Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Physical Activity Pyramid
Загружено:
jusang16Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Physical Activity Pyramid
Загружено:
jusang16Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Physical activity
- describes all forms of large muscle movements including sports, dance, games, work, lifestyle activities and exercise for fitness.
Exercise
- physical activity done for a purpose of
getting fit.
1 metabolic equivalent (MET)
- amount of
energy expended at rest.
Health Benefits of Physical Activity
Reduces the risk hypokinetic diseases. Improves cardio-vascular health.
Enhances mental health and function.
Improves strength and muscular endurance. Improves flexibility.
Promotes greater lean body mass and less
Promotes better bone development. Reduces the effect of acquired aging.
Improves physical appearance and gives opportunity for
successful experience and social interaction. Promotes resistance to fatigue. Improves wellness.
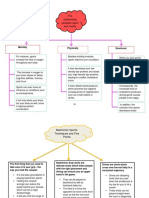
Physical activity pyramid classifies activities by types and
associated benefits.
Level 1- Lifestyle physical activity is encouraged as part of
everyday living and can contribute significantly to good health, wellness and fitness.
Level 2- Active aerobics and sports are activities that can be performed for relatively long period of time and good for cardiovascular fitness. Level 3- Flexibility and muscle fitness activities are planned activities to develop flexibility, muscular strength and endurance. Level 4- Long periods of inactivity should be minimized.
Principles of Physical Activity
Overload Principle
- that one must perform physical activity greater than normal amounts (overload) to get improvement in physical fitness or health benefits.
Principle of Progression - indicates the need to gradually increase overload to
achieve optimal fitness.
Principle of Specificity - indicates the need for a specific type of exercise to
improve each fitness component or fitness of a specific part of the body.
Principle of Reversibility - indicates the disuse or inactivity results in loss of benefits achieved as a result of overload. Principle of Diminished Return - the more benefits one gain as a result of inactivity, the harder the additional benefits to achieve.
Principle of Rest and Recovery - that indicates that adequate rest is needed to allow the body to adapt and recover from exercise.
Principle of Individuality indicates that overload provides unique benefits to each individual based on the unique characteristics of that person.
The FITT Formula
- A formula used to describe the frequency, intensity, and the
length of the time for physical activity to produce benefits. (When FITT is used, the second T refers to the type of physical activity). Frequency - physical activity must be performed regularly to be effective - how often? Intensity - physical activity must be intense enough to require more exertion (overload) than normal to produce benefits. - how hard?
Time - physical activity must be done for an adequate length of time to be effective. - how long? Type - the mode of physical activity. - What?
Вам также может понравиться
- Physical Education Copy 2Документ47 страницPhysical Education Copy 2Praise Buenaflor100% (4)
- PE and Health - Grade 11Документ112 страницPE and Health - Grade 11Joseph P. CagconОценок пока нет
- Physical Education 2: Recreational Activities: Prepared byДокумент7 страницPhysical Education 2: Recreational Activities: Prepared byJuvy Arabos FerreonОценок пока нет
- Physical Fitness Test Score CardДокумент1 страницаPhysical Fitness Test Score CardJohn Louis GerianОценок пока нет
- Organization and Management DefinedДокумент168 страницOrganization and Management DefinedElla Marie MonteОценок пока нет
- Self ConceptДокумент10 страницSelf ConceptFèdòrá MischkáОценок пока нет
- Bp22 - Distinction Between Estafa and BP 22Документ1 страницаBp22 - Distinction Between Estafa and BP 22jusang16Оценок пока нет
- Benefits On Physical ActivityДокумент18 страницBenefits On Physical ActivitySueBatОценок пока нет
- Hizon Notes - Land Titles & DeedsДокумент62 страницыHizon Notes - Land Titles & Deedsjusang16100% (4)
- Emotional Quotient Essay For Emotional Intelligence Final ProjectДокумент9 страницEmotional Quotient Essay For Emotional Intelligence Final ProjectSheffield Maravilla100% (1)
- Reinforcement and Extinction of Operant BehaviorДокумент22 страницыReinforcement and Extinction of Operant BehaviorJazmin GarcèsОценок пока нет
- Business Personal StatementДокумент2 страницыBusiness Personal StatementBojan Ivanović50% (2)
- Assessment Rubric For Powerpoint Presentations Beginning Developing Accomplish Ed Exemplary PointsДокумент4 страницыAssessment Rubric For Powerpoint Presentations Beginning Developing Accomplish Ed Exemplary PointsyatzirigОценок пока нет
- Cartooning Unit Plan Grade 9Документ12 страницCartooning Unit Plan Grade 9api-242221534Оценок пока нет
- BP22 bouncing checks law overviewДокумент9 страницBP22 bouncing checks law overviewjusang16100% (1)
- BP22 bouncing checks law overviewДокумент9 страницBP22 bouncing checks law overviewjusang16100% (1)
- Health Optimizing Physical Education (Hope) 1 Grade 11 Exercise For FitnessДокумент17 страницHealth Optimizing Physical Education (Hope) 1 Grade 11 Exercise For FitnessPaul Francis LagmanОценок пока нет
- Lesson 1 Safety Practices in Sports and ExerciseДокумент17 страницLesson 1 Safety Practices in Sports and ExerciseMr. CRAFTОценок пока нет
- (CN) Republic v. Estonilo 7Документ7 страниц(CN) Republic v. Estonilo 7jusang16Оценок пока нет
- Nine Steps From Idea To Story 5Документ43 страницыNine Steps From Idea To Story 5Jom Jean100% (1)
- Gymnastics: Brief History of GymnasticsДокумент50 страницGymnastics: Brief History of GymnasticsHillary Dwainee R. LorenzoОценок пока нет
- Abellana vs. People, Et Al., Aug. 17, 2011 (Case)Документ5 страницAbellana vs. People, Et Al., Aug. 17, 2011 (Case)jusang16Оценок пока нет
- Pe Grade 12 1st Sem Unit 1Документ32 страницыPe Grade 12 1st Sem Unit 1sherwin dela cruzОценок пока нет
- Letter To The Editor About Animal Cruelty Prevention MonthДокумент1 страницаLetter To The Editor About Animal Cruelty Prevention MonthKayla EllsworthОценок пока нет
- Brief History and Nature of DanceДокумент15 страницBrief History and Nature of DanceSarah GanganОценок пока нет
- Softball LectureДокумент7 страницSoftball LectureDanica Ching100% (1)
- MMWДокумент10 страницMMWKim LiatОценок пока нет
- PHE Lesson 3Документ6 страницPHE Lesson 3Via Mae VirtousaОценок пока нет
- Lesson 2common Sports InjuriesДокумент15 страницLesson 2common Sports InjuriesMr. CRAFTОценок пока нет
- Recreation: High and Low ImpactДокумент11 страницRecreation: High and Low ImpactLei Dulay100% (1)
- Principles of ExerciseДокумент11 страницPrinciples of ExerciseJudane Delos ReyesОценок пока нет
- Fitness GoalsДокумент19 страницFitness GoalsFernandez AnjoОценок пока нет
- IDEA Mandates Adapted Physical EducationДокумент6 страницIDEA Mandates Adapted Physical EducationSchool Matters100% (1)
- HOPE 1 Module 1Документ9 страницHOPE 1 Module 1Lordy Joy Geralde CalimpusanОценок пока нет
- Recreation, Physical Fitness & WellnessДокумент10 страницRecreation, Physical Fitness & WellnessBianca GeagoniaОценок пока нет
- Self-Concept, Self-Esteem, and Exercise: A 39-Character GuideДокумент14 страницSelf-Concept, Self-Esteem, and Exercise: A 39-Character Guidemaharajsaini4229Оценок пока нет
- Recreational Games: Pe 12 - H.O.P.E. - Recreation Fo R LifeДокумент16 страницRecreational Games: Pe 12 - H.O.P.E. - Recreation Fo R LifeDomz DomanicoОценок пока нет
- Always Be Yourself, Express Yourself, Have Faith in Yourself, Do Not Go Out and Look For A Successful Personality and Duplicate It"Документ2 страницыAlways Be Yourself, Express Yourself, Have Faith in Yourself, Do Not Go Out and Look For A Successful Personality and Duplicate It"Rufo Daskeo Jr.Оценок пока нет
- The Lifelong Benefits of Physical EducationДокумент33 страницыThe Lifelong Benefits of Physical EducationMichael EncarnacionОценок пока нет
- Let's Get Started: Answer SheetДокумент6 страницLet's Get Started: Answer SheetJoseph Angelo SayОценок пока нет
- GymnasticsДокумент32 страницыGymnasticsKimberly Gayle ChingОценок пока нет
- Homeroom Guidance G10 Q1M3 PDFДокумент28 страницHomeroom Guidance G10 Q1M3 PDFRAINIER DE JESUS100% (1)
- Health, Stress and Worklife Balance Pogram. - Notes - RДокумент58 страницHealth, Stress and Worklife Balance Pogram. - Notes - RPrasad KulkarniОценок пока нет
- Core Training and Body Movement FundamentalsДокумент4 страницыCore Training and Body Movement FundamentalsMariefe Amada100% (1)
- Module I (Geec 107)Документ57 страницModule I (Geec 107)Marooning ManОценок пока нет
- Hagen's Theory of EntrepreneurshipДокумент7 страницHagen's Theory of EntrepreneurshipSoraYoku ch. /空欲Оценок пока нет
- The Power of Personal DeclarationsДокумент2 страницыThe Power of Personal DeclarationspaulОценок пока нет
- FITT Principles of TrainingДокумент3 страницыFITT Principles of TrainingXiscoОценок пока нет
- Physical Education: A Foundation for Lifelong WellnessДокумент12 страницPhysical Education: A Foundation for Lifelong WellnessPanJan BalОценок пока нет
- Physical Fitness 1Документ17 страницPhysical Fitness 1Shene Rvi Ann SarmientoОценок пока нет
- FittДокумент12 страницFittreynaldo casipleОценок пока нет
- Instructional Module: Republic of The Philippines Nueva Vizcaya State University Bayombong, Nueva VizcayaДокумент7 страницInstructional Module: Republic of The Philippines Nueva Vizcaya State University Bayombong, Nueva VizcayaAkemi YeonОценок пока нет
- The Relationship Between Sport and Health: Mentally Physically EmotionalДокумент2 страницыThe Relationship Between Sport and Health: Mentally Physically EmotionalNur Aishah Sazali100% (1)
- Physical Fitness TestДокумент8 страницPhysical Fitness Testalaskador03Оценок пока нет
- Overview and Nature of DataДокумент41 страницаOverview and Nature of DataMiguel Xerxes VillacrucisОценок пока нет
- Math language guideДокумент31 страницаMath language guideDJ Free MusicОценок пока нет
- P. E. and Health ReportДокумент20 страницP. E. and Health ReportLESSLY ABRENCILLOОценок пока нет
- Fitness Program Crit BДокумент3 страницыFitness Program Crit Bapi-361656924Оценок пока нет
- It Is Normal For The Muscles To Increase in Size As A Result of Resistance TrainingДокумент1 страницаIt Is Normal For The Muscles To Increase in Size As A Result of Resistance TrainingMary Ann CamachoОценок пока нет
- Learning Activity Sheet Las On Hope 3Документ8 страницLearning Activity Sheet Las On Hope 3thyroneОценок пока нет
- How a Society is OrganizedДокумент13 страницHow a Society is Organizedlove, kendrick100% (1)
- Applied Economics: Porter's Five Forces AnalysisДокумент12 страницApplied Economics: Porter's Five Forces AnalysisYen SantosОценок пока нет
- Basketball DiscussionДокумент34 страницыBasketball DiscussionJadeal28Оценок пока нет
- Fuel For PerformanceДокумент8 страницFuel For PerformanceRasell de LunaОценок пока нет
- Being Healthy and Fit in Simple Terms Means Taking Good Care of The Body PDFДокумент3 страницыBeing Healthy and Fit in Simple Terms Means Taking Good Care of The Body PDFolympianbestОценок пока нет
- PATHFIT 1 Module 1 FinalДокумент18 страницPATHFIT 1 Module 1 FinalKim Yessamin Madarcos100% (1)
- Pe 01 Week 2Документ4 страницыPe 01 Week 2Miguel Sebastian TorresesОценок пока нет
- Physical Education and HealthДокумент9 страницPhysical Education and HealthcdainielpgОценок пока нет
- Health Optimizing Physical Education 4: 3Rd Quarter: (Duration: Weeks 1-2)Документ13 страницHealth Optimizing Physical Education 4: 3Rd Quarter: (Duration: Weeks 1-2)Zedy GullesОценок пока нет
- PDF 20220909 090326 0000Документ26 страницPDF 20220909 090326 0000Alliyah vannsОценок пока нет
- Physical Fitness Short Note Final (Autosaved)Документ139 страницPhysical Fitness Short Note Final (Autosaved)Mullisaa Sabaa HimuureeОценок пока нет
- Simon v. CHR, GR 100150, Jan.5, 1994Документ17 страницSimon v. CHR, GR 100150, Jan.5, 1994jusang16Оценок пока нет
- Oposa V FactoranДокумент22 страницыOposa V FactorantheresagriggsОценок пока нет
- PNB v. Tan Ong Zse 5Документ4 страницыPNB v. Tan Ong Zse 5jusang16Оценок пока нет
- Baldoza vs. DimaanoДокумент7 страницBaldoza vs. DimaanoClarisse Ann MirandaОценок пока нет
- Ledesma Vs Municipality of Iloilo G.R. No. 26337 December 17, 1926Документ3 страницыLedesma Vs Municipality of Iloilo G.R. No. 26337 December 17, 1926Zack SeiferОценок пока нет
- Siasat v. IACДокумент5 страницSiasat v. IACjusang16Оценок пока нет
- (CN) Yngson v. Sec. of Agriculture and Nat. Res. 5Документ7 страниц(CN) Yngson v. Sec. of Agriculture and Nat. Res. 5jusang16Оценок пока нет
- Ledesma Vs Municipality of Iloilo G.R. No. 26337 December 17, 1926Документ3 страницыLedesma Vs Municipality of Iloilo G.R. No. 26337 December 17, 1926Zack SeiferОценок пока нет
- Angeles v. PNRДокумент5 страницAngeles v. PNRjusang16Оценок пока нет
- PNB v. Tan Ong Zse 5Документ6 страницPNB v. Tan Ong Zse 5jusang16Оценок пока нет
- (CN) Bureau of Forestry v. CA and Gallo 4Документ5 страниц(CN) Bureau of Forestry v. CA and Gallo 4jusang16Оценок пока нет
- RP Vs EnriquezДокумент3 страницыRP Vs EnriqueznazhОценок пока нет
- Doles v. AngelesДокумент10 страницDoles v. Angelesjusang16Оценок пока нет
- Doles v. AngelesДокумент10 страницDoles v. Angelesjusang16Оценок пока нет
- Doles v. AngelesДокумент10 страницDoles v. Angelesjusang16Оценок пока нет
- Types of Employment in The PhilippinesДокумент2 страницыTypes of Employment in The Philippinesschating2Оценок пока нет
- Summary of Benefits PDFДокумент2 страницыSummary of Benefits PDFbluepriscyОценок пока нет
- Criminal Law Guide on Bouncing Checks & Libel PenaltiesДокумент5 страницCriminal Law Guide on Bouncing Checks & Libel Penaltiesjusang16Оценок пока нет
- Phil. Com v. Globe TelecomДокумент9 страницPhil. Com v. Globe Telecomjusang16Оценок пока нет
- Employer Defenses For Penalizing or Terminating EmployeesДокумент1 страницаEmployer Defenses For Penalizing or Terminating Employeesjusang16Оценок пока нет
- Types of Employment in The PhilippinesДокумент2 страницыTypes of Employment in The Philippinesschating2Оценок пока нет
- Legal Interest Rules of ApplicationДокумент3 страницыLegal Interest Rules of Applicationjusang16Оценок пока нет
- Valenzuela Vs People of The PhilДокумент15 страницValenzuela Vs People of The PhilNiknik CaguironОценок пока нет
- People of The Philippines, Appellee, vs. Arnulfo Orande Y Chavez, AppellantДокумент8 страницPeople of The Philippines, Appellee, vs. Arnulfo Orande Y Chavez, AppellantFredamoraОценок пока нет
- Nottingham Trent University Course SpecificationДокумент7 страницNottingham Trent University Course Specificationariff.arifinОценок пока нет
- Resume and Cover LetterДокумент4 страницыResume and Cover Letterapi-281290606Оценок пока нет
- Use Your Shoe!: Suggested Grade Range: 6-8 Approximate Time: 2 Hours State of California Content StandardsДокумент12 страницUse Your Shoe!: Suggested Grade Range: 6-8 Approximate Time: 2 Hours State of California Content StandardsGlenda HernandezОценок пока нет
- Teacher Training in Pakistan: Overview of Challenges and Their Suggested SolutionsДокумент10 страницTeacher Training in Pakistan: Overview of Challenges and Their Suggested SolutionsNaem AhmadОценок пока нет
- CPD Guideline ManualДокумент58 страницCPD Guideline ManualDawood ShaikhОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan-MI Maarif My BedroomДокумент7 страницLesson Plan-MI Maarif My BedroomAmy Amelia MulyaОценок пока нет
- Theresa Farrell 20120529170641Документ73 страницыTheresa Farrell 20120529170641Anirban RoyОценок пока нет
- Bridge Month Programme English (R2)_240402_205400Документ17 страницBridge Month Programme English (R2)_240402_205400shivamruni324Оценок пока нет
- Note 1 - LAM, ArchitectДокумент29 страницNote 1 - LAM, Architectn_euda100% (1)
- Authentic Assessment For English Language Learners: Nancy FooteДокумент3 страницыAuthentic Assessment For English Language Learners: Nancy FooteBibiana LiewОценок пока нет
- Past Tense PronunciationДокумент2 страницыPast Tense PronunciationStefania PerezОценок пока нет
- Web Systems Subject OutlineДокумент11 страницWeb Systems Subject OutlineJoshОценок пока нет
- A Govt. of India EnterpriseДокумент11 страницA Govt. of India Enterprisebabakumaresh1982Оценок пока нет
- Coursera MHJLW6K4S2TGДокумент1 страницаCoursera MHJLW6K4S2TGCanadian Affiliate Marketing UniversityОценок пока нет
- Department of Education: Grade & Section Advanced StrugllingДокумент4 страницыDepartment of Education: Grade & Section Advanced StrugllingEvangeline San JoseОценок пока нет
- Julie Ann NocheДокумент17 страницJulie Ann NocheMargareth De VillaОценок пока нет
- Stem Activity Lesson PlanДокумент3 страницыStem Activity Lesson Planapi-579419696Оценок пока нет
- Eng 149 - Language Learning Materials Development HandoutДокумент45 страницEng 149 - Language Learning Materials Development HandoutHanifa PaloОценок пока нет
- Bagbag Ii, Rosario, Cavite: Surname Given Name M.IДокумент8 страницBagbag Ii, Rosario, Cavite: Surname Given Name M.IBonRobertОценок пока нет
- Orchard Growers Success StoriesДокумент3 страницыOrchard Growers Success StoriesBrendan Troy JavierОценок пока нет
- Director Human Resources Management in Northern VA Resume Jessica ErnstДокумент3 страницыDirector Human Resources Management in Northern VA Resume Jessica ErnstJessicaErnst1Оценок пока нет
- Literary AnalysisДокумент3 страницыLiterary Analysisapi-298524875Оценок пока нет
- 3rd Quarter ToolkitДокумент10 страниц3rd Quarter ToolkitDimple BolotaoloОценок пока нет
- Passionate self-improver shaped by perseveranceДокумент3 страницыPassionate self-improver shaped by perseverancejasleensilkОценок пока нет
- RESUMEДокумент2 страницыRESUMERyan Jay MaataОценок пока нет