Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Vsepr Theorypreap08
Загружено:
vishakhshukla100%(1)100% нашли этот документ полезным (1 голос)
143 просмотров15 страницThe Shapes of Molecules are determined by the bonding inside the molecules and the electrons in bonds. A molecule can possess polar bonds and still be nonpolar. The shapes of some molecules are best explained by the orbital hybridization model.
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
vsepr_theorypreap08
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThe Shapes of Molecules are determined by the bonding inside the molecules and the electrons in bonds. A molecule can possess polar bonds and still be nonpolar. The shapes of some molecules are best explained by the orbital hybridization model.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
100%(1)100% нашли этот документ полезным (1 голос)
143 просмотров15 страницVsepr Theorypreap08
Загружено:
vishakhshuklaThe Shapes of Molecules are determined by the bonding inside the molecules and the electrons in bonds. A molecule can possess polar bonds and still be nonpolar. The shapes of some molecules are best explained by the orbital hybridization model.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 15
VSEPR Theory
The Shape of Molecules
Molecular Polarity
• Polar Molecule – molecule that has a definite positive and negative
end.
• A molecule can possess polar bonds and still be nonpolar.
• If the polar bonds are evenly (or symmetrically) distributed, the bond
dipoles cancel and do not create a molecular dipole.
• For example, the three bonds in a molecule of BF3 are significantly
polar, but they are symmetrically arranged around the central boron
atom. (No side of the molecule has more negative or positive charge
than another side, and so the molecule is nonpolar)
• A water molecule is polar because
◘ its O-H bonds are significantly polar
◘ its bent geometry makes the distribution of those polar bonds
asymmetrical.
• The side of the water molecule containing the more electronegative
oxygen atom is partially negative, and the side of the molecule
containing the less electronegative hydrogen atoms is partially positive.
Try a Few!
• CH4 • Nonpolar molecule
• PCl5 • Nonpolar molecule
• NH3 • Polar Molecule
NH4+1 • Nonpolar Ion
•
• Polar Molecule
• CH3Cl
• Polar Molecule
• H2S
• Polar Molecule
• CO • Nonpolar Molecule
• SF6 • Polar Molecule
• HBr
VSEPR Theory
• Molecular Geometry – shapes of Molecules.
◘ The shapes of molecules are determined by the
bonding inside the molecules & the electrons in
bonds.
• VSEPR Theory (Valence Shell Electron Pair
Repulsion) – all the electrons in an atom will
repel each other.
◘ Electrons in bonds & nonbonding electron pairs
will spread out as far as possible.
Shapes of Molecules
# of atoms bonded # of lone pairs of Shape Bond Angle
to central atom electrons
2,3 0 Linear 180°
2 2 Bent 104.5°
3 0 Trigonal planar 120°
3 1 Trigonal pyramidal 107°
4 0 Tetrahedral 109.5°
5 0 Trigonal 90°, 120°
bipyramidal
6 0 Octahedral 90°
Linear
Bent
Trigonal Planar
Trigonal Pyramidal
Tetrahedral
Trigonal Bipyramidal
Octahedral
Hybrid Orbitals
• Hybrid Orbitals – the shapes of some molecules are best
explained by the orbital hybridization model.
• Orbitals are hybridized when two or more atomic orbitals of
similar energy on the same atom are “mixed” to make the
same amount of new, equivalent hybrid orbitals.
◘ sp – one s and one p orbital are mixed to make 2 sp orbitals
◘ sp2 – one s and two p orbitals are mixed to make 3 sp2 orbitals
◘ sp3 – one s and three p orbitals are mixed to make 4 sp3 orbitals
• Coordinate Compounds: Trigonal bipyramidal &
octahedral molecules.
◘ Middle atom has more than 8 electrons.
Hybridization
Number of electron pairs Shapes Hybridization
around central atom
(including bonds)
2 Linear sp
3 Trigonal planar sp2
4 Trigonal pyramidal, sp3
tetrahedral, bent
5 Trigonal dsp3
bipyramidal
6 Octahedral d2sp3
Trivia Time!
Who was the first president to be
born in a hospital?
Jimmy Carter (Born in 1924,
president 1977 – 1980)
Вам также может понравиться
- Titrationspreap 1Документ12 страницTitrationspreap 1vishakhshuklaОценок пока нет
- Predicting Products of Chemical ReactionsДокумент12 страницPredicting Products of Chemical ReactionsvishakhshuklaОценок пока нет
- Percent CompositionpreapДокумент10 страницPercent CompositionpreapvishakhshuklaОценок пока нет
- Ka KB KsppreapДокумент14 страницKa KB KsppreapvishakhshuklaОценок пока нет
- Intrototheperiodictablepre ApДокумент11 страницIntrototheperiodictablepre ApvishakhshuklaОценок пока нет
- Inter Molecular ForcesДокумент8 страницInter Molecular ForcesvishakhshuklaОценок пока нет
- Organic Chemistry: The Chemistry of CarbonДокумент9 страницOrganic Chemistry: The Chemistry of CarbonvishakhshuklaОценок пока нет
- Dalton's and Boyle's LawДокумент11 страницDalton's and Boyle's LawvishakhshuklaОценок пока нет
- Empirical FormulaДокумент12 страницEmpirical FormulavishakhshuklaОценок пока нет
- Balancing Equations Pre APДокумент21 страницаBalancing Equations Pre APvishakhshuklaОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Lecture 35 PDFДокумент20 страницLecture 35 PDFRachit ShahОценок пока нет
- Leveraging Fermentation Heat Transfer Data To Better Understand Metabolic ActivityДокумент8 страницLeveraging Fermentation Heat Transfer Data To Better Understand Metabolic ActivityKimberly TamayoОценок пока нет
- Ultrahigh Piezoelectricity in Ferroelectric Ceramics by DesignДокумент7 страницUltrahigh Piezoelectricity in Ferroelectric Ceramics by DesignGabriel MoreiraОценок пока нет
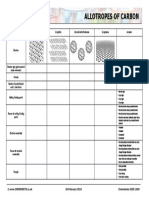
- Chemsheets GCSE 1069 Allotropes of CarbonДокумент1 страницаChemsheets GCSE 1069 Allotropes of CarbonNoah KellerОценок пока нет
- ExChEL Group Study Session 13 - Day 1 ExaminationДокумент15 страницExChEL Group Study Session 13 - Day 1 ExaminationRochelle Louise SampagaОценок пока нет
- Second Law of Thermodynamics: T T Q QДокумент10 страницSecond Law of Thermodynamics: T T Q Qnellai kumarОценок пока нет
- Q1 Test3 Test 4Документ31 страницаQ1 Test3 Test 4Jennelyn PerezОценок пока нет
- GCSE Practical Guide Chemistry ElectrolysisДокумент12 страницGCSE Practical Guide Chemistry Electrolysisr aОценок пока нет
- Midterm Exam - MCQ - TFQ - ENGI8690-9114 - W2019Документ5 страницMidterm Exam - MCQ - TFQ - ENGI8690-9114 - W2019Mohammad HaqОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Chemical ThermodynamicsДокумент57 страницFundamentals of Chemical ThermodynamicstОценок пока нет
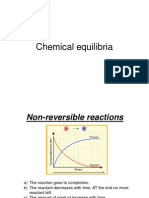
- Chemical EquilibriaДокумент15 страницChemical EquilibriaiceggОценок пока нет
- Temperature Regulation During Exercises: Dr. Ghousia ShahidДокумент26 страницTemperature Regulation During Exercises: Dr. Ghousia ShahidAflaha KhanОценок пока нет
- Kinetics Prelim Take Home Exam December 25 2017Документ2 страницыKinetics Prelim Take Home Exam December 25 2017Michelle Mendoza100% (1)
- Review On Nanomaterials: Synthesis and Applications: ArticleДокумент10 страницReview On Nanomaterials: Synthesis and Applications: ArticleDhanunjayaОценок пока нет
- Coal GasificationДокумент11 страницCoal GasificationPratik RanjanОценок пока нет
- TechTip GC Liners 1Документ4 страницыTechTip GC Liners 1bnechitaОценок пока нет
- Photoelectric Effect: Dual Nature of Matter and RadiationsДокумент21 страницаPhotoelectric Effect: Dual Nature of Matter and RadiationsVishesh SheraОценок пока нет
- Lewis MathesonДокумент5 страницLewis MathesonDaniela SotoОценок пока нет
- Highly Luminescent N-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots From Lemon JuiceДокумент8 страницHighly Luminescent N-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots From Lemon JuiceJoaquim RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Context Clues: "Using Context Clues in The Sentences or Paragraph"Документ4 страницыContext Clues: "Using Context Clues in The Sentences or Paragraph"Rizki fitriana dewiОценок пока нет
- Cape Open ComsolДокумент37 страницCape Open ComsolLuis Alberto GuzmánОценок пока нет
- Pre Notes 6th Semcode CH 604Документ42 страницыPre Notes 6th Semcode CH 604SurajPandeyОценок пока нет
- Study of Beta Ray AbsorptionДокумент4 страницыStudy of Beta Ray AbsorptionWasimОценок пока нет
- 2 ND Michlaslab 402Документ4 страницы2 ND Michlaslab 402michialdasОценок пока нет
- Lean Oil Absorption 02Документ14 страницLean Oil Absorption 02Shri JrОценок пока нет
- Bes - REDOX TITRATION PDFДокумент3 страницыBes - REDOX TITRATION PDFAvi Thakur100% (1)
- Advanced Syngas Technology: Dr. Ronald Britton, Methanex Corporation, Canada Mr. Robert Kirkpatrick andДокумент7 страницAdvanced Syngas Technology: Dr. Ronald Britton, Methanex Corporation, Canada Mr. Robert Kirkpatrick andMarcelo Varejão CasarinОценок пока нет
- Proton Exchange MembraneДокумент22 страницыProton Exchange MembraneHanifan Lidinillah100% (1)
- CAPE Biology Notes Module 1Документ9 страницCAPE Biology Notes Module 1JordanОценок пока нет
- EvaporatorДокумент5 страницEvaporatorLimanto Lee89% (9)