Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Dynamics of Circular Motion Revised 1st Term - 11 - 12
Загружено:
RA MemijeОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Dynamics of Circular Motion Revised 1st Term - 11 - 12
Загружено:
RA MemijeАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Dynamics of Circular
Motion
Types of Circular Motion
Centripetal Force
Centripetal Acceleration
Horizontal Circle
Vertical Circle
Banking of Curves
Conical Pendulum
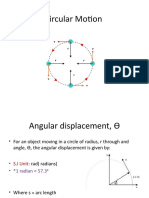
CIRCULAR MOTION
- Motion of a body in a curved path
TYPES:
Uniform Circular Motion, UCM motion with
constant speed
Ex. A car rounding an oval at 30 KPH
Non-Uniform circular Motion, NUCM a roller
coaster car that slows down and speeds up as it
moves around a vertical loop.
Uniform Circular Motion
DEFINITION OF UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION
Uniform circular motion is the motion of an object
traveling at a constant speed on a circular path.
V
V S
r
Conversion:
1 rev = 360 = 2 rad
c
In uniform circular motion, the speed is constant, but the
direction of the velocity vector is not constant.
90 = + | o
90 = +u o
u | =
Centripetal Acceleration
r
t v
v
v A
=
A
r
v
t
v
2
=
A
A
r
v
a
c
2
=
S
Concept in Uniform Circular Motion
A Body Moving In Circular Path on a
Flat Horizontal Surface
Forces Acting on a Body When Rotated forming a
Vertical Circle (when along the horizontal)
Vertical Circular Motion
r
v
m mg F
N
2
1
1
=
r
v
m mg F
N
2
3
3
= +
r
v
m F
N
2
2
2
=
r
v
m F
N
2
4
4
=
Verti
Vertical Circle A Rotating Ferris Wheel
Period & Frequency
Period, T - time it takes for the object to travel once around
the circle. (sec)
Frequency, f no. of cycles or no. of revolutions that the
body makes in 1 sec
(rev/sec, cycles/sec, hertz)
v
r
T
=
2t
r
= 1/
Centripetal Force
Thus, in uniform circular motion there must be a net
force to produce the centripetal acceleration.
The centripetal force is the name given to the net force
required to keep an object moving on a circular path.
The direction of the centripetal force always points toward
the center of the circle and continually changes direction
as the object moves.
r
v
m ma F
c c
2
= =
Banked Curves
On an unbanked curve, the static frictional force
provides the centripetal force.
Car Rounding a Flat Curve at Constant Speed
Banked Curves
On a frictionless banked curve, the centripetal force is the
horizontal component of the normal force. The vertical
component of the normal force balances the cars weight.
Banked Curves ( Neglecting Friction)
r
v
m n F
c
2
sin = = u
mg n = u cos
rg
v
2
tan = u
n
n cos
Banked Curves
Example : The Daytona 500
The turns at the Daytona International Speedway have a
maximum radius of 316 m and are steely banked at 31
degrees. Suppose these turns were frictionless. At what
speed would the cars have to travel around them?
rg
v
2
tan = u
u tan rg v =
( )( ) ( ) mph 96 s m 43 31 tan s m 8 . 9 m 316
2
= =
v
Summary
rectilinear
Summary
Sample Problems
A Tire-Balancing Machine
1. The wheel of a car has a radius of 0.29m and it being rotated
at 830 revolutions per minute on a tire-balancing machine.
Determine the speed at which the outer edge of the wheel is
moving.
The Effect of Speed on Centripetal Force
2. The model airplane has a mass of 0.90 kg and moves at
constant speed on a circle that is parallel to the ground.
The path of the airplane and the guideline lie in the same
horizontal plane because the weight of the plane is balanced
by the lift generated by its wings. Find the tension in the 17 m
guideline for a speed of 19 m/s.
Sample Problems
3.
5.
4.
Sample Problems
7.
6.
vertical.
Conical Pendulum
8. The 4-kg in the figure is
attached to a vertical rod by
means of two strings. When
the system rotates about
the axis of the rod, the
strings are extended as
shown and the tension in
the upper string is 80 N.
a) What is the tension in the
lower cord?
b) b) How many revolutions
per minute does the system
make?
Вам также может понравиться
- Dynamics of Circular Motion 14154Документ18 страницDynamics of Circular Motion 14154Paulo RemullaОценок пока нет
- PHY10 WK09 Circular MotionДокумент21 страницаPHY10 WK09 Circular MotionJed Efraim EspanilloОценок пока нет
- Dynamics of Circular Motion (Edited)Документ21 страницаDynamics of Circular Motion (Edited)Carol FernandoОценок пока нет
- Circular MotionДокумент12 страницCircular MotionWendy TangОценок пока нет
- CH 05Документ28 страницCH 05api-96362001Оценок пока нет
- Circular MotioДокумент51 страницаCircular MotioRusher AkoОценок пока нет
- Circular Motion and GravitationДокумент29 страницCircular Motion and GravitationSteb LaniОценок пока нет
- Uniform Circular MotionДокумент46 страницUniform Circular MotionAllen EspinosaОценок пока нет
- Circular MotionДокумент42 страницыCircular Motionrgk966c275Оценок пока нет
- Uniform Circular MotionДокумент42 страницыUniform Circular MotionStacey Camille100% (1)
- 102 Mechanics Lecture 4bДокумент32 страницы102 Mechanics Lecture 4bJayОценок пока нет
- Dynamics of Circular MotionДокумент35 страницDynamics of Circular MotionEmmaren SabridoОценок пока нет
- Physics Chapter 5Документ38 страницPhysics Chapter 5Jamie NguyenОценок пока нет
- Ch.9 Circular MotionДокумент10 страницCh.9 Circular MotionJoanne Aga EslavaОценок пока нет
- Mechanics 5 Dynamics of a rigid bodyДокумент16 страницMechanics 5 Dynamics of a rigid bodyClarence PieterszОценок пока нет
- 6B Circular Motion & Gravitation 2020-2021Документ46 страниц6B Circular Motion & Gravitation 2020-2021RandominicОценок пока нет
- Circular Motion and Gravitation ExplainedДокумент25 страницCircular Motion and Gravitation ExplainedTypeNameОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5: Laws of Motion Class: XI Subject: Physics: Topic: Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion, Banking of RoadДокумент5 страницChapter 5: Laws of Motion Class: XI Subject: Physics: Topic: Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion, Banking of RoadKirtan KumarОценок пока нет
- t1 Circualr Mtion A2Документ12 страницt1 Circualr Mtion A2Hamail MustafaОценок пока нет
- Circular Motion For StudentДокумент56 страницCircular Motion For Studentbobbyhaha05Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 10 11Документ60 страницChapter 10 11sharathОценок пока нет
- Review: Circular Motion: AP PhysicsДокумент14 страницReview: Circular Motion: AP PhysicsXin ChenОценок пока нет
- PHY 400 - Chapter 6 - Rotational MotionДокумент30 страницPHY 400 - Chapter 6 - Rotational MotionJacob OrtizОценок пока нет
- 10 Kinamatics of Rotation UCMДокумент27 страниц10 Kinamatics of Rotation UCMRamachandranPerumalОценок пока нет
- CH-11 Gyroscopic CoupleДокумент4 страницыCH-11 Gyroscopic Couplecılem cıuОценок пока нет
- g484 Module 2 4 2 1circular MotionДокумент8 страницg484 Module 2 4 2 1circular Motionapi-236179294Оценок пока нет
- Circular Motion and Gravity NotesДокумент7 страницCircular Motion and Gravity NotesChee K Wong100% (1)
- Circular Motion Uniform Circular MotionДокумент4 страницыCircular Motion Uniform Circular MotionAbhishek ParasharОценок пока нет
- 6. Circular MotionДокумент42 страницы6. Circular Motionmonsterrider135Оценок пока нет
- CH 6Документ23 страницыCH 6rhl5761Оценок пока нет
- Motion in A CircleДокумент39 страницMotion in A CircleYerene YenОценок пока нет
- Uniform Circular MotionДокумент27 страницUniform Circular MotionUrmila GОценок пока нет
- Circular MotionДокумент5 страницCircular Motionkakaleclement303Оценок пока нет
- Uniform Circular MotionДокумент11 страницUniform Circular MotionAnne Margaret AlmedaОценок пока нет
- Circular MotionДокумент34 страницыCircular Motionclaimstudent3515Оценок пока нет
- Topic 4 Circular MotionДокумент36 страницTopic 4 Circular MotionMirahmad FadzlyОценок пока нет
- Rotational MotionДокумент11 страницRotational Motionaisaspa725Оценок пока нет
- Learning Target (Daily)Документ4 страницыLearning Target (Daily)Yousif Jamal Al Naqbi 12BEОценок пока нет
- 5 Uniform Circular MotionДокумент15 страниц5 Uniform Circular MotionLeslie MorrisОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 Rot Motion GravityДокумент4 страницыChapter 7 Rot Motion Gravityjoe termОценок пока нет
- Physics 170 - Mechanics: Circular MotionДокумент24 страницыPhysics 170 - Mechanics: Circular MotionSteve IsaacsОценок пока нет
- PHYS101 - CO2 Rotational KinematicsДокумент41 страницаPHYS101 - CO2 Rotational KinematicsAngelika Valencia100% (2)
- Circular MotionДокумент26 страницCircular MotionPepc MaОценок пока нет
- Rot Motion NotesДокумент63 страницыRot Motion NotesCherry OcampoОценок пока нет
- Circular Motion (1)Документ59 страницCircular Motion (1)wandankosi09Оценок пока нет
- Rotational MotionДокумент46 страницRotational MotionMuhammadIzharОценок пока нет
- Physics Project On Circular MotionДокумент22 страницыPhysics Project On Circular Motionishan67% (3)
- Physics Project Made by Ishan GuptaДокумент22 страницыPhysics Project Made by Ishan GuptaishanОценок пока нет
- Engineering PhysicsДокумент33 страницыEngineering PhysicsLeony PanjaitanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 - Circular MotionДокумент26 страницChapter 7 - Circular Motionsheil.cogayОценок пока нет
- WEEK 7 Rotational MotionДокумент35 страницWEEK 7 Rotational MotionsyafiqahizzatiОценок пока нет
- 10 - Circular MotionДокумент27 страниц10 - Circular MotionKeith SmithОценок пока нет
- Module 1Документ17 страницModule 1robejr2013Оценок пока нет
- PHY106 Finals Lesson 4Документ12 страницPHY106 Finals Lesson 4Temothy Earl UrmenitaОценок пока нет
- Gyroscope NotesДокумент26 страницGyroscope NotesLauria LavdaОценок пока нет
- Circular Motion Jahjah 8888888888888 1Документ42 страницыCircular Motion Jahjah 8888888888888 1Yay SandovalОценок пока нет
- Fallsem2021-22 Mee2004 Ela Vl2021220103306 Reference Material Dom ManualДокумент52 страницыFallsem2021-22 Mee2004 Ela Vl2021220103306 Reference Material Dom ManualmetaschimatismoúsОценок пока нет
- Uniform Circular MotionДокумент35 страницUniform Circular Motioniril liquezОценок пока нет
- Ref 4Документ8 страницRef 4RA MemijeОценок пока нет
- Microbial CelluloseДокумент18 страницMicrobial CelluloseRaghav Goyal0% (1)
- 01 Equipment Design Report FormatДокумент15 страниц01 Equipment Design Report FormatRA MemijeОценок пока нет
- Philippines' largest oil refining company profileДокумент2 страницыPhilippines' largest oil refining company profileRA MemijeОценок пока нет
- 2014-6-69 - P-Characterisation of Composites of Bacterial Cellulose and Poly (Vinyl Alcohol) Obtained by Different Methods - P PDFДокумент6 страниц2014-6-69 - P-Characterisation of Composites of Bacterial Cellulose and Poly (Vinyl Alcohol) Obtained by Different Methods - P PDFRA MemijeОценок пока нет
- FM RS 08 15 Final Billing Form v.1Документ1 страницаFM RS 08 15 Final Billing Form v.1RA MemijeОценок пока нет
- Specs and ShitДокумент1 страницаSpecs and ShitRA MemijeОценок пока нет
- Installation InstructionsДокумент1 страницаInstallation InstructionsBicá Valgy de SousaОценок пока нет
- How To Play HEVCДокумент1 страницаHow To Play HEVCMike de MesaОценок пока нет
- Offline Cleaning of Heat ExchangersДокумент4 страницыOffline Cleaning of Heat ExchangersRA MemijeОценок пока нет
- Philippines' largest oil refining company profileДокумент2 страницыPhilippines' largest oil refining company profileRA MemijeОценок пока нет
- Heat ExchangersДокумент48 страницHeat ExchangersRiccat Shio'TangОценок пока нет
- Thesis Research Revision Summary FormДокумент1 страницаThesis Research Revision Summary FormRA Memije0% (1)
- Use of Bacterial Cellulose Glycerol PolyvinylДокумент4 страницыUse of Bacterial Cellulose Glycerol PolyvinylRA MemijeОценок пока нет
- MEBДокумент33 страницыMEBDiego MorenoОценок пока нет
- Acetylene DM 100 C2H2 PDSДокумент2 страницыAcetylene DM 100 C2H2 PDSRA MemijeОценок пока нет
- Major Disaster CauseДокумент2 страницыMajor Disaster CauseRA MemijeОценок пока нет
- UltimateДокумент6 страницUltimateRA MemijeОценок пока нет
- Using Gain (Fixed KC) : DiagramДокумент19 страницUsing Gain (Fixed KC) : DiagramRA MemijeОценок пока нет
- LNG OverviewДокумент36 страницLNG OverviewSyam TawakkalОценок пока нет
- Two Phase FlowДокумент5 страницTwo Phase FlowRA MemijeОценок пока нет
- Removed Flash Drum Mat BalДокумент2 страницыRemoved Flash Drum Mat BalRA MemijeОценок пока нет
- ValvesДокумент31 страницаValvesRA MemijeОценок пока нет
- On LNG and FLNGДокумент46 страницOn LNG and FLNGRA MemijeОценок пока нет
- Biochemical Engineering Journal: Shangde Sun, Xiaowei ChenДокумент7 страницBiochemical Engineering Journal: Shangde Sun, Xiaowei ChenRA MemijeОценок пока нет
- Major Disaster CauseДокумент6 страницMajor Disaster CauseRA MemijeОценок пока нет
- Ms. Nancy Caringal Memije: 1480 Governor'S Drive Brgy - Bancal Carmona, Cavite 4116Документ2 страницыMs. Nancy Caringal Memije: 1480 Governor'S Drive Brgy - Bancal Carmona, Cavite 4116RA MemijeОценок пока нет
- Kinetics of Enzyme DeactivationДокумент3 страницыKinetics of Enzyme DeactivationRA MemijeОценок пока нет
- Particles LT 2 Lau Memije TimbrezaДокумент4 страницыParticles LT 2 Lau Memije TimbrezaRA MemijeОценок пока нет
- Absorption 2nd1415Документ25 страницAbsorption 2nd1415RA MemijeОценок пока нет
- Plate Bending Element Formulation and Stiffness Matrix DevelopmentДокумент6 страницPlate Bending Element Formulation and Stiffness Matrix DevelopmentSeyhan ÖzenОценок пока нет
- Conduction, Convection, & RadiationДокумент14 страницConduction, Convection, & Radiationyuvionfire100% (1)
- Carrfoster 2Документ5 страницCarrfoster 2SauravОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Linear KinematicsДокумент26 страницChapter 3 Linear KinematicsKuldeep SinghОценок пока нет
- Martin Hermann, Masoud Saravi - Nonlinear Ordinary Differential Equations - Analytical Approximation and Numerical Methods-Springer (2016) PDFДокумент320 страницMartin Hermann, Masoud Saravi - Nonlinear Ordinary Differential Equations - Analytical Approximation and Numerical Methods-Springer (2016) PDFHugo Mayorga100% (1)
- 3 RPM and 6 RPMДокумент4 страницы3 RPM and 6 RPMAnonymous T32l1RОценок пока нет
- Vibration Case HistoriesДокумент56 страницVibration Case HistoriesanuprajaОценок пока нет
- Lucia 1995 Rock-FabricPetrophysical Classification of Carbonate Pore SpaceДокумент26 страницLucia 1995 Rock-FabricPetrophysical Classification of Carbonate Pore SpaceMarcos Antonio Romero Arteaga100% (1)
- Load CalculationsДокумент5 страницLoad Calculationsarif_rubinОценок пока нет
- Tuning Equation of State ModelsДокумент34 страницыTuning Equation of State Modelswelltest vspОценок пока нет
- P Ractical Approaches To Fast Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Muy BuenoДокумент28 страницP Ractical Approaches To Fast Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Muy BuenoJavier Joao Lloyd IglesiasОценок пока нет
- Design of 10m Span RCC Slab CulvertДокумент105 страницDesign of 10m Span RCC Slab CulvertD.V.Srinivasa Rao100% (4)
- Determining Height with a TransitДокумент6 страницDetermining Height with a TransitMОценок пока нет
- Joint Design For Reinforced Concrete Buildings: P Ei ErДокумент79 страницJoint Design For Reinforced Concrete Buildings: P Ei ErSergey MatyuninОценок пока нет
- Jacobs Co Algebra IntroДокумент190 страницJacobs Co Algebra IntrozmthОценок пока нет
- The role of root canal fillings in endodontic successДокумент9 страницThe role of root canal fillings in endodontic successYassir MudharОценок пока нет
- CGR 16050 2019 2020 1Документ1 страницаCGR 16050 2019 2020 1Chandan Prasad KushwahaОценок пока нет
- Molecular Partition Function ExplainedДокумент18 страницMolecular Partition Function ExplainedAnimasahun Olamide HammedОценок пока нет
- Alarms Manual (ENGLISH)Документ12 страницAlarms Manual (ENGLISH)FadFadОценок пока нет
- Pore Structure of Air-Entrained Hardened Cement PasteДокумент9 страницPore Structure of Air-Entrained Hardened Cement Paste1mattelliottОценок пока нет
- PMM WordДокумент3 страницыPMM WordShrey R DhanawadkarОценок пока нет
- High-Efficiency Solar Inverter Test Report SummaryДокумент17 страницHigh-Efficiency Solar Inverter Test Report Summarybharath prabhuОценок пока нет
- AADE Review of Lost Circulation Materials and Treatments With An Updated ClassificationДокумент9 страницAADE Review of Lost Circulation Materials and Treatments With An Updated ClassificationMuhamad IrfanОценок пока нет
- Microplan - Katalog 2016 ENДокумент55 страницMicroplan - Katalog 2016 END.T.Оценок пока нет
- Dual Nature of LightДокумент15 страницDual Nature of LightUriahs Victor75% (4)
- Adaptive Followup Mastering PhysicsДокумент8 страницAdaptive Followup Mastering PhysicsElloani Ross Arcenal PitogoОценок пока нет
- Material Balance On A 2 Unit DistillationsДокумент6 страницMaterial Balance On A 2 Unit Distillationsnhalieza1067Оценок пока нет
- Mock C4 Paper Key ConceptsДокумент4 страницыMock C4 Paper Key ConceptsWojtek BażantОценок пока нет
- Love My LifeДокумент5 страницLove My LifeLinda Veronica0% (1)
- Clarke and Park TransfomationДокумент9 страницClarke and Park TransfomationGREATJUSTGREATОценок пока нет