДокумент53 страницыDC Motor DrivesManoj NОценок пока нет
- 2 Modeling of DC MachinesДокумент23 страницы2 Modeling of DC MachinessubhasishpodderОценок пока нет
- DC Motors Speed RegulationДокумент80 страницDC Motors Speed RegulationZargham RanaОценок пока нет
- Lecture DC MachinesДокумент40 страницLecture DC MachinesgeslincarlombetahОценок пока нет
- Power Electronics 2 Eletrical DrivesДокумент123 страницыPower Electronics 2 Eletrical DrivesNaga Ananth100% (1)
- DC-DC Converter Drives Regenerative and Rheostatic BrakingДокумент37 страницDC-DC Converter Drives Regenerative and Rheostatic BrakingShivachandra ChavanОценок пока нет
- InverterДокумент26 страницInverterGs SuОценок пока нет
- Drives and Controls Lab Manual1 PDFДокумент58 страницDrives and Controls Lab Manual1 PDFDinesh ReddyОценок пока нет
- PE1 - Lect 1-PN Junction Diode PrinciplesДокумент32 страницыPE1 - Lect 1-PN Junction Diode PrinciplesAbdel-aziz SamiОценок пока нет
- DC MotorДокумент47 страницDC MotorArun SaraswathyОценок пока нет
- AlternatorДокумент84 страницыAlternatorVignesh Kumar100% (1)
- Lossofexcitation 130805045350 Phpapp01Документ52 страницыLossofexcitation 130805045350 Phpapp01ahvaz1392bОценок пока нет
- DC Shunt Motor Load Test Simulation & ResultsДокумент6 страницDC Shunt Motor Load Test Simulation & ResultsBaba YagaОценок пока нет
- Brushed DC Motor Speed Control with Encoder and H-BridgeДокумент50 страницBrushed DC Motor Speed Control with Encoder and H-BridgeMohammed Benlamlih100% (7)
- Class DutyДокумент58 страницClass DutyHarsha AnantwarОценок пока нет
- Veículos Elétricos e Híbridos - Power Electronics and MotorsДокумент111 страницVeículos Elétricos e Híbridos - Power Electronics and MotorsBruno VescoviОценок пока нет
- ECE 3101 Industrial Electronics: Chopper DrivesДокумент17 страницECE 3101 Industrial Electronics: Chopper Drives17031 Nazmul HasanОценок пока нет
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1От EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Рейтинг: 2.5 из 5 звезд2.5/5 (3)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2От EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Оценок пока нет
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlОт EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Electrical Correcting Elements in Automatic Control and Regulation CircuitsОт EverandElectrical Correcting Elements in Automatic Control and Regulation CircuitsОценок пока нет
- System TheoryДокумент17 страницSystem TheoryMichael CampbellОценок пока нет
- CMOS Fabrication Technologies and Process Design RulesДокумент14 страницCMOS Fabrication Technologies and Process Design RulesSelva KumarОценок пока нет
- EEE ConferenceДокумент4 страницыEEE ConferenceMichael CampbellОценок пока нет
- TNEB TANGEDCO AE Previous Papers - Civil PDFДокумент21 страницаTNEB TANGEDCO AE Previous Papers - Civil PDFMichael CampbellОценок пока нет
- Bannari Amman Institute of Technology, Sathyamangalam Department of EEEДокумент18 страницBannari Amman Institute of Technology, Sathyamangalam Department of EEEMichael CampbellОценок пока нет
- TNEB TANGEDCO AE Previous Papers - MathematicsДокумент40 страницTNEB TANGEDCO AE Previous Papers - MathematicsMichael CampbellОценок пока нет
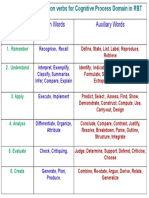
- Auxillary Words - FinalДокумент1 страницаAuxillary Words - FinalMichael CampbellОценок пока нет
- TNEB TANGEDCO AE Previous Papers - Civil PDFДокумент21 страницаTNEB TANGEDCO AE Previous Papers - Civil PDFMichael CampbellОценок пока нет
- 14 Point s1 Eee - DEcДокумент9 страниц14 Point s1 Eee - DEcMichael CampbellОценок пока нет
- Auxillary Words - FinalДокумент1 страницаAuxillary Words - FinalMichael CampbellОценок пока нет
- Opamp CircuitДокумент24 страницыOpamp Circuitlinuxlism100% (1)
- Opamp CircuitДокумент24 страницыOpamp Circuitlinuxlism100% (1)
- DC Characteristics of Opamps ExplainedДокумент23 страницыDC Characteristics of Opamps ExplainedMichael CampbellОценок пока нет
- SOI Process Using Sapphire as an InsulatorДокумент14 страницSOI Process Using Sapphire as an InsulatorMichael CampbellОценок пока нет
- Logic FamiliesДокумент116 страницLogic FamiliesMichael CampbellОценок пока нет
- Thermal Considerations: Introduction To Electric Drives - Module 1Документ12 страницThermal Considerations: Introduction To Electric Drives - Module 1Michael CampbellОценок пока нет
- November 2017 (v1) QP - Paper 4 CIE Chemistry IGCSEДокумент16 страницNovember 2017 (v1) QP - Paper 4 CIE Chemistry IGCSEGhulam Mehar Ali ShahОценок пока нет
- NTS Test 02 (ANS REQ)Документ6 страницNTS Test 02 (ANS REQ)talal hussainОценок пока нет
- ONGC - Internship - Report Please Don't Edit Directly Make A Copy of This FileДокумент65 страницONGC - Internship - Report Please Don't Edit Directly Make A Copy of This File19024 Fenil PatelОценок пока нет
- Republic of The Philippines Cordillera Administrative Region Municipality of TanudanДокумент1 страницаRepublic of The Philippines Cordillera Administrative Region Municipality of Tanudanpablo gayodanОценок пока нет
- All India Test Series (2023-24)Документ22 страницыAll India Test Series (2023-24)Anil KumarОценок пока нет
- Specification: Constant Current Discharge Characteristics: A (25)Документ2 страницыSpecification: Constant Current Discharge Characteristics: A (25)GeorgeОценок пока нет
- X1jet MX Manual PDFДокумент97 страницX1jet MX Manual PDFrithik srivastavaОценок пока нет
- KeirseyДокумент28 страницKeirseyapi-525703700Оценок пока нет
- Numerical Reasoning Practice Test Answers: de Roza Education and Research 2016Документ2 страницыNumerical Reasoning Practice Test Answers: de Roza Education and Research 2016johnОценок пока нет
- DNV Publication ListДокумент14 страницDNV Publication ListmohammadazraiОценок пока нет
- Radio WavesДокумент17 страницRadio WavesStuart Yong100% (1)
- I-WEB - Com.vn Manual 498031910Документ94 страницыI-WEB - Com.vn Manual 498031910IBJSC.comОценок пока нет
- BiochemistryДокумент39 страницBiochemistryapi-290667341Оценок пока нет
- Doctors Qualifications ExplainedДокумент2 страницыDoctors Qualifications ExplainedKaushika KalaiОценок пока нет
- Fever With Rash in Table Form.Документ4 страницыFever With Rash in Table Form.Azizan HannyОценок пока нет
- Construction Safety Plan GuideДокумент13 страницConstruction Safety Plan Guideemmanueloboh92% (24)
- Write An Essay About The First of Hari Raya DayДокумент1 страницаWrite An Essay About The First of Hari Raya DayShan Tzt50% (4)
- Uco Bank Final (Simple Charts)Документ40 страницUco Bank Final (Simple Charts)gopal8726Оценок пока нет
- Jecoliah J. Joel: Brampton, ON Phone: (647) - 980-1712 Email: Skills and AbilitiesДокумент2 страницыJecoliah J. Joel: Brampton, ON Phone: (647) - 980-1712 Email: Skills and Abilitiesapi-347643327Оценок пока нет
- Pride and Prejudice ScriptДокумент25 страницPride and Prejudice ScriptLaura JaszczОценок пока нет
- International Journal of Diabetes ResearchДокумент6 страницInternational Journal of Diabetes ResearchJulenda CintarinovaОценок пока нет
- Elo TecДокумент2 страницыElo TecMimi MimiОценок пока нет
- Raising Indigenous Chickens in UgandaДокумент9 страницRaising Indigenous Chickens in Ugandashemks79% (38)
- Regulatory Updates on Japan's MO169 Medical Device Quality Management OrdinanceДокумент7 страницRegulatory Updates on Japan's MO169 Medical Device Quality Management OrdinanceHong XuyenОценок пока нет
- NMND - Sustainable Food Centre Thesis Crit 4Документ67 страницNMND - Sustainable Food Centre Thesis Crit 4Nik Ahmad Munawwar Nik DinОценок пока нет
- Manual Book HHO Generator Joko Energy 20Документ72 страницыManual Book HHO Generator Joko Energy 20HusamZarourОценок пока нет
- (Vikhroli West) : Raj LegacyДокумент4 страницы(Vikhroli West) : Raj LegacyNEHA NОценок пока нет
- Commuter Students and Involvement Theory: Rowan Digital WorksДокумент67 страницCommuter Students and Involvement Theory: Rowan Digital WorksDark LegendОценок пока нет
- Homemade Litmus Paper ExperimentДокумент3 страницыHomemade Litmus Paper ExperimentEmmanuelle NazarenoОценок пока нет
- Hawaii Hotel Performance by WeekДокумент1 страницаHawaii Hotel Performance by WeekHonolulu Star-AdvertiserОценок пока нет