Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Kidney Quiz - Path Exam 3
Загружено:
tatti999Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Kidney Quiz - Path Exam 3
Загружено:
tatti999Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
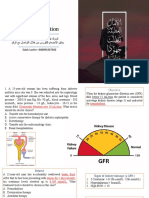
1. An adult patient has a serum urea nitrogen of 50 mg/dL with creatinine 5.8 mg/dL.
The presence of which of the following urinalysis findings is most indicative of glomerulonephritis as a cause for these findings: A. Oval fat bodies B. Proteinuria C. Red blood cell casts D. Broad waxy casts E. White blood cell casts
2. A 32-year-old woman has had a cough for several days along with increasing weakness. She is surprised by the appearance of a small amount of red-tinged sputum. Over the next day she notes some small nodular purple lesions beneath the skin of her lower extremities. There are no significant findings on physical examination. Her chest x-ray shows bilateral interstitial markings but no areas of consolidation and no masses. A urinalysis reveals microscopic hematuria and proteinuria. Her antinuclear antibody test is negative, but she has antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies. A renal biopsy shows a necrotizing glomerulonephritis without immune deposition. These findings are most characteristic for which of the following diseases: : A. Diffuse scleroderma B. Systemic lupus erythematosus C. Post-infectious glomerulonephritis D. Microscopic polyarteritis E. Hemolytic-uremic syndrome
3. A 40-year-old man has the sudden onset of severe lower abdominal pain one evening. He notes the presence of bloody urine. Physical examination reveals no abdominal tenderness or masses, and bowel sounds are active. An abdominal CT scan reveals a small bright rounded object in the region of the left ureter. The underlying cause for these findings is most likely to be: A. Hypercalciuria B. Hyperparathyroidism C. Urinary tract infection D. Gout E. Cystinosis
4. A 57-year-old man has been bothered by arthritis. As a consequence, without reading the labels on over-the-counter medications, he has consumed large quantities (greater than 3 gm per year) of analgesics (aspirin, phenacitin, acetaminophen) for the past 10 years. He now has chronic renal failure. Which of the following is the most likely pathologic finding in this patient A. Acute tubular necrosis B. Transitional cell carcinoma C. Chronic interstitial nephritis D. Diffuse glomerulosclerosis E. Urinary tract lithiasis
5. If the foot processes are effaced in minimal change disease, then why do serum proteins leak into the urine more readily: A. Fenestrations in endothelial cells are enlarged. B. The anionic charge barrier is lost. C. The basement membrane is attenuated. D. Type IV collagen is lost. E. Glomerular filtration pressure is increased.
6. A 61-year-old man with a history of diabetes mellitus has been on hemodialysis for the past 12 years. During that time he has continued working and has had no major illnesses. Which of the following findings most likely would be present in his kidneys as a consequence of the chronic hemodialysis A. Multiple cystic dilations of medullary collecting ducts B. Normal left kidney but enlarged right right kidney with variably-sized cysts C. Markedly enlarged kidneys with multiple cysts along with a polycystic liver D. Bilaterally enlarged cystic kidneys along with congenital hepatic fibrosis E. Multiple 1 to 2 cm cortical and medullary cysts within small kidneys bilaterally
7. The microscopic findings at autopsy of slightly small kidneys with a granular surface and the microscopic appearance of scattered hyalinized glomeruli, interstitial fibrosis with focal tubular atrophy, and arteriolar thickening in a 75-year-old woman with normal renal function most strongly suggests: A. Nodular glomerulosclerosis B. Malignant nephrosclerosis C. Analgesic abuse nephropathy D. Benign nephrosclerosis E. Chronic pyelonephritis
8. A 26-year-old African-American man has had a history of painful abdominal crises. He has a hemoglobin electrophoresis performed that shows 96% Hgb S, 3% Hgb A2, and 1% Hgb F. Which of the following findings is LEAST likely to be present: A. Decreased renal concentrating ability B. Heamaturia C. Reduced viscosity of blood D. Renal infarcts E. Papillary necrosis
9. A 28-year-old man has increasing malaise with myalgias and arthralgias for the past month. He notes a lot of foam in the toilet when he urinates. He is developing peripheral edema. A urinalysis shows: sp gr 1.012, pH 6, 4+ protein, 1+ blood, and no glucose or ketones. he has a positive antinuclear antibody and negative antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody. He receives a course of corticosteroid therapy and does not improve. A renal biopsy is performed and shows increased mesangial cells and matrix, with reduplication of basal lamina seen by electron microscopy. There is granular deposition of C3 and IgG on immunofluoresence. Which of the following diseases is he most likely to have: : A. Nodular and diffuse glomerulosclerosis B. Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis C. Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis D. Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis E. Minimal change disease
10. A 6-year-old girl has had dysuria with multiple bacterial urinary tract infections diagnosed over the past 2 years. There are no abnormal findings on physical examination. A urinalysis reveals increased WBCs but no hematuria, proteinuria, or glucosuria. An abdominal ultrasound reveals that the kidneys are of normal size and consistency, but that there is mild hydroureter on the right. Voiding cystourethrography reveals obstruction on the right at the level of the bladder. Which of the following conditions is most likely to be present: A. Transitional cell carcinoma B. Abnormal ureteral insertion (Vesicoureteral reflex) C. Schistosomiasis D. Ureteritis cystica E. Ureteral calculus
11. A 60-year-old woman has anemia, vertebral bone
pain, and sudden onset of renal failure. A renal biopsy shows pink, amorphous, irregular glomerular deposits which by immunohistochemical staining contain only irregular fibrils in a beta-pleated sheet. She has a serum urea nitrogen of 48 mg/dL, creatinine 2.8 mg/dL, total protein 8.5 g/dL, and albumin 3.9 g/dL. The most likely diagnosis is A. Multiple myeloma B. Systemic lupus erythematosus C. Metastatic breast carcinoma D. Diabetes mellitus E. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
12. A 51-year-old woman has had multiple urinary tract infections for most of her adult life. She does not have any other significant medical problems. A physical examination reveals no abnormal findings. A variety of bacterial organisms, including Streptococcus, Proteus, and Escherichia have been cultured, and the infections have responded to antibiotic therapy. An intravenous urogram and voiding cystourethrogram have shown no evidence for obstruction. Which of the following long-term renal complications is most likely to develop in this patient: A. Polycystic change B. Acute pyelonephritis C. Transitional cell carcinoma D. Obstructive nephropathy E. Benign nephrosclerosis
13. An 11-year-old boy was seen by the family physician because of increasing lethargy. Urinalysis revealed 3+ proteinuria, found to be due to both albumin and transferrins, but no glucosuria or blood was present. A 24 hour urine protein was 2.1 gm. His serum complement C3 and C4 were normal. His antinuclear antibody test was negative. The child did improve by corticosteroid therapy. The most likely diagnosis is: A. Membranous glomerulonephritis B. Minimal change disease (MCD) C. Systemic lupus erythematosus D. Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis E. Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis
14. A 40-year-old man comes to the emergency room early in the morning because of excruciating pain in the lower abdomen. The pain has come in waves for several hours. A urinalysis reveals hematuria, but no proteinuria, glucosuria, or WBCs. The most likely underlying problem in this setting is: A. Transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder B. Prostatic hyperplasia with obstructive uropathy C. Idiopathic hypercalciuria with calcium oxalate stone D. Acute pyelonephritis with staghorn calculus E. Gout with uric acid stone
15. A 46-year-old African-American man died suddenly, and the medical examiner investigated. She found a large right basal ganglia hemorrhage that resulted from arteriosclerosis of small cerebral arterial branches. Which of the following findings was most likely to have been present in his kidneys: A. Fibromuscular dysplasia B. Vasculitis with mononuclear cell infiltrates C. A linear pattern of glomerular capillary IgG deposition by immunofluorescence D. Arteriolar fibrinoid necrosis with microhemorrhages E. Nodular glomerulosclerosis
Вам также может понравиться
- Urinary Tract ReviewДокумент12 страницUrinary Tract ReviewJessica MooreОценок пока нет
- KGMC BLOCK L 2023. Revisedd (Follow Yellow)Документ29 страницKGMC BLOCK L 2023. Revisedd (Follow Yellow)noorОценок пока нет
- Please Select The One BEST Answer.: Gastrointestinal Pathophysiology Exam 2005 Tufts University School of MedicineДокумент8 страницPlease Select The One BEST Answer.: Gastrointestinal Pathophysiology Exam 2005 Tufts University School of MedicineJafer DetamoОценок пока нет
- Medicine/Medicine 6th Year 2016Документ31 страницаMedicine/Medicine 6th Year 2016abmad t45Оценок пока нет
- Pathology BДокумент5 страницPathology Bttdjhg2p6kОценок пока нет
- 2014 - GUS SystemДокумент44 страницы2014 - GUS SystemBea AnabellaОценок пока нет
- SP Pathology MCQДокумент17 страницSP Pathology MCQMuhammad Bilal80% (5)
- Heme QuestionsДокумент28 страницHeme QuestionsChenthanKrishОценок пока нет
- Block 2Документ14 страницBlock 2PaolaОценок пока нет
- MCQs Glomerular Injury Pathogenesis, Nephritic SyndromeДокумент5 страницMCQs Glomerular Injury Pathogenesis, Nephritic SyndromeIshita SinghОценок пока нет
- ProvimiДокумент13 страницProvimialbert lukaОценок пока нет
- 2019 Explanation k2Документ261 страница2019 Explanation k2berdaderagaОценок пока нет
- Musawi 25Документ22 страницыMusawi 25Full MarksОценок пока нет
- Pathology Exam AnswersДокумент14 страницPathology Exam AnswersRana ElОценок пока нет
- Case Studies - MIC3002Документ28 страницCase Studies - MIC300217206404 STUDENTОценок пока нет
- MCQsДокумент21 страницаMCQsZweОценок пока нет
- Pathology of Hemodynamic Disorders 1 and 2 Practice Questions-1Документ26 страницPathology of Hemodynamic Disorders 1 and 2 Practice Questions-1JCОценок пока нет
- Utah KidneyДокумент16 страницUtah KidneyChristineGonzalesОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 QuizДокумент11 страницChapter 1 QuizROHITОценок пока нет
- Renal PediatricДокумент48 страницRenal PediatricEslam R. Almassri100% (1)
- Usmle OncologyДокумент41 страницаUsmle Oncologypremiumapxtodoctorforbsavt2467Оценок пока нет
- Swammy Plab 1 MockДокумент32 страницыSwammy Plab 1 Mockfreelancer08Оценок пока нет
- Tropical MCQS: C. Visceral LeishmaniasisДокумент29 страницTropical MCQS: C. Visceral Leishmaniasisساره ابوالقاسمОценок пока нет
- Heme Quiz 1-3Документ14 страницHeme Quiz 1-3Søren KierkegaardОценок пока нет
- CASE 25: Acute PancreatitisДокумент3 страницыCASE 25: Acute PancreatitisJeanine Angela CuliliОценок пока нет
- 5th Year 112 PediatricsДокумент12 страниц5th Year 112 PediatricsAmjad A. Amir100% (2)
- Soal Compilee Hemato-Oncology FK UPH 2014Документ23 страницыSoal Compilee Hemato-Oncology FK UPH 2014CitraОценок пока нет
- C. Liver Function Test (Child Pugh Criteria-To See Albumin and Bilirubin)Документ26 страницC. Liver Function Test (Child Pugh Criteria-To See Albumin and Bilirubin)Nadhirah ZulkifliОценок пока нет
- Hema 1Документ23 страницыHema 1Labshare MDCОценок пока нет
- RENALMCQДокумент5 страницRENALMCQkrishnadoctor1Оценок пока нет
- NBME 1 RatioДокумент87 страницNBME 1 RatioBugs Caslib100% (1)
- NBME 2 Block 1-4 EditedДокумент88 страницNBME 2 Block 1-4 EditedMayank Gogna100% (2)
- Med PDFДокумент16 страницMed PDFIbn SinaОценок пока нет
- mcq renalفاطمه جاسم محمدДокумент4 страницыmcq renalفاطمه جاسم محمدFatema Al-KananiОценок пока нет
- 03 GRAT - Blood Vessel DisordersДокумент4 страницы03 GRAT - Blood Vessel DisordersjuanОценок пока нет
- Review Mcqs For 2016 Systemic PathologyДокумент8 страницReview Mcqs For 2016 Systemic PathologySameer100% (1)
- 500 SBA Gen SystemicДокумент27 страниц500 SBA Gen Systemicnob2011nob50% (2)
- RENAL and Reproductive Systems - Q & AДокумент13 страницRENAL and Reproductive Systems - Q & AThulasi tootsieОценок пока нет
- Blood Vessels QuizДокумент28 страницBlood Vessels Quiztatti999Оценок пока нет
- Afrm Sample Questions Module 1-19-11 2012Документ16 страницAfrm Sample Questions Module 1-19-11 2012Muvenn KannanОценок пока нет
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma Causing Severe.1057Документ1 страницаHepatocellular Carcinoma Causing Severe.1057Vardan KocharОценок пока нет
- แนวข้อสอบ National license - Hematology PDFДокумент7 страницแนวข้อสอบ National license - Hematology PDFTanawat SingboonОценок пока нет
- NBME 2 Block 1-4 All IncludedДокумент112 страницNBME 2 Block 1-4 All Included3592648Оценок пока нет
- NBME 2 BlocksДокумент112 страницNBME 2 Blocks3592648Оценок пока нет
- Haematology Paper A MCQs Jul 2017 BatchДокумент9 страницHaematology Paper A MCQs Jul 2017 Batchjoyim75843Оценок пока нет
- Renal Path Review 2Документ11 страницRenal Path Review 2Sundar RamanathanОценок пока нет
- Model Questions For Annual 2009: Special PathologyДокумент3 страницыModel Questions For Annual 2009: Special PathologyAbid HussainОценок пока нет
- Hematology FinalДокумент14 страницHematology FinalTop Music100% (1)
- Nbme 2 Block 1-4Документ112 страницNbme 2 Block 1-4lk0704Оценок пока нет
- GI and Hemagology & Oncology QuizДокумент41 страницаGI and Hemagology & Oncology Quizwalt65Оценок пока нет
- Boron Intrebari Pentru Evaluare enДокумент42 страницыBoron Intrebari Pentru Evaluare enAna0% (1)
- Nbme 2Документ98 страницNbme 2oskie7Оценок пока нет
- Medicine/Medicine 4th Year 2016Документ25 страницMedicine/Medicine 4th Year 2016abmad t45Оценок пока нет
- Materi Ujian UroДокумент32 страницыMateri Ujian Urodidit_fajar_NОценок пока нет
- Renal Path Q'sДокумент20 страницRenal Path Q'skank_sОценок пока нет
- Final Year New MCQsДокумент2 страницыFinal Year New MCQsAbira KhanОценок пока нет
- A Gastro Tahun Lalu - Tahun IniДокумент12 страницA Gastro Tahun Lalu - Tahun IniDella Tamara RindasiwiОценок пока нет
- Ophtalmology Record Acute Glaucoma: Examiner: DR. Dr. Gilbert W. Simanjuntak, SP.M (K)Документ6 страницOphtalmology Record Acute Glaucoma: Examiner: DR. Dr. Gilbert W. Simanjuntak, SP.M (K)Rashellya RasyidaОценок пока нет
- Uremic Encephalopathy-ReviewДокумент30 страницUremic Encephalopathy-ReviewFeddyFebriyantoManurung100% (1)
- AMCA Study Guide PhlebotomyДокумент34 страницыAMCA Study Guide Phlebotomyayoonia100% (1)
- Annexure IДокумент372 страницыAnnexure IsfarithaОценок пока нет
- Voluntary Blood DonationДокумент8 страницVoluntary Blood DonationJessa CanonigoОценок пока нет
- LMC ICD-10 PowerPointДокумент77 страницLMC ICD-10 PowerPointNicholas HenryОценок пока нет
- The Scoring Clinical Index For OnychomycosisДокумент4 страницыThe Scoring Clinical Index For OnychomycosisPatricia Avalos C.Оценок пока нет
- Patient Profile-C in The WДокумент17 страницPatient Profile-C in The WPj TignimanОценок пока нет
- USMLE Step 3 Sample Questions For The Test PDFДокумент69 страницUSMLE Step 3 Sample Questions For The Test PDFmarkОценок пока нет
- Breeder Hatchery Bio SecurityДокумент43 страницыBreeder Hatchery Bio SecurityAzam RafiqueОценок пока нет
- Goris PDFДокумент24 страницыGoris PDFAndrew WongОценок пока нет
- Anger Management Best Practice HandbookДокумент122 страницыAnger Management Best Practice HandbookRomanic Mihaela100% (6)
- Recommendations From The Guideline For Pcos-NoprintДокумент16 страницRecommendations From The Guideline For Pcos-NoprintpopasorinemilianОценок пока нет
- Arixtra: (Fondaparinux Sodium) InjectionДокумент26 страницArixtra: (Fondaparinux Sodium) InjectionTri Purma SariОценок пока нет
- Green Power DistributionДокумент30 страницGreen Power DistributionRazvan MarcuОценок пока нет
- Hizon, DrugsДокумент4 страницыHizon, DrugsDan HizonОценок пока нет
- AntibioticsДокумент53 страницыAntibioticsMaheen IdreesОценок пока нет
- Endocrine Methodologies Chapter 4 9-1.2012 PDFДокумент26 страницEndocrine Methodologies Chapter 4 9-1.2012 PDFLeora LiОценок пока нет
- Psycho-Oncology - The 6 Phases of Cancer EbookДокумент101 страницаPsycho-Oncology - The 6 Phases of Cancer EbookAndré Amorim100% (2)
- Treatment and Prognosis of IgA Nephropathy - UpToDate PDFДокумент52 страницыTreatment and Prognosis of IgA Nephropathy - UpToDate PDFDerian Yamil Bustamante AngelОценок пока нет
- Basic Theories of Traditional Chinese Medicine PDFДокумент194 страницыBasic Theories of Traditional Chinese Medicine PDFElanghovan Arumugam100% (31)
- CestodesДокумент39 страницCestodesNachiket Vijay PotdarОценок пока нет
- The Pathophysiology of Otosclerosis: Review of Current ResearchДокумент6 страницThe Pathophysiology of Otosclerosis: Review of Current ResearchFelipeAsenjoÁlvarezОценок пока нет
- OPD Schedule (November 2021)Документ32 страницыOPD Schedule (November 2021)Ajay DherwaniОценок пока нет
- 2022 - ACLS - Handbook 1 30 13 30 PDFДокумент18 страниц2022 - ACLS - Handbook 1 30 13 30 PDFJefferson MoraОценок пока нет
- Serovar Australis: Leptospira Serovar Data SheetДокумент1 страницаSerovar Australis: Leptospira Serovar Data SheetfrankyОценок пока нет
- Scripta Medica Volume 44 Issue 1Документ68 страницScripta Medica Volume 44 Issue 1Zdravko GrubacОценок пока нет
- Electronic Surgical Logbook For Orthopedic Residents AcceptanceДокумент7 страницElectronic Surgical Logbook For Orthopedic Residents AcceptanceKhalil ur RehmanОценок пока нет
- Nejme 2305752Документ2 страницыNejme 23057525fqkqkcdhtОценок пока нет
- 8 Principles of White Crane Kung FuДокумент3 страницы8 Principles of White Crane Kung Fuanattā100% (4)